Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BS UNIT 3 Cheating PDF
Uploaded by
Ashutosh NayakCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BS UNIT 3 Cheating PDF
Uploaded by
Ashutosh NayakCopyright:
Available Formats
1.What is Dispersion? 2.OBJECTIVES OF 3.PROPERTIES OF A GOOD 4.MEASURES OF DISPERSION?
MEASURING MEASURE OF
Dispersion refers to DISPERSION? DISPERSION? a. Absolute measure of
the variations of the dispersion
items among To determine the Easy to understand
themselves / around reliability of an _Expressed in the same units
an average. average Simple to calculate which data is expressed.
_Ex: Rupees, Kgs,
Greater the variation To compare the Uniquely defined Ltr, Km etc.
amongst different variability of two or
items of a series, the more series Based on all observations b. Relative measure of
more will be the dispersion
dispersion. For facilitating the use Not affected by extreme _In the form of ratio or
of other statistical observations percentage, so is independent
As per Bowley, measures of units.
“Dispersion is a Capable of further algebraic _It is also called Coefficient of
measure of the Basis of Statistical treatment Dispersion.
variation of the Quality Control
items”.
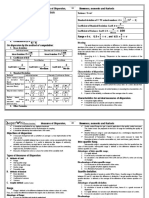
5.METHODS OF 6. What is Range(R)? 7. Range 8. INTERQUARTILE RANGE &
MEASURING a. Merits: QUARTILE DEVIATION?
DISPERSION? a. It is the simplest 1.Simple to understand 1.Interquartile Range is the
measures of 2.Easy to calculate difference between the
a. Range dispersion 3.Widely used in statistical quality upper quartile (Q3) and the
b. In quartile range b. It is defined as the control lower quartile (Q1).
and quartile deviation difference between b. Demerits: 2.It covers dispersion of midd
c. Mean Deviation the largest and 1. Can’t be calculated in open 50% of the items of the series
d. Standard Deviation smallest values in the ended distributions Symbolically, Interquartile
e. Coefficient of series 2.Not based on all the Range = Q3 – Q1
Variants c. R = L – S observations 3.Quartile Deviation is half of
f. Lorenz Curve R = Range, L = Largest 3.Affected by sampling the interquartile range. It is
Value, S = Smallest fluctuations also called Semi Interquartile
Value 4.Affected by extreme values Range
Coefficient of Range = 4. Symbolically, Quartile
L-S/L+S Deviation = 𝑄3 −𝑄1 /2
8. INTERQUARTILE 9. MEAN DEVIATION 10. MEAN DEVIATION – SHOR
RANGE & QUARTILE (M.D.)? CUT METHOD?
DEVIATION? a. It is also called a. If value of the average
5. Coefficient of Average Deviation comes out to be in fractions,
Quartile Deviation: It b. It is defined as the the calculation of M.D. by
Σ |𝑋 −𝑋|/N
is the relative arithmetic average of would become quite
measure of quartile the deviation of the tedious. In such cases, the
deviation. various items of a following formula is used:
series computed from
6. Coefficient of Q.D. measures of central b. M.D. =Σ𝑓𝑋 𝐴 − Σ𝑓𝑋 𝐵 − Σ𝑓 𝐴 –
=𝑄3 −𝑄1 /𝑄3+𝑄1 tendency like mean or Σ𝑓(𝑋 𝑜𝑟 𝑀)/N
median.
