Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indus Valley Civilization: Presented by
Uploaded by
Aravind Ecr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views21 pagesOriginal Title
presetation-170421140844
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views21 pagesIndus Valley Civilization: Presented by
Uploaded by
Aravind EcrCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
Indus Valley Civilization
Presented by:
Md. Saiful Islam(2010135017)
Shahnaj Shemul(2010135019)
R.M Shafiullah Khan(2010135024)
Dept. of Geography and Environment
Shahjalal University of Science and Technology
Sylhet-3114, Bangladesh
Indus Valley
The Indus valley
civilization was one of the
world’s first great urban
civilizations. It flourished
in the vast Indus river
plains and adjacent
regions, in what are now
parts of Afghanistan,
Pakistan and north-
western India.
Beginning
Around five thousand years ago, an important civilization
developed on the Indus River floodplain named the Indus
Valley Civilization (IVC) which was a Bronze Age
Civilization (3300-1300 BCE; mature period 2600-1900
BCE).
Evolution of the Indus Valley
civilization
6500-5000 BC: Early food producing era.
5000-2600 BC: Regionalization era.
(3300-2600 BC: Early Harappan).
2600-1900 BC: Intregation era. (mature Harappan)
1900-1300BC: Localisation era. (Late Harappan)
1300-300BC: Post Indus tradition.
Discovery and Excavation
Indus Valley was first described
in 1842 by Charles Masson in
his ’’Narrative of Various
Journeys in Balochistan,
Afghanistan, and the Punjab”,
where locals talked of an
ancient city.
In 1872–75 Alexander
Cunningham published the first
Harappan seal (with an
erroneous identification as
Brahmi letters).
Finally, an excavation
campaign was started under Sir
John Hubert Marshall in 1921–
22.
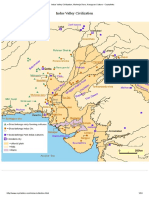
Geography of Indus Valley
The geography of the Indus Valley put the civilizations that arose
there in a highly similar situation to those in Egypt and Peru, with
rich agricultural lands being surrounded by highlands, desert,
and ocean.
the civilization extended east into the Ghaggar-Hakra
Rivervalley and the upper reaches Ganges-Yamuna Doab; it
extended west to the Makran coast of Balochistan,
The Indus Valley Civilization encompassed most of Pakistan,
extending from Balochistan to Sindh, and extending into modern
day Indian states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Punjab,
with an upward reach to Rupar on the upper Sutlej.
Recently, Indus sites have been discovered in Pakistan's
northwestern Frontier Province as well. Other IVC colonies can
be found in Afghanistan while smaller isolated colonies can be
found as far away as Turkmenistan and in Gujarat.
Geography of Indus Valley(cont.)
Cities
Mohenjo-Daro Harappa
To the north is a citadel or At the upper site of valley,
raised area.In Mohenjo-Daro,
the another city was situated
the citadel is built on an
architectural platform about named Harappa. This civilization is
45 feet above the plain. also called Harappa civilization.
Culture of Indus Valley Civilization
Religion
Some Indus valley seals
show swastikas, which are found
in other religions worldwide,
especially in Indian
religions such
as Hinduism, Buddhism, and
Jainism.
The earliest evidence for
elements of Hinduism are
alleged to have been present
before and during the early
Harappan period.
Shiva lingam have been found in
the Harappan remains.
Culture of Indus Valley
Civilization(cont.)
Writing System
Between 400 and as
many as 600 distinct Indus
symbols have been found
on seals, small tablets,
ceramic pots and more than
a dozen other materials,
including a "signboard" that
apparently once hung over
the gate of the inner citadel
of the Indus city of
Dholavira.
Culture of Indus Valley
Civilization(cont.)
Trade and transportation
The Indus civilization's economy
appears to have depended
significantly on trade, which was
facilitated by major advances in
transport technology.
The IVC may have been the first
civililzation to use wheeled
transport.
They have been used boat and
sea-going craft for transportation.
