Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of IMCI Case Management
Uploaded by
janesky09Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of IMCI Case Management
Uploaded by
janesky09Copyright:
Available Formats
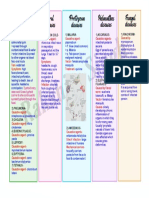
CHECK FOR GENERAL DANGER • Is the child able to drink or breastfeed? • Convulsions in this illness?
SIGNS: ASK • Does the child vomit everything? • Is the child lethargic or unconscious?
CHILD 2 MONTHS TO 5 YEARS: ASSESS CLASSIFY TREATMENT
• Give ceftriaxone IMI (80mg/kg) and if child < 6
Any General Danger Sign
DOES THE CHILD HAVE COUGH SEVERE mths also give cotrimoxazole
OR
OR DIFFICULT BREATHING? PNEUMONA OR • Give O2 and check blood sugar
Chest Indrawing
VERY SEVERE • If stridor, nebulize with adrenalin
OR
• For how long? DISEASE • Keep child warm and refer URGENTLY to
Stridor in a calm child
• Count the breaths in one minute hospital
• Look for chest indrawing • Give amoxycillin for 5 days
• Look and listen for stridor or Fast breathing PNEUMONIA • Consider symptomatic HIV
wheeze • Follow up in 2 days
• Soothe the throat and relieve the cough
Age Fast breathing No signs of pneumonia or very • If coughing for more than 21 days consider TB
2 - 12 mths = 50 or > breaths/min COUGH OR COLD
1 – 5 yrs = 40 or > breaths/min
severe disease or asthma
• Follow-up 5 days if not better
DOES THE CHILD HAVE Two of the following signs:
DIARRHOEA? • Lethargic or unconscious • Start Fluids for Plan C
• For how long? • Sunken eyes DIARRHOEA WITH • Refer URGENTLY to hospital
• If >14 days, has child lost • Not able to drink or drinking SEVERE • Give frequent sips of ORS on the way, continue
weight? poorly DEHYDRATION breastfeeding
• Is there blood in the stool? • Skin pinch goes back very slowly • Keep the child warm
• What Rx is the mother giving? (>2 secs)
• Look at child’s general condition Two of the following signs:
• Look for sunken eyes. • Restless or irritable DIARRHOEA WITH • Give fluids: Plan B
• Offer the child fluids. • Sunken eyes SOME • Continue breastfeeding or feeding
• Pinch the skin of the abdomen • Child drinks eagerly and is thirsty DEHYDRATION • Follow up in 2 days if not improving
• Skin pinch goes back slowly
• Give fluid and food to Rx diarrhoea
CLASSIFY FOR DEHYDRATION Not enough signs to classify NO VISIBLE
at home: Plan A
(All children with diarrhoea) as severe or some dehydration DEHYDRATION
• Follow up in 5 days if not improving
• Rx for dehydration if present
SEVERE
CLASSIFY FOR PERSISTENT • Child has signs of dehydration • Refer URGENTLY to hospital
PERSISTENT
DIARRHOEA • Child has history of weight loss • Give Vit. A unless given in last month
DIARRHOEA
(If diarrhoea for 14 or more days) • Give frequent sips of ORS on the way
• Counsel the mother about feeding
• No dehydration PERSISTENT • Give Vit. A unless given in last month
• No history of weight loss DIARRHOEA • Consider symptomatic HIV infection
• Follow up in 5 days
• Rx for dehydration if present
CLASSIFY FOR DYSENTERY • Child has signs of dehydration SEVERE
• Refer URGENTLY to hospital
(If diarrhoea with blood) • Child less than 12 months of age DYSENTERY
• Give frequent sips of ORS on the way
• Give ciprofloxacin for 3 days
• Blood in stool DYSENTERY
• Follow-up in 2 days
Give quinine for severe malaria (first dose)
Any General Danger Sign
DOES THE CHILD HAVE A Give first dose of an appropriate antibiotic
OR VERY SEVERE
FEVER? Treat the child to prevent low blood sugar
Stiff neck FEBRILE
HIGH – RISK MALARIA Give one dose of paracetamol in clinic for high
OR DISEASE
THEN ASK: fever(38.5°C or above)
Bulging fontanelle
• For how long? Refer URGENTLY to hospital
• If more than 7 days, has fever Give oral co-artemether or other recommended
been present every day? antimalarial
• Has the child had measles Give one dose of paracetamol in clinic for high fever
within the last 3 months? Fever (by history or feels hot or (38.5°C or above)
MALARIA
temperature 37.5°C** or above) Advise mother when to return imm.