You might also like
- Dispersion (Measures of Variability)Document42 pagesDispersion (Measures of Variability)9278239119100% (3)
- Unit 2 Measures of Dispersion: StructureDocument16 pagesUnit 2 Measures of Dispersion: StructurePranav ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Dispersion 26-11-2023Document41 pagesDispersion 26-11-2023Arundhati ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Dispersion TheoryDocument7 pagesDispersion TheorySIVARANJANI PNo ratings yet
- 7242 - Measures of Dispersion 1 11Document11 pages7242 - Measures of Dispersion 1 11Àbhî RvrøçkzNo ratings yet
- Measures of variabilityDocument3 pagesMeasures of variabilityEleonor DapigNo ratings yet
- 7 Measures of DispersionDocument12 pages7 Measures of DispersionDr Mryhan AdelNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Stats TextDocument31 pagesUNIT 4 Stats TextShreya CNo ratings yet
- Dispersion: (Measures of Variability)Document93 pagesDispersion: (Measures of Variability)Muskan SinghalNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion - Range, Variance - Standard Deviation - Co-Efficient of VariationDocument5 pagesMeasures of Dispersion - Range, Variance - Standard Deviation - Co-Efficient of VariationM ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Measure of DispersionDocument64 pagesMeasure of DispersionMuhammad Atif SheikhNo ratings yet
- Economics Term 2Document8 pagesEconomics Term 2Tanishka MehtaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variability-April19-1Document88 pagesMeasures of Variability-April19-1RizellLoey ParkNo ratings yet
- Midterm Project Gec 3Document29 pagesMidterm Project Gec 3Leoncio Jr. ReyNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Measures of DispersionDocument11 pagesChapter4 Measures of DispersionRoshan KCNo ratings yet
- Meaning of DispersionDocument24 pagesMeaning of DispersionDhairyaa BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Sts ReviewerDocument15 pagesSts ReviewerAYEZZA SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Disperson SkwenessOriginalDocument10 pagesDisperson SkwenessOriginalRam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Assessment 2Document5 pagesModule 1 Assessment 2Carp EvaNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMS MT 21 LAB NotesDocument47 pagesMIDTERMS MT 21 LAB NotesMa. Joanna Catherine LopezNo ratings yet
- 3.measures of DispersionDocument10 pages3.measures of DispersionNchumthung JamiNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument14 pagesMeasures of Dispersionmani.nNo ratings yet
- Mba Unit-2Document2 pagesMba Unit-2Corporate exam cellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Descriptives StatisticsDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Descriptives StatisticsKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Lesson# 4 Measure of Dispersion: Department of Statistics FC College University, LahoreDocument63 pagesLesson# 4 Measure of Dispersion: Department of Statistics FC College University, LahoreUsama Ayyub RanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 - Measures of DisperstionDocument19 pagesChapter-4 - Measures of DisperstionKebede HaileNo ratings yet
- Measure of DispersionDocument66 pagesMeasure of DispersionPuttu Guru PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 - Measures of DisperstionDocument21 pagesChapter-4 - Measures of DisperstionM BNo ratings yet
- Lbolytc Chapter 3: Numerical Descriptive MeasuresDocument3 pagesLbolytc Chapter 3: Numerical Descriptive MeasuresRuss FajardoNo ratings yet
- This Section Presents Concepts Related To Using and Interpreting The Following MeasuresDocument24 pagesThis Section Presents Concepts Related To Using and Interpreting The Following MeasuresmichelleNo ratings yet
- Handnote Chapter 4 Measures of DispersioDocument45 pagesHandnote Chapter 4 Measures of DispersioKim NamjoonneNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument8 pagesMeasures of DispersionGabrielle Anne CarlosNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion and Variation in StatisticsDocument5 pagesMeasures of Dispersion and Variation in StatisticsBethelhem AshenafiNo ratings yet
- Requisites For An Ideal Measures of DispersionDocument9 pagesRequisites For An Ideal Measures of DispersionAKSHIT KAKANI 1941007100% (1)
- Measures of DispersionDocument3 pagesMeasures of DispersionSethu RNo ratings yet
- Measures of Dispersion, Relative Standing and Shape: No. Biostat - 8 Date:25.01.2009Document49 pagesMeasures of Dispersion, Relative Standing and Shape: No. Biostat - 8 Date:25.01.2009pradeepNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Measures of Variation and Skewness: 9.0 ObjectivesDocument24 pagesUnit 9 Measures of Variation and Skewness: 9.0 ObjectivesTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics MeasuresDocument45 pagesBiostatistics MeasuresHarshitha LokeshNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Assessment Data with StatisticsDocument11 pagesAnalyzing Assessment Data with StatisticsEmily PestañoNo ratings yet
