Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Value Stream Q-Basics: Maintenance (TPM) Test Equipment
Uploaded by
Rodolfo M. PortoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Value Stream Q-Basics: Maintenance (TPM) Test Equipment
Uploaded by
Rodolfo M. PortoCopyright:
Available Formats
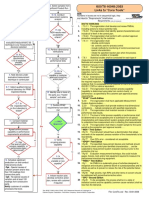
Principle 1 | Stop Sign Principle 2 | Andon Cord Principle 3 | Instructions Principle 4 | Process Parameters
Value Stream Customer complaints are communi-
cated within the production site and, if
In the event of deviations in quali-
ty or if control limits are exceeded
Safety, health, production, and in-
spection instructions are complied
The target values/tolerances for
all stated process parameters
Q-Basics
possible, displayed directly at the sta- in the value stream (source, make, with. 5S standards are put in place are observed.
tion in question. Using problem-solving deliver), the employee needs to and observed.
techniques, they are processed in a stop the process or escalate.
fast and systematic manner. The sup-
ply chain is promptly informed.
Principle 5 | Measurement/ Principle 6 | Check the Checker Principle 7 | Total Productive Principle 8 | Tools Principle 9 | Restart
Test Equipment Maintenance (TPM)
Measuring and test equipment is The “check the checker” principle A maintenance standard is in- Each tool has a defined service life; Restart after disruptions is clearly
defined, and monitoring intervals is applied, and the “checker’s” stalled and observed at every the current status must be recog- regulated for all machinery and
are observed. suitability is ensured. station. nizable. A quality evaluation must equipment.
be carried out during installation,
removal or disassembly.
Principle 10 | Labeling Principle 11 | Rework/Scrap Principle 12 | Dropped Parts Principle 13 | Correct Product Principle 14 | Remaining Items
Products and containers are The handling of rejected parts Any products that fall on the floor, Only the correct product may The handling of remaining items/
labeled according to the set and those to be reworked is into the machine or cannot be be provided for removal and quantities is clearly regulated.
standard. clearly regulated. classified must be scrapped. assembly.
Version 2.0 Responsible for the content: C/QM
You might also like
- QNET ROTPENT Laboratory - Student ManualDocument36 pagesQNET ROTPENT Laboratory - Student ManualKomang PutraNo ratings yet
- Paper Airplane Exercise: Provided To NWLEAN by Tim Leach of Northrup Grumman, May 98Document15 pagesPaper Airplane Exercise: Provided To NWLEAN by Tim Leach of Northrup Grumman, May 98chteo1976No ratings yet
- Telstar Cryodos Laboratory Freeze Dryer - User ManualDocument20 pagesTelstar Cryodos Laboratory Freeze Dryer - User Manualtaioba2010No ratings yet
- CD-00519-002 Anh N en 2018-07-06Document2 pagesCD-00519-002 Anh N en 2018-07-06Nicole de Castro RoveriNo ratings yet
- Deviations - Definition and Requirements: LOGFILE No. 10 / April 2013 Maas & Peither AG - GMP PublishingDocument3 pagesDeviations - Definition and Requirements: LOGFILE No. 10 / April 2013 Maas & Peither AG - GMP PublishingKamran AlamNo ratings yet
- AIE-PR-PRJ-004 - Anomaly Management Procedure Rev 01Document17 pagesAIE-PR-PRJ-004 - Anomaly Management Procedure Rev 01faraz_muslimNo ratings yet
- Process Safety AwarenessDocument19 pagesProcess Safety AwarenessiekazalyNo ratings yet
- Distributed Control System Operation (Intermediate)Document2 pagesDistributed Control System Operation (Intermediate)AliNo ratings yet
- Preview ANSI+ASQ+Z1.4-2003+ (R2013)Document8 pagesPreview ANSI+ASQ+Z1.4-2003+ (R2013)mlk1971No ratings yet
- Implementation of The RCM Approach at Xa0103048 Edf NPPS: Current StatusDocument8 pagesImplementation of The RCM Approach at Xa0103048 Edf NPPS: Current StatusSamNo ratings yet
- Api Monogram Program/Erw 20'' (Api 5L) : Embosal Steel Mills LLCDocument2 pagesApi Monogram Program/Erw 20'' (Api 5L) : Embosal Steel Mills LLCRavi TyagiNo ratings yet
