Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lect5 Slides
Uploaded by
enovas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Lect5_slides
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views8 pagesLect5 Slides
Uploaded by
enovasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Physics 2A: Lecture 6
Today’s Agenda
§ Kinematics in 2-D
§ Quick Recap of last lecture
§ Position
§ Velocity
§ Acceleration
§ Special case: Constant acceleration in 2-D
§ Constant acceleration equations
§ Examples: Projectile motion
Physics 201: Lecture 5, Pg 1
Start Recording!
Physics 201: Lecture 5, Pg 2
Clicker Question 1
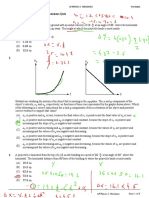
The motion of a cart moving along a horizontal surface is described by the
motion diagram shown in part (a) of the figure. The position of the cart is
measure every 0.5 s. Asked to suggest a qualitative graph of velocity-
versus-time that would correspond to this motion three of your classmates
sketch the following graphs shown in parts (b)–(d) of the figure. Which
graph is correct?
1. (b)
2. (c)
3. (d)
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 3-3
Clicker Question 2
Based on the u(t) curve in the figure, which of the following
statements is necessarily true for the time interval shown?
1. Acceleration is a constant.
2. The object passes through the position x = 0.
3. The object’s velocity is never zero.
4. The object is always moving in the same direction.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 3-4
Clicker Question 3
A ball is thrown downward (not dropped) from the top of
a tower. After being released, its downward acceleration
will be
1. greater than g.
2. exactly g.
3. smaller than g.
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 3-5
Clicker Question 4:
A uniformly accelerating car starting at rest travels a
distance x and reaches a velocity v in a certain time
interval. At the point that the same car has travelled a
distance of 5x what is its velocity?
a) 2 v
b) 5 v
c) 2.5 v
d) 2.24 v
e) 1.73 v
Physics 201: Lecture 5, Pg 6
Physics 201: Lecture 5, Pg 7
Clicker Question 5:
Ball A is thrown upwards off a cliff with speed v0.
Ball B is thrown downwards off the cliff with the
same speed. How will the velocities of the two
balls compare when they hit the bottom?
(a) Ball A will have a larger velocity
(b) Ball B will have a larger velocity
(c) The balls will have the same velocity
Physics 201: Lecture 5, Pg 8
You might also like
- Presentation: Motion in One DimensionDocument169 pagesPresentation: Motion in One DimensionJosé Ángel Ripoll AyolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Two-Dimensional Kinematics: Conceptual QuestionsDocument70 pagesChapter 4 Two-Dimensional Kinematics: Conceptual Questionssal27adamNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Constant AccelerationDocument17 pagesUnit 2: Constant AccelerationMatthew DiDonatoNo ratings yet
- M Non Inertial Frames WatermarkDocument7 pagesM Non Inertial Frames WatermarkRamani kanta DeulayNo ratings yet
- Generalphysics1 q1 Mod3 Motion-In-Two-Dimensions v1-1Document30 pagesGeneralphysics1 q1 Mod3 Motion-In-Two-Dimensions v1-1Park JiminshiiNo ratings yet
- Lect7 SlidesDocument15 pagesLect7 SlidesenovasNo ratings yet
- Apy1 Kinematics Review - 2015 - KeyDocument13 pagesApy1 Kinematics Review - 2015 - KeyemadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document25 pagesChapter 3NUR 'AIN NAJIHAH BINTI MAAROFNo ratings yet
- Seond Quiz AnswersDocument8 pagesSeond Quiz AnswersOmar AlbstkiNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 q1 Week 3Document24 pagesGeneral Physics 1 q1 Week 3Chool Cydrick B. BascosNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Physics For ScientisDocument17 pagesSolution Manual For Physics For ScientisgoncaloNo ratings yet
- Phys211 - 221 Labatorial02 SP2023Document10 pagesPhys211 - 221 Labatorial02 SP2023Jason SummatNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 P I June 2023Document6 pagesGrade 12 P I June 2023LangelihleNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Not For SaleDocument32 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Not For SaleJayneth Pagasian AceroNo ratings yet
- 9th Physics Revision Work-Sheets 2023-24-095745Document6 pages9th Physics Revision Work-Sheets 2023-24-095745Sidhant LodhiNo ratings yet
- Physics Projectile Motion NotesDocument6 pagesPhysics Projectile Motion Notessohamdey100% (1)
- 3NBB0 - Problems Chapter 2Document4 pages3NBB0 - Problems Chapter 2JhonNo ratings yet
- The Roots Science Academy Pind Dadan KhanDocument2 pagesThe Roots Science Academy Pind Dadan KhanAnonymous 117cflkW9WNo ratings yet