During the Early Harappan period,
similarities in pottery, seals,
figurines, ornaments, etc.
document intensive caravan trade
with Central Asia and the Iranian
plateau.
Culture of Indus Valley
Civilization(cont.)
Arts and Crafts
Various sculptures,
seals, pottery, gold jewelry,
and anatomically detailed
figurines in terracotta,
bronze, and steatite have
been found at excavation
sites.
A number of gold, terra-
cotta and stone figurines of
girls in dancing poses. These
terra-cotta figurines
included cows, bears,
monkeys, and dogs.
Culture of Indus Valley
Civilization(cont.)
Arts and Crafts
Many crafts "such as shell
working, ceramics, and
agate and glazed steatite
bead making" were used in
the making of necklaces,
bangles, and other
ornaments from all phases
of Harappan sites.
Some make-up and toiletry
items that were found in
Harappan contexts still have
similar counterparts in
modern India. Fragment of large deep vesel
Culture of Indus Valley
Civilization(cont.)
Subsistence
food production was largely indigenous to the Indus
Valley.
It is known that the people of Mehrgarh used
domesticated wheats and barley, and the major
cultivated cereal crop was naked six-row barley, a
crop derived from two-row barley.
Achievements
Carefully Planned Cities
The cities of the Indus
Valley Civilization were
well-organised and solidly
built out of brick and
stone.
Their drainage systems,
wells and water storage
systems were the most
sophisticated in the
ancient world.
Achievements(cont.)
Science & Technology
The people of the Indus
Civilization achieved great
accuracy in measuring length,
mass, and time.
They were among the first to
develop a system of uniform
weights and measures.
Harappans evolved some new
techniques in metallurgy and
produced copper, bronze, lead,
and tin.
The engineering skill of the
Harappans was remarkable,
especially in building docks.
Achievements(cont.)
Writing Skill Government
The people of the Indus Valley There was no single ruler but
Civilization also developed a several: Mohenjo-daro had a
writing system which was used separate ruler, Harappa
for several hundred year another, and so forth.
Harappa society
had no ruler,
everybody
enjoyed equal
status.
Effects on Human Civilization
Actually each and every achievement make an important
effects on sub-continental culture.
The Indus Valley Civilization may have been the first
civililzation to use wheeled transport. These advances
may have included bullock carts that are identical to
those seen throughout South Asian teritory today, as well
as boats.
Their well organized urbanization system make an effects
on next civilization.
Some of the crafts which were found in Harappa
civilization are still practised in the subcontinent today.
Decline of Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley civilization
was declined at late 1900
BC. There are various theory
for describe of destruction
of this civilization. Some are
given briefly:
The Aryan Invasion Theory
Many scholars gave a
theories that an invasion of
the Aryans into the
subcontinent was the cause
of this dispersal. But there is
currently no historical or
archaeological record which
shows that the Aryan people
ever invaded the region.
Decline of Indus Valley Civilization(cont.)
The Evidence Of Natural Disaster
The most common held theory used to explain the decline of
the Harrapan culture is that climatic changes lead to a long term
drought. This environmental disaster, coupled with repeated floods
that devastated the arable land.
The Possibility Of An Ancient Tsunami
Some geophysicists have begun to theorize that such a disaster
could have been responsible for the end of Harrapan civilization.
This theory is based upon the premise that a massive wave could
have reached inland, traveling up the Indus and Saraswati Rivers
simultaneously.
The Saraswati River Runs Dry
The geological record does show that the Saraswati River, one
of the main arteries of trade for the Harrapans, dried up completely
sometime during the early 20th century B.C.E.
