Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Physics Formula
Uploaded by
Adamu Ahmad100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
160 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
160 views2 pagesBasic Physics Formula
Uploaded by
Adamu AhmadCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
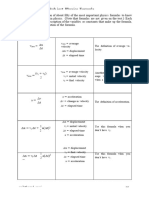
Basic Physics Formulas - Part I
Average Speed Formula (s)
The average speed is the average of speed of a moving body for the overall
distance that it has covered.
d
s =—
t
Where,
s = Average speed
d = Total distance travelled
t = Total time taken to cover the distance
Acceleration Formula (a)
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change in velocity to the change in time.
It is denoted by symbol a.
v-u
a=
t
Where,
a = Acceleration
u = Initial Velocity
v = Final Velocity
t = Time taken
Density Formula (ρ)
The density of material shows the denseness of it in a specific given area.
m
ρ =—
Where, V
ρ = Density
m = Mass of the body
V = Total time taken to cover the distance
Newton’s Second Law
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the force can be expressed by
the product of mass and acceleration of the body.
F=mxa
Where,
F = Density
m = Mass of the body
a = Acceleration
Power Formula (P)
The capacity to do some work is termed as Energy. The Energy spent to do
work in a unit amount of time is termed as Power.
W
P =—
t
Where,
P = Power
W = Work done
t = Time taken
Basic Physics Formulas - Part II
Weight Formula
Weight is the force which an object experience due to gravity.
W=mxg
Where,
W = Weight
m = Mass of the body
g = Acceleration due to gravity
Pressure Formula (P)
The pressure is defined as the amount of force applied per unit area of the
object.
F
P =—
A
Where,
P = Pressure
F = Force applied
A = Total area of the object
Kinetic Energy Formula (K. E.)
Kinetic energy is the energy that is possessed by a body due to its state of
motion.
1
KE = — x m x v2
2
Where,
KE = Kinetic Energy
m = Mass of the body
v = Velocity of the body
Ohm’s law Formula (P)
Current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential
difference between two endpoints of the conductor.
V=IxR
Where,
V = Voltage measured in Volts
I = Current flowing through the conductor in Amperes
R = Resistance of the conductor in Ohm.
Frequency Formula (f)
The pressure is defined as the amount of force applied per unit area of the
object.
V
f=—
λ
Where,
f = Frequency of the wave
V = Velocity or wave speed
λ = Wavelength of the wave
You might also like
- Project Report On Cyclone SeparatorDocument17 pagesProject Report On Cyclone SeparatorAniruddha DasNo ratings yet
- Coal Miners SuitDocument4 pagesCoal Miners SuitSudipta BainNo ratings yet
- SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY SlideshareDocument11 pagesSPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY SlideshareLotachukwu Ernest EzeNo ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Notes For All Semester of EEE, Mech, IT, Civil, CSE, ECE Download PDF - BrainkartDocument25 pagesAnna University Engineering Notes For All Semester of EEE, Mech, IT, Civil, CSE, ECE Download PDF - BrainkartM.V. TVNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Nozzles PDFDocument69 pagesCh-1 Nozzles PDFCh. Muhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- BTech Heat and Mass Transfer Theory Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesBTech Heat and Mass Transfer Theory Exam QuestionsSuryaNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Between HCV and LCVDocument5 pagesDifferentiate Between HCV and LCVhamza jelaniNo ratings yet
- B Tech Project Guidelines 1112013-14Document3 pagesB Tech Project Guidelines 1112013-14Dinesh GudavalliNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Course Material (As Per OU Syllabus)Document90 pagesPower Plant Engineering Course Material (As Per OU Syllabus)m udaya kumarNo ratings yet
- Nozzles and Diffusers, Turbines, Compressors and Pumps, Heat Exchangers, and Throttling DevicesDocument19 pagesNozzles and Diffusers, Turbines, Compressors and Pumps, Heat Exchangers, and Throttling Devicesvicencio390% (1)
- Percent Error DifferencePercent - Error - DifferenceDocument2 pagesPercent Error DifferencePercent - Error - DifferenceSadia Sharmin NilimaNo ratings yet
- Kinematicsof Particles - Rectilinear Motion: KinematicsDocument98 pagesKinematicsof Particles - Rectilinear Motion: KinematicsVinoth RajaguruNo ratings yet