- Conceptest Clicker Questions: Physics, 4 EditionDocument29 pagesConceptest Clicker Questions: Physics, 4 EditionstephensreenivasulutNo ratings yet
- Course Contact: Kinematics Conceptual QuestionsDocument9 pagesCourse Contact: Kinematics Conceptual QuestionsOluwanifemi OjoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Phy220Document25 pagesChapter 3-Phy220Jordan TuckerNo ratings yet
- F5 Physics L34Document33 pagesF5 Physics L34WuileapNo ratings yet
- AP C Mech 1. Unit 1. Kinematics One Dimensional Motion Part 3Document12 pagesAP C Mech 1. Unit 1. Kinematics One Dimensional Motion Part 3moonidiveNo ratings yet
- Aiatstyjm2017pt1 SolutionDocument34 pagesAiatstyjm2017pt1 Solutiontanmoy bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2Patrick LenguajeNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Conceptual QuestionsDocument3 pagesKinematics Conceptual QuestionsAbhi 7No ratings yet
- Physical Sciences 2017 P1Document15 pagesPhysical Sciences 2017 P1NameNo ratings yet
- Modules: Quarter 4 - Weeks 1 - 4Document41 pagesModules: Quarter 4 - Weeks 1 - 4rebadullafrancheskaNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers 3rd Edition Knight Test Bank 1Document13 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers 3rd Edition Knight Test Bank 1helen100% (52)
- Quickcheck Questions: Motion in One DimensionDocument57 pagesQuickcheck Questions: Motion in One DimensionArda ÇekmeceNo ratings yet
- M01 Knig9404 Ism C01 PDFDocument17 pagesM01 Knig9404 Ism C01 PDFnorma_jeannNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Physics QP Key 2Document20 pagesHsslive Xi Physics QP Key 2Aswin M ShenoyNo ratings yet
- MockFMA 2021Document12 pagesMockFMA 2021DeekshaNo ratings yet
- Course Code: Course Name: Academic Year: Semester: Instructor: Section NumberDocument14 pagesCourse Code: Course Name: Academic Year: Semester: Instructor: Section NumberAhmed ShreefNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 MIDTERM ExamDocument2 pagesPhysics 1 MIDTERM ExamKent Paul Camara UbayubayNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For College Physics 11th Edition Raymond A Serway Chris VuilleDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For College Physics 11th Edition Raymond A Serway Chris Vuilleconcreteprimula2ppwr100% (14)
- Namma Kalvi 10th Science Important Study Material EM 221604Document168 pagesNamma Kalvi 10th Science Important Study Material EM 221604walkerfreefireytNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: All India Test SeriesDocument14 pagesFiitjee: All India Test SeriesKamran AKHTAR100% (1)
- Kinematics Test W SolutionsDocument5 pagesKinematics Test W SolutionsNicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- q1 General Physics Module 4Document13 pagesq1 General Physics Module 4Ciara Adrianne Tiongzon - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Practice Paper 2022-23Document11 pagesClass 11 Physics Practice Paper 2022-23Curiosity SatisfiedNo ratings yet
- Week 01 Motion WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeek 01 Motion WorksheetKrystian BonghanoyNo ratings yet
- GENP6 Week 3 (Gonzales, April Joy S.)Document11 pagesGENP6 Week 3 (Gonzales, April Joy S.)April Joy GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Physics Kinematics Worksheet: (A) (B) (C) (D)Document4 pagesPhysics Kinematics Worksheet: (A) (B) (C) (D)tutorpluskemangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Kinematics: Quick Check (Page 23)Document4 pagesChapter 2 Kinematics: Quick Check (Page 23)muhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Classroom Response System "Clicker" Questions For by Randall D. KnightDocument21 pagesClassroom Response System "Clicker" Questions For by Randall D. KnightkgdasldhNo ratings yet
- 2019 FY12 CEPhysics Detailed SolutionsDocument48 pages2019 FY12 CEPhysics Detailed SolutionsMesake Manumalo TofingaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physical Sciences Mechanics - CompressDocument15 pagesGrade 12 Physical Sciences Mechanics - Compresshopemandi25No ratings yet
- CP Projectile Motion WebquestDocument4 pagesCP Projectile Motion Webquestjethro38% (8)
- Physics 1st YearDocument2 pagesPhysics 1st YearRashid JalalNo ratings yet
- Physics Entry Exam (Non-Science Stu.) : Choose The Best Answer From The Options That Follow Each QuestionDocument5 pagesPhysics Entry Exam (Non-Science Stu.) : Choose The Best Answer From The Options That Follow Each QuestionMr Ahmed AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimention TestDocument4 pagesMotion in One Dimention TestEllouise PotgieterNo ratings yet
- QQ 02Document17 pagesQQ 02Mostafa BayoumyNo ratings yet
- IX Physics MotionDocument9 pagesIX Physics Motionhaadiya aliNo ratings yet
- ABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Document2 pagesABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Ashish GargNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q4 Mod2Document20 pagesSci9 Q4 Mod2robelynjoypobleteNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Solutions Problem 1: Concept Questions: Briefly Answer The Following QuestionsDocument10 pagesExam 1 Solutions Problem 1: Concept Questions: Briefly Answer The Following Questions45698722No ratings yet
- Lect8 SlidesDocument14 pagesLect8 SlidesenovasNo ratings yet
- Lect6 SlidesDocument21 pagesLect6 SlidesenovasNo ratings yet
- Lect7 SlidesDocument15 pagesLect7 SlidesenovasNo ratings yet
- Lect10 SlidesDocument12 pagesLect10 SlidesenovasNo ratings yet
- Leap-G7 Q3 W3 Motion-Graphs Ongkikomarilyn Sdo-DasmarinasDocument5 pagesLeap-G7 Q3 W3 Motion-Graphs Ongkikomarilyn Sdo-DasmarinasMary Grace Sambayan LlanesNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Tuesday 7 June 2005 Afternoon Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument4 pagesEdexcel GCE: Tuesday 7 June 2005 Afternoon Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesMargarita SatrakiNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument19 pagesProbabilityPRIYANKA PRATHAPANNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Klik Gambar Ini: Tps Utbk 2020 Kecepatan, Jarak, Dan Waktu By: MatematikawanDocument2 pagesPembahasan Klik Gambar Ini: Tps Utbk 2020 Kecepatan, Jarak, Dan Waktu By: MatematikawanEurico AdityaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi MaterialDocument316 pagesClass Xi MaterialShlok MishraNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion Problems With AnswersDocument28 pagesUniform Circular Motion Problems With AnswersElmer VillegasNo ratings yet
- Activity 9Document3 pagesActivity 9Rizza Mae ReponteNo ratings yet
- Sbi Po Q&aDocument72 pagesSbi Po Q&aRitobrotoNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Questions On Chapters Like: This Book Comprehensively Covers 250Document54 pagesProblem Solving Questions On Chapters Like: This Book Comprehensively Covers 250GOKUL HenryNo ratings yet
- A Simulation Model To Study Bunching Effect of A Truck-Shovel SystemDocument17 pagesA Simulation Model To Study Bunching Effect of A Truck-Shovel Systemenrike zamoraNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument25 pagesCircular MotionChiaHalimNo ratings yet
- Number Theory Assignment HelpDocument15 pagesNumber Theory Assignment HelpmathsassignmenthelpNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 3 - 2023Document7 pagesMathematics Form 3 - 2023Daniel JDansoNo ratings yet
- Buggy Lab ReportDocument6 pagesBuggy Lab ReportAidan SwiatlowskiNo ratings yet
- IMSO 2015 SCIENCE Experiments 2Document8 pagesIMSO 2015 SCIENCE Experiments 2Thanh DinhNo ratings yet
- 5054 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2023) PDFDocument85 pages5054 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2023) PDF330Sa kNo ratings yet
- Selina Solution Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 6Document20 pagesSelina Solution Concise Maths Class 10 Chapter 6Soureesh MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Placement PapersDocument0 pagesPlacement PapersmailmanugsNo ratings yet
- Munyua, M - Determining The Magnitude of Wind Loads On Structures in Kenya According To The Eurocodes 2021-01-12Document8 pagesMunyua, M - Determining The Magnitude of Wind Loads On Structures in Kenya According To The Eurocodes 2021-01-12opulitheNo ratings yet
- Motion (Final TTB) 1-42Document42 pagesMotion (Final TTB) 1-42Anisha PanditNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Project PDFDocument7 pagesMechatronics Project PDFTrived DoijodNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 3 NotesDocument52 pagesPhysics Form 3 NotesDISHON100% (5)
- 16 Planar Kinematics of Rigid BodyDocument47 pages16 Planar Kinematics of Rigid BodyzackziffiNo ratings yet
- Dimensi Fisika MekanikaDocument20 pagesDimensi Fisika MekanikaanggiaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Air Lines Sample ExamDocument11 pagesEthiopian Air Lines Sample Exammearig22292% (192)
- Aptitude Basic Mathematics 1Document46 pagesAptitude Basic Mathematics 1Parth PatelNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Q4 - SLM14Document16 pagesPhysical Science - Q4 - SLM14ALJON EMPERADONo ratings yet
- Fastest Land Animal-FormattedDocument4 pagesFastest Land Animal-FormattedGerald EdmundsNo ratings yet
- Calculus MCQDocument15 pagesCalculus MCQStephen Lloyd Gerona100% (1)
- 2021-2.0 Vehicle Dynamics - UploadDocument74 pages2021-2.0 Vehicle Dynamics - UploadMudit Maheshwari100% (1)