Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WEEK 11 & 12 (Part 1) (CYTO)
Uploaded by
Hershei Vonne BaccayCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WEEK 11 & 12 (Part 1) (CYTO)
Uploaded by
Hershei Vonne BaccayCopyright:
Available Formats
Hershei Vonne M.
Baccay
BSMT 2- Set 1
ACTIVITY:
Answer the following questions based in your own understanding from the lesson.
1. Distinguish among a euploid, aneuploid, and polyploid cell.
- Euploid cells have a normal or exact number of chromosomes, indicating that
they have a complete set of normal 23 chromosomes. Aneuploid cells, on the
other hand, have too many or too few chromosomes. They have one or more
chromosomes that are not multiple copies of the complete number of
chromosomes. Lastly, the polyploid cells are those that have more than two
sets of homologous chromosomes, as well they have an inexact or incorrect
numbers of chromosomes.
2. Explain how analysis of fetal DNA in the maternal circulation can provide
information about a trisomy.
- The presence of fetal DNA in the maternal circulation can be used to diagnose
trisomy and provides information about trisomy wherein fetal DNA is extracted
from maternal plasma and tested using quantitative PCR. In addition, before or
during the tenth week of birth, this is used to identify births that are likely to
have a trisomy. In the analysis of fetal DNA in the maternal circulation, DNA is
extracted from the chorion. A negative test result indicates that the infant does
not have trisomy. If the result comes out negative for other chromosomal
defects that the lab searched for, the infant is unlikely to be affected. If the result
is positive, the fetus has a higher chance of getting the abnormality identified.
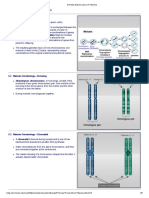
3. Distinguish among three types of translocations.
- Two chromosomes and one divides in each chromosome are involved in
reciprocal translocation. The divided segments of the two chromosomes
involved in reciprocal translocation will be swapped or exchanged. It is in
charge of chromosomal segment exchange between two non-homologous
chromosomes. While non-reciprocal translocation includes the transfer of a
chromosomal segment from one non-homologous chromosome to another.
When someone has 45 chromosomes instead of the normal46, this is known
as Robertsonian translocation. When two chromosomes get stuck together,
they form a single long chromosome, which then connects to another at the
centromere.
4. Describe how a ring chromosome forms.
- When a chromosome's arms are joined together or when an abnormal
chromosome's at which the end of each chromosome’s arm has been lost and
the broken arms have been reunited or rejoined in order for the chromosome
to create a ring-like shape or appearance. The deletion of terminal regions in
the p and q arms is followed by the fusion of the two ends to form ring
chromosomes. In addition, they are often formed by the fusion of subtelomeric
or telomeric chromosomal regions which is normally involve gene copy number
loss.
You might also like
- 2 Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument26 pages2 Chromosomal Abnormalitiesmuhammad zakriaNo ratings yet
- Alleles Can Also Come Together To Product Incomplete DominanceDocument6 pagesAlleles Can Also Come Together To Product Incomplete DominanceRachel MaguireNo ratings yet
- PBL 4 FullDocument5 pagesPBL 4 FullRomi RajaNo ratings yet
- Soma ( Body)Document4 pagesSoma ( Body)Joe AjaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Title: Study of Chromosomes in Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesExperiment 1: Title: Study of Chromosomes in Cell DivisionCerebrus GallantNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal Aberrations Just in CaseDocument8 pagesChromosomal Aberrations Just in CaseJahn Alaina DadoNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument3 pagesChromosomal AbnormalitiesMelodogyne Alay-ayNo ratings yet
- Genetic Linkage: Presented By:ayush Jain (Alm 3008) University of Agricultural Science, BangloreDocument32 pagesGenetic Linkage: Presented By:ayush Jain (Alm 3008) University of Agricultural Science, BangloreTeflon SlimNo ratings yet
- Aneuploidy GeneticsDocument7 pagesAneuploidy Geneticslinh myNo ratings yet
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Disorders and Diseases That Result From The Malfunction of The Cell During The Cell CycleDocument73 pagesDisorders and Diseases That Result From The Malfunction of The Cell During The Cell Cyclekuramachakra13No ratings yet
- 4 Genetics Lecture - Karyotyping of Normal Male, Female and Different Chromosomal Anomalies.Document43 pages4 Genetics Lecture - Karyotyping of Normal Male, Female and Different Chromosomal Anomalies.AMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics: Chromosome Banding & Barr Body DR Charu Khosla, 24/4/20, 10.45-11.45 AmDocument90 pagesCytogenetics: Chromosome Banding & Barr Body DR Charu Khosla, 24/4/20, 10.45-11.45 Amsonal aranha100% (2)
- Biology Project: Chromosomal DisorderDocument44 pagesBiology Project: Chromosomal DisorderArun Kumar ANo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: MetacentricDocument12 pagesChromosomes: MetacentricMuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- SasangDocument11 pagesSasangVince Cinco ParconNo ratings yet
