Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ce 271-Fluid Mechanics Venturimeter Experiment: - Purpose
Uploaded by
sssssOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ce 271-Fluid Mechanics Venturimeter Experiment: - Purpose
Uploaded by
sssssCopyright:
Available Formats
CE 271-FLUID MECHANICS
VENTURIMETER EXPERIMENT
• Purpose
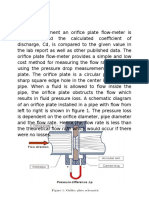
The Venturimeter shown schematically in Figure 1 is a mechanism used to measure the flow rate of the
fluid flowing through the pipe in closed systems. The working principle is based on Bernoulli and
Continuity equation. Venturimeter experiment enables practical understanding of concepts such as
static pressure, dynamic pressure, total pressure, energy conversion and energy losses. In this context,
the venturimeter experiment aims to determine the volumetric flow rate of the fluid flowing in the pipe
at different flow rates by applying Bernoulli and Continuity equations in the laboratory.
• Theory
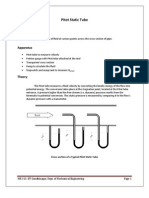
The venturimeter is shown schematically in Figure 1. A measurable pressure difference is provided by
a gradual contraction and re-expansion in the pipe cross-sectional area. In the meantime, although
energy loss occurs as a result of sudden contraction and expansion, this loss is neglected in order to
derive the venturi equation.
Figure 1. Venturimeter
As a result of applying Bernoulli equation between two points where there is a maximum pressure
difference on the same streamline for a large number of flows, the velocity and flow rate values of the
flow can be found.
In line with this principle, the flow rate can be determined with the Venturimeter, which has a variable
cross-section flow shown in Figure 1.
• EXPERIMENT PROCEDURE
In Figure 2, the test system consists of a venturimeter or Venturi tube, a narrowing-expanding
circular section pipe, manometers placed at certain points to measure the venturimeter pressure
losses, a valve with no venturimeter outlet to adjust the flow rate, hydraulic water and pump.
Figure 2
• EXPERIMENT
The venturimeter is connected to the hydraulic water outlet with a plastic pipe and the water is fed from
the hydraulic water tank to the pump. First, the pump is started and the hydraulic bench's inlet valve is
opened slowly. Pipe type pressure gauges vent valves are opened and the discharge valve is closed so
that all pressure gauges are filled with water. Simultaneous loading of the inlet and outlet valves to
keep the water in the pressure gauges at high traceable levels. The system air is removed by opening
the air intake taps on the pressure measurement tubes. By moving the static pressure and shaft at all
points, the bonding is adhered and not The volumetric water flow rate is calculated by measuring a
wash at the discharge valve outlet and the filling time of the water with a timer. Experiments are
repeated for different flow rates.
Qexp h1 h2 h3 h4 h5 h6 h7 h8 h9 h10
m3/s mmH2O mmH2O mmH2O mmH2O mmH2O mmH2O mmH2O mmH2O mmH2O mmH
O
Q1d
Q2d
Q3d
GROUP NUMBER: DATE:
ASSISTANT NUMBER: SIGNITURE:
You might also like
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1A M1Document7 pagesMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1A M1Arthur LongwardNo ratings yet
- Edinburgh Handedness Inventory AssessmentDocument1 pageEdinburgh Handedness Inventory Assessmentandy94264100% (1)
- Flow MeasurementDocument11 pagesFlow MeasurementRaj Ven100% (1)
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Internoise-2015-437 - Paper - PDF Sound Standard Gas TurbineDocument8 pagesInternoise-2015-437 - Paper - PDF Sound Standard Gas TurbinePichai ChaibamrungNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts GuideDocument38 pagesFlow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts GuideAhmad AryNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument41 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ManualrajmaljatNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in Pipes: Experiment # 4Document4 pagesEnergy Losses in Pipes: Experiment # 4محمد جوادNo ratings yet
- Black Iron Amended PEA PDFDocument372 pagesBlack Iron Amended PEA PDFemerson sennaNo ratings yet
- Test 2: Section 1Document5 pagesTest 2: Section 1Wall HarryNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 - Flow MeasurementDocument24 pagesExperiment 4 - Flow MeasurementKhairil Ikram67% (6)
- Flow Meter MeasurementDocument12 pagesFlow Meter Measurementrahman75% (8)
- Calibration of VenturimeterDocument5 pagesCalibration of VenturimeterRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Flow MeasurementDocument10 pagesFlow Measurementiroshauk67% (3)
- Rotameter Calibration SetupDocument5 pagesRotameter Calibration SetupnidhidarklordNo ratings yet
