Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Planea Tu Viaje Guía Moderno Con Rectángulos Negros Con Fondo Blanco Infografía
Uploaded by
David Cagua CuadrosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Planea Tu Viaje Guía Moderno Con Rectángulos Negros Con Fondo Blanco Infografía
Uploaded by
David Cagua CuadrosCopyright:
Available Formats
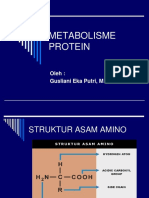
Urea cycle
disorders
Amino acid turnover in the body results in excessive ammonia
production. In addition, ammonia is produced by intestinal
urease-positive bacteria as well as constantly during amino
acid metabolism. Hence, ammonia needs to be detoxified
appropriately and the urea cycle performs the critical
function of converting ammonia into urea.
THE ENZYMES ASSOCIATED WITH THE ENZYMES ASSOCIATED WITH THE
AMMONIA PRODUCTION UREA CYCLE AND ITS DISORDERS
Under baseline conditions, ammonia is produced Ornithine activates urea synthesis and described
through the catabolism of glutamine by the urea cycle as the pathway, which converts
glutaminase, glutamate dehydrogenase and ammonia into urea prior to excretion via the
bacterial deaminase. In addition, urea is kidney. The biochemical reaction that produces
metabolized to ammonia by bacterial urease. urea from ammonia is performed mainly in the
The second route of ammonia production is the liver and to a much lesser extent in the kidney.
nitrogen metabolism associated with amino acid
catabolism.
CARBAMOYLPHOSPHATE SYNTHETASE 1 N-ACETYLGLUTAMATE SYNTHASE
CPS1 catalyzes the condensation of ammonia and NAGS catalyzes the conversion of glutamate and
bicarbonate into carbamoylphosphate in the acetyl-CoA to NAG, which is the allosteric
mitochondrial matrix, which requires an activator of CPS1. Mutations of the NAGS gene,
allosteric activator, NAG, magnesium, located on 17q21.3, lead to a deficiency of NAG
and ATP. CPS1 is the rate limiting enzyme of the and a defect of CPS1, which cannot convert
urea cycle. ammonia into carbamoylphosphate in the absence
of NAG.
ORNITHINE TRANSCARBAMYLASE ARGININOSUCCINATE SYNTHETASE 1
OTC catalyzes the synthesis of citrulline from ASS1 conjugates citrulline and aspartate in the
carbamoylphosphate and ornithine. The OTC gene cytosol of hepatocytes to generate
is located on Xp21.1. Thus, OTC deficiency is, argininosuccinate. The ASS1 gene is located on
as the only UCD, an X-linked genetic disease. 9q34, and ASS1 deficiency is an autosomal
recessive disorder with broad phenotypic
variability.
CITRIN ARGININOSUCCINATE LYASE
Citrin acts as a mitochondrial membrane ASL is a cytosolic enzyme which catalyzes
aspartate–glutamate transporter encoded by argininosuccinate to arginine and fumarate.
SLC25A15, a gene localized on 7q21.3. Mutations Mutations of this gene result in
in this gene result in defective citrin argininosuccinic aciduria, which is an autosomal
activity, reducing aspartate export from the recessive disorder,and tissue accumulation of
mitochondria to the cytosol, leading to a argininosuccinate.
condition in which aspartate is not available as
ASS substrate to generate argininosuccinate in
the liver.
MITOCHONDRIAL ORNITHINE
ARGINASE 1 TRANSPORTER
ARG1 catalyzes the hydrolysis of arginine to The transport of ornithine from the cytosol to
ornithine and urea as the final step in the urea the mitochondrial matrix and the export of
cycle. citrulline from the mitochondrion into the
Mutations of this gene cause defective ARG1 cytosol is carried out by ORNT1.
activity and comprise an autosomal recessive Mutations of this gene cause ornithine
disorder that exhibits phenotypic translocase deficiency.
variability.
Metabolic cascade of the urea cycle in the liver.
Ammonia toxicity: Ammonia easily crosses the blood-brain barrier in its non-
ionized form. Once a metabolic crisis has developed, a large amount of
ammonia can accumulate in the blood and also the brain. Hyperammonemia
causes neurological dysfunction such as tremor, ataxia, seizures, coma, and
death.
