Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kumkang Aluminium Formwork Technology: Pujari Bhargavi S., A. G. Shelake
Uploaded by
Lewoye BantieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kumkang Aluminium Formwork Technology: Pujari Bhargavi S., A. G. Shelake
Uploaded by
Lewoye BantieCopyright:
Available Formats
www.ijcrt.
org © 2018 IJCRT | Volume 6, Issue 2 April 2018 | ISSN: 2320-2882
KUMKANG ALUMINIUM FORMWORK
TECHNOLOGY
1
Pujari Bhargavi S., 2 A. G. Shelake
1
Student M.E. Construction and Management, 2Assistant Professor
1
Department of Civil Engineering,
1
R. M.D Sinhgad School Of Engineering Warje, Pune, India
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Abstract : Kumkang is a new and modified aluminium formwork technology which helps in faster completion of the construction
works. Kumkang aluminium formwork technology is nearing solution to rising demands of housing in India. With changing
times, new processes and materials are being used. The most important aspects that decide the success rate in construction are
Time, Speed, Quality, Cost and Safety of works. FORMWORK SYSTEMS are key factors that decide the time, speed, quality
and safety in construction. Formwork system basically moved from wooden to steel, and now from steel to Aluminium.
Significant use of advanced formwork is suitable for complex construction processes and also provides best results in cost
effectiveness. In this paper we shall deal with comparison of KUMKANG FORMWORK which a type of aluminium formwork
(AF) with conventional formwork.
IndexTerms - Aluminium form-works (AF), Kumkang Formwork, cost, Speed, Quality, Safety of works.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
I. INTRODUCTION
Aluminium formwork is concurring the world of construction in today’s date. To meet the ever increasing demands of the
population contractors, investors and engineers are striving hard to reduce cost of construction and making housing economical.
Pre-fabricated technology, formwork technology, Precast technology are various technologies which cater speed in construction.
Due to ever increasing population and extreme migration cities are getting over crowded. Migration leads to increase in
number of slums. In this paper I am introducing a 7 days floor technique. This technique is extremely time saving, and gives a
superior quality of construction. The most effective means available for the construction of high, medium and low rise mass
housing RCC structures. It is a precision-engineered formwork fabricated in Aluminum. Monolithic pouring. Walls, columns,
slabs & beam are poured together..
II. KUMKANG ALUMINIUM FORMWORK TECHNIQUE
General
Kumkang technique is a revolutionary aluminum formwork technique which is forming its base in construction field. It was
invented in Korea in 1979.This formwork system is suitable for both residential &commercial construction. Kumkang formwork
system is in today’s date is most trustful, safe, and up-to-date formwork technology available in market. This is a unique
formwork system in which walls, columns, beams, staircase, balconies along with door and window opening are cast in place.
The aluminum used in making the formwork is Aluminum A6061-T6 having specific gravity. Composition composed by
aluminum are Inner wall panel- slab corner and beam, Slab panel and support- In corner and hunch and accessory- wall tie/ round
pin/ wedge pin.
Components used in Kumkang Aluminium formwork technique
1. SLAB PANELS- The slab panel will be used to support the concrete weight during concrete pouring and casting.
2. WALL PANELS - Wall panels are available in various sizes and in Kumkang formwork technique they can be
customized as per the need of the architectural design. .
3. PIPE PROP SUPPORT- It remains under the prop head. Pipe support along with prop head remains in place until two
levels are casted. The pipe support is used to support the weight of slab during pouring and casting.
4. SLAB CORNER- Acts as a connection wall panel and slab panel. Slab corner is of two types slab corners inner and
outer.
5. PROP HEAD: Used to join mid beam and end beam, pipe support is placed under the prop.
6. WEDGS, LONG PINS AND ROUND PINS: Long pin along with wedge pin is used to fix joint pin with prop head and
beams. Round pin and Wedge pins are used in securing flat ties.
7. FLAT TIES: Flat tie is used to join the wall panel to opposite side panel. Use of no, of wall panels depends on wall
panel’s height.
8. PVC SLEEVES: PVC Sleeve as name suggests is a sleeve parse PVC material coating. Flat tie is inserted inside this
sleeve; its function is to protect the flat tie to be casted within the concrete.
9. WALLER BRACKET AND SQUARE TIE: The Waller bracket and square pipes are used to allow the horizontal
straightness of the wall panel as well as wall surface after casting.
