Professional Documents
Culture Documents
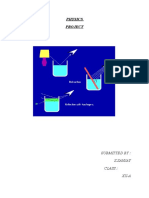
Scattering
Uploaded by
M AhmadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scattering
Uploaded by
M AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
Scattering
is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical
processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or
sound, is forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-
uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which
they pass.
Scattering, in physics, a change in the direction of motion of a particle
because of a collision with another particle. As defined in physics, a
collision can occur between particles that repel one another, such as two
positive (or negative) ions, and need not involve direct physical contact of the
particles.
Reflection is when light bounces off an object. If the surface is smooth and
shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same
angle as it hit the surface. This is called specular reflection. ... Most of the
things we see are because light from a source has reflected off it.
Total internal reflection, in physics, complete reflection of a ray of light
within a medium such as water or glass from the surrounding surfaces back
into the medium. The phenomenon occurs if the angle of incidence is greater
than a certain limiting angle, called the critical angle.
Refraction, in physics, the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to
another caused by its change in speed.
1. critical angle
2. the angle of incidence beyond which rays of light passing through a denser medium
to the surface of a less dense medium are no longer refracted but totally reflected.
Snell's law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is
equivalent to the ratio of phase velocities in the two media, or equivalent to the reciprocal of
the ratio of the indices of refraction:
You might also like
- Dual Nature of LightDocument15 pagesDual Nature of LightUriahs Victor75% (4)
- Reflection and RefractionDocument3 pagesReflection and RefractionGokulSubramanianNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Properties of Waves Including Light and Sound: What Is Wave Motion?Document11 pagesTopic 3 Properties of Waves Including Light and Sound: What Is Wave Motion?PichakornNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document56 pagesOptics 1hh8860033No ratings yet
- LIGHT - Advanced PhysicsDocument71 pagesLIGHT - Advanced PhysicsMaria Victoria Ignacio CaseriaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Propagation of LightDocument86 pagesNature and Propagation of LightMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 2 - Week 5Document20 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 2 - Week 5Cristian Steven Murillo100% (1)
- Optical PhenomenaDocument12 pagesOptical PhenomenaSharlene YagoNo ratings yet
- Properties of LightDocument6 pagesProperties of LightSteffi Bianca U. BelenNo ratings yet
- 5 Heat Budget of EarthDocument4 pages5 Heat Budget of EarthVasimNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Myna RafananDocument2 pagesReflection of Myna Rafananapi-260591778No ratings yet
- Reflection 2Document1 pageReflection 2ShobhitNo ratings yet
- General Explanation: LightDocument2 pagesGeneral Explanation: LightAzreen Anis azmiNo ratings yet
- General ExplanationDocument3 pagesGeneral ExplanationMaui ShihtzuNo ratings yet
- Tyndall EffectDocument13 pagesTyndall EffectSharlene YagoNo ratings yet
- 23104B0028 Extcps9Document2 pages23104B0028 Extcps9aafatthedaringNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument17 pagesPhysicsSANJAY SNo ratings yet
- Light Waves and ColorDocument14 pagesLight Waves and ColorSrinivasa Rao GuggilamNo ratings yet
- Q4 Physical Sci Module 2Document6 pagesQ4 Physical Sci Module 2Cakelee CortiñasNo ratings yet
- Property of Lights HardDocument6 pagesProperty of Lights HardYippeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Propagation of Light: ReflectionDocument15 pagesUnit 2: Propagation of Light: ReflectionPoojaNo ratings yet
- The Part of LightDocument4 pagesThe Part of LightMaxNo ratings yet