CLINICAL INVESTIGATION AND THE
SYMPTOMS LABORATORY
TESTS FOR DIAGNOSIS
1. Presymptomatic form: identified by UCDs should be primarily suspected when a
predelivery diagnosis (see the “prenatal patient presents with hyperammonemia without
testing”) or neonatal screening tests. metabolic acidosis and with a normal blood
2. Neonatal-onset form: neurological symptoms glucose level.
associated with hyperammonemia during the ARG and ASL deficiencies are distinguished
neonatal period. by elevated concentrations of arginine and
3. Late-onset form: neurological symptoms with argininosuccinic acid, respectively.
hyperammonemia persist from infancy through
adulthood, and are triggered by several triggers
leading to catabolic states.
TESTING FOR PLASMA AMMONIA LEVELS AMINO ACID ANALYSIS
Premature neonates: <150 μmol/L (255 μg/dl) The plasma and urinary amino acid profiles in
Term neonates: <100 μmol/L (170 μg/dl) patients with UCDs can show specific changes.
Infants and children: <40 μmol/L (68 μg/dl) Hence, amino acid analysis is used for the
Adolescents and adults: 11–32 μmol/L (19–54 initial biochemical diagnosis of UCDs.
μg/dl)
URINARY OROTIC ACID ENZYME ACTIVITY ANALYSIS
Orotic acid is an intermediate in pyrimidine Enzyme activity assays can help confirming the
biosynthesis. The urinary excretion of orotic diagnosis and the residual activity if the
acid is increased in many UCDs including defects genetic test does not give a clear result. Liver
of OTC, ASS, ASL, ARG1, and ORNT1 tissue, the intestinal mucosa, erythrocytes, and
fibroblasts can be used for enzyme activity
assay in some of the UCDs.
GENETIC ANALYSIS PRENATAL TESTING
Genetic testing is the method of choice to Prenatal testing in UCDs is available in several
confirm the diagnosis of a UCD nowadays. The countries for pregnancy termination in the
sensitivity of genetic analysis varies between severe cases. This may also be indicated in
the different disorders but is at least milder UCDs or for NAGS deficiency for
80%. psychological reasons and to prepare for
perinatal management.
Treatment: It is urgent to reduce the plasma ammonia level and protect
against brain damage when hyperammonemia is noted.
CLINICAL TREATMENT LIVER TRANSPLANT
In the acute phase, hemodialysis or LT is able to normalize the plasma ammonia
hemodiafiltration are the most efficient levels in UCD patients.
treatments for reducing the plasma ammonia The quality of life substantially improved in
concentration. The dialysis method depends on all of these surviving children. A normalization
the condition of the affected patient, the of diet and a reduction in hospital admissions
available equipment, and the experience of the were observed.
dialysis team. For instance, continuous Almost all of the cases improved or completely
hemodiafiltration is often used in neonates recovered after LT.
because of the greater safety and tolerability. LT is not a perfect therapy because there are
In the chronic phase, preventing both a small amounts of defective enzymes that are
catabolic condition and a recurrence of still present in the kidney, gut and brain. The
hyperammonemia is important. Any form of physiological importance of cerebral expression
catabolism, tissue damage and bleeding are of some urea cycle enzymes, such as ASL and ARG,
triggering events to prevent. A protein- has been reported. In addition, the plasma
restricted diet and formula should be concentration of citrulline is not corrected by
maintained and high-caloric intake is needed, LT, so citrulline supplementation is still
which is the mainstay of long-term management required for OTC or CPS1 deficiency patients
that is based on minimizing the nitrogen load on after LT.
the urea cycle life-long unless LT is performed.
Human ammonia generation and metabolism.
Bibliography: Matsumoto, S., Häberle, J., Kido, J., Mitsubuchi,
H., Endo, F., & Nakamura, K. (2019). Urea cycle disorders—update.
