Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diskusi 4 Structure III
Uploaded by
Centia Beby Sekar RiniCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diskusi 4 Structure III
Uploaded by
Centia Beby Sekar RiniCopyright:
Available Formats
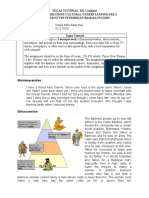
In Module 7, we learn about CONDITONAL SENTENCE II. It is divided into several types.
The first one
is about activity that might happen while other talk about something that might not happen or
improbability.
1. USING PROGRESSIVE VERB FORM
We use it for something that might happen. Common Form would + be + infinitive + ing
.
I would be going home if it were not raining right now
If I were living in London, I would be mastering English
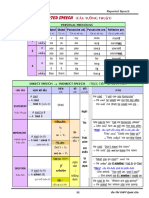
2. OMITTING IF
We do not use ‘If’ in this case. By taking off ‘If’ we do not change the meaning of the sentence.
It applies for Conditional Type 1 that uses ‘should’ in the sentence and Conditional Type 2 that uses
‘were’ in the sentence
If she should come, ask her to wait (Should she come, ask her to wait)
If I werer you, I would be so happy (Were I you, I would be so happy)
3. VERB FORM FOLLOWING WISH
This conditional is used to express a wish for a certain period of time.
I wish + the simple past
( I wish she weren’t coming to my house) > It is talking about present time. The
speaker wishes that ‘she’ does not come to her house, but the fact she is in her house
at the moment.
I wish + the past perfect
(I wish I hadn’t said that) > It is talking about a regret in the past. The speaker wishes she
does not do that thing in the past, but she does. Oppositely, somone whishe does something in
the past, but the fatc she/he does not.
4. OTHER TYPES OF CONDITIONAL SENTENCES (AS IF – AS THOUGH)
- She acts as if she knew me so well
(she gives the impression that she knows me so well, but she (probably) doesn't
know me
- She acted as if she had known me so well
(it seems that she has known m, but she (probably) hasn’t or we don't know whether
he has or not)
It is cloudy as if it is going to rain. Kalimat disamping bisa diartikan
cuaca yang mendung seolah-olah akan turun hujan. Pada
kenyataannya, pada saat itu hujan belum turun. bisa saja memang
turun hujan, namun belum terjadi.
but use 'were, had, and should'
If I were you, I would be angry to her
You would have passed the exam if you had studied harder.
If she should come, ask her to wait
5.
1. Conditional sentences
that use a Progressive Verb or active verb. We talk for something that might happen. Common Form
would + be + infinitive + ing
1. If it had not raining, I would have gone to market
We use it for talking about IMPROBABILITY. It means, describing the things in the future that are
impossible in the present or the things in the future that are unlikely.
If + simple past, present conditional (would + infinitive)
1. If it rained, you would get wet.
2. You wouldn't be so tired if you went to bed earlier.
While Using Progressive verb form. We talk for something that might happen. Common Form would
+ be + infinitive + ing
If it were not raining right now, I would go for a walk
If I were living in Canada, I would be working at a bank
In this case, we don’t use WAS after I and It, but WERE.