- Orifice MeterDocument15 pagesOrifice Metermurad67% (3)
- Fluids Lab Experiment:07 Name: Estimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter ApparatusDocument5 pagesFluids Lab Experiment:07 Name: Estimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter ApparatusDarivan DuhokiNo ratings yet
- 6 Orifice MeterDocument2 pages6 Orifice MeterMickey S LNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document22 pagesCH 5Ina Marie LampitocNo ratings yet
- JJ 308 Experiment 1Document4 pagesJJ 308 Experiment 1Edmond Emmanuel LeeNo ratings yet
- Mech. Engg. DepartmentDocument37 pagesMech. Engg. DepartmentHamza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 (Thermofluids Lab)Document32 pagesLab 4 (Thermofluids Lab)Adnan Nanda0% (1)
- Objective of Experiment. Equipment Set-Up. Theory of Experiment. Procedure. Results & Calculations. Discussion of The Results. ConclusionDocument11 pagesObjective of Experiment. Equipment Set-Up. Theory of Experiment. Procedure. Results & Calculations. Discussion of The Results. ConclusionAmmar Al-AghbariNo ratings yet
- 5 VenturiDocument3 pages5 VenturiMickey S LNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitDocument65 pagesFlow Measurement in Closed ConduitjohnmayardNo ratings yet
- Chemical Lab ReportDocument17 pagesChemical Lab Reportoprudra2000No ratings yet
- Lab Session 03 UptadeDocument7 pagesLab Session 03 UptadeAbdullah SahirNo ratings yet
- B21ME030 Lab3 PDFDocument8 pagesB21ME030 Lab3 PDFJaydeep Prajapati (B21ME030)No ratings yet
- Flowmeter Demonstration Lab ReportDocument25 pagesFlowmeter Demonstration Lab ReportEZWANNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 (Flowmeter Demonstration)Document23 pagesLab 4 (Flowmeter Demonstration)Muhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Im316 Flow MeasurementDocument67 pagesIm316 Flow MeasurementSelvarajNo ratings yet
- Venturimeter, Orificemeter & Rotameter Calibration Set-Up: Experiment No. 4Document9 pagesVenturimeter, Orificemeter & Rotameter Calibration Set-Up: Experiment No. 4Somya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Chemical EngineeringDocument32 pagesFaculty of Chemical EngineeringArif HanafiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7Document7 pagesExperiment No 7Faizan Ahmed67% (3)
- Method of Flow Measurement ..Document12 pagesMethod of Flow Measurement ..anuj kanadeNo ratings yet
- Volume flow rate guideDocument8 pagesVolume flow rate guidetfkthe46No ratings yet
- ReviewDocument31 pagesReviewkarlobrondialNo ratings yet
- ECHELON ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING LABDocument36 pagesECHELON ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING LABsaurav rajNo ratings yet
- Calibrate Venturi & Orifice MetersDocument7 pagesCalibrate Venturi & Orifice Metersrohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5: AIM: To Measure Fluid Flow by (A) ORIFICE METER and (B) V-NOTCHDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 5: AIM: To Measure Fluid Flow by (A) ORIFICE METER and (B) V-NOTCHVipul SolankiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document3 pagesExperiment 3MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Pitot Static TubeDocument4 pagesPitot Static TubeVrushiket PatilNo ratings yet
- Ce6412 04Document114 pagesCe6412 04karthickaryanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Measurement Lab ReportDocument16 pagesFluid Flow Measurement Lab Reportقاسمي عندامNo ratings yet
- Masinde Muliro University of Science and TechnologyDocument51 pagesMasinde Muliro University of Science and TechnologyKelvho GitongaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab MannualDocument14 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab MannualAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- FM CompleteDocument19 pagesFM Completenini jasniNo ratings yet
- Study of Pitot Tube - Air: Experiment No. 4 (A)Document9 pagesStudy of Pitot Tube - Air: Experiment No. 4 (A)Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Report Coefficient of DischargeDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Report Coefficient of DischargewaqarNo ratings yet
- B21ME030 Lab4 PDFDocument8 pagesB21ME030 Lab4 PDFJaydeep Prajapati (B21ME030)No ratings yet
- 02 Venturi MeterDocument5 pages02 Venturi MeterMehedi Hasan0% (1)
- FM Lab ManualDocument9 pagesFM Lab ManualAbhimanyu Singh BhatiNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument8 pagesVenturi MeterSwati SachanNo ratings yet
- MEE-361-Flow Measurement - UpdatedDocument35 pagesMEE-361-Flow Measurement - UpdatedSalvation EnarunaNo ratings yet