Journal Of Human Genetics, 64(9), 833-847. doi: 10.1038/s10038-
019-0614-4
You might also like
- UAS KARBOHIDRAT 2-DikonversiDocument18 pagesUAS KARBOHIDRAT 2-DikonversiumayaNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle Disorder: Group 3Document22 pagesUrea Cycle Disorder: Group 3AdrianNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Urea Cycle DisorderDocument22 pagesGroup 3 Urea Cycle DisorderAdrianNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle Disorders: Moderator: Dr. A.K Bala Speaker: Dr. Aradhana MishraDocument28 pagesUrea Cycle Disorders: Moderator: Dr. A.K Bala Speaker: Dr. Aradhana MishraIndranil DuttaNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia: 3.1.-Una Patologia On Està Implicada. Modificació Estructural I Funcional (100 Paraules) (Jose)Document4 pagesWikipedia: 3.1.-Una Patologia On Està Implicada. Modificació Estructural I Funcional (100 Paraules) (Jose)jcasanovas1995No ratings yet
- Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids. Metabolic Defects in Amino Acid MetabolismDocument36 pagesGlucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids. Metabolic Defects in Amino Acid MetabolismTHENEXTSTEPNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle DisordersDocument28 pagesUrea Cycle DisordersIndranil DuttaNo ratings yet
- Urea CycleDocument11 pagesUrea CycleRohit VinayNo ratings yet
- Hyperammonemia in ReviewDocument16 pagesHyperammonemia in ReviewIka KusumaNo ratings yet
- HyperammonemiaDocument10 pagesHyperammonemiaAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- IBMDocument54 pagesIBMhaidernadhem57No ratings yet
- Investigation of Plasma Protein DisordersDocument10 pagesInvestigation of Plasma Protein DisordersJosiah BimabamNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualDocument5 pagesInborn Errors of Metabolism: Intensive Care Nursery House Staff ManualwarishNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Urea SynthesisDocument14 pagesInborn Errors of Urea SynthesisDaryl Jacob Bigay100% (1)
- Urgencias Actualización 33Document10 pagesUrgencias Actualización 33Roli CuizzNo ratings yet
- Rinkal 2Document38 pagesRinkal 2Vidhin ThumbarNo ratings yet
- Journal Club: Paolo Dametto January 2013Document42 pagesJournal Club: Paolo Dametto January 2013Олег ЕвсюковNo ratings yet
- 32 IndianDocument3 pages32 IndianPrateek Kumar PandaNo ratings yet
- HYPERAMMONEMIADocument10 pagesHYPERAMMONEMIANaisha JNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport Disorders of Amino AcidsDocument5 pagesMembrane Transport Disorders of Amino Acidsz000zaNo ratings yet
- Recognizingandmanaginga Metaboliccrisis: Peter R. Baker IiDocument15 pagesRecognizingandmanaginga Metaboliccrisis: Peter R. Baker IiSara RamírezNo ratings yet
- Biochem QuestionsDocument15 pagesBiochem QuestionsSamantha SerraoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22.1 Urea Cycle DefectsDocument3 pagesChapter 22.1 Urea Cycle Defectspriyanshu mathurNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Protein: Oleh: Gusliani Eka Putri, M.SiDocument65 pagesMetabolisme Protein: Oleh: Gusliani Eka Putri, M.Sipuskesmas patamuanNo ratings yet
- Clinchem 1565Document4 pagesClinchem 1565ghfkhgfjhfgNo ratings yet
- Inborn ErrorsDocument16 pagesInborn ErrorsSophia PerdidoNo ratings yet
- Bone markers and collagen breakdown testsDocument11 pagesBone markers and collagen breakdown testsFrancesco De PalmaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Tests for Proteins and Tumor MarkersDocument12 pagesClinical Chemistry Tests for Proteins and Tumor MarkersClark Lopez100% (1)
- Aspartate AminotransferaseDocument6 pagesAspartate AminotransferaseHusna Nur FitrianaNo ratings yet
- 10 Amylase, Lipase, Gamma Glutamyl Transferase, Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase, Cholinesterase and 5-NucleotidaseDocument29 pages10 Amylase, Lipase, Gamma Glutamyl Transferase, Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase, Cholinesterase and 5-NucleotidaseFrances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure and Anaesthesia Update 18Document4 pagesChronic Renal Failure and Anaesthesia Update 18ashishpandeygNo ratings yet