- Refraction Lesson 3 and 4Document17 pagesRefraction Lesson 3 and 4Yohanes FevianNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesDifference Between Reflection and RefractionFarooq TariqNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesRefraction of LightannmarieNo ratings yet
- JEEVISINGHEDocument6 pagesJEEVISINGHEAdvitiya 1245No ratings yet
- RefractionDocument2 pagesRefractionJhanry Esguerra PinedaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Mark Chap 3 Light Lessons 1 To 6Document30 pagesGroup 4 Mark Chap 3 Light Lessons 1 To 6allanrnmanaloto100% (1)
- Partial Refraction & Total Internal ReflectionDocument2 pagesPartial Refraction & Total Internal ReflectionJonathan JayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Propagation of LightDocument36 pagesWeek 3 Propagation of Lightjenicaoctaviano27No ratings yet
- Finals Assignment 1 - Bu3Document3 pagesFinals Assignment 1 - Bu3Jhossa EpondulanNo ratings yet
- Specular Diffuse:, or in Other Words, The Angle of Incidence Equals The Angle of ReflectionDocument4 pagesSpecular Diffuse:, or in Other Words, The Angle of Incidence Equals The Angle of ReflectionMaui ShihtzuNo ratings yet
- Reflection (Physics)Document3 pagesReflection (Physics)WantyzNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light and Its Applications: Ain Shams Engineering Journal May 2020Document14 pagesRefraction of Light and Its Applications: Ain Shams Engineering Journal May 2020Thirumal BNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes LightsDocument3 pagesLecture Notes LightsRhonoelle Reevenujlah100% (1)
- Topic 3 WavesDocument11 pagesTopic 3 WavesharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Behaviors of LightDocument102 pagesBehaviors of Lightemil_masagca1467No ratings yet
- Physical Science m3Document32 pagesPhysical Science m3pikabohhNo ratings yet
- Unidad 2: Paso 3: Modos de Propagación Y Polarización en Las Ondas ElectromagnéticasDocument16 pagesUnidad 2: Paso 3: Modos de Propagación Y Polarización en Las Ondas ElectromagnéticasJuan Jose PerdomoNo ratings yet
- PhysicalSciencePerformanceTask Script Jade Group3 SecondQuarter2022-2023 PDFDocument4 pagesPhysicalSciencePerformanceTask Script Jade Group3 SecondQuarter2022-2023 PDFDo KyungsooNo ratings yet
- Light and SoundDocument6 pagesLight and Soundnavita gulatiNo ratings yet
- Basic PhysicsDocument14 pagesBasic PhysicsDrone SmartShooterNo ratings yet
- Institute of Physics Submitted To: Dr. Muhammad Irfan Sahib Submitted By: Hammad Ghaffar Roll No. F20BPHYS3E01009Document8 pagesInstitute of Physics Submitted To: Dr. Muhammad Irfan Sahib Submitted By: Hammad Ghaffar Roll No. F20BPHYS3E01009Hoomi ShbNo ratings yet
- Investigation 2.0Document12 pagesInvestigation 2.0GnalixNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Week3Document14 pagesPhysics 2 Week3basurahangyujNo ratings yet
- Wavelike Behaviors of LightDocument3 pagesWavelike Behaviors of LightLeon MathaiosNo ratings yet
- Light 1Document20 pagesLight 1Susan MathewNo ratings yet
- Theory of Light and ColorDocument50 pagesTheory of Light and Colorelijah jirah binadayNo ratings yet
- Refraction 2Document3 pagesRefraction 2savannahk15No ratings yet
- AbstractDocument3 pagesAbstractRenz Louise NestorNo ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument11 pagesLight NotesNaveed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Project in PhysicsDocument20 pagesProject in PhysicsCareyl Mae VergaraNo ratings yet
- What Are The Principles of Optics and Light WavesDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Principles of Optics and Light WavesAdilNo ratings yet
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical ScienceDocument13 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS - Physical SciencePau FranciscoNo ratings yet
- What Does HuygenDocument3 pagesWhat Does Huygenjohn earl cosioNo ratings yet
- Light Acts As A Wave and A ParticleDocument19 pagesLight Acts As A Wave and A ParticleJhanice Pejo PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Reflection and RefractionDocument11 pagesReflection and RefractionNikki GuisonNo ratings yet
- Light (Physics)Document10 pagesLight (Physics)Cherry Pie Muñoz JimenoNo ratings yet