Working cycle of Kumkang Aluminium Formwork.
DAY 1 – Erecting wall reinforcement.
DAY 2- Erecting Formwork
DAY 3- Slab reinforcement and electrical fittings
IJCRT1893160 International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT) www.ijcrt.org 9
www.ijcrt.org © 2018 IJCRT | Volume 6, Issue 2 April 2018 | ISSN: 2320-2882
DAY 4- Completing Electrical works and overall checking
DAY 5- Concrete pouring
DAY 6- De-shuttering and vertical formwork
DAY 7- De-shuttering slab and beam panels
DAY 8- Overall checking and finishing works
III. METHODOLOGY
KUMKANG ALUMINIUM FORMWORK WORKING METHOD EXECUTED INSITU:
1. Once the freeze versions of architectural and structural drawings are obtained, detail drawing of Mock up shuttering is
obtained. Based on mockup drawing the formwork panels are assembled .
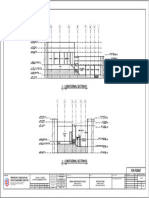
Figure 1 :Mock-Up Shuttering Drawing – All walls.
It would be cumbersome while execution if there is any revision in architectural and structural drawing.
Figure2: Mock-Up Shuttering according to Drawing.
2. Surveyor provides marking on columns, reinforcement of columns work start after that THECI is done which is to keep
formwork in line, and then fixing of shuttering is done.
3. Once the wall panels are erected, Slab panels are erected, then reinforcement of slab and beam is conducted after
checking of reinforcement is done, slab along with beams, columns and wall is done.
IJCRT1893160 International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT) www.ijcrt.org 10
www.ijcrt.org © 2018 IJCRT | Volume 6, Issue 2 April 2018 | ISSN: 2320-2882
Figure 3:Monolithic slab, beam and wall casting.
4. As rapid hardening cement is used, only 48 hrs curing is needed.
IV. WORKDONE AND RESULTS
CASE STUDY I:
The selected project for this case study is actually a project on development of a housing society (396 units). The STAR
TOWER is basically consisting 4 towers of dwelling unit, which are tower1, tower2, tower3 and tower4. This project is developed
by SKYi developers. These 4 blocks will be constructed in 8 level heights that locate 396 units of residential area, a ground level
car park area and mechanical and electrical equipments. But for tower4, the number of residential area that will be constructed in
actually 80 units. Other facilities compiled are a unit of guard post, playing courts, recreation area, playground and a unit of
disposal area. The site location in bhugoan Pune.
The study has been carried out on Site were Kumkang Technique is being executed.
Name of Project : “STAR TOWER” Manas Lake, Bhugoan, Pune.
A housing society project by SkyI developers.
Name Of Project Manager: Raju Shaikh
No of Floors: G + 8/ 2BHK/ 3 towers, G+ /1BHK Tower
Construction Method Adopted: Kumkang Aluminium Formwork Technology.
Plan: plan of tower 1. (Rest similar as tower 1)
Figure 4:Plan of tower no 1.
The specifications of aluminum formworksystems is shown in the Table below
Table 1: Aluminium Formwork
Sir no. Description Unit of Measurement Aluminum
L=2300-2450
1 Size Of Panel Millimeter
W= As per design
2 Cost of Product Rs/sqm 110$ i.e 7500
3 No. of repetition No 150-300
4 Skilled Labour Rs/day 550
IJCRT1893160 International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT) www.ijcrt.org 11
www.ijcrt.org © 2018 IJCRT | Volume 6, Issue 2 April 2018 | ISSN: 2320-2882
5 Unskilled labour Rs/day 400
6 Salvage value Rs/kg 120Rs/KG
7 Additional items --- Tie rod, Wing nut
Estimation of cost incurred in completion of major structural activities performed site by using Kumkang tqchnique.
Table 1: Cost of construction by Kumkang technology.