Omitting If is a conditional sentence that does not use 'if' but uses 'were, had, and should'
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument5 pagesModal VerbsDAVID GAINACK SENENo ratings yet
- b2.1_-_unit_7_-_grammarDocument7 pagesb2.1_-_unit_7_-_grammarcristina.lopez.castro96No ratings yet
- Situations and Their Consequences. We Will Study The Use of Following WordsDocument6 pagesSituations and Their Consequences. We Will Study The Use of Following WordsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Course ExplanationsDocument17 pagesConditionals Course ExplanationsEmily MillsNo ratings yet
- Probability: Happening / Will Happen. We Often Call These 'Modals of Deduction' or 'Speculation' or 'Certainty' orDocument4 pagesProbability: Happening / Will Happen. We Often Call These 'Modals of Deduction' or 'Speculation' or 'Certainty' orWinnieNo ratings yet
- Perfect English GrammarDocument4 pagesPerfect English GrammarNguyễn Thu YênNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs ExplainedDocument5 pagesModal Verbs ExplainedMarcela CoroleaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Conditionals ExplainedDocument11 pagesAdvanced Conditionals ExplainedGeorge PetreNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument23 pagesConditionalsCarmen BugnarNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument4 pagesModal VerbsSimona LNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 7) Conditional SentencesDocument21 pages(Lecture - 7) Conditional SentencesN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Could Have, Should Have, Would HaveDocument3 pagesCould Have, Should Have, Would HaveAtento a cherchaNo ratings yet
- Sažeta Gramatika Engleskog JezikaDocument10 pagesSažeta Gramatika Engleskog JezikaKristina StojanovićNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives GuideDocument15 pagesGerunds and Infinitives GuideGuadalupe George PolvoNo ratings yet
- P6 Contional IfDocument22 pagesP6 Contional IfVolcom OfficialNo ratings yet
- Lectia 3Document5 pagesLectia 3Tavy92No ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument22 pagesConditionalshappyindriyono2402100% (1)
- Learning Activity - 8 Conditional Sentences: When, As Soon As, Until, Before, Unless, and So On, May Take Place of IfDocument8 pagesLearning Activity - 8 Conditional Sentences: When, As Soon As, Until, Before, Unless, and So On, May Take Place of IfSulistya Ningsih Pratiwi AzzahNo ratings yet
- GR ConmixedDocument20 pagesGR ConmixedJason WNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Modals - Seventh Semester 2022 ADocument7 pagesUnit 7 Modals - Seventh Semester 2022 ASaldivarNo ratings yet
- Could Have, Should Have, Would HaveDocument2 pagesCould Have, Should Have, Would HavePedro BeltreNo ratings yet
- Could Have, Should Have, Would HaveDocument5 pagesCould Have, Should Have, Would HavePargol ShobeiriNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument29 pagesConditional SentencesMuhammad QaisNo ratings yet
- Fiuture and Future in The PastDocument11 pagesFiuture and Future in The PastElena PorceanuNo ratings yet
- If + Present Simple: Type 1 ConditionalDocument6 pagesIf + Present Simple: Type 1 ConditionalWinnieNo ratings yet
- Lectia III: Conditionals si fraze conditionaleDocument6 pagesLectia III: Conditionals si fraze conditionaleender8421No ratings yet
- If clauses & conditional sentences explainedDocument21 pagesIf clauses & conditional sentences explainedAngélica Lizeth Cervantes GonzálezNo ratings yet
- 1.a.IF-CLAUSES (0,1,2,3.types) - 2-2Document2 pages1.a.IF-CLAUSES (0,1,2,3.types) - 2-2joanaNo ratings yet
- 04.lectia IIIDocument4 pages04.lectia IIIMaxim MariusNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs Explained: Uses, Forms & ExamplesDocument38 pagesModal Verbs Explained: Uses, Forms & ExamplesAliceNo ratings yet