LOOK AND FEEL: Follow-up in 2 days if fever persists
• Look or feel for stiff neck. If fever is present every day for more than 7 days,
• Look for runny nose. refer forassessment
Look for signs of MEASLES
• Generalized rash and Any General Danger Sign Give quinine for severe malaria (first dose) unless no
• One of these: cough, runny nose, OR malaria risk
or red eyes. Stiff neck VERY SEVERE Give first dose of an appropriate antibiotic
OR FEBRILE Treat the child to prevent low blood sugar
Bulging fontanelle DISEASE Give one dose of paracetamol in clinic for high fever
LOW – RISK MALARIA (Malaria rapid test or positive (38.5°C or above)
or negative or not done) Refer URGENTLY to hospital
Give oral co-artemether or other recommended
antimalarial
Give one dose of paracetamol in clinic for high fever
NO runny nose and
(38.5°C or above)
NO measles and MALARIA
Advise mother when to return immediately
NO other cause of fever
Follow-up in 2 days if fever persists
If fever is present every day for more than 7 days,
refer for assessment
Give one dose of paracetamol in clinic for high fever
• Runny nose PRESENT or (38.5°C or above)
FEVER -
• Measles PRESENT or Advise mother when to return immediately
MALARIA
• Other cause of fever Follow-up in 2 days if fever persists
UNLIKELY
PRESENT If fever is present every day for more than 7 days,
refer forassessment
Give Vitamin A treatment
• Any general danger sign or Give first dose of an appropriate antibiotic
SEVERE
If the child has measles now • Clouding of cornea or If clouding of the cornea or pus draining from the
COMPLICATED
or within the last 3 months: • Deep or extensive mouth eye, apply
MEASLES
ulcers tetracycline eye ointment
• Look for mouth ulcers. Are they Refer URGENTLY to hospital
deep and extensive? Give Vitamin A treatment
• Look for pus draining from the MEASLES WITH If pus draining from the eye, treat eye infection with
• Pus draining from the eye or
eye. EYE OR MOUTH tetracycline eye ointment
• Mouth ulcers
• Look for clouding of the cornea. COMPLICATIONS If mouth ulcers, treat with gentian violet
Follow-up in 2 days.
• Measles now or within the
MEASLES Give Vitamin A treatment
last 3 months
CHILD 2 MONTHS TO 5 YEARS: ASSESS CLASSIFY TREATMENT
DOES THE CHILD HAVE AN Tender swelling behind the ear MASTOIDITIS • Give ceftriaxone IMI and refer
EAR PROBLEM? URGENTLY to hospital
• Ear pain • Rx amoxycillin for 5 days
• Ear pain? OR ACUTE EAR INFECTION • If ear discharge teach mother dry
• Is there ear discharge? If yes for • Red tympanic membrane wicking and consider symptomatic HIV
how long? OR • Analgesia and follow up in 5 days if pain
• Pus draining from the ear < 14 CHRONIC EAR or discharge persists
days INFECTION • Teach mother dry wicking
• Pus draining from the ear > 14 • Consider symptomatic HIV
days • Follow up in 14 days
• No ear pain and no pus
NO EAR INFECTION • No Rx
draining
CHECK FOR MALNUTRITION • Very low weight (<60% exp’d)
AND ANAEMIA OR • Vit. A unless given in the last month
• Visible severe wasting SEVERE MALNUTRITION • Refer URGENTLY to hospital
• Has the child lost weight? OR • Check blood sugar and keep warm
• Plot the weight on the RTHC • edema of both feet
• Look for visible severe wasting • Low weight • Consider Vit. A and mebendazole
• Feel for oedema of both feet OR • Check and treat for oral thrush
• Poor weight gain NOT GROWING WELL • Consider symptomatic HIV, TB contact
OR • Assess feeding and counsel
• Mother reports weight loss • Follow up in 14 days
• Not low weight and... • Check feeding
• Look for palmar pallor GROWING WELL
• Good weight gain • Consider Vit A and mebendazole
• Check hemoglobin level
• Severe palmar pallor OR • Refer URGENTLY to hospital
SEVERE ANAEMIA
• Hb < 6 g/dl • Keep the child warm
• Some palmar pallor OR • Rx with iron and counsel about feeding
ANAEMIA
• Hb < 10 g/dl • Follow up in14 days
• No pallor and Hb > 10 g/dl NO ANAEMIA • No additional Rx
ASSESS FOR SYMPTOMATIC • Any pneumonia now • Offer HIV testing for mother and
HIV INFECTION: • Ear discharge now or in the past? SUSPECTED child if status unknown
• Low weight for age SYMPTOMATIC HIV • Start co-trimoxazole prophylaxis
• 3 OR MORE POSITIVE • Poor weight gain or weight loss? (3 or > positive findings) • Counsel the mother
FINDINGS OF THESE 8 • Persistent diarrhoea in last 3 • Follow up for counselling about results
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS months?