KUMKANG CONSTRUCTON- STAR
QUANTIY 15880
TOWER 15880SQFT
SCOPE OF WORK UNITS
CONCRETE STEEL RATE/UNIT TOTAL SQ.FT
Laying Plain Cement Concrete
1 cum 72.775 __ 4500 327487.5 20.63
Laying Reinforced cement
2 cum 335.03 __ 4525 1507635 94.94
concrete
Laying reinforcement (Footing)
3 Kg __ 11651 0 605852 38.16
Laying Reinforced cement
4 Cum 77.26 __ 4525 347670 21.893577
concrete(column)
Laying reinforcement (column)
5 Kg __ 20,223 58 1172934 73.87
Laying Reinforced cement
6 Cum 56.71 __ 4525 256612.75 16.16
concrete(beams)
LAYING RCC SLAB
7 Cum 111.21 __ 4525 503225.25 31.69
Laying reinforcement (beams)
8 Kg __ 11,328 58 657024 41.37
Laying reinforcement (Slab)
9 Kg __ 6,761 58 392138 24.7
Shuttering
10 Sq ft Consider 1 sqft __ 32.24
395.65
CASE STUDY II:
The selected project for this case study is a residential cum commercial development. It is a housing society with 2 towers (64
units). The LAXMI NIVAS is basically a dwelling unit developed by Fortune Vastushilpa Developers LLP. The possession of
the flats is in 2020. This block will be constructed in 8 level heights that locate 32 units of residential area, a ground level car park
area , mechanical and electrical equipments. The site location in Alandi, Pune.
TABLE3: CONVETIONAL FORMWORK
SR Unit of
Description Aluminum
NO Measurement
01 Size Of Panel Millimeter L=3000
IJCRT1893160 International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT) www.ijcrt.org 12
www.ijcrt.org © 2018 IJCRT | Volume 6, Issue 2 April 2018 | ISSN: 2320-2882
W= As per
design
02 Cost of Product Rs/sqm 500
03 No. of repetition No 5-7
04- Skilled Labour RS/day 451
05 Unskilled labour Rs/day 258
Estimation of cost incurred in completing major construction activities by conventional technique.
Table5: Cost of construction by conventional technique
CONVNTIONAL
QUANTIY CONSTRUCTON- 14715
SCOPE OF UNIT
LAXMI NIVAS
WORK S
CONCR RATE/
STEEL TOTAL SQ.FT
ETE UNIT
Laying Plain
Cement 42.50
1 cum 160 __ 4000 640000
Concrete
Laying
Reinforced 330.
2 cum __ 5700 1881000 127.8
00
cement concrete
Laying
reinforcement
3 Kg __ 12000 0 756000 51.38
(Footing)
Laying
Reinforced
cement
4 Cum 95.00 __ 5700 541500 36.80
concrete(column
Laying
reinforcement
5 Kg __ 23930 63 1507590 102.46
(column)
Laying
6 Cum 130.00 __ 5700 741000 50.36
Reinforced
IJCRT1893160 International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT) www.ijcrt.org 13
www.ijcrt.org © 2018 IJCRT | Volume 6, Issue 2 April 2018 | ISSN: 2320-2882
cement
concrete(beams)
LAYING RCC
7 Cum 145.00 __ 5700 826500 56.17
SLAB
Laying
reinforcement
8 Kg __ 28000 63 1764000 119.88
(beams)
Laying
reinforcement
9 Kg __ 9500 63 598500 40.68
(slab)
Shuttering Consider
10 Sq ft __ 185.00
1 sqft
814.00
Cost analysis:
Total cost analysis for material consumed and labor rates needed to complete the activity.
TIME COSTRENTS:
1. Kumkang aluminium system
For slab cycling that totally depend upon availability of workmanship for the shuttering work and we considering 8th floor only.
Here we are considering only one tower
1st slab – 21 days
2nd slab – 15 days
3rd to 8th slab – 48days (@ 8 days per floor)
Total – 87 days = 4 months + 2 months for finishing works approx considering 26 working days per month.
2. Conventional Formwork system.
For slab cycling that totally depend upon availability of workmanship for the shuttering work and we consider up to 8th floor
only.
1st slab – 21days curing + 7 days scaffolding
2nd to 6th slab – 33.5 days/ slab
= 167 days
7th and 8th slab – 36 days / slab = 72 days
Total- 267 days ;
That is: 9 months + 2 months for finishing works .
V. RESULTS
It is seen that there is substantial cost and time saving by adopting Kumkang Formwork Technique.