You might also like
- INDUS VALLEY PPT by VaibhavDocument20 pagesINDUS VALLEY PPT by Vaibhavsandhaya1830No ratings yet
- 2.1.1. Indus Valley CivilizationDocument17 pages2.1.1. Indus Valley Civilizationcontrax8No ratings yet
- Ancient India for Kids - Early Civilization and History | Ancient History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandAncient India for Kids - Early Civilization and History | Ancient History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilisationDocument3 pagesIndus Valley CivilisationAmarinder BalNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilisationDocument4 pagesIndus Valley CivilisationRohan PandhareNo ratings yet
- Harappan Civilization Brief NoteDocument9 pagesHarappan Civilization Brief Notearshitagupta2004No ratings yet
- Ancient History of India: The Indus Valley CivilizationDocument18 pagesAncient History of India: The Indus Valley CivilizationAROKYASWAMY LNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ANCIENT HISTORY OF INDIA 2Document3 pagesChapter 1 ANCIENT HISTORY OF INDIA 2Hum h banaras keNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ANCIENT HISTORY OF INDIA 2 MergedDocument22 pagesChapter 1 ANCIENT HISTORY OF INDIA 2 MergedriyaNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationsDocument2 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationsShamaimNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization PDF Study Material by ENTRANCEGEEKDocument5 pagesIndus Valley Civilization PDF Study Material by ENTRANCEGEEKDeepa AnoopNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument5 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationsaqib nawazNo ratings yet
- A Dibur Rahman Human TiesDocument12 pagesA Dibur Rahman Human Tiesindia cybercafeNo ratings yet
- Indus River Valley Civilization DiscoveryDocument4 pagesIndus River Valley Civilization DiscoveryArslan AsifNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument5 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationSaimaNo ratings yet
- Harappan Civilization or Indus Valley CivilizationDocument6 pagesHarappan Civilization or Indus Valley Civilizationkeshavnaikk789No ratings yet
- PrOject On Indus CivilisatiOnDocument17 pagesPrOject On Indus CivilisatiOnJoyakim DavisNo ratings yet
- Ali Indus ValleyDocument39 pagesAli Indus ValleyAli Azhar RajputNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization FactsDocument12 pagesIndus Valley Civilization FactsSøûrâv Kümär RøyNo ratings yet
- A Short History of India: From the Earliest Civilisations and Myriad Kingdoms, to Today's Economic PowerhouseFrom EverandA Short History of India: From the Earliest Civilisations and Myriad Kingdoms, to Today's Economic PowerhouseRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Ancient India Brought Ideas That Spread WorldwideDocument4 pagesAncient India Brought Ideas That Spread WorldwideOyon Nur newazNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Indus River Valley Civilization (1)Document4 pages1 - The Indus River Valley Civilization (1)Hira AzharNo ratings yet
- The Indus Valley Civilization Was A Bronze Age CivilizationDocument3 pagesThe Indus Valley Civilization Was A Bronze Age CivilizationChinmoy TalukdarNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument4 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationsanam azizNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument24 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationDan Matinca100% (1)
- Culture of Indus ValleyDocument20 pagesCulture of Indus Valleykunalkataria100% (1)
- The Indus Valley CivilisationDocument3 pagesThe Indus Valley CivilisationTwinkle BarotNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument16 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationcarlosnestor100% (1)
- Indus River Valley CivilizationsDocument4 pagesIndus River Valley CivilizationsM4 TechsNo ratings yet
- Explore Early South Asian Cultures of the Indus Valley CivilizationDocument56 pagesExplore Early South Asian Cultures of the Indus Valley Civilizationzain malikNo ratings yet