• Enlarged lymph nodes in 2 or
SYMPTOMATIC HIV
more of the following 3 sites: • Counsel mother about her health
UNLIKELY
Neck, axilla or groin and precautions against HIV infection
(< 3 positive findings)
• Oral thrush
• Parotid gland enlargement
INFANT: 1 WEEK - 2 MONTHS ASSESS CLASSIFY TREATMENT
CHECK FOR One of the following signs:
POSSIBLE • Fast breathing 60 or > breaths/min. (Repeat if
BACTERIAL fast)
INFECTION • Severe chest indrawing (deep and easy to see)
• Nasal flaring or grunting
• Convulsions • Give IMI ceftriaxone (80mg/kg)
• Bulging fontanelle • Give O2
• Umbilical redness extending to skin, and or • Give rectal diazepam if convulsing
POSSIBLE SERIOUS
draining pus • Check and Rx low blood sugar
BACTERIAL INFECTION
• Fever (> 37.5C) or low body temperature • Refer URGENTLY to hospital
(<35.5C) • Continue breastfeeding
• Many or severe skin pustules (> 5 pustules) • Keep the child warm
• Lethargic, unconscious or less than normal
movements
• Apnea attacks
• Not taking feeds or taking feeds poorly
• Jaundice worsening or still present after 2 weeks
• Red umbilicus • Give erythromycin for 7 days
LOCAL BACTERIAL
• Skin pustules • For eye infection give ceftriaxone IMI
INFECTION
• Pus draining from the eye • Advise mother on care of the infection
NO BACTERIAL
None of the above signs: • Relevant health counselling
INFECTION
CHECK FOR FEEDING • Not able to feed • Give IMI ceftriaxone (80mg/kg)
NOT ABLE TO FEED
PROBLEM OR LOW WEIGHT IN • Infant not able to attach to breast • Check blood sugar and keep warm
BREASTFED BABIES: • Not suckling at all • Refer URGENTLY to hospital
• Not suckling at all
• Advise on breastfeeding esp.
• Infant not well attached to breast
correct positioning and attachment
• Infant not suckling effectively
FEEDING PROBLEM OR • Breastfeed > 8x in 24 hrs and at
• Less than 8 breastfeeds in 24 hrs
NOT night
• Infant receiving other foods
GROWING WELL • Breastfeed more, reducing other
• Low weight for age or poor wt.