Table 6: Percentage savings in time and cost
PERCENTAGE
SR NO
DIFFERENCE
STAR LAXMI
TOWER NIVAS
30.82% COST
1 V1= 395.65 V2= 814.06
SAVED
T2= 267 23.09% TIME
2 T1=87 days
days SAVED
IJCRT1893160 International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT) www.ijcrt.org 14
www.ijcrt.org © 2018 IJCRT | Volume 6, Issue 2 April 2018 | ISSN: 2320-2882
Chart 1: Comparative bar chart of Cost and Time consumed by Kumkang technique andConventionltechnique
VI CONCLUSION
There significant changes in concrete construction as per the date. Pioneering companies in modern formwork system are
Peri, doka, tunnel formwork, meva, Mivan. Trying to cover the major aspects Cost and Time then quality, aesthetics, speed, safety
during construction I will infer that Kumkang Aluminium formwork provides a very high quality construction at a high
speed.This Kumkang Aluminium Formwork technology has great potential for application in India to provide affordable housing
to its rising population
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
I take an opportunity to acknowledge the enormous guidance and excellence co-operation extended towards me by all concerned
in the department. First we would like to express our sincere thanks to my Guide Prof. A. G. Shelake for his valuable guidance
and constant encouragement which enables me to execute our work. I sincerely thank all the staff from Civil Department for their
help, guidance for the idea of the project. Finally I would like to thank industrial experts for giving m valuable time and material
needed, and to all who help me directly or indirectly in successful completion of our project report.
REFERENCES
1. Ashish Wagmare(2017), “Comparision of conventional, Aluminum and Tunnel formwork” IJERT,
ISSN 0974- 3154 .
2. K. Loganathan, K.E Vishwanatahn(2016). “A study report on cost, duration and quality analyisis of
different formwork in high-rise building” IJSER, Volume 7, Issue 4.
3. Information on – http://www.mivan.com
4. Information on – http://www.kumkangkind.com
5. Information on – http://www.indiamart.com
6. Mr. Shankar Bimal Banerjee. “Mivan technology”IJIERT, march2015, ISSN: 2394:3696.
7. D.M. Wijesekara “Cost Effective and Speedy Construction for High- Rise Building in Sri
lanka”Using Aluminium Panel System Formworks.”ACRPS- 2012
8. Raymond WongWaiMan, “ Application of formwork for high rise building structures- The Hong
Kong Case” Division of building Science and Technology- City University of Hong Kong.
IJCRT1893160 International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT) www.ijcrt.org 15
You might also like
- Kumkang FormworkDocument5 pagesKumkang FormworkSolomon Nega100% (1)
- Spot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingFrom EverandSpot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingNo ratings yet
- Mivan ShutteringDocument4 pagesMivan ShutteringWanda BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Reinforced building design and cost estimation case studyDocument8 pagesReinforced building design and cost estimation case studyPacha Khan KhogyaniNo ratings yet
- Technical Report FORMATDocument8 pagesTechnical Report FORMATmaneeshNo ratings yet
- Mivan TechnologyDocument6 pagesMivan TechnologyIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Mivan 5 PDFDocument9 pagesMivan 5 PDFUtkarsh SuranaNo ratings yet
- File 2Document9 pagesFile 2leovinNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Detailing of RCC StructureDocument8 pagesReinforcement Detailing of RCC Structurevkagarwa2000No ratings yet
- 8 Comparative Analysis of Tunnel Formwork and AluminiumDocument3 pages8 Comparative Analysis of Tunnel Formwork and Aluminiumnazi nazNo ratings yet
- File 9Document4 pagesFile 9leovinNo ratings yet
- Wire Drawing Industry ProfileDocument10 pagesWire Drawing Industry ProfileSabhaya ChiragNo ratings yet
- Working of MivanDocument5 pagesWorking of MivanAnuja JadhavNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Pressure Die CastingDocument11 pagesAluminium Pressure Die CastingMarcos100% (1)
- Design and Fabrication of Roll Bending Machine: April 2018Document3 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Roll Bending Machine: April 2018Manfred GithinjiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Alluformwork and Conventional Formwork in Pune RegionDocument8 pagesComparative Analysis of Alluformwork and Conventional Formwork in Pune RegionleovinNo ratings yet