- Probability: Happening / Will Happen. We Often Call These 'Modals of Deduction' or 'Speculation' or 'Certainty' orDocument4 pagesProbability: Happening / Will Happen. We Often Call These 'Modals of Deduction' or 'Speculation' or 'Certainty' orWinnieNo ratings yet
- Advanced Conditionals ExplainedDocument10 pagesAdvanced Conditionals ExplainedZitheeq UmarNo ratings yet
- First Conditional: When You Visit, We Might Go To The ParkDocument6 pagesFirst Conditional: When You Visit, We Might Go To The ParkRaquel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence by Group 9Document21 pagesConditional Sentence by Group 9Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument13 pagesConditionalsCande LopezNo ratings yet
- Learn Conditional SentencesDocument3 pagesLearn Conditional SentencesYoga PramudanaNo ratings yet
- Grammar SummaryDocument48 pagesGrammar SummaryBelén EscuderoNo ratings yet
- BachillerDocument5 pagesBachillerFatima VazquezNo ratings yet
- Condition Sentences Type 0-3Document12 pagesCondition Sentences Type 0-3noklkn1003No ratings yet
- Unit 7 Conditional Sentences (Type 0-3) : UsageDocument10 pagesUnit 7 Conditional Sentences (Type 0-3) : UsageMi Pipi100% (1)
- Conditional Sentence Types 0, 1, 2, 3Document2 pagesConditional Sentence Types 0, 1, 2, 3Vanja Đorđevic100% (2)
- Conditionals 1Document22 pagesConditionals 1Olguita H. PastorNo ratings yet
- Could HaveDocument4 pagesCould HaveYuliia VoronkevychNo ratings yet
- 1 and 2 ConditionalDocument4 pages1 and 2 ConditionalAnita P.No ratings yet
- Modul Kelas Xi 2020-2021Document12 pagesModul Kelas Xi 2020-2021adilNo ratings yet
- Conditionals and If SentencesDocument15 pagesConditionals and If SentencesjeuxdelumiereNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument7 pagesConditionalsKiara QuispeNo ratings yet
- Grammar Explanation b1Document21 pagesGrammar Explanation b1Paola GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Have To + Infinitive Must + Infinitive Should + InfinitiveDocument5 pagesHave To + Infinitive Must + Infinitive Should + InfinitivebrayanNo ratings yet
- GR Ammar Reference: Unit 1Document6 pagesGR Ammar Reference: Unit 1Juan Saraiva PrudencianoNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument9 pagesGrammarp4cvmx5cjzNo ratings yet
- If I See Andrew at The MeetingDocument3 pagesIf I See Andrew at The MeetingRirin SetiYaniNo ratings yet
- Subjunctive: Structure of The SubjunctiveDocument6 pagesSubjunctive: Structure of The SubjunctivearnitarahmiNo ratings yet
- Zero Conditional Explained in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesZero Conditional Explained in 40 CharactersWindy KadeNo ratings yet
- Learn conditional sentences and wishes in EnglishDocument5 pagesLearn conditional sentences and wishes in EnglishLiliana CiubotariuNo ratings yet
- The Briefest English Grammar and Punctuation Guide Ever!From EverandThe Briefest English Grammar and Punctuation Guide Ever!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Holistic Healthy Care (HHC) CertificateDocument1 pageHolistic Healthy Care (HHC) CertificateCentia Beby Sekar RiniNo ratings yet
- Skala Pengukuran-TranslateDocument10 pagesSkala Pengukuran-TranslateCentia Beby Sekar RiniNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument1 pageTranslationCentia Beby Sekar RiniNo ratings yet
- TUGAS TUTORIAL KE-1 (Online) Kode Pbis4102/Cross Cultural Understanding/Sks 2 Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesTUGAS TUTORIAL KE-1 (Online) Kode Pbis4102/Cross Cultural Understanding/Sks 2 Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa InggrisCentia Beby Sekar RiniNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - LTDocument4 pagesReported Speech - LTnguyenvladimir73No ratings yet