- MEASURES OF DISPERSION AND RELATIVE STANDINGDocument53 pagesMEASURES OF DISPERSION AND RELATIVE STANDINGPrudhvi raj Panga creationsNo ratings yet
- DispersionDocument31 pagesDispersionMd Nazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument7 pagesMarketingDigit GoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 and 5Document27 pagesCHAPTER 4 and 5MistireselassieNo ratings yet
- Measure of Dispersion Kurtosi, Skiwness UseDocument42 pagesMeasure of Dispersion Kurtosi, Skiwness UseJOHN TUMWEBAZENo ratings yet
- 11 Stat 6 Measures of DispersionDocument17 pages11 Stat 6 Measures of Dispersioneco protectionNo ratings yet
- Dav realNOTESDocument7 pagesDav realNOTESmanavbangaNo ratings yet
- ECO The Final PPT DispersionDocument34 pagesECO The Final PPT DispersionAmrita SharmaNo ratings yet
- SD and MADDocument23 pagesSD and MADlyca janeNo ratings yet
- Definition of DispersionDocument4 pagesDefinition of Dispersionpyam94No ratings yet
- Measures of Variation IntroductionDocument7 pagesMeasures of Variation IntroductionEshetu GeletuNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument17 pagesMeasures of DispersionMd IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Module-1 2Document32 pagesModule-1 2Ctrl-Alt-DelNo ratings yet
- Chapter Summary Ch03Document3 pagesChapter Summary Ch03Mansi DabhiNo ratings yet
- MAT2001 Measures of VariationDocument22 pagesMAT2001 Measures of VariationBharghav RoyNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variation in StatisticsDocument20 pagesMeasures of Variation in StatisticsBharghav RoyNo ratings yet
- BSA - PUT - SEM I - 21-22 SolutionDocument16 pagesBSA - PUT - SEM I - 21-22 SolutionRizwan SaifiNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument11 pagesMeasures of DispersionAshish kumar ThapaNo ratings yet
- Research IV - QTR 3 - Week 3Document7 pagesResearch IV - QTR 3 - Week 3andrei bercadezNo ratings yet
- Standard Deviation DefinitionDocument4 pagesStandard Deviation DefinitionMd. Nazmul Hasan NurNo ratings yet
- Sample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignFrom EverandSample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignNo ratings yet
- A Brief Note On Your Understanding of Regression, Linear Regression and Multiple Linear RegressionDocument2 pagesA Brief Note On Your Understanding of Regression, Linear Regression and Multiple Linear RegressionAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Respect Others With Compassion and EmpathyDocument1 pageRespect Others With Compassion and EmpathyAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Documentary QuestionsDocument1 pageDocumentary QuestionsAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- General English Cia 3 Component 2Document1 pageGeneral English Cia 3 Component 2Ashutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- A Brief Note On Your Understanding of Regression, Linear Regression and Multiple Linear RegressionDocument2 pagesA Brief Note On Your Understanding of Regression, Linear Regression and Multiple Linear RegressionAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Hed ExamDocument1 pageHed ExamAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Eco CiaDocument16 pagesEco CiaAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Viva Update For BSDocument10 pagesViva Update For BSAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Ashutosh Nayak 20111508 - Cia 3 (Ii)Document3 pagesAshutosh Nayak 20111508 - Cia 3 (Ii)Ashutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Ashutosh Nayak 20111508 Ge SubmissionDocument1 pageAshutosh Nayak 20111508 Ge SubmissionAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Business StatsDocument5 pagesSyllabus: Business StatsAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- General English Cia 3 Component 2Document2 pagesGeneral English Cia 3 Component 2Ashutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Business StatsDocument5 pagesSyllabus: Business StatsAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument1 pageTime TableAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Viva Update For BSDocument10 pagesViva Update For BSAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument1 pageTime TableAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Irp Parameters For Comparative Analysis of Companies of An IndustryDocument2 pagesIrp Parameters For Comparative Analysis of Companies of An IndustryAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Eco CiaDocument16 pagesEco CiaAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- 23-3 Should Monetary Policy Be Made by Rule Rather Than by Discretion?Document2 pages23-3 Should Monetary Policy Be Made by Rule Rather Than