- 1by17cv020 - Internship PresentationDocument30 pages1by17cv020 - Internship PresentationMani K CNo ratings yet
- Welding Electrodes: Profile No.: 235 NIC Code:27102Document12 pagesWelding Electrodes: Profile No.: 235 NIC Code:27102ram prasad100% (1)
- fin_irjmets1645090099Document7 pagesfin_irjmets1645090099ks312105No ratings yet
- Aluminium Forms SystemDocument46 pagesAluminium Forms SystemHazbullah ShajiNo ratings yet
- One-storey fabricated steel structure workshopDocument10 pagesOne-storey fabricated steel structure workshopAbhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- Research On Construction Technology of Frame StrucDocument6 pagesResearch On Construction Technology of Frame StrucIjadunola John BelovedNo ratings yet
- Motorized Concrete Mixer Technology ProposalDocument9 pagesMotorized Concrete Mixer Technology Proposallabemanza03No ratings yet
- MIVAN ShutteringDocument4 pagesMIVAN ShutteringSyed Ahraz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Shuttering Design & Cost Comparisons: Rawal Meet Hemant, Bharakhada Mayank Prakash, Dhawde Akash AnkushDocument5 pagesShuttering Design & Cost Comparisons: Rawal Meet Hemant, Bharakhada Mayank Prakash, Dhawde Akash AnkushmjrulezNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Report of Residential BuildingDocument40 pagesStructural Analysis Report of Residential BuildingPrakash Singh RawalNo ratings yet
- Commercial MansionDocument4 pagesCommercial MansionPriyaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Bridge Girders Using Different Codes IJERTV8IS070188Document8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Bridge Girders Using Different Codes IJERTV8IS070188Pritesh RAINo ratings yet
- Industrial Origami A ReviewDocument5 pagesIndustrial Origami A ReviewIJIRAE- International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced EngineeringNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Transparent Concrete: International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)Document6 pagesAn Overview On Transparent Concrete: International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)NikhilNo ratings yet
- SPPP'S, Karmayogi Engineering College, Pandharpur: & Organize Special IssueDocument8 pagesSPPP'S, Karmayogi Engineering College, Pandharpur: & Organize Special IssueAnonymous Ygz2shJhJaNo ratings yet
- Aluminium FormworkDocument14 pagesAluminium FormworkebinVettuchirayil100% (6)
- Formwork Analysis Analysis of Formwork Types for Cost Optimization in Multistory BuildingsDocument3 pagesFormwork Analysis Analysis of Formwork Types for Cost Optimization in Multistory BuildingsCIVIL DEPARTMENT MMANTCNo ratings yet
- Seminar on Internship SumanthDocument39 pagesSeminar on Internship Sumanthsumanthkrishnas25No ratings yet
- A Product Study On Cost Analysis in Stud India PVT - LTDDocument10 pagesA Product Study On Cost Analysis in Stud India PVT - LTDPrasanth AyyappanNo ratings yet
- Mivan Shuttering Report: Submitted To: Mr. Jigar Hathi Wala (Research Mentor) Submitted By: ANIMESH NARAYANDocument13 pagesMivan Shuttering Report: Submitted To: Mr. Jigar Hathi Wala (Research Mentor) Submitted By: ANIMESH NARAYANAnimesh Narayan Singh100% (1)
- Pressure Die Casting - Al - NewDocument17 pagesPressure Die Casting - Al - Newhardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- ROEURTH Sarakyuth Induu MethoddDocument3 pagesROEURTH Sarakyuth Induu Methoddmeassarak0No ratings yet
- Irjet V7i3585Document9 pagesIrjet V7i3585CIVIL DEPARTMENT AVCENo ratings yet
- Pre-Engineered Building - A New Trend of Industrial Building: (Volume3, Issue8)Document2 pagesPre-Engineered Building - A New Trend of Industrial Building: (Volume3, Issue8)wonderskiranNo ratings yet
- Design and Detailing of RC Jacketting For Concrete Columns: ArticleDocument6 pagesDesign and Detailing of RC Jacketting For Concrete Columns: Articleamanh7618No ratings yet
- Pump HouseDocument6 pagesPump HouseHitesh GajeraNo ratings yet
- JIMMA UNIVERSITY INTERNS' MANUFACTURING EXPERIENCEDocument41 pagesJIMMA UNIVERSITY INTERNS' MANUFACTURING EXPERIENCEAmanuelNo ratings yet
