Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Notes: Chapter - 16 Light
Uploaded by
n.ananthapadmanabhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Notes: Chapter - 16 Light
Uploaded by
n.ananthapadmanabhanCopyright:
Available Formats
www.ncrtsolutions.
in
Key Notes
Chapter – 16
Light
• Light: The natural agent that stimulates sight and makes things visible. Light is reflected
from all surfaces.
• Regular reflection takes place when light is incident on smooth, polished and regular
surfaces.
• Diffused/irregular reflection takes place from rough surfaces.
• Reflection of Light: Bouncing back of light after striking the surface, in the same
medium, is called reflection.
• Types of Reflection:
(i) Regular Reflection: When a narrow beam of light strikes a mirror, the light will
not reach your eye unless your eye is positioned at just the right place where the
law of reflection is satisfied.
(ii) Diffused or Irregular Reflection: When light is incident upon a rough surface, it
is reflected in many directions.
• Two laws of reflection are
• The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
• Incident ray, reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to the reflecting
surface, lie in the same plane.
• Image formed in a plane mirror undergoes lateral inversion.
• Two mirrors inclined to each other give multiple images.
• Beautiful patterns are formed in a kaleidoscope because of multiple reflections.
• Sunlight, called white light, consists of seven colours.
• Splitting of light into its constituent colours is known as dispersion.
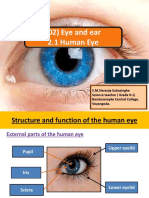
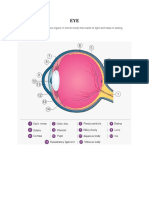
• Important parts of the eye are cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina and optic nerve.
• A normal eye can see nearby and distant objects clearly.
• Visually challenged persons can read and write using Braille system.
• Visually challenged persons develop their other senses more sharply to improve their
interaction with their environment.
• Parts of Human Eye:
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Material Downloaded From http://www.ncrtsolutions.in
www.ncrtsolutions.in
Key Notes
(i) Cornea: Transparent bulge on the front surface of the eyeball which protects the
eye and helps in refraction of light.
(ii) Iris: Coloured diaphragm behind the cornea which controls the amount of light
entering the eye.
(iii) Pupil: Dark hole in the middle of iris through which light enters the eye.
(iv) Eye lens: Transparent, crystalline structure behind pupil and iris.
(v) Ciliary muscles: Hole the eye lens in position and control the focal length of the
eye lens.
(vi) Retina: Surface of the rear part of the eyeball where the light entering the eye is
focused.
(vii) Rods and Cones: Rod cells respond to the brightness of light while cone cells
respond to colours.
(viii) Blind spot: It is the least sensitive point where no rodsd and cones are present.
(ix) The space between the cornea and the eye lens is filled with aqueous humour.
(x) The space between the eye lens and the retina is filled with vitreous humour.
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
Material Downloaded From http://www.ncrtsolutions.in
You might also like
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Chapter 16 - LightDocument30 pagesClass 8 - Chapter 16 - LightsanaNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Sense Organ - EyeDocument28 pages13.2 Sense Organ - EyeMuhammad Amin SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- CBSE 8 Science CBSE - Light, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - LightDocument5 pagesCBSE 8 Science CBSE - Light, Free Test Papers, Sample Questions, HOTS Questions and Notes, CBSE - LightR.Shruti 1040-12No ratings yet
- PHY_VIII_CH16_LIGHT_NOTES_BY_ANKUR_SHARMA (5)Document6 pagesPHY_VIII_CH16_LIGHT_NOTES_BY_ANKUR_SHARMA (5)jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Human Eye AnatomyDocument3 pagesLight Reflection and Human Eye AnatomyArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - LightDocument3 pagesS - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - LightVector HuntNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Power PointDocument36 pagesHuman Eye Power Pointlourdescuaresma838No ratings yet
- 13-Physiology of The Eye and RefractionDocument16 pages13-Physiology of The Eye and RefractionwidyawirapNo ratings yet
- 6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Document35 pages6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- (Anatomy of The Eye) STUDY!!!Document1 page(Anatomy of The Eye) STUDY!!!Analisa LacaranNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear 2.1 Human EyeDocument12 pagesEye and Ear 2.1 Human Eyechakshana kannangaraNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Health ShekhanDocument9 pagesTechnical College of Health ShekhanSaadNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Light: The Science of SightDocument7 pagesIntroduction to Light: The Science of SightShivang GuptaNo ratings yet
