Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Software Verification: EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001
Uploaded by
võ hoàng tháiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Software Verification: EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001
Uploaded by
võ hoàng tháiCopyright:
Available Formats
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: SAFE
REVISION NO.: 4
EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001
Post-Tensioned Slab Design
PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
The purpose of this example is to verify the slab stresses and the required area of
mild steel strength reinforcing for a post-tensioned slab.
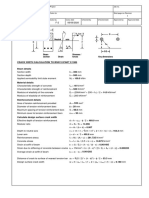
A one-way, simply supported slab is modeled in SAFE. The modeled slab is 254
mm thick by 914 mm wide and spans 9754 mm as shown in shown in Figure 1.
Prestressing tendon, Ap
Mild Steel, As
229 mm
254 mm
25 mm
Length, L = 9754 mm 914 mm
Elevation Section
Figure 1 One-Way Slab
EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001 - 1
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: SAFE
REVISION NO.: 4
A 254-mm-wide design strip is centered along the length of the slab and has been
defined as an A-Strip. B-strips have been placed at each end of the span,
perpendicular to Strip-A (the B-Strips are necessary to define the tendon profile).
A tendon with two strands, each having an area of 99 mm2, was added to the A-
Strip. The self weight and live loads have been added to the slab. The loads and
post-tensioning forces are as follows:
Loads: Dead = self weight, Live = 4.788 kN/m2
The total factored strip moments, required area of mild steel reinforcement, and
slab stresses are reported at the mid-span of the slab. Independent hand
calculations were compared with the SAFE results and summarized for verification
and validation of the SAFE results.
GEOMETRY, PROPERTIES AND LOADING
Thickness T, h = 254 mm
Effective depth d = 229 mm
Clear span L = 9754 mm
Concrete strength f 'c = 30 MPa
Yield strength of steel fy = 400 MPa
Prestressing, ultimate fpu = 1862 MPa
Prestressing, effective fe = 1210 MPa
Area of Prestress (single strand) Ap = 198 mm2
Concrete unit weight wc = 23.56 KN/m3
Modulus of elasticity Ec = 25000 N/mm3
Modulus of elasticity Es = 200,000 N/mm3
Poisson’s ratio = 0
Dead load wd = self KN/m2
Live load wl = 4.788 KN/m2
TECHNICAL FEATURES OF SAFE TESTED
Calculation of the required flexural reinforcement
Check of slab stresses due to the application of dead, live, and post-tensioning
loads.
RESULTS COMPARISON
Table 1 shows the comparison of the SAFE total factored moments, required mild
steel reinforcing, and slab stresses with independent hand calculations.
EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001 - 2
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: SAFE
REVISION NO.: 4
Table 1 Comparison of Results
INDEPENDENT SAFE
FEATURE TESTED DIFFERENCE
RESULTS RESULTS
Factored moment,
165.9 165.9 0.00%
Mu (Ultimate) (kN-m)
Transfer Conc. Stress, top
5.057 5.057 0.00%
(D+PTI), MPa
Transfer Conc. Stress, bot
2.839 2.839 0.00%
(D+PTI), MPa
Normal Conc. Stress, top
10.460 10.465 0.05%
(D+L+PTF), MPa
Normal Conc. Stress, bot
8.402 8.407 0.06%
(D+L+PTF), MPa
Long-Term Conc. Stress, top
7.817 7.817 0.00%
(D+0.5L+PTF(L)), MPa
Long-Term Conc. Stress, bot
5.759 5.759 0.00%
(D+0.5L+PTF(L)), MPa
Table 2 Comparison of Design Moments and Reinforcements
Reinforcement Area
(sq-cm)
Design Moment
National Annex Method (kN-m) As+
SAFE 166.41 16.39
CEN Default, Norway,
Slovenia and Sweden
Calculated 166.41 16.37
SAFE 166.41 16.90
Finland , Singapore and UK
Calculated 166.41 16.88
SAFE 166.41 17.30
Denmark
Calculated 166.41 17.28
COMPUTER FILE: EUROCODE 2-04 PT-SL-001.FDB
CONCLUSION
The SAFE results show an acceptable comparison with the independent results.
EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001 - 3
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: SAFE
REVISION NO.: 4
HAND CALCULATIONS:
Design Parameters:
Mild Steel Reinforcing Post-Tensioning
f’c = 30MPa fpu = 1862 MPa
fy = 400MPa fpy = 1675 MPa
Stressing Loss = 186 MPa
Long-Term Loss = 94 MPa
fi = 1490 MPa
fe = 1210 MPa
m, steel = 1.15
m, concrete = 1.50
1.0 for fck ≤ 50 MPa
0.8 for fck ≤ 50 MPa
Prestressing tendon, Ap
Mild Steel, As
229 mm
254 mm
25 mm
Length, L = 9754 mm 914 mm
Elevation Section
Loads:
Dead, self-wt = 0.254 m 23.56 kN/m3 = 5.984 kN/m2 (D) 1.35 = 8.078 kN/m2 (Du)
Live, = 4.788 kN/m2 (L) 1.50 = 7.182 kN/m2 (Lu)
Total = 10.772 kN/m2 (D+L) = 15.260 kN/m2 (D+L)ult
=10.772 kN/m2 0.914 m = 9.846 kN/m, u = 15.260 kN/m2 0.914 m = 13.948 kN/m
wl12
= 13.948 9.754 8 = 165.9 kN-m
2
Ultimate Moment, M U
8
EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001 - 4
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: SAFE
REVISION NO.: 4
f A
Ultimate Stress in strand, f PS f SE 7000d 1 1.36 PU P l
fCK bd
1862(198)
1210 7000(229) 1 1.36 9754
30(914) 229
1361 MPa
Ultimate force in PT, Fult , PT AP ( f PS ) 2 99 1361 1000 269.5 kN
CEN Default, Norway, Slovenia and Sweden:
Design moment M = 166.4122 kN-m
M
Compression block depth ratio: m 2
bd f cd
166.4122
0.1736
0.914 0.229 2 1 30000 1.50
Required area of mild steel reinforcing,
1 1 2m = 1 1 2(0.1736) 0.1920
f bd 1(30 /1.5)(914)(229)
AEquivTotal cd 0.1920 2311 mm
2
f yd 400 /1.15
1366
AEquivTotal AP AS 2311 mm
2
400
1361
AS 2311 198 1637 mm
2
400
Finland, Singapore and UK:
Design moment M = 166.4122 kN-m
M
Compression block depth ratio: m
bd 2f cd
166.4122
0.2042
0.914 0.229 2 0.85 30000 1.50
Required area of mild steel reinforcing,
1 1 2m = 1 1 2(0.2042) 0.23088
EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001 - 5
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: SAFE
REVISION NO.: 4
f bd 0.85(30 /1.5)(914)(229)
AEquivTotal cd 0.23088 2362 mm
2
f yd 400 /1.15
1366
AEquivTotal AP AS 2362 mm
2
400
1361
AS 2362 198 1688 mm
2
400
Denmark:
Design moment M = 166.4122 kN-m
M
Compression block depth ratio: m
bd 2f cd
166.4122
0.1678
0.914 0.229 2 1.0 30000 1.45
Required area of mild steel reinforcing,
1 1 2m = 1 1 2(0.1678) 0.1849
f bd 1.0(30 /1.45)(914)(229)
AEquivTotal cd 0.1849 2402 mm
2
f yd 400 /1.20
1366
AEquivTotal AP AS 2402 mm
2
400
1361
AS 2402 198 1728 mm
2
400
Check of Concrete Stresses at Midspan:
Initial Condition (Transfer), load combination (D+PTi) = 1.0D+0.0L+1.0PTI
Tendon stress at transfer = jacking stress stressing losses =1490 186 = 1304 MPa
The force in the tendon at transfer = 1304 197.4 1000 257.4 kN
Moment due to dead load, M D 5.984 0.914 9.754 8 65.04 kN-m
2
Moment due to PT, M PT FPTI (sag) 257.4 102 mm 1000 26.25 kN-m
F M M PT 257.4 65.04 26.23
Stress in concrete, f PTI D
A S 0.254 0.914 0.00983
where S = 0.00983m3
EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001 - 6
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: SAFE
REVISION NO.: 4
f 1.109 3.948 MPa
f 5.058(Comp) max, 2.839(Tension) max
Normal Condition, load combinations: (D+L+PTF) = 1.0D+1.0L+1.0PTF
Tendon stress at normal = jacking stressing long-term=1490 186 94 = 1210 MPa
The force in tendon at normal = 1210 197.4 1000 238.9 kN
Moment due to dead load M D 5.984 0.914 9.754 8 65.04 kN-m
2
Moment due to live load M L 4.788 0.914 9.754 8 52.04 kN-m
2
Moment due to PT, M PT FPTI (sag) 238.9 102 mm 1000 24.37 kN-m
Stress in concrete for (D+L+PTF),
F M M PT 238.8 117.08 24.37
f PTI D L
A S 0.254 0.914 0.00983
f 1.029 9.431