- Structural Failures Case StudiesDocument33 pagesStructural Failures Case StudiesRakesh7770No ratings yet
- MivanDocument101 pagesMivanDipak KaleNo ratings yet
- Project Profile On Hard Chromium PlatingDocument13 pagesProject Profile On Hard Chromium PlatingKishora BhatNo ratings yet
- Irjet V7i9635Document7 pagesIrjet V7i9635valengape13No ratings yet
- Report Project CompleteDocument41 pagesReport Project CompletesitijarahmadzinNo ratings yet
- Mudhra Presentation PDFDocument27 pagesMudhra Presentation PDFsk2689No ratings yet
- Design of Conical Roof Structure for Liquid Sulphur Storage TankDocument7 pagesDesign of Conical Roof Structure for Liquid Sulphur Storage TankSaravanan Silamban100% (1)
- 13 Wos AnalysisanddesignofbuildingDocument9 pages13 Wos AnalysisanddesignofbuildingDepartment of Civil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Commercial Cum Residential Building by Using STAAD ProDocument7 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Commercial Cum Residential Building by Using STAAD ProTarun TaruNo ratings yet
- Irjet V5i4722Document3 pagesIrjet V5i4722wendiezemene2124No ratings yet
- 2nd Draft Stair ProposaDocument7 pages2nd Draft Stair ProposaSamwovenNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Ordinary and Supa Sections of Cold Formed SteelDocument4 pagesComparative Study of Ordinary and Supa Sections of Cold Formed SteelamokeNo ratings yet
- 13 Wos AnalysisanddesignofbuildingDocument9 pages13 Wos AnalysisanddesignofbuildingRevathiNo ratings yet
- Aluminium CastingDocument35 pagesAluminium CastingAnkur Aggarwal100% (1)
- Development of 40ka Earthing Switch by Using Industrial Product Design ModelDocument10 pagesDevelopment of 40ka Earthing Switch by Using Industrial Product Design Modelachaugule_1No ratings yet
- Mivan - A Versetile FormworkDocument25 pagesMivan - A Versetile FormworkSAMIR SHANWARE100% (1)
- Emu AssignmentDocument9 pagesEmu AssignmentLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is Evaluation CambridgeDocument42 pages1.1 What Is Evaluation CambridgeLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- 1.3 How To Randomize CambridgeDocument86 pages1.3 How To Randomize CambridgeLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Why Randomize?: Jim Berry Cornell UniversityDocument50 pagesWhy Randomize?: Jim Berry Cornell UniversityLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- A Dynamic CGE Modelling Approach For Analyzing Trade-Offs in Climate Change Policy Options: The Case of Green Climate FundDocument42 pagesA Dynamic CGE Modelling Approach For Analyzing Trade-Offs in Climate Change Policy Options: The Case of Green Climate FundLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Smart PlsDocument23 pagesSmart PlsLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia 2030: The Pathway To Prosperity: Ten Years Perspective Development Plan (2021 - 2030)Document37 pagesEthiopia 2030: The Pathway To Prosperity: Ten Years Perspective Development Plan (2021 - 2030)Lewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Econ 607 Linear Regression AssignmentDocument2 pagesEcon 607 Linear Regression AssignmentLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Ousam OutputDocument25 pagesOusam OutputLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Assignment I - E-May 2021Document3 pagesAssignment I - E-May 2021Lewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Ch21 2015 3Document32 pagesCh21 2015 3Lewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Private Equity & Venture Capital: in The Middle East & AfricaDocument16 pagesPrivate Equity & Venture Capital: in The Middle East & AfricaLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Keynesian IS-LM Model PDFDocument15 pagesKeynesian IS-LM Model PDFRupesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- IS LM20IntroductionDocument12 pagesIS LM20IntroductionLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Keynesian Macroeconomics Without The LM CurveDocument22 pagesKeynesian Macroeconomics Without The LM CurvejohnpaulcorpusNo ratings yet
- Advanced MacroeconomicsDocument82 pagesAdvanced MacroeconomicsLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Macro ThoughtDocument32 pagesCh2 Macro ThoughtLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microeconomics - Problem Set 1Document3 pagesAdvanced Microeconomics - Problem Set 1pcr123100% (1)