- Is Ex Pir Ing: Title Repair and Overhaul Valves Level 4 Credits 5Document4 pagesIs Ex Pir Ing: Title Repair and Overhaul Valves Level 4 Credits 5Deepak RajanNo ratings yet
- 8 Process Safety Awareness PresentationDocument27 pages8 Process Safety Awareness PresentationVincent Magtibay67% (3)
- JD - Panel Officer NPKDocument2 pagesJD - Panel Officer NPKPriyu SakhareNo ratings yet
- C 1188 - 91 R97 - QzexodgDocument8 pagesC 1188 - 91 R97 - QzexodgPrakash MakadiaNo ratings yet
- ISO/TS 16949:2002 Links To "Core Tools"Document1 pageISO/TS 16949:2002 Links To "Core Tools"ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Dana Corporation: SKB SKB 16MAR11 14OCT11-Sec 5.1 ESSTV - EP026 1 of 7Document7 pagesDana Corporation: SKB SKB 16MAR11 14OCT11-Sec 5.1 ESSTV - EP026 1 of 7LynetteNo ratings yet
- KI KO Balance Log Book RevisedDocument42 pagesKI KO Balance Log Book Revisedmelimaul07No ratings yet
- Author - Brian G Hudson, ABB Engineering Services: Figure 1 - Issues Faced by Offshore OperatorsDocument11 pagesAuthor - Brian G Hudson, ABB Engineering Services: Figure 1 - Issues Faced by Offshore Operatorsfares-slamaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variances (OK Na!)Document6 pagesStandard Costing and Variances (OK Na!)Jane Michelle EmanNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Gap AssessmentDocument28 pagesQuality Management Gap AssessmentVanessa GurrolaNo ratings yet
- Imp of Calibration PDFDocument11 pagesImp of Calibration PDFjaga deeshNo ratings yet
- Operating Procedures, Safety Procedures & TrainingDocument51 pagesOperating Procedures, Safety Procedures & TrainingashwaniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Masoom QA-GMP-QCDocument75 pagesDr. Masoom QA-GMP-QCMuhammad Masoom AkhtarNo ratings yet
- PTW - Standard - Operating - Procedures 2Document51 pagesPTW - Standard - Operating - Procedures 2FOZCANNo ratings yet
- Barrier Management (PRS192a)Document2 pagesBarrier Management (PRS192a)imafishNo ratings yet
- QAD Procedure - Inspection & Testing (Inprocess & Final Inspection)Document1 pageQAD Procedure - Inspection & Testing (Inprocess & Final Inspection)suman100% (2)
- Halonix Technologies Private Limited Supplier Audit Check SheetDocument1 pageHalonix Technologies Private Limited Supplier Audit Check Sheetatul sachanNo ratings yet
- New Concept For Alarm Structure and Management in Dcs SystemsDocument4 pagesNew Concept For Alarm Structure and Management in Dcs SystemsputraevoIII76No ratings yet
- Samcis - Ae212 - Module 12 Standard CostingDocument22 pagesSamcis - Ae212 - Module 12 Standard CostingMamaril John NathanielNo ratings yet
- 06.QC.T - 7 Steps of Quality MaintenanceDocument17 pages06.QC.T - 7 Steps of Quality MaintenancevictorNo ratings yet
- QSCP-92 - Welding MachinesDocument3 pagesQSCP-92 - Welding Machineszaheeruddin_mohdNo ratings yet
- QSD111.07 Control of Nonconforming Material Policy - Rev112Document6 pagesQSD111.07 Control of Nonconforming Material Policy - Rev112CTTONo ratings yet
- Supplier Audit Check SheetDocument5 pagesSupplier Audit Check SheetMotive Post100% (2)
- Instrumentation and Control in Process DiagramsDocument5 pagesInstrumentation and Control in Process DiagramsPlay DineNo ratings yet
- Safe Home Audit Tool FY21Document4 pagesSafe Home Audit Tool FY21Nayo Bravo SáezNo ratings yet
- AaDocument5 pagesAaMjhayeNo ratings yet
- Ornekleme 8Document1 pageOrnekleme 8zikacu6129No ratings yet
- Cosme Finals CoverageDocument6 pagesCosme Finals CoverageMary Joy CalooyNo ratings yet
- TTP Coming Out of Shutdown Start Up FundamentalsDocument3 pagesTTP Coming Out of Shutdown Start Up FundamentalsCraig PartridgeNo ratings yet
- SOP in Use QualificationDocument4 pagesSOP in Use QualificationDharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- TEMPLATE FOR OPERATIONAL QUALIFICATION PROTOCOL - Pharmaceutical GuidanceDocument7 pagesTEMPLATE FOR OPERATIONAL QUALIFICATION PROTOCOL - Pharmaceutical GuidanceMSL India100% (2)