- SWAIN LAPKIN 2002 Talking It ThroughDocument20 pagesSWAIN LAPKIN 2002 Talking It ThroughMayara Cordeiro100% (1)
- Games and Optional Activities Flashcard Games More Games: Simon SaysDocument1 pageGames and Optional Activities Flashcard Games More Games: Simon SaysВладислава ЩербинаNo ratings yet
- English Plus PrelimDocument2 pagesEnglish Plus PrelimDhey DagunoNo ratings yet
- Manual de Uso WINIX ZERO Pro ES v2 PDFDocument23 pagesManual de Uso WINIX ZERO Pro ES v2 PDFPERSONALNo ratings yet
- Adjective: Adverbs of MannerDocument6 pagesAdjective: Adverbs of MannerTracy Chow100% (1)
- Second Term ExaminationDocument14 pagesSecond Term Examinationemily andersonNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal B.inggrisDocument11 pagesLatihan Soal B.inggrisAsep RdsNo ratings yet
- G1 THE PARTS OF SPEECHDocument162 pagesG1 THE PARTS OF SPEECHgenesismarie64No ratings yet
- 1st BACHILLERATO EXAM PRACTICE: COMPARISONS AND SUPERLATIVESDocument4 pages1st BACHILLERATO EXAM PRACTICE: COMPARISONS AND SUPERLATIVESrosarioNo ratings yet
- Compulsory Subject ENGLISH (801) : Classes Xi & XiiDocument8 pagesCompulsory Subject ENGLISH (801) : Classes Xi & XiiAvinash DeepNo ratings yet
- Mock Interview ReflectionDocument4 pagesMock Interview Reflectionapi-616168546No ratings yet
- Theme 2 - School!Document15 pagesTheme 2 - School!Ma. Lalaine Paula ZapataNo ratings yet
- فاعلية-الرّسوم-المتحركة-في-تطوير-الأداء-اللّغويّ-لدى-الأطفال (1)Document13 pagesفاعلية-الرّسوم-المتحركة-في-تطوير-الأداء-اللّغويّ-لدى-الأطفال (1)ofkirrachida15No ratings yet
- نمونه سوال زبان یازدهم نوبت اول-2Document9 pagesنمونه سوال زبان یازدهم نوبت اول-2Masoumeh RassouliNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Degrees of Comparison I: A) Supply The Comparative of Equality. (As... As / So... As)Document8 pagesAdjectives Degrees of Comparison I: A) Supply The Comparative of Equality. (As... As / So... As)Denilson José Olúwáfẹ́miNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan for EnglishDocument5 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan for EnglishAdrian PanganNo ratings yet
- AP Chinese Study Guide - 40 Character TitleDocument8 pagesAP Chinese Study Guide - 40 Character TitlePinkyNo ratings yet
- Prueba Unidad 1-2Document4 pagesPrueba Unidad 1-2Nora CrespoNo ratings yet
- B1 - Grammar - Exercise - 1ADocument1 pageB1 - Grammar - Exercise - 1AFernando Alameda TorijanoNo ratings yet
- Julia's Family TreeDocument1 pageJulia's Family TreeLutfi FaiztantiaNo ratings yet
- Business English 3rd YearDocument92 pagesBusiness English 3rd YearОльга НерушNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in LAS - Fatima 2020Document2 pagesPerformance Task in LAS - Fatima 2020Jhomar LozanoNo ratings yet
- Improving Students' Vocabulary Mastery Using ESA MethodDocument11 pagesImproving Students' Vocabulary Mastery Using ESA MethodAndriany SuciarahmanyNo ratings yet
- Quiz 7 1Document5 pagesQuiz 7 1jose manuelNo ratings yet
- Allst7 Tests Unit1 VersionaDocument9 pagesAllst7 Tests Unit1 Versionaeva pintoNo ratings yet
- Sss Ss Ss SS: Sssssssssssssssssssssssss Sssssssssssssssssssssssss Sssssssssssssssssssssssss SssssssssssssDocument2 pagesSss Ss Ss SS: Sssssssssssssssssssssssss Sssssssssssssssssssssssss Sssssssssssssssssssssssss SssssssssssssHani LAHMERNo ratings yet
- General and Specific Statement LP-1Document6 pagesGeneral and Specific Statement LP-1Vince TubinNo ratings yet
- Advanced NLP With Spacy Chapter2Document28 pagesAdvanced NLP With Spacy Chapter2Fgpeqw100% (1)
- Present-Simple-And-Present-Continuous-For-The-Future 12-05-2020Document14 pagesPresent-Simple-And-Present-Continuous-For-The-Future 12-05-2020Mercy TilleriaNo ratings yet