foods
gain
• Follow up weight gain
• Oral thrush
• Nystatin drops
• Using a feeding bottle
• Not low weight and feeding well NO FEEDING PROBLEM • Relevant health counselling
You might also like
- Npi Format For Rle 1Document9 pagesNpi Format For Rle 1Patricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Resource Unit On Common Drugs (LRDR Rotation)Document37 pagesResource Unit On Common Drugs (LRDR Rotation)kiamoiNo ratings yet
- Post Test - Psych-Prof. Alviz - SCDocument4 pagesPost Test - Psych-Prof. Alviz - SCKristen FajilanNo ratings yet
- Leopold S ManeuverDocument5 pagesLeopold S Maneuverastak ghisingNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPZmiaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cva Verb1Document2 pagesAssessment Cva Verb1JhiLy 사랑의 케빈 우No ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanTenth Ann ModanzaNo ratings yet
- Chn-Herbal MedicineDocument5 pagesChn-Herbal MedicineBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Community Organizing Participatory Action ResearchDocument29 pagesCommunity Organizing Participatory Action ResearchNoreen PadillaNo ratings yet
- NCP NCM 109 Post Partum PeritonitisDocument2 pagesNCP NCM 109 Post Partum PeritonitisHoney MacabuhayNo ratings yet
- NCP - ERDocument5 pagesNCP - ERAnnelore ArcayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities For Oxygen AdministrationDocument3 pagesNursing Responsibilities For Oxygen AdministrationJahseh WolfeNo ratings yet
- KardexDocument2 pagesKardexKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Palmar Long Quiz Ratio AnswersDocument153 pagesPalmar Long Quiz Ratio AnswersPatrisha May MahinayNo ratings yet
- Endorsement SheetDocument1 pageEndorsement SheetLucelle MarieNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Nitumusiina Billy Admitted With Acute Otitis Media and TonsillitisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Nitumusiina Billy Admitted With Acute Otitis Media and TonsillitisNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Health-Perception-Health-Management PatternDocument3 pagesHealth-Perception-Health-Management PatternBela MillenaNo ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument11 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryAyah GarciaNo ratings yet
- N U R S I N G Care Plan For AterosclerosiDocument2 pagesN U R S I N G Care Plan For AterosclerosiRoxy TofyNo ratings yet
- IMCI SL LecDocument143 pagesIMCI SL LecJmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- UTI Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesUTI Discharge Plankimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- ISBAR PneumoniaDocument1 pageISBAR PneumoniaLerma Pagcaliwangan0% (1)
- Discharge Plan CapDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan Capalexander abasNo ratings yet
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDocument4 pagesContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- Case 1Document1 pageCase 1Patricia Ysabelle LedesmaNo ratings yet
- CHN (Community Health Nursing)Document7 pagesCHN (Community Health Nursing)Sarah Jane MaganteNo ratings yet
- Female Perineal CareDocument8 pagesFemale Perineal CareMushy_ayaNo ratings yet
- LRDR ProceduresDocument67 pagesLRDR ProceduresJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- Situation 1Document18 pagesSituation 1Maler De VeraNo ratings yet
- Health Care Delivery System & COPARDocument52 pagesHealth Care Delivery System & COPARDharylle Cariño100% (1)
- Intradermal Sterile Water InjectionDocument4 pagesIntradermal Sterile Water InjectionYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- NCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Document5 pagesNCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Kevin_Remollo_2431No ratings yet
- Drug Study For Postpartum MothersDocument5 pagesDrug Study For Postpartum MothersnnicakoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPDocument7 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesHyperthermiaLeolene Grace BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Andrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- CefotaximeDocument3 pagesCefotaximeMargotNo ratings yet
- Answer: 1Document4 pagesAnswer: 1Jeffrey ViernesNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs of LaborDocument13 pagesDanger Signs of LaborBenj Villanueva50% (2)
- Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements R/T Diarrhea Due To Excessive OutputDocument2 pagesImbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements R/T Diarrhea Due To Excessive OutputMark BarengNo ratings yet
- Disaster Preparedness - Leadership and Coordination in Disaster in Health Care System With LectureDocument29 pagesDisaster Preparedness - Leadership and Coordination in Disaster in Health Care System With LectureArvie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nurses Progress NotesDocument2 pagesNurses Progress NotesCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Document3 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument4 pagesNCP ErljarseniornNo ratings yet
- ORESOL Is "Oral Glucose-ElectrolyteDocument4 pagesORESOL Is "Oral Glucose-ElectrolyteMichelle ViduyaNo ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document2 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDocument2 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Nov 24Document25 pagesDiagnostic Exam Nov 24genita.keziahandrea100% (1)