- Chemical Pathology 2 - Plasma ProteinsDocument5 pagesChemical Pathology 2 - Plasma ProteinsaNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of Metabolism and Introduction To Cancer GeneticsDocument9 pagesInborn Error of Metabolism and Introduction To Cancer GeneticsviancaNo ratings yet
- Notes 02 Clinical Chemistry 2Document6 pagesNotes 02 Clinical Chemistry 2Brent LagartoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Metabolism and Diabetes MellitusDocument63 pagesCarbohydrates Metabolism and Diabetes Mellitusapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Plasma Amino Acids Levels in Obesity and Insulin ResistanceDocument13 pagesPlasma Amino Acids Levels in Obesity and Insulin ResistanceNick FInerNo ratings yet
- Non-Protein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument6 pagesNon-Protein Nitrogen CompoundspixiedustNo ratings yet
- MRCP EndocrineDocument94 pagesMRCP EndocrineMarwan M.100% (3)
- 9. Plasma Proteins-IDocument41 pages9. Plasma Proteins-IZoraiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Plasmatic Protein Structure and DisordersDocument24 pagesPlasmatic Protein Structure and DisordersMaria Amelia MercaNo ratings yet
- Disorders Potassium 2023-24Document18 pagesDisorders Potassium 2023-24Francisco C. Belloso HornaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry-1 - 1Document13 pagesBiochemistry-1 - 1khaledNo ratings yet
- AmLyte 13 Package Insert-EnDocument21 pagesAmLyte 13 Package Insert-EnGuneyden GuneydenNo ratings yet
- Lacture 5Document116 pagesLacture 5Ahmed Makky JafarNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentFrom EverandFast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Aromatic Amino AcidsDocument6 pagesDisorders of Aromatic Amino AcidsJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Lectures - Biochemistry 1 - 2021-2022 Prof Version 6.01 - 23-24-201-231Document31 pagesLectures - Biochemistry 1 - 2021-2022 Prof Version 6.01 - 23-24-201-231Ken M'voulaboloNo ratings yet
- Hyper AmmoniaDocument10 pagesHyper AmmoniaThamizh Arasi Vinayagam100% (1)
- Abetalipoproteinemia The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human GeneticsDocument4 pagesAbetalipoproteinemia The Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Geneticsanisa auliaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Application of EnzymesDocument6 pagesClinical Application of EnzymesTemesgen MucheyeNo ratings yet
- Hyperammonemia: Department of BiochemistryDocument7 pagesHyperammonemia: Department of BiochemistryMohammed MNo ratings yet
- Hyperammonemia: Department of BiochemistryDocument7 pagesHyperammonemia: Department of BiochemistryMohammed MNo ratings yet
- hyperammonemia^Jنور الهدى الهدى حسين الماسDocument7 pageshyperammonemia^Jنور الهدى الهدى حسين الماسMohammed MNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle 1Document25 pagesUrea Cycle 1Tanvi ShindeNo ratings yet
- CDD Is 2013151 ADocument10 pagesCDD Is 2013151 ADalton JLNo ratings yet
- Oka 2Document10 pagesOka 2Nina lucia Paulino AngelesNo ratings yet
- Wa0028.Document46 pagesWa0028.Ziyadan AtiqueNo ratings yet
- Pain Management Nursing: Theresa Mallick-Searle, MS, RN-BC, Anp-Bc, Barbara St. Marie, PHD, AgpcnpDocument6 pagesPain Management Nursing: Theresa Mallick-Searle, MS, RN-BC, Anp-Bc, Barbara St. Marie, PHD, AgpcnpDavid Cagua CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Cannabinoids For Treatment of Chronic Non-Cancer Pain A Systematic Review of Randomized TrialsDocument10 pagesCannabinoids For Treatment of Chronic Non-Cancer Pain A Systematic Review of Randomized TrialsDavid Cagua CuadrosNo ratings yet