- GDJP Important 2 Marks and 16 Marks With AnswerDocument18 pagesGDJP Important 2 Marks and 16 Marks With AnswerMechanical Engg DeptNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Electromagnetic Wave and Geometrical OpticsDocument93 pagesUnit 6: Electromagnetic Wave and Geometrical Opticskidanemariam HabtemariamNo ratings yet
- FEA Interview Questions Module 1Document22 pagesFEA Interview Questions Module 1Namit MishraNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument48 pagesCastingghaset50% (2)
- Distance vs Displacement, Speed vs Velocity - The Physics of MotionDocument20 pagesDistance vs Displacement, Speed vs Velocity - The Physics of MotionJessa Mea CamerioNo ratings yet
- TOM Lecture 1: Introduction to Theory of MachinesDocument6 pagesTOM Lecture 1: Introduction to Theory of MachinesYogesh DandekarNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis RatesDocument26 pagesFactors Affecting Photosynthesis RatesriyashreeNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Element Lecture 1Document45 pagesDesign of Machine Element Lecture 1Loay MohammedNo ratings yet
- Flowmaster TheoryDocument68 pagesFlowmaster TheoryCarolina Oliveira MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Ch1 PS (Sec A&b) Fall 2017 LectureDocument20 pagesCh1 PS (Sec A&b) Fall 2017 LecturealiNo ratings yet
- Solar Car Model PresentationDocument22 pagesSolar Car Model PresentationanilNo ratings yet
- Activity ProposalDocument2 pagesActivity ProposalAkosiabandoned JorjeNo ratings yet
- Production EquipmentDocument27 pagesProduction EquipmentBalamurugan ThangaveluNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument68 pagesGasesAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Technical Densities Reference GuideDocument3 pagesTechnical Densities Reference GuidedjgiumixNo ratings yet
- Refresh CRT OperationDocument12 pagesRefresh CRT OperationAreej Al Majed0% (1)
- MIN-305 Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial - 1Document2 pagesMIN-305 Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial - 1Ayush JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Mom Lab ManualDocument77 pagesMom Lab ManualHammad SubhaniNo ratings yet
- Multi Type ForkliftDocument46 pagesMulti Type ForkliftlokeshNo ratings yet
- BJT Basics 1Document69 pagesBJT Basics 1Sarvesh RajbharNo ratings yet
- Class - 1&2 IntroductionDocument33 pagesClass - 1&2 IntroductionharinaathanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics FundamentalsDocument80 pagesFluid Mechanics FundamentalsRaj SamuelNo ratings yet
- Portable Electric Power Tilling Machine Project ReviewDocument8 pagesPortable Electric Power Tilling Machine Project ReviewP KalaivaniNo ratings yet
- Oml 751 Testing of MaterialsDocument35 pagesOml 751 Testing of MaterialsAngel SelvaNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Finite Element Analysis of Elevator Buckets: January 2016Document9 pagesModelling and Finite Element Analysis of Elevator Buckets: January 2016Arief RachmanNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions (TD)Document9 pagesInterview Questions (TD)anil gautamNo ratings yet
- Heat Equation Sci LabDocument7 pagesHeat Equation Sci LabVíctor QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument12 pagesFuels and CombustionAbhishek PrasadNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Turbo MachinesDocument6 pagesBasic Principles of Turbo Machinesbinho58100% (1)
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1Ammar AltafNo ratings yet
- ADI Two-Step Austempering StudyDocument26 pagesADI Two-Step Austempering StudyartikscindianNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Air Standarad CyclesDocument6 pagesMCQ On Air Standarad Cyclessatish448100% (1)
- Fuels and CombustionDocument25 pagesFuels and CombustionDave Andrew PapaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae-Professor 30-05-2018Document8 pagesCurriculum Vitae-Professor 30-05-2018Meer Mustafa AliNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Question BankDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Question BankOyedotun TundeNo ratings yet
- Equivalence of Clausius and Kelvin-Planck StatementsDocument6 pagesEquivalence of Clausius and Kelvin-Planck Statementsashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Test Assignment: Solution Numerical 1Document9 pagesMechanical Engineering Test Assignment: Solution Numerical 1Raj PatelNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines:: I.C and E.C EnginesDocument4 pagesInternal Combustion Engines:: I.C and E.C EnginesTariq AslamNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics-1 Semester AssignmentDocument9 pagesThermodynamics-1 Semester AssignmentShahZaib AnwarNo ratings yet