by Discretion?Ashutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Review of Ge ClassesDocument1 pageReview of Ge ClassesAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- BS UNIT 3 Cheating PDFDocument2 pagesBS UNIT 3 Cheating PDFAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- IRP Formats 2021Document11 pagesIRP Formats 2021Ashutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter I: Industry Profile: Market CapitalizationDocument3 pagesChapter I: Industry Profile: Market CapitalizationAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter I-Industry ProfileDocument20 pagesChapter I-Industry ProfileAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- IRP Formats 2021Document11 pagesIRP Formats 2021Ashutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter I: Industry Profile: Market CapitalizationDocument3 pagesChapter I: Industry Profile: Market CapitalizationAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- IRP Formats 2021Document11 pagesIRP Formats 2021Ashutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Irp Parameters For Comparative Analysis of Companies of An IndustryDocument3 pagesIrp Parameters For Comparative Analysis of Companies of An IndustryAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter I: Industry Profile: Market CapitalizationDocument3 pagesChapter I: Industry Profile: Market CapitalizationAshutosh NayakNo ratings yet
- Sampling and The Sampling DistributionDocument31 pagesSampling and The Sampling Distributionmd1sabeel1ansariNo ratings yet
- Statistics GlossaryDocument3 pagesStatistics Glossaryapi-3836734No ratings yet
- The de Martonne Aridity Index in Calabria Southern PDFDocument10 pagesThe de Martonne Aridity Index in Calabria Southern PDFCorduneanu FlavianaNo ratings yet
- Statistics SummaryDocument10 pagesStatistics SummaryAhmed Kadem ArabNo ratings yet
- 041 FIV B.MATHS WAZAELIMU - COM Tanganyika DC Mock, 2023Document4 pages041 FIV B.MATHS WAZAELIMU - COM Tanganyika DC Mock, 2023Rawalid BikongoroNo ratings yet
- GRIP FORCE MEASUREMENTDocument9 pagesGRIP FORCE MEASUREMENTarunpattanoorNo ratings yet
- Black BeltDocument9 pagesBlack BeltshashankNo ratings yet
- đề tríDocument7 pagesđề tríDung NgọcNo ratings yet
- Perception by Picciano (2002)Document20 pagesPerception by Picciano (2002)Rizky AjaNo ratings yet
- Some Common Probability DistributionsDocument92 pagesSome Common Probability DistributionsAnonymous KS0gHXNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Statistics and Data Handling in Analytical ChemistryDocument16 pagesActivity 1: Statistics and Data Handling in Analytical ChemistryKhristel PenoliarNo ratings yet
- Research Jargon GuideDocument6 pagesResearch Jargon GuideBienne JaldoNo ratings yet
- ANOVA Analysis of VarianceDocument25 pagesANOVA Analysis of Variancemashraf_397037No ratings yet
- CSAT-Book-for-UPSC-PDF AllDocument59 pagesCSAT-Book-for-UPSC-PDF AllIntresting Tube0% (1)
- Understanding Statistical Tests: Original ReportsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Statistical Tests: Original ReportsDipendra Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems Basic StatisticsDocument44 pagesDecision Support Systems Basic StatisticsMarthinus MaraisNo ratings yet
- AP Stat Test 1 - 2004-2005Document5 pagesAP Stat Test 1 - 2004-2005Monina JonesNo ratings yet
- Work Study Reviewer: 1. A Work Sampling Study Was Conducted On A Particular Machine and The Result IsDocument10 pagesWork Study Reviewer: 1. A Work Sampling Study Was Conducted On A Particular Machine and The Result IsSheryll PascobilloNo ratings yet
- P.1 Biasedness - The Bias of On Estimator Is Defined As:: Chapter Two EstimatorsDocument8 pagesP.1 Biasedness - The Bias of On Estimator Is Defined As:: Chapter Two EstimatorsFerekkanNo ratings yet
- استاندارد Wbgt Iso 7243Document13 pagesاستاندارد Wbgt Iso 7243MRFNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET wk7 1Document4 pagesWORKSHEET wk7 1Louise Joseph PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 29 - Alberta Math Grade 7 Unit 7 - Statistical Analysis Final AssessmentDocument19 pages29 - Alberta Math Grade 7 Unit 7 - Statistical Analysis Final AssessmentTanya KapurNo ratings yet
- MTH302 Quiz3Document13 pagesMTH302 Quiz3shahaan786100% (4)
- III Measures of Central TendencyDocument38 pagesIII Measures of Central TendencyIsaac AffamNo ratings yet
- 16Document34 pages16admin2146No ratings yet
- Lecture1Document51 pagesLecture1Kimberley Oh100% (1)
- Myp Math Standard Unit 01Document6 pagesMyp Math Standard Unit 01Suran LeeNo ratings yet
- Bank Loan Case - StudyDocument21 pagesBank Loan Case - StudyRahul Shirude100% (1)
- rr220105 Probability and StatisticsDocument8 pagesrr220105 Probability and StatisticsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- 2.discrete Random VariablesDocument67 pages2.discrete Random VariablesDeephikaKoppulian0% (1)