- Thermo Fisher KonvejerovDocument13 pagesThermo Fisher KonvejerovSitthichai ChaikhachatNo ratings yet
- Past Year Questions SMSDocument6 pagesPast Year Questions SMShanina1176No ratings yet
- Gas Detection As A Risk Mitigation TechniqueDocument8 pagesGas Detection As A Risk Mitigation TechniqueFede Martinez100% (2)
- Standard Operating Procedure: Manalo, Alyssa A. Bs-Pharmacy Angeles University FoundationDocument69 pagesStandard Operating Procedure: Manalo, Alyssa A. Bs-Pharmacy Angeles University FoundationAlyssa Manalo100% (1)
- 63 Leak TesterDocument6 pages63 Leak Testersystacare remediesNo ratings yet
- 00-SATP-busway, Rev01Document9 pages00-SATP-busway, Rev01islam mohamedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Condition Assessment Lesson Presentation - 023711Document75 pagesLesson 5 - Condition Assessment Lesson Presentation - 023711Enrique BonaventureNo ratings yet
- HEMM Maintenance - ConceptDocument12 pagesHEMM Maintenance - ConceptDinesh Kumar Mali100% (1)
- The 7 Steps of Process-FMEA: Step 1: Planning and PreparationDocument2 pagesThe 7 Steps of Process-FMEA: Step 1: Planning and PreparationTarun PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- PRO427 Monitoring Measurement CalibrationDocument6 pagesPRO427 Monitoring Measurement CalibrationMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- 8.7 Nonconforming Outputs: Previous NextDocument10 pages8.7 Nonconforming Outputs: Previous Nextgayathrisrk001No ratings yet
- KaizenDocument32 pagesKaizenAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- QAD Procedure - Control of Non-Conforming Products P2Document2 pagesQAD Procedure - Control of Non-Conforming Products P2sumanNo ratings yet
- Haccp PlanDocument1 pageHaccp Planjlordmercader100% (1)
- Manufacturing and Service Operations: Learning Block 7 Maintenance and QualityDocument26 pagesManufacturing and Service Operations: Learning Block 7 Maintenance and Qualitymohammad baniissaNo ratings yet
- Vernier CalipersDocument4 pagesVernier CalipersVinod KGNo ratings yet
- System Analysis - Noddy GuideDocument2 pagesSystem Analysis - Noddy Guidegeorge moyoNo ratings yet
- Vms 3 User Manual: 3-Rath Kalibrier+Prüftechnik GMBH & Co. KGDocument33 pagesVms 3 User Manual: 3-Rath Kalibrier+Prüftechnik GMBH & Co. KGRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- THERMOVAC Transmitter: TTR 101 N, TTR 101 N S Operating Manual 300544655 - 002 - C1Document42 pagesTHERMOVAC Transmitter: TTR 101 N, TTR 101 N S Operating Manual 300544655 - 002 - C1Rodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- White Paper Aluvac Outgassing Rates Web en PDFDocument8 pagesWhite Paper Aluvac Outgassing Rates Web en PDFRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- Forklift Safety Poster EnglishDocument1 pageForklift Safety Poster EnglishRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- Burner Bic TechinfoDocument53 pagesBurner Bic TechinfoRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- Plasma Nitriding - Especially in The Gear Industry: Andreas Gebeshuber Ralph Trigueros Rübig GMBH & Co KG - AustriaDocument56 pagesPlasma Nitriding - Especially in The Gear Industry: Andreas Gebeshuber Ralph Trigueros Rübig GMBH & Co KG - AustriaRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- White Paper Thermische Stabilitt Web enDocument5 pagesWhite Paper Thermische Stabilitt Web enRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- White Paper Aluvac Knife Edge Stability Web enDocument5 pagesWhite Paper Aluvac Knife Edge Stability Web enRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- Rotary Vane Pump Pumping Speed Chart PDFDocument1 pageRotary Vane Pump Pumping Speed Chart PDFRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- Forsythe R. - The Blast Furnace and The Manufacture of Pig Iron PDFDocument376 pagesForsythe R. - The Blast Furnace and The Manufacture of Pig Iron PDFRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- Busch 0872-900-823 R 5 0025-0101 E & 0250 C 0511 PDFDocument20 pagesBusch 0872-900-823 R 5 0025-0101 E & 0250 C 0511 PDFRodolfo M. PortoNo ratings yet