- Formulas for Physics and EngineeringDocument6 pagesFormulas for Physics and EngineeringArav BharadiaNo ratings yet
- Facts and Formulas 3 RefDocument13 pagesFacts and Formulas 3 Refrania deifNo ratings yet
- Physics Review PapersDocument18 pagesPhysics Review Papersyoonmimikyaw2008No ratings yet
- Here Are Some Basic Physics FormulasDocument3 pagesHere Are Some Basic Physics FormulasCrisanto BorjalNo ratings yet
- Physics Reference PDFDocument12 pagesPhysics Reference PDFRonald Chester LorenzanaNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Academic Physics 600dpiDocument6 pagesQuick Study Academic Physics 600dpiMartin BotrosNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Definations and EquationsDocument19 pagesMid Term Definations and Equationsellastella682008No ratings yet
- Work and Energy DefinitionsDocument2 pagesWork and Energy DefinitionsDerick PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 A2 Physics Problems STEM-N ASICODocument11 pagesPhysics 1 A2 Physics Problems STEM-N ASICOChristian Paul A. AsicoNo ratings yet
- OpI 200500591 PDFDocument372 pagesOpI 200500591 PDFShahnam GhasediNo ratings yet
- Gear FailureDocument27 pagesGear FailureSheri KhosoNo ratings yet
- Section 7 - Separation EquipmentDocument9 pagesSection 7 - Separation Equipmentlulis171No ratings yet
- Clamping BushingsDocument6 pagesClamping BushingsshelarsanjayNo ratings yet
- BS4 End TermDocument2 pagesBS4 End TermShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Inbal Deluge ValveDocument4 pagesInbal Deluge ValveNelson Eduardo Zárate SalazarNo ratings yet
- DonalsonDocument6 pagesDonalsonrockyttpmcNo ratings yet
- DucatiDocument23 pagesDucatiKvk TorettoNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Paper DSRDocument4 pagesAsphalt Paper DSRyazqaNo ratings yet
- Auto Turning Fuel ValveDocument30 pagesAuto Turning Fuel ValveMahesh Dondapati67% (3)
- TMN-SD1 Service and Parts Update GuideDocument33 pagesTMN-SD1 Service and Parts Update GuideJacquelineNo ratings yet
- BSD EurocodeDocument187 pagesBSD EurocodeAndreea Nan50% (2)
- 2018/01/19 Diagnostic Trouble Code List (UENR1209)Document10 pages2018/01/19 Diagnostic Trouble Code List (UENR1209)Derrick AramNo ratings yet
- 512 Army Base WorkshopDocument8 pages512 Army Base WorkshopSinZahoNo ratings yet
- Affnan's Aquaponics: Improving Siphon Design for Greater EfficiencyDocument16 pagesAffnan's Aquaponics: Improving Siphon Design for Greater EfficiencyJuan Carlos FernandezNo ratings yet
- Design of Slender Tall Buildings For Wind and EarthquakeDocument110 pagesDesign of Slender Tall Buildings For Wind and EarthquakemayasNo ratings yet
- Measure Engine Performance and Calculate Key ParametersDocument28 pagesMeasure Engine Performance and Calculate Key ParametersbroNo ratings yet
- Pressure Regulating Valve Valvulas by Pass Catalogo EquigasDocument1 pagePressure Regulating Valve Valvulas by Pass Catalogo EquigasecsuperalNo ratings yet
- Fuel Delivery ComponentsDocument4 pagesFuel Delivery ComponentsSirleh Saleh100% (1)
- Thermo Activity 4, 5Document4 pagesThermo Activity 4, 5Karl Christian Fajardo100% (1)
- Aalborg XW SuperheaterDocument2 pagesAalborg XW SuperheaterPanagiotisNo ratings yet
- Compressor EMI45HER (LBP) - DatasheetDocument4 pagesCompressor EMI45HER (LBP) - DatasheetSamuel OsmagNo ratings yet
- 836T Pressure Controls and SwitchesDocument30 pages836T Pressure Controls and SwitchesKyle StackNo ratings yet
- Kaithi Doc NewDocument8 pagesKaithi Doc Newkarthik reddyNo ratings yet
- Actros 5 3340SDocument5 pagesActros 5 3340Sjames noobNo ratings yet
- Tufail MaboodDocument3 pagesTufail MaboodMickey DalbeheraNo ratings yet
- MICHAEL FARDIS Seismic Isolation Principles and PracticeDocument69 pagesMICHAEL FARDIS Seismic Isolation Principles and PracticeozuygurNo ratings yet
- Course On Structural StabilityDocument3 pagesCourse On Structural StabilityVenkatesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Toyo Pumps Specification Sheet & Quotation: DEC Series Heavy Duty Vertical Cantilever PumpDocument4 pagesToyo Pumps Specification Sheet & Quotation: DEC Series Heavy Duty Vertical Cantilever PumpNicolas Celis Perez100% (1)
- Caribbean Examinations Council: Timetable May-June 2013Document12 pagesCaribbean Examinations Council: Timetable May-June 2013Ashley Maxwell0% (1)