- Energy Loss Factors for Pipe FittingsDocument5 pagesEnergy Loss Factors for Pipe FittingsChristine Joyce A. CortezNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS Lab ManualDocument65 pagesFLUID MECHANICS Lab ManualPaulNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument23 pagesLab ReportAmy Farhana100% (1)
- Compare Flow Rates Using Mass Flow Meter and RotameterDocument15 pagesCompare Flow Rates Using Mass Flow Meter and RotameterIkhmal FirdausNo ratings yet
- Orifice Mouthpiece ManualDocument5 pagesOrifice Mouthpiece ManualgpradiptaNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement with Venturi MeterDocument7 pagesFlow Measurement with Venturi MeterJessray RepunteNo ratings yet
- Flow Meter Procedure: Rotameter, Venturi, OrificeDocument3 pagesFlow Meter Procedure: Rotameter, Venturi, OrificeZafirah Zaidi100% (1)
- REDocument1 pageREsssssNo ratings yet
- Ce 274-Engineering Hydraulics Flow Under A Sluce Gate and The Hydraulics Jump ExperimentDocument1 pageCe 274-Engineering Hydraulics Flow Under A Sluce Gate and The Hydraulics Jump ExperimentsssssNo ratings yet
- CFD AssignmentDocument2 pagesCFD AssignmentApurba Roy0% (2)
- CFD Analysis of Backward-Facing Step FlowDocument16 pagesCFD Analysis of Backward-Facing Step FlowsssssNo ratings yet
- Sadv Adfasd FDocument1 pageSadv Adfasd FsssssNo ratings yet
- Sadv Adfasd F DF DF DSF SFDocument1 pageSadv Adfasd F DF DF DSF SFsssssNo ratings yet
- Full Scale Tests of Heat Strengthened Glass With Ceramic FritDocument17 pagesFull Scale Tests of Heat Strengthened Glass With Ceramic FritKároly FurusNo ratings yet
- Pic Optimax-I-Connect Brochure 2021 en 0Document13 pagesPic Optimax-I-Connect Brochure 2021 en 0Selim RezaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of STEM learning approach among Malaysian secondary studentsDocument11 pagesEffectiveness of STEM learning approach among Malaysian secondary studentsJHON PAUL REGIDORNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Reference Books: No. Name Author PublisherDocument1 pageMathematics Reference Books: No. Name Author PublisherDelicateDogNo ratings yet
- MTEX Plot Pole Figures and Inverse Pole FiguresDocument9 pagesMTEX Plot Pole Figures and Inverse Pole FiguresIniyan Thiruselvam Navaladi KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- IB PHYSICS 2.4 Presentation All UnitDocument34 pagesIB PHYSICS 2.4 Presentation All UnitJustCallMeLarryNo ratings yet
- DLL All Subjects 2 q4 w8 d2Document8 pagesDLL All Subjects 2 q4 w8 d2Kinder DarpingNo ratings yet
- Stress Distribution in The Temporomandibular Joint After Mandibular Protraction A Three-Dimensional Finite Element StudyDocument10 pagesStress Distribution in The Temporomandibular Joint After Mandibular Protraction A Three-Dimensional Finite Element StudySelvaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 (Ap229d 3c)Document11 pagesGroup 4 (Ap229d 3c)aremyulNo ratings yet
- Sets ProbabilityDocument33 pagesSets ProbabilityGaithNo ratings yet
- Lab 4B Moles of Iron and CopperDocument6 pagesLab 4B Moles of Iron and CopperLaura Sitar0% (1)
- ANZ Aboriginal history, culture, and demographicsDocument13 pagesANZ Aboriginal history, culture, and demographicsЛада ПоселянинаNo ratings yet
- Terex Operator TrainingDocument4 pagesTerex Operator TrainingJohn100% (48)
- Automatic Optimization and Elastic ConstantsDocument15 pagesAutomatic Optimization and Elastic ConstantsFebriman ZendratoNo ratings yet
- Percorso Ii: The Led Roadway Lighting..Document2 pagesPercorso Ii: The Led Roadway Lighting..ChangKhenNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 MicroDocument14 pagesQuiz 2 MicroRoy CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Slab Design: 6,000MM X 4900MMDocument21 pagesSlab Design: 6,000MM X 4900MMJohnPhilip2000 GeraldizoNo ratings yet
- Ba Etamatic Dlt2001 16 Aen 195Document156 pagesBa Etamatic Dlt2001 16 Aen 195Banu EdoNo ratings yet
- Amx4+ Renewal PartsDocument132 pagesAmx4+ Renewal Partsluilorna27No ratings yet
- Ipc TM 650Document10 pagesIpc TM 650Jose Pablo VenegasNo ratings yet
- SDT Pipedrive Sales Dashboard TemplateDocument10 pagesSDT Pipedrive Sales Dashboard TemplateMANEESH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Feature DetectionDocument7 pagesJurnal Feature DetectionSalsabila FristiaNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 2 - Article Review - Opm530Document2 pagesIndividual Assignment 2 - Article Review - Opm530Amir HafiyNo ratings yet
- Top Insights: Briefing: A Short Sampling of Our Content Related To This Topic. The Report For Your TeamDocument1 pageTop Insights: Briefing: A Short Sampling of Our Content Related To This Topic. The Report For Your TeamALICIA PATIÑO MOLINANo ratings yet
- ECG Synthtetic - Cloudias - 07311840000004Document8 pagesECG Synthtetic - Cloudias - 07311840000004Wheel ChairNo ratings yet