f 10.460(Comp) max, 8.402(Tension) max
Long-Term Condition, load combinations: (D+0.5L+PTF(L)) = 1.0D+0.5L+1.0PTF
Tendon stress at normal = jacking stressing long-term = 1490 186 94 = 1210 MPa
The force in tendon at normal, = 1210 197.4 1000 238.9 kN
Moment due to dead load, M D 5.984 0.914 9.754 8 65.04 kN-m
2
Moment due to live load, M L 4.788 0.914 9.754 8 52.04 kN-m
2
Moment due to PT, M PT FPTI (sag) 238.9 102 mm 1000 24.37 kN-m
Stress in concrete for (D+0.5L+PTF(L)),
F M M PT 238.9 91.06 24.33
f PTI D 0.5 L
A S 0.254 0.914 0.00983
f 1.029 6.788
f 7.817(Comp) max, 5.759(Tension) max
EXAMPLE Eurocode 2-04 PT-SL-001 - 7
You might also like
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionFrom EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNo ratings yet
- Practical Design to Eurocode 2 BasicsDocument85 pagesPractical Design to Eurocode 2 BasicsajayNo ratings yet
- Advance Reinforce Concrete Design Final PaperDocument7 pagesAdvance Reinforce Concrete Design Final PaperBryan ChooiNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Slab DesignDocument29 pagesReinforced Concrete Slab DesignMapanguriSitoeNo ratings yet
- Crack Width ConcreteDocument1 pageCrack Width ConcreteRuemu Godwin InikoriNo ratings yet
- Bitexco Financial Tower rises as symbol of Vietnam's global emergenceDocument9 pagesBitexco Financial Tower rises as symbol of Vietnam's global emergenceyamibarisonziNo ratings yet
- Crack Width Check BS5400 4Document5 pagesCrack Width Check BS5400 4saravanan4286100% (1)
- Chapter05 - Plane Frame and Grid EqDocument63 pagesChapter05 - Plane Frame and Grid EqAgus BaeNo ratings yet
- CMM Hybrid Columns: Brochure 38-01 EDocument4 pagesCMM Hybrid Columns: Brochure 38-01 EGurpreet Singh BhatiaNo ratings yet
- AD 261 - Elastic Modulus of AnglesDocument1 pageAD 261 - Elastic Modulus of Anglessymon ellimacNo ratings yet
- Prokon Combined FootingDocument14 pagesProkon Combined FootingAl-Ain Homes100% (1)
- 107-s38 - Nonlinear Analysis of Cross Sections Under Axial Load and Biaxial BendingDocument10 pages107-s38 - Nonlinear Analysis of Cross Sections Under Axial Load and Biaxial BendingbllldNo ratings yet
- Masonry Unit 4Document11 pagesMasonry Unit 4Pavithra Yuvraj100% (1)
- Eurocode 7 Geotechnical Limit AnalysisDocument19 pagesEurocode 7 Geotechnical Limit AnalysisPurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Time History AnalysisDocument4 pagesTime History AnalysisYoussef AliNo ratings yet
- Clark1976 PDFDocument10 pagesClark1976 PDFLuis Ariel B. MorilloNo ratings yet
- Deltabeam EngDocument20 pagesDeltabeam EngAmir OmeraševićNo ratings yet
- End Block Design-1Document14 pagesEnd Block Design-1potpotvolksNo ratings yet
- Bzdawka Composite Column Calculation ExamplesDocument62 pagesBzdawka Composite Column Calculation Examplesjust meNo ratings yet
- Minimum Thickness For Ductile RC Structural Walls: Y.H. Chai, S.K. KunnathDocument12 pagesMinimum Thickness For Ductile RC Structural Walls: Y.H. Chai, S.K. KunnathDavid FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Classification of Cross-SectionDocument20 pagesChapter 2 - Classification of Cross-SectionMuhd Zuhairi100% (2)
- Assignment 2 CA3703.2016Document6 pagesAssignment 2 CA3703.2016wilsonNo ratings yet
- Pre-Stressed Concrete PDFDocument75 pagesPre-Stressed Concrete PDFUmer WaheedNo ratings yet
- Intro To EC2 PDFDocument8 pagesIntro To EC2 PDFSamulus Q100% (1)
- Ec3 VerificcariDocument7 pagesEc3 VerificcariNeamtu NeamtuNo ratings yet
- Timber Joist Design BS5268Document3 pagesTimber Joist Design BS5268Zheny FortinNo ratings yet