- The Role of Cannabinoids in Neurodeoenerative Diseases: Elsevier PiiDocument23 pagesThe Role of Cannabinoids in Neurodeoenerative Diseases: Elsevier PiiDavid Cagua CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Lipids and Lipoproteins - Endotext - NCBI BookshelfDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Lipids and Lipoproteins - Endotext - NCBI BookshelfDavid Cagua CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms and Regulation of Cholesterol HomeostasisDocument3 pagesMechanisms and Regulation of Cholesterol HomeostasisDavid Cagua CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Planea Tu Viaje Guía Moderno Con Rectángulos Negros Con Fondo Blanco InfografíaDocument2 pagesPlanea Tu Viaje Guía Moderno Con Rectángulos Negros Con Fondo Blanco InfografíaDavid Cagua CuadrosNo ratings yet
- The Glyoxylate Pathway ExplainedDocument8 pagesThe Glyoxylate Pathway Explainedrahul pNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Light and Dark Reaction of PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesCompare and Contrast Light and Dark Reaction of PhotosynthesisSari Mae R. AragonNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Report 4Document8 pagesEnzyme Report 4Hema KannanNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument35 pagesElectron Transport ChainNusrat JahanNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz in Science 9Document2 pagesLong Quiz in Science 9Kuya Tiong TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument21 pagesAnaerobic RespirationRex IanNo ratings yet
- How Cells Release Stored EnergyDocument57 pagesHow Cells Release Stored EnergykylevNo ratings yet
- Case Study Bio Lactic AcidDocument9 pagesCase Study Bio Lactic Acidfarah syamimiNo ratings yet
- FA Synthesis 2019Document37 pagesFA Synthesis 2019Mohan bhargavNo ratings yet
- U-5 Energy Transformation PDFDocument41 pagesU-5 Energy Transformation PDFHawi kelbessaNo ratings yet
- Student Book 2Document101 pagesStudent Book 2helena coelho odaNo ratings yet
- Amphibolic Nature of Krebs Cycle: How What We Are Is What We EatDocument33 pagesAmphibolic Nature of Krebs Cycle: How What We Are Is What We EatMargaret SannohNo ratings yet
- Urea CycleDocument3 pagesUrea CycleHshshdhdNo ratings yet
- Bab.4. AnabolismeDocument14 pagesBab.4. AnabolismeSurniSajaNo ratings yet
- Cell respiration processes and the Krebs cycleDocument7 pagesCell respiration processes and the Krebs cycleDemilogicNo ratings yet
- Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Peroxide Signaling in Higher PlantsDocument275 pagesNitric Oxide and Hydrogen Peroxide Signaling in Higher PlantsJ. Enrique BlandonNo ratings yet
- Increased Fat Oxidation Is The Cause of Kidney Damage Ray Peat ForumDocument1 pageIncreased Fat Oxidation Is The Cause of Kidney Damage Ray Peat ForumPiscis PtmNo ratings yet
- AP Bio HW 9 091016Document5 pagesAP Bio HW 9 091016haithere123No ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument2 pagesGlycolysisapi-323720899No ratings yet
- Respirasi Sel: PracticeDocument2 pagesRespirasi Sel: PracticeteahockNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 5 Estimating TerDocument9 pagesExercise No. 5 Estimating Termarjourie cadampogNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and AtpDocument20 pagesMetabolism and AtpAbdul Rafay ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Atp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesDocument6 pagesAtp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesJhondel GuirrenNo ratings yet
- Bms2 Integration of MetabolismDocument42 pagesBms2 Integration of MetabolismhohoylandNo ratings yet
- BP203 T. BIOCHEMISTRY (Theory) These Topics Was Completed Unit I BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesBP203 T. BIOCHEMISTRY (Theory) These Topics Was Completed Unit I BiomoleculesDeepakNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument22 pagesRespiration in PlantsTabada NickyNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Week 8Document4 pagesScience 9 Week 8lenNo ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation by SatishDocument12 pagesBiological Oxidation by SatishBiochemistry DenNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Module 2Document3 pagesBiochemistry Module 2Sanee ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Worksheet-R06answersDocument3 pagesCell Respiration Worksheet-R06answersAllison KhooNo ratings yet