- Cradle of Indian CultureDocument8 pagesCradle of Indian CultureicereiNo ratings yet
- History of South Asia 1Document11 pagesHistory of South Asia 1NOOB KINGNo ratings yet
- Ix-History-Lesson-1 The Harappan CivilisationDocument25 pagesIx-History-Lesson-1 The Harappan CivilisationsrayicsephysicsNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indus Valley CivilizationDocument2 pagesAncient Indus Valley CivilizationRUTHERSON SNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization Upsc Notes 79Document7 pagesIndus Valley Civilization Upsc Notes 79sarennibaran365No ratings yet
- Ancient History 05 - Daily Notes - (Sankalp (UPSC 2024) )Document12 pagesAncient History 05 - Daily Notes - (Sankalp (UPSC 2024) )nigamkumar2tbNo ratings yet
- Indus Civilization History NotesDocument9 pagesIndus Civilization History Notesmohammad azimNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument51 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationsyedmirsyedNo ratings yet
- "Assignment'': Submitted To: Ma'Am Ambreen Submitted By: Marwa Cno: 01 Class: Bs Computer Science Semester 2Document6 pages"Assignment'': Submitted To: Ma'Am Ambreen Submitted By: Marwa Cno: 01 Class: Bs Computer Science Semester 2Marwa HussainNo ratings yet
- Harappan CivilizationDocument66 pagesHarappan CivilizationJnanam33% (3)
- Gujarat Administrative Services Prelims Full Syllabus History Indus Valley CivilizationDocument9 pagesGujarat Administrative Services Prelims Full Syllabus History Indus Valley CivilizationAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument11 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationJarar AleeNo ratings yet
- Histroy of Indus Valley Civilizaton 55Document25 pagesHistroy of Indus Valley Civilizaton 55Wasil AliNo ratings yet
- HarappanDocument6 pagesHarappanJHP CreationsNo ratings yet
- Ancient HistoryDocument164 pagesAncient Historyrahuldewangan651No ratings yet
- INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION: ANCIENT SOCIETY ALONG INDUS RIVERDocument29 pagesINDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION: ANCIENT SOCIETY ALONG INDUS RIVERjahangirNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument6 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationkami9709100% (1)
- Harappan CivilisationDocument23 pagesHarappan CivilisationMadhuleena deb roy100% (1)
- Indus Valley CivilisationDocument51 pagesIndus Valley Civilisationplast_adesh100% (1)
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument9 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationMonideep Banerjee100% (1)
- Assignment No.1Document35 pagesAssignment No.1Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- The Indus Valley Civilisation (Harappan Civilisation) : Dr. Hetalben Dhanabhai SindhavDocument7 pagesThe Indus Valley Civilisation (Harappan Civilisation) : Dr. Hetalben Dhanabhai SindhavN SHNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument13 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationDevika SinghNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indus Valley CivilizationDocument16 pagesAncient Indus Valley CivilizationlavanyaNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument11 pagesIndus Valley Civilizationerfan441790No ratings yet
- The Harappan CivilizationDocument6 pagesThe Harappan Civilizationzxcv2010100% (1)
- History NotesDocument47 pagesHistory NotesYadvendra Singh RanaNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization Short Note PDFDocument13 pagesIndus Valley Civilization Short Note PDFGautam krNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization - The Rise and Fall of the Harappan CultureDocument115 pagesIndus Valley Civilization - The Rise and Fall of the Harappan Cultureshubham kumar100% (1)
- Ws Class 6Document2 pagesWs Class 6Aravind EcrNo ratings yet
- GRADE -8 HISTORY WORK SHEET 1Document2 pagesGRADE -8 HISTORY WORK SHEET 1Aravind EcrNo ratings yet
- VI Political ScienceDocument18 pagesVI Political ScienceAravind EcrNo ratings yet