- Resumen Semana 1 Clase de OftalmologiaDocument3 pagesResumen Semana 1 Clase de OftalmologiaIsis MartinezNo ratings yet
- What Makes Up An EyeDocument3 pagesWhat Makes Up An EyenandhantammisettyNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and the Human EyeDocument17 pagesLight Reflection and the Human EyeAkshaya Swati RNo ratings yet
- Perception and Coordination Lesson 1.2Document4 pagesPerception and Coordination Lesson 1.2Lovely CruzxNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear - 2019Document3 pagesEye and Ear - 2019Mr. RWord100% (1)
- Light Lesson 3Document13 pagesLight Lesson 3rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs Guide: Classification, Structure & FunctionsDocument26 pagesSense Organs Guide: Classification, Structure & FunctionsArpan AdhikariNo ratings yet
- L05 Special Senses WAnsDocument52 pagesL05 Special Senses WAnsKa Yan LAUNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Sec4 BioDocument10 pagesHuman Eye Sec4 BioFrancine TheophilaNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Document9 pagesNotebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Adhya MisraNo ratings yet
- Eyes Health AssessmenttDocument34 pagesEyes Health AssessmenttMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- Info Sheet 4 - 1Document8 pagesInfo Sheet 4 - 1Francis ObmergaNo ratings yet
- 27 Physiology of Visual Analyzer (2)Document39 pages27 Physiology of Visual Analyzer (2)siwap34656No ratings yet
- Anaphy Special Senses NotesDocument6 pagesAnaphy Special Senses NotesThieza Mecca LucenaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The EyesDocument61 pagesAssessing The EyessrslytrdNo ratings yet
- Vision: Chapter 9: SensesDocument21 pagesVision: Chapter 9: SenseshoneykrizelNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Light PDFDocument5 pagesClass 8 Light PDFMamta JoshiNo ratings yet
- 10science EyesDocument36 pages10science EyesChuNie TangNo ratings yet
- Light - Class NotesDocument6 pagesLight - Class Noteskirankarnawat29No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eyes-BiopsyDocument20 pagesAnatomy of Eyes-BiopsynandanitriadiningsihNo ratings yet
- Eye Dissection Report Write Up 2014Document8 pagesEye Dissection Report Write Up 2014api-351895935No ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument1 pageHuman EyeLaksh KhatriNo ratings yet
- Human Is One of The Sense Organs in Human Body That Reacts To Light and Helps in Seeing ObjectsDocument10 pagesHuman Is One of The Sense Organs in Human Body That Reacts To Light and Helps in Seeing ObjectsKp ParmarNo ratings yet
- Prerna Subramanian X-C 25 Presentation Scientific SkillsDocument12 pagesPrerna Subramanian X-C 25 Presentation Scientific SkillsPrerna S ManianNo ratings yet
- 3 - Dimaano, Jerome M. - LensesDocument6 pages3 - Dimaano, Jerome M. - LensesJerome DimaanoNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Human Eye Ebook 2017Document15 pagesVisibleBody Human Eye Ebook 2017Sandra RubianoNo ratings yet
- Light Class 8 NotesDocument6 pagesLight Class 8 Notesthecakebox2007No ratings yet
- 11 2 LS EyeDocument63 pages11 2 LS EyeAdhi PandayNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument26 pagesHuman EyeUmar ShadNo ratings yet
- Eye PhysiologyDocument11 pagesEye PhysiologyAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Working of Human EyeDocument13 pagesWorking of Human EyeVikashKeshavNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Human EyeDocument10 pagesStructure and Function of The Human EyeSyed MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Special Senses: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document13 pagesSpecial Senses Special Senses: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Jewel Alexis Mendoza AGAYANNo ratings yet
- Science Q2-Parts and Functions of The EyesDocument31 pagesScience Q2-Parts and Functions of The EyesRovi ChellNo ratings yet
- Science Information - Grade 8Document52 pagesScience Information - Grade 8Bindu SNo ratings yet
- Special Senses EYEDocument27 pagesSpecial Senses EYENadiabloshii NadiabloshiiNo ratings yet
- 12.2 Structure and Function of Eye NewDocument74 pages12.2 Structure and Function of Eye NewHai KhaiNo ratings yet
- L5 - 2 - Special SensesDocument87 pagesL5 - 2 - Special Sensesbotchwaylilian17No ratings yet
- WS - Eye Structure and Function WORDDocument4 pagesWS - Eye Structure and Function WORDAlvand HormoziNo ratings yet
- Light: Transparent ObjectsDocument4 pagesLight: Transparent ObjectsAshutosh DattaNo ratings yet
- CH Light NotesDocument14 pagesCH Light Notesvk040903No ratings yet
- An Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainDocument59 pagesAn Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainIsarra AmsaluNo ratings yet