- RC Desktop Toolkit v2Document27 pagesRC Desktop Toolkit v2pbharadwaj545No ratings yet
- What Is Sustained Load?: 1 AnswerDocument1 pageWhat Is Sustained Load?: 1 AnswerDonald HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Bridge Bearings, Expansion Joints & ParapetsDocument81 pagesBridge Bearings, Expansion Joints & ParapetsSAMNo ratings yet
- Culvert End Section PlansDocument19 pagesCulvert End Section PlansHemanthNo ratings yet
- Development LengthDocument22 pagesDevelopment LengthAlok MamNo ratings yet
- RAPT Beam AnalysisDocument16 pagesRAPT Beam Analysisvikramjain66No ratings yet
- Unrestrained BeamDocument3 pagesUnrestrained BeamGanesh Konar100% (1)
- Design of Prestressed Concrete StructuresDocument2 pagesDesign of Prestressed Concrete Structuresvineela saiNo ratings yet
- Review Paper (Shear Wall)Document9 pagesReview Paper (Shear Wall)Patel HiralNo ratings yet
- Deflection Calculation of Concrete Floors TN292 PDFDocument38 pagesDeflection Calculation of Concrete Floors TN292 PDFSheik Mohamed LiakathNo ratings yet
- Engeurocode Training - En1994-1-1 PDFDocument34 pagesEngeurocode Training - En1994-1-1 PDFAbdulla AljundiNo ratings yet
- Lateral-Torsional Buckling of Cold-Formed Zed-Purlins Partial-Laterally Restrained by Metal SheetingDocument11 pagesLateral-Torsional Buckling of Cold-Formed Zed-Purlins Partial-Laterally Restrained by Metal SheetingReaditReaditNo ratings yet
- Design and analysis of inclined columnsDocument6 pagesDesign and analysis of inclined columnsRabindraUpretiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Elastic FoundationsDocument24 pagesChapter Four Elastic Foundationssebastian9033No ratings yet
- British Problem 5 PDFDocument5 pagesBritish Problem 5 PDFelixnzNo ratings yet
- Models For Punching Shear Capacity in Concrete SlabsDocument166 pagesModels For Punching Shear Capacity in Concrete SlabsZoran BonicNo ratings yet
- Spandrel Flexural Design: Technical NoteDocument11 pagesSpandrel Flexural Design: Technical Notetomxxx34No ratings yet
- CVL-243 Reinforced Concrete Design Semester 1, 2020-21: Sahil Bansal, IIT Delhi 1Document23 pagesCVL-243 Reinforced Concrete Design Semester 1, 2020-21: Sahil Bansal, IIT Delhi 1Ekant YadavNo ratings yet
- EC2-Shear and TorsionDocument9 pagesEC2-Shear and TorsionDonald HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Handbook To Bc1 2023Document59 pagesHandbook To Bc1 2023cklconNo ratings yet
- CE2155 Structural Mechanics and Materials IntroductionDocument44 pagesCE2155 Structural Mechanics and Materials IntroductionJuliaNo ratings yet
- Staggered Truss ExampleDocument5 pagesStaggered Truss ExampleFrederico DonagemmaNo ratings yet
- Comflor Composite Floor Deck Brochure UKDocument68 pagesComflor Composite Floor Deck Brochure UKSuciu Bogdan AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Strut Tie Model Transfer SlabDocument182 pagesStrut Tie Model Transfer Slabshish0iitrNo ratings yet
- Composite ColumnDocument73 pagesComposite ColumnraymondNo ratings yet
- Example: Determination of Loads On A Building EnvelopeDocument8 pagesExample: Determination of Loads On A Building EnvelopeZarko KrusarevNo ratings yet
- MS Thesis BarandunDocument71 pagesMS Thesis BarandunmgrubisicNo ratings yet
- Long Term Deflection in Concrete BeamsDocument6 pagesLong Term Deflection in Concrete BeamsRenganayagi BalajiNo ratings yet
- PT Beam 28m SpanDocument14 pagesPT Beam 28m SpanDicky DjayadiNo ratings yet
- Post-Tensioned Beam Design Step-by-Step CalculationDocument30 pagesPost-Tensioned Beam Design Step-by-Step CalculationLau Kim HwaNo ratings yet