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 pagesCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposNo ratings yet
- 1st History PEdiaDocument6 pages1st History PEdiaDeepak BamNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument13 pagesCommunity Health NursingXandra Basnillo100% (1)
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideSetiram Zenitram50% (2)
- Breastfeeding FinalDocument25 pagesBreastfeeding FinalWengel RedkissNo ratings yet
- Chapter 014 PSDocument12 pagesChapter 014 PSJann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- NP1 NotesDocument6 pagesNP1 NotesGrace TangoNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Document1 pageDysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessesDocument65 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessesJocel LañasNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness: Chart BookletDocument81 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness: Chart BookletReadcast EFNo ratings yet
- Care of The Child Applying Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses (Imci)Document22 pagesCare of The Child Applying Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses (Imci)Jesena SalveNo ratings yet
- National Control of Dirrheal Diseases (CDD) Program ObjectivesDocument6 pagesNational Control of Dirrheal Diseases (CDD) Program ObjectivesJoy FucananNo ratings yet
- Fiji Communicable Disease Surveillance and Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 1Document133 pagesFiji Communicable Disease Surveillance and Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 1roddy narayanNo ratings yet
- Acrylonitrile PDFDocument5 pagesAcrylonitrile PDFDEja RaZiNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion and Primary Health Care PDFDocument34 pagesHealth Promotion and Primary Health Care PDFKavya S Mohan100% (2)
- Modern Theories of Disease CausationDocument113 pagesModern Theories of Disease CausationdsenpenNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases in HumansDocument1 pageCommon Diseases in HumansDilipsingh RajputNo ratings yet
- 2chain of DiseaseDocument43 pages2chain of Diseaseyuuki konno100% (1)
- RAM Revised For PR1418Document1 pageRAM Revised For PR1418rwerwerwNo ratings yet
- w11 HE385 Future TrendsDocument20 pagesw11 HE385 Future TrendsKathlyn PactorananNo ratings yet
- Newton 1997Document1 pageNewton 1997Nobody0% (1)
- HEPATITIS A (Infectious Hepatitis)Document3 pagesHEPATITIS A (Infectious Hepatitis)Lovely Ann AyapanaNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Senam Kaki Terhadap Kadar Glukosa Darah Dan Nilai ABI Penderita DMDocument6 pagesPengaruh Senam Kaki Terhadap Kadar Glukosa Darah Dan Nilai ABI Penderita DMSetyardiNo ratings yet
- Obesity: Making Healthier Lifestyle ChoicesDocument1 pageObesity: Making Healthier Lifestyle ChoicesAn QuanNo ratings yet
- Bahan CA 1Document11 pagesBahan CA 1fk unswagatiNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B VaccinationDocument5 pagesHepatitis B Vaccinationhap hazardNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Lifestyle DiseasesDocument17 pagesPrevention of Lifestyle Diseasesjohn mills100% (1)
- 2021.07.21 LWV Corpus Christi Lead Contamination in Drinking Water Study & Position Statement - NCDocument13 pages2021.07.21 LWV Corpus Christi Lead Contamination in Drinking Water Study & Position Statement - NCcallertimesNo ratings yet
- Bped 102-Notes Maintenance of THR BodyDocument3 pagesBped 102-Notes Maintenance of THR Bodytherealisaac.No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Maternal MortalityDocument31 pagesAssignment 1 Maternal MortalityPriyanka SheoranNo ratings yet
- Capitulo Riesgo FletcherDocument19 pagesCapitulo Riesgo FletcherAnita MacdanielNo ratings yet
- IU Vaccine LawsuitDocument55 pagesIU Vaccine LawsuitJoe Hopkins100% (2)
- Unit - Two - Infection Control - Universal PrecautionsDocument31 pagesUnit - Two - Infection Control - Universal Precautionsvirtus_kuwaitNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument27 pagesCHNSamantha Marie100% (1)
- Maria Diaz Martinez 7260 SW 163RD AVE MIAMI, FL 33193: Test ReportDocument2 pagesMaria Diaz Martinez 7260 SW 163RD AVE MIAMI, FL 33193: Test ReportEddy Luis Hernández HernándezNo ratings yet
- Cancer Antigen (Ca) 15.3: Subtypes of Breast CancerDocument4 pagesCancer Antigen (Ca) 15.3: Subtypes of Breast Cancerडा. सत्यदेव त्यागी आर्यNo ratings yet
- Jerwin JournalDocument3 pagesJerwin JournaljerwiNo ratings yet
- Ncma217 - PostpartumDocument12 pagesNcma217 - Postpartumanjie kamidNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology CourseworkDocument8 pagesEpidemiology Courseworkettgyrejd100% (2)
- Kenneth Cooper Poster Presentation For The Ex Sci BoardDocument1 pageKenneth Cooper Poster Presentation For The Ex Sci Boardapi-639699202No ratings yet
- Bacillus Calmette - Guérin: Oral Polio VaccineDocument1 pageBacillus Calmette - Guérin: Oral Polio VaccineElleNo ratings yet
- Guideline URTI in South Africa 2008Document9 pagesGuideline URTI in South Africa 2008Febbe Nadia Okky LucianaNo ratings yet