- Sense OrgansDocument64 pagesSense Organsabdulazeez AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- 181 Anatomy Eyes and EarsDocument23 pages181 Anatomy Eyes and Earsmuhammad chughtaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Light Class 8Document15 pagesChapter 16 Light Class 8Amaira KalsiNo ratings yet
- 181 Anatomy Eyes and EarsDocument23 pages181 Anatomy Eyes and EarsAnita YadavNo ratings yet
- 8 Geography NCERT Chapter PDFDocument11 pages8 Geography NCERT Chapter PDFSaturdhan RaajNo ratings yet
- Key Notes: Chapter - 16 LightDocument2 pagesKey Notes: Chapter - 16 Lightn.ananthapadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Std08 I Social Science EMDocument78 pagesStd08 I Social Science EMn.ananthapadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Key Notes: Chapter - 16 LightDocument2 pagesKey Notes: Chapter - 16 Lightn.ananthapadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- 1 9th Social Sura Guide 2019 2020 Sample Materials Tamil MediumDocument101 pages1 9th Social Sura Guide 2019 2020 Sample Materials Tamil Mediumn.ananthapadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Motor-Catalog English 2013 PDFDocument80 pagesMotor-Catalog English 2013 PDFILham Dwi PutraNo ratings yet
- PCC 3300 PDFDocument6 pagesPCC 3300 PDFdelangenico4No ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Purpose - TitusDocument46 pagesModule 2 - The Purpose - TitusEnp Titus VelezNo ratings yet
- Mora Solvendi (Delay of The Debtor)Document11 pagesMora Solvendi (Delay of The Debtor)John Paul100% (1)
- Emerson Field Tools Quick Start GuideDocument48 pagesEmerson Field Tools Quick Start Guidepks_2410No ratings yet
- A Ghost StoryDocument10 pagesA Ghost StoryTrần MạnhNo ratings yet
- CAPITAL ALLOWANCE - Exercise 3 (May2021)Document2 pagesCAPITAL ALLOWANCE - Exercise 3 (May2021)NORHAYATI SULAIMANNo ratings yet
- Se Lab Da-2Document12 pagesSe Lab Da-2Anvesh PenkeNo ratings yet
- A. Pawnshops 4. B. Pawner 5. C. Pawnee D. Pawn 6. E. Pawn Ticket 7. F. Property G. Stock H. Bulky Pawns 8. I. Service Charge 9. 10Document18 pagesA. Pawnshops 4. B. Pawner 5. C. Pawnee D. Pawn 6. E. Pawn Ticket 7. F. Property G. Stock H. Bulky Pawns 8. I. Service Charge 9. 10Darwin SolanoyNo ratings yet
- What Is ReligionDocument15 pagesWhat Is ReligionMary Glou Melo PadilloNo ratings yet
- 2013 KTM 350 EXC Shop-Repair ManualDocument310 pages2013 KTM 350 EXC Shop-Repair ManualTre100% (7)
- Deconstuctionist CriticismDocument3 pagesDeconstuctionist CriticismStephanie PVNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument57 pagesOsteoporosisViviViviNo ratings yet
- Calculating Calories for Weight Training SuccessDocument12 pagesCalculating Calories for Weight Training SuccessFadil Arif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- EasyGreen ManualDocument33 pagesEasyGreen ManualpitoupitouNo ratings yet
- First Communion Liturgy: Bread Broken and SharedDocument11 pagesFirst Communion Liturgy: Bread Broken and SharedRomayne Brillantes100% (1)
- Density and Buoyancy Practice Test AnswersDocument9 pagesDensity and Buoyancy Practice Test AnswersYesha ShahNo ratings yet
- SMEspdfDocument13 pagesSMEspdflilpumpdidnothingwrong dNo ratings yet
- Effect of Acids and Bases on Fibre Tensile StrengthDocument15 pagesEffect of Acids and Bases on Fibre Tensile StrengthVIKASH SHARMA100% (1)
- Business Decision Making Assignment (July 2015)Document23 pagesBusiness Decision Making Assignment (July 2015)Michael Oppong100% (1)
- g6 Sws ArgDocument5 pagesg6 Sws Argapi-202727113No ratings yet
- Diesel Engines 16V 4000 M23/M33: 50 HZ 60 HZDocument2 pagesDiesel Engines 16V 4000 M23/M33: 50 HZ 60 HZAlberto100% (1)
- Ume Mri GuideDocument1 pageUme Mri GuideHiba AhmedNo ratings yet
- SCM Software Selection and EvaluationDocument3 pagesSCM Software Selection and EvaluationBhuwneshwar PandayNo ratings yet
- Consumer Perception of Digital Payment Modes in IndiaDocument14 pagesConsumer Perception of Digital Payment Modes in Indiakarthick50% (2)
- Researching Indian culture and spirituality at Auroville's Centre for Research in Indian CultureDocument1 pageResearching Indian culture and spirituality at Auroville's Centre for Research in Indian CultureJithin gtNo ratings yet
- Villariba - Document Analysis - Jose RizalDocument2 pagesVillariba - Document Analysis - Jose RizalkrishaNo ratings yet
- BS KashmiryatDocument67 pagesBS KashmiryatWaqas AhmedNo ratings yet
- USD - DPF Cleaning Machine - POSEYDON1000 - PolDocument8 pagesUSD - DPF Cleaning Machine - POSEYDON1000 - PolAbaidi RabieNo ratings yet
- 100 Answers To Common English QuestionsDocument9 pages100 Answers To Common English Questionsflemus_1No ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityFrom EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (380)
- Professor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellFrom EverandProfessor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)