- SeeDocument71 pagesSeeSindu SukumarNo ratings yet
- 07 - Notional LoadingDocument3 pages07 - Notional LoadingnsureshbabuNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Distributed Sensing For Shrinkage and Tension Stiffening MeasurementDocument12 pagesDistributed Sensing For Shrinkage and Tension Stiffening Measurementvõ hoàng tháiNo ratings yet
- Uniform Building Code Volume 21997Document545 pagesUniform Building Code Volume 21997raymond100% (1)
- Uniform Building Code Volume 21997Document545 pagesUniform Building Code Volume 21997raymond100% (1)
- 15-Nguyen Van Thin-Bai Bao28!3!2007Document8 pages15-Nguyen Van Thin-Bai Bao28!3!2007Vo Dinh ThaoNo ratings yet
- Distributed Sensing For Shrinkage and Tension Stiffening MeasurementDocument12 pagesDistributed Sensing For Shrinkage and Tension Stiffening Measurementvõ hoàng tháiNo ratings yet
- SeeDocument71 pagesSeeSindu SukumarNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Tension Stiffening EffectDocument11 pagesTension Stiffening Effectvõ hoàng tháiNo ratings yet
- Tension Stiffening EffectDocument11 pagesTension Stiffening Effectvõ hoàng tháiNo ratings yet
- The Post Tension Slabs: - ENG - Mohamed Mostafa. - Post Tension Engineer at CSS (Concrete Stressing Systems)Document31 pagesThe Post Tension Slabs: - ENG - Mohamed Mostafa. - Post Tension Engineer at CSS (Concrete Stressing Systems)võ hoàng tháiNo ratings yet
- 15-Nguyen Van Thin-Bai Bao28!3!2007Document8 pages15-Nguyen Van Thin-Bai Bao28!3!2007Vo Dinh ThaoNo ratings yet
- Aalami CI Mar03 PaperDocument7 pagesAalami CI Mar03 PaperWalter CastilloNo ratings yet
- Slab-on-Ground DesignDocument28 pagesSlab-on-Ground DesignvNo ratings yet
- Etabs PT Slab DesignDocument649 pagesEtabs PT Slab DesignEmanuelRodriguezElera100% (1)
- 190102-DC10.5-Expansive and Stable Soils-Public ReviewDocument66 pages190102-DC10.5-Expansive and Stable Soils-Public Reviewvõ hoàng thái100% (1)
- Kesimira Qonita (18930066)Document12 pagesKesimira Qonita (18930066)Kesimira QonitaNo ratings yet
- Examen - SR - Correction 2021Document7 pagesExamen - SR - Correction 2021Malek JELASSINo ratings yet
- (9781783475537 - The Neuroscience of Organizational Behavior) IntroductionDocument4 pages(9781783475537 - The Neuroscience of Organizational Behavior) IntroductionMiguelNo ratings yet
- Biomechanical Considerations For The Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethDocument13 pagesBiomechanical Considerations For The Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethSoraya BouchammaNo ratings yet
- UID 104 Unity CollaborationDocument4 pagesUID 104 Unity CollaborationMary Joyce AvendańoNo ratings yet
- Finals Quiz 1 ReviewerDocument20 pagesFinals Quiz 1 ReviewerAngelo DongonNo ratings yet
- Kajian Pengaruh Variasi Penambahan Bahan Accelerator Terhadap Parameter Beton Memadat Mandiri Dan Kuat Tekan Beton Mutu TinggiDocument7 pagesKajian Pengaruh Variasi Penambahan Bahan Accelerator Terhadap Parameter Beton Memadat Mandiri Dan Kuat Tekan Beton Mutu TinggiHilda NurhelfitrianingsihNo ratings yet
- Metrology and Measurement SystemsDocument18 pagesMetrology and Measurement SystemssalemNo ratings yet
- Branches of Forensic ScienceDocument4 pagesBranches of Forensic ScienceIan owisoNo ratings yet
- Geographic AtmosphereDocument2 pagesGeographic AtmosphereLexter FalloNo ratings yet
- Iso Roof-Guard 1066 enDocument2 pagesIso Roof-Guard 1066 enMahmut AlmalahNo ratings yet
- Ch. 32 - Optical ImagesDocument19 pagesCh. 32 - Optical ImagesAbdallah IslaihNo ratings yet
- Applied SimulationDocument32 pagesApplied SimulationMeşgulRüyalarımıNo ratings yet