- Kar Yo TypingDocument34 pagesKar Yo TypingAzry MustapaNo ratings yet
- Bio511 c2Document51 pagesBio511 c2Athirah JeffryNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Reference NotesDocument19 pagesGenetics - Reference NotesThanusri Vasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- In Eukaryotes and Hot PlateDocument7 pagesIn Eukaryotes and Hot PlateNadya Nur TrianaNo ratings yet
- 7882Document8 pages7882Hamid NiazmandNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and Genetic DisordersDocument4 pagesChromosomes and Genetic DisordersSakshamNo ratings yet
- Numerical Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDocument2 pagesNumerical Chromosomal AbnormalitiesPradip SahaNo ratings yet
- Genetic TranslocationDocument4 pagesGenetic TranslocationMoiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Yu-LiCosmo He - Unit 5 Chapter 15Document5 pagesYu-LiCosmo He - Unit 5 Chapter 15Fat CatNo ratings yet
- Nondisjunction DefinitionDocument10 pagesNondisjunction DefinitionKesyaNo ratings yet
- Variation in Struture of ChromosomeDocument51 pagesVariation in Struture of ChromosomedrhydrogenNo ratings yet
- General Cytogenetics InformationDocument11 pagesGeneral Cytogenetics Informationjo_jo_mania100% (1)
- Inversions - Mosaicism: Autosomal DisordersDocument44 pagesInversions - Mosaicism: Autosomal DisordersZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Karyotype Activity GoodDocument12 pagesKaryotype Activity GoodSATZU MALAKASNo ratings yet
- Karyotype Lab PDFDocument5 pagesKaryotype Lab PDFwelfredo yuNo ratings yet
- 8 - Chromosomal MutationDocument11 pages8 - Chromosomal MutationKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Fetal DevelopmentDocument16 pagesGenetics and Fetal DevelopmentLikoh TimothyNo ratings yet
- Robertsonian Chromosome Translocations What Is A Chromosome Translocation?Document8 pagesRobertsonian Chromosome Translocations What Is A Chromosome Translocation?Merjema BahtanovićNo ratings yet
- ChromosomeDocument25 pagesChromosomenebullaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument42 pagesMeiosisSindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- Lec-6 Chromosomes and KaryotypingDocument37 pagesLec-6 Chromosomes and KaryotypingAshraful Islam NayeemNo ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument9 pagesChromosomestayyabaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise 6 1Document10 pagesLaboratory Exercise 6 1Sofia CamamaNo ratings yet
- Sitogenetika&variasi GenetikDocument147 pagesSitogenetika&variasi GenetikDiniNo ratings yet
- Fs39 Klinefelter SyndromeDocument4 pagesFs39 Klinefelter SyndromeDivya LakhaniNo ratings yet
- S.Y.B.Sc Semester III Botany Paper II Unit II:CytogeneticsDocument95 pagesS.Y.B.Sc Semester III Botany Paper II Unit II:CytogeneticsQueen1982 K100% (1)
- Bio101 1Document43 pagesBio101 1usmansulaiman655No ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 7. Patterns of InheritanceDocument5 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 7. Patterns of InheritanceArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Meiosis-Performance TaskDocument10 pagesLesson 2 Meiosis-Performance TaskaceNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal DisordersDocument25 pagesChromosomal DisordersPUSHKAR PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal AberrationsDocument17 pagesChromosomal AberrationsHajiRab NawazNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Structure: Chromosomal Changes Occur in Three Basic Categories: Rearrangement, Aneuploidy, and PolyploidyDocument56 pagesChromosome Structure: Chromosomal Changes Occur in Three Basic Categories: Rearrangement, Aneuploidy, and PolyploidyBryce WatsonNo ratings yet
- Cell Division For Grade 8Document8 pagesCell Division For Grade 8Janella RedrinoNo ratings yet
- Discovery of Linkage: William Bateson and R.C. Punnett Were Working With Several Traits in Sweet Peas, Notably A Gene ForDocument12 pagesDiscovery of Linkage: William Bateson and R.C. Punnett Were Working With Several Traits in Sweet Peas, Notably A Gene ForYhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Terms &cell Division: DR KibeDocument39 pagesEmbryonic Terms &cell Division: DR KibeDenis KaguiNo ratings yet
- Lacerna, Roselyn T. Lab Activity WorksheetDocument6 pagesLacerna, Roselyn T. Lab Activity WorksheetRoselyn LacernaNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument45 pagesGenetics김가온No ratings yet
- 3 1 and 3 2Document28 pages3 1 and 3 2api-235355872No ratings yet
- Karyotyping ActivityDocument4 pagesKaryotyping ActivityYSOBELLATHERESE BILOLONo ratings yet
- Riview of Lit 2Document17 pagesRiview of Lit 2api-3806162No ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To GeneticsDocument5 pages01 Introduction To Geneticsprat.medbooksNo ratings yet
- Clase 4 - JACDocument103 pagesClase 4 - JACMATEO SEBASTIAN RODRIGUEZ TORRESNo ratings yet
- Chromo Syndromes XIDocument12 pagesChromo Syndromes XIRosyadiAdnan100% (1)
- 1 Molecular GeneticsDocument10 pages1 Molecular GeneticsAbdullah Sawalha100% (1)