- Composite Rev7 PDFDocument36 pagesComposite Rev7 PDFlawlawNo ratings yet
- (Hopper) Has Management Accounting Research Been CriticalDocument21 pages(Hopper) Has Management Accounting Research Been CriticalRafi Aulia AdipradanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter SS-1 Signals and SystemsDocument49 pagesChapter SS-1 Signals and SystemsalokNo ratings yet
- Tree Is A Tree That Is Not RootedDocument3 pagesTree Is A Tree That Is Not RootedVinoth GodiNo ratings yet
- Kyle CVDocument3 pagesKyle CVKyle ByrneNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument6 pagesAnswer All Questions in This SectionSK100% (1)
- Kohinoor SquareDocument5 pagesKohinoor SquareAmar NeethiNo ratings yet
- TAFL EXTERNAL Practical LISTDocument2 pagesTAFL EXTERNAL Practical LISTcompiler&automataNo ratings yet
- Decision Analysis Solution To Solved Problems: 9.S1 New Vehicle IntroductionDocument8 pagesDecision Analysis Solution To Solved Problems: 9.S1 New Vehicle IntroductionIrina AlexandraNo ratings yet
- (Michigan Teacher Training) Jerry G. Gebhard-Teaching English As A Foreign or Second Language - A Teacher Self-Development and Methodology Guide-The University of Michigan Press (2013)Document9 pages(Michigan Teacher Training) Jerry G. Gebhard-Teaching English As A Foreign or Second Language - A Teacher Self-Development and Methodology Guide-The University of Michigan Press (2013)eva17% (6)
- Emeng Chapter 1 Hakhakhak 1Document29 pagesEmeng Chapter 1 Hakhakhak 1AllenPonceNo ratings yet
- Pharmacovigilance EnglishDocument4 pagesPharmacovigilance EnglishImmad AlviNo ratings yet
- The Theory-Practice Gap - Impact of Professional-Bureaucratic Work Conflict On Newly Qualified NursesDocument13 pagesThe Theory-Practice Gap - Impact of Professional-Bureaucratic Work Conflict On Newly Qualified Nursesapi-3701957100% (1)
- Nama: Asnur Saputra NIM: F1A220034 Kelas: B Prodi: S1 StatistikaDocument7 pagesNama: Asnur Saputra NIM: F1A220034 Kelas: B Prodi: S1 StatistikaAsnur SaputraNo ratings yet
- Nature Hike OutlineDocument2 pagesNature Hike Outlineapi-273457875No ratings yet
- School-Age Motivation Questionnaire: Not at ALL Like Me Exactly Like MeDocument2 pagesSchool-Age Motivation Questionnaire: Not at ALL Like Me Exactly Like MeRandy HoweNo ratings yet
- Zone Reiki Level 2Document12 pagesZone Reiki Level 2Tineke100% (2)
- Q3 GR8 Las 5Document7 pagesQ3 GR8 Las 5Raquel ConelNo ratings yet
- Preventive and Social Medicine Public Health PDFDocument10 pagesPreventive and Social Medicine Public Health PDFRaj Subedi100% (2)
- Maths Program Proforma Yr 6 t2Document57 pagesMaths Program Proforma Yr 6 t2api-237136245No ratings yet
- LogDocument228 pagesLogibrahima diallo0% (1)
- Progressive Printing: Book 4Document25 pagesProgressive Printing: Book 4Jacob PruittNo ratings yet
- Advanced Inorganic Chemistry - ROBERT L. CARTERDocument15 pagesAdvanced Inorganic Chemistry - ROBERT L. CARTERBRUNO RAMOS DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Mattern - Senses and SocietyDocument26 pagesMattern - Senses and SocietyShannon MatternNo ratings yet
- Jerry Vigil CVDocument2 pagesJerry Vigil CVMktNeutralNo ratings yet
- South Africa'S National Biodiversity Strategy and Action PlanDocument108 pagesSouth Africa'S National Biodiversity Strategy and Action PlanPlandeAccionPNBNo ratings yet
- 004Document119 pages004svsreeramaNo ratings yet
- Tower Crane Slew Brakes SalmanDocument2 pagesTower Crane Slew Brakes SalmanAbbas RoziminNo ratings yet
- The Police and Politics in IndiaDocument23 pagesThe Police and Politics in IndiaAnonymous 8kD4bG7No ratings yet
- Baron Cohen My NotesDocument2 pagesBaron Cohen My NotesTariq RehmanNo ratings yet