- Teachers Without Borders Programme: Brought To You byDocument5 pagesTeachers Without Borders Programme: Brought To You bynyashadzashe munyatiNo ratings yet
- ACIC - The Professional Criminal Intelligence PractitionerDocument15 pagesACIC - The Professional Criminal Intelligence PractitionerWendell Miles De ArmasNo ratings yet
- BG800 PPT IntroductionDocument25 pagesBG800 PPT IntroductionsegedNo ratings yet
- The Six-Flow Reactor Technology A Review PDFDocument17 pagesThe Six-Flow Reactor Technology A Review PDFTysir SarhanNo ratings yet
- TAU 2 Course Material v2.1Document40 pagesTAU 2 Course Material v2.1sreenathNo ratings yet
- 02 WholeDocument155 pages02 WholeTayeb CheliremNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching on Geriatric AssessmentDocument9 pagesClinical Teaching on Geriatric AssessmentANITTA SNo ratings yet
- Galileo (Satellite Navigation)Document21 pagesGalileo (Satellite Navigation)irayoNo ratings yet
- Sendai Framework For DRRDocument19 pagesSendai Framework For DRRAryaaaNo ratings yet
- Math 7, Q1, Wk4, Day 2Document3 pagesMath 7, Q1, Wk4, Day 2dennis sombilonNo ratings yet
- The Role of Strategies in SuccessDocument2 pagesThe Role of Strategies in SuccessGeorge DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Map Work: Types of MapsDocument18 pagesMap Work: Types of Mapshussain korirNo ratings yet
- Kelas Xii - May I Help You - Chapter 1Document2 pagesKelas Xii - May I Help You - Chapter 1Syifa Fauziah50% (2)
- Cambridge Global Perspectives Primary Lesson PackDocument16 pagesCambridge Global Perspectives Primary Lesson PackThin Thant ThantNo ratings yet
- SPECIFICATIONS For Constant Temperature and Humidity ChamberDocument5 pagesSPECIFICATIONS For Constant Temperature and Humidity Chamber彭以和No ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Writing Thesis StatementsDocument32 pagesLesson 2: Writing Thesis StatementsUnknownNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Artificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindFrom EverandArtificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityFrom EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesFrom EverandMastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkFrom EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Robotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryFrom EverandRobotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsFrom EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCFrom EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.From EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Modeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesFrom EverandModeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationFrom EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Learning Robotics, with Robotics, by Robotics: Educational RoboticsFrom EverandLearning Robotics, with Robotics, by Robotics: Educational RoboticsNo ratings yet
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!From EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Create Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandCreate Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceNo ratings yet
- Design and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsFrom EverandDesign and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsMarco CecarelliNo ratings yet
- RoboNexus: Bridging Realms: The Confluence of Mechanics, Electronics, and ProgrammingFrom EverandRoboNexus: Bridging Realms: The Confluence of Mechanics, Electronics, and ProgrammingNo ratings yet