- LearningTask2 AdvTechDocument2 pagesLearningTask2 AdvTechHershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- September 5, 2021 Mark 7:31-37: Gospel ReflectionDocument1 pageSeptember 5, 2021 Mark 7:31-37: Gospel ReflectionHershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- ETYMOLOGYDocument1 pageETYMOLOGYHershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Activity 1Document6 pagesWaste Management Activity 1Hershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Activity 1Document6 pagesWaste Management Activity 1Hershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- Is Consistent in The Given Period/artwork. Do Not Forget To Cite Your ReferencesDocument7 pagesIs Consistent in The Given Period/artwork. Do Not Forget To Cite Your ReferencesHershei Vonne Baccay100% (1)
- PMLS Professional Organization ActivityDocument4 pagesPMLS Professional Organization ActivityHershei Vonne Baccay100% (1)
- Closing PrayerDocument1 pageClosing PrayerHershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- Hershei Vonne M. Baccay BSMT 1 (Set 1)Document2 pagesHershei Vonne M. Baccay BSMT 1 (Set 1)Hershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- WEEK3LabManual Page 2and6Document3 pagesWEEK3LabManual Page 2and6Hershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- Learning Task (PURCOM)Document1 pageLearning Task (PURCOM)Hershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 (Bacte Lab)Document5 pagesActivity 1 (Bacte Lab)Hershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Genbio 1 Q1Document26 pagesSummative Test Genbio 1 Q1Duane0% (1)
- Dwnload Full Nursing A Concept Based Approach To Learning Volume I II and III 1st Edition Pearson Services Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Nursing A Concept Based Approach To Learning Volume I II and III 1st Edition Pearson Services Test Bank PDFmichaelcalhounjtypaegbnk100% (11)
- Gen EdDocument57 pagesGen EdCeasar Ryan AsuncionNo ratings yet
- This Set of Molecular Biology Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument392 pagesThis Set of Molecular Biology Multiple Choice QuestionsRohit ChavariyaNo ratings yet
- Zool Science SyllabusDocument38 pagesZool Science Syllabusriya dasNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument20 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeShivansh Shrivastava100% (1)
- Biochemistry (The Chemistry of Life)Document8 pagesBiochemistry (The Chemistry of Life)kimashleymandronNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture NotesDocument108 pagesCell Biology Lecture NotesMert PolatNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument11 pagesNucleusKaysean MielNo ratings yet
- GenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Document20 pagesGenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Ethan Erika BionaNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksheet For Remedial StudentsDocument25 pagesBiology Worksheet For Remedial Studentsbaretoodo785No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition MahonDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition MahonEricBlankenshipkcfes100% (40)
- The Nucleus (Methods in Molecular Biology Ed 3Document221 pagesThe Nucleus (Methods in Molecular Biology Ed 3Adolfo López100% (1)
- Structure of RnaDocument44 pagesStructure of RnaAditi CharakNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Plan-in-Science-8 - Cell DivisionDocument18 pagesLesson-Plan-in-Science-8 - Cell DivisionMaricris Ranara100% (1)
- Biology Module 1: Cells As The Basis of LifeDocument4 pagesBiology Module 1: Cells As The Basis of LifeDilan Karandana100% (1)
- Q2 Science7 LAS W4ADocument14 pagesQ2 Science7 LAS W4AGINA OTARANo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument28 pagesLesson 3 - Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsloki67% (3)
- Lelm 209Document4 pagesLelm 209Ankit YadavNo ratings yet
- Quipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellDocument17 pagesQuipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellPhil Christian MerinoNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary BiologyDocument9 pagesEvolutionary BiologyAravind TrNo ratings yet
- Science Tech Class 2 Basic Biology Lyst4385 Lyst7065Document66 pagesScience Tech Class 2 Basic Biology Lyst4385 Lyst7065UdishaSinghNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein: Lecture OutlineDocument15 pagesFrom Gene To Protein: Lecture OutlineEiann Jasper LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Organism 3 MSDocument6 pagesOrganisation of The Organism 3 MSJ.Chang ChangNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and Cell Structures: General Biology Week 1Document80 pagesCell Theory and Cell Structures: General Biology Week 1Joseph Gabriel CruzNo ratings yet
- Rajah 1 Di Bawah Menunjukkan Struktur Sejenis Sel.: Bahagian A (20 Markah)Document12 pagesRajah 1 Di Bawah Menunjukkan Struktur Sejenis Sel.: Bahagian A (20 Markah)maysaraNo ratings yet
- Basic A&p Booklet Short Version 3Document228 pagesBasic A&p Booklet Short Version 3Hilary Christopher100% (1)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.1 CellDocument9 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.1 CellJosebeth CairoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Pipe Cleaner LabDocument3 pagesMeiosis Pipe Cleaner Labmaeko nayuNo ratings yet
- Cell Analogy Project 2021Document3 pagesCell Analogy Project 2021api-249551710No ratings yet