- 1 The IS/LM Model (Romer Chapter 5)Document2 pages1 The IS/LM Model (Romer Chapter 5)Lewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Aggregate SSDocument13 pagesCh4 Aggregate SSLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Ch5 OpeneconomyDocument17 pagesCh5 OpeneconomyLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Ch1introand MeasureDocument65 pagesCh1introand MeasureLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Aggregate DDDocument67 pagesCh3 Aggregate DDLewoye BantieNo ratings yet
- USA V Brandon Hunt - April 2021 Jury VerdictDocument3 pagesUSA V Brandon Hunt - April 2021 Jury VerdictFile 411No ratings yet
- CLASS 7B Result Software 2023-24Document266 pagesCLASS 7B Result Software 2023-24JNVG XIB BOYSNo ratings yet
- L.G.B.T. Fiction: Book ReviewDocument4 pagesL.G.B.T. Fiction: Book ReviewDejana KosticNo ratings yet
- Beaba Babycook Recipe BookDocument10 pagesBeaba Babycook Recipe BookFlorina Ciorba50% (2)
- Kent Thiry IndictmentDocument10 pagesKent Thiry IndictmentMichael_Roberts2019No ratings yet
- Use VCDS with PC lacking InternetDocument1 pageUse VCDS with PC lacking Internetvali_nedeleaNo ratings yet
- 3.part I-Foundations of Ed (III)Document25 pages3.part I-Foundations of Ed (III)Perry Arcilla SerapioNo ratings yet
- IFCRecruitment Manual 2009Document52 pagesIFCRecruitment Manual 2009Oklahoma100% (3)
- MSc Thesis on VAW in PhilippinesDocument100 pagesMSc Thesis on VAW in Philippineselma cutamoraNo ratings yet
- STS Lesson 1-2Document23 pagesSTS Lesson 1-2zarnaih SmithNo ratings yet
- Teresita Dio Versus STDocument2 pagesTeresita Dio Versus STmwaike100% (1)
- A-7 Longitudinal SectionDocument1 pageA-7 Longitudinal SectionarjayymerleNo ratings yet
- QRT1 WEEK 8 TG Lesson 22Document5 pagesQRT1 WEEK 8 TG Lesson 22Bianca HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4 - Group 6Document15 pagesLab Report 4 - Group 6ClarisshaNo ratings yet
- Policy - SIM Cards Point of Sale Registration EngDocument6 pagesPolicy - SIM Cards Point of Sale Registration EngSHALOM SHUMBANo ratings yet
- Sec 4 RA 6713 & Sec 3 RA 3019 OutlineDocument4 pagesSec 4 RA 6713 & Sec 3 RA 3019 OutlineAivan Charles TorresNo ratings yet
- Processing, Handling and Storage of Agricultural Product 2Document6 pagesProcessing, Handling and Storage of Agricultural Product 2LittleagleNo ratings yet
- Credit As A Means of Investment in Medieval Islamic TradDocument6 pagesCredit As A Means of Investment in Medieval Islamic TradIfanaNo ratings yet
- 10th IIT Foundation PDFDocument170 pages10th IIT Foundation PDFbondala pavan100% (1)
- Alex Tissandier Affirming Divergence PDFDocument194 pagesAlex Tissandier Affirming Divergence PDFDwi PlatomoNo ratings yet
- Ky203817 PSRPT 2022-05-17 14.39.33Document8 pagesKy203817 PSRPT 2022-05-17 14.39.33Thuy AnhNo ratings yet
- A Powerful Graphic Liquid Crystal Display: Column #47, March 1999 by Lon GlaznerDocument16 pagesA Powerful Graphic Liquid Crystal Display: Column #47, March 1999 by Lon GlaznerVijay P PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- Document Application and Review FormDocument1 pageDocument Application and Review FormJonnel CatadmanNo ratings yet
- MSDS Hygisoft Surface Disinfectant, Concentrate - PagesDocument5 pagesMSDS Hygisoft Surface Disinfectant, Concentrate - PagesDr. Omar Al-AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Duttaphrynus Melanostictus,: Errata VersionDocument11 pagesDuttaphrynus Melanostictus,: Errata Versionutama 3002No ratings yet
- Json Cache 1Document5 pagesJson Cache 1Emmanuel AmoahNo ratings yet
- 100 Answers To Common English QuestionsDocument9 pages100 Answers To Common English Questionsflemus_1No ratings yet
- Coleção Bernoulli Ensino Médio 2020 - 100% BNCC by Bernoulli Sistema de Ensino - IssuuDocument1 pageColeção Bernoulli Ensino Médio 2020 - 100% BNCC by Bernoulli Sistema de Ensino - IssuuVitor OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Fabric Trademark and Brand Name IndexDocument15 pagesFabric Trademark and Brand Name Indexsukrat20No ratings yet
- Balint Training System 1948Document16 pagesBalint Training System 1948Laura Acosta100% (2)