- SivawordDocument46 pagesSivawordAravind EcrNo ratings yet
- Harappan Civilization: (Also Known As Indus Civilization)Document24 pagesHarappan Civilization: (Also Known As Indus Civilization)MANIKANDANNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley Civilization: Presented byDocument21 pagesIndus Valley Civilization: Presented byAravind EcrNo ratings yet
- Mobility Consulting Engineer - Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesMobility Consulting Engineer - Job DescriptionEdwin BrandNo ratings yet
- Programme VDZ CongressDocument2 pagesProgramme VDZ CongresssaeedhoseiniNo ratings yet
- Lost (Andfound?) in Translation:Feminisms InhemisphericdialogueDocument18 pagesLost (Andfound?) in Translation:Feminisms InhemisphericdialogueLucas MacielNo ratings yet
- Economics Class XDocument34 pagesEconomics Class Xbhupenderrana100% (8)
- John D. Woodward JR., Nicholas M. Orlans, Peter T. Higgins-Biometrics-McGraw-Hill - Osborne (2003) PDFDocument463 pagesJohn D. Woodward JR., Nicholas M. Orlans, Peter T. Higgins-Biometrics-McGraw-Hill - Osborne (2003) PDFZoran Felendeš0% (1)
- An Interview with Novelist Anita BrooknerDocument12 pagesAn Interview with Novelist Anita BrooknerlupearriegueNo ratings yet
- Application For Admission To Master of Computer Applications (MCA) COURSES, KERALA: 2010-2011Document5 pagesApplication For Admission To Master of Computer Applications (MCA) COURSES, KERALA: 2010-2011anishbaiNo ratings yet
- Indian Initiatives in Traceability Approaching Towards Single Window CertificationDocument55 pagesIndian Initiatives in Traceability Approaching Towards Single Window CertificationAman KhannaNo ratings yet
- Finalplansw PDFDocument146 pagesFinalplansw PDFOffice of PlanningNo ratings yet
- Notification SouthzoneDocument3 pagesNotification Southzonevarsha rathoreNo ratings yet
- In The Court of Hon'Ble District Judge Pune, at Pune CAVEAT APPLICATION NO. - OF 2012Document2 pagesIn The Court of Hon'Ble District Judge Pune, at Pune CAVEAT APPLICATION NO. - OF 2012AniketNo ratings yet
- Tom Barry - International Skateboarder!: Lesson 2 HomeworkDocument1 pageTom Barry - International Skateboarder!: Lesson 2 HomeworkMr TrungNo ratings yet
- Smoke Values and Cut-Off Speeds Per Engine Type: en-GBDocument7 pagesSmoke Values and Cut-Off Speeds Per Engine Type: en-GBruanNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Highlights for Salon Beauty VenusDocument20 pagesBusiness Plan Highlights for Salon Beauty VenusEzike Tobe ChriszNo ratings yet
- 2 2005Document13 pages2 2005VinothKumarDhananjayan100% (1)
- GST Reg 06-1Document3 pagesGST Reg 06-1Sylvian NicholasNo ratings yet
- Complaint Before A MagistrateDocument12 pagesComplaint Before A MagistrateZuhair SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ipsas 35 SummaryDocument6 pagesIpsas 35 SummaryWilson Mugenyi KasendwaNo ratings yet
- Palladio's Architectural Works and InfluenceDocument1 pagePalladio's Architectural Works and InfluencerebeccafroyNo ratings yet
- Holy Child Multi-Purpose Cooperative: Gender and Development CommitteeDocument6 pagesHoly Child Multi-Purpose Cooperative: Gender and Development CommitteeRam KuizonNo ratings yet
- PT TRP Mod 6Document26 pagesPT TRP Mod 6Вікторія Давидюк0% (1)
- Beasts of BurdenDocument2 pagesBeasts of BurdenGks06No ratings yet
- 5 Characteristics-Defined ProjectDocument1 page5 Characteristics-Defined ProjectHarpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- BMC Public HealthDocument21 pagesBMC Public HealthDaniel JhonsonNo ratings yet
- Acheiving Audience Involvement PGDocument2 pagesAcheiving Audience Involvement PGapi-550123704No ratings yet
- Haj Committee of India: Tat Tory o Yoft e Ry I yDocument11 pagesHaj Committee of India: Tat Tory o Yoft e Ry I ysayyedarif51No ratings yet
- People v. Orita DigestDocument3 pagesPeople v. Orita Digestkathrynmaydeveza100% (3)
- Chapter 11Document48 pagesChapter 11Rasel SarkerNo ratings yet
- Rate Analysis m25Document2 pagesRate Analysis m25Biswajit Sinha100% (4)
- Legal Studies Book v8 XIDocument184 pagesLegal Studies Book v8 XIMuskaan GuptaNo ratings yet