Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy of Large Intestine - 041020094918
Uploaded by
flickers xxx0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesThe vermiform appendix is a narrow tube located in the right iliac fossa attached to the back of the cecum. It varies in length from 2-20 cm on average. The appendix has a complete peritoneal covering and receives its blood supply from appendicular vessels that branch off the ileocolic artery. The submucosa contains rich lymphoid tissue. Acute appendicitis is the most common cause of acute abdomen and can be difficult to diagnose due to the variable positioning of the appendix.
Original Description:
Original Title
Anatomy of large intestine_041020094918
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe vermiform appendix is a narrow tube located in the right iliac fossa attached to the back of the cecum. It varies in length from 2-20 cm on average. The appendix has a complete peritoneal covering and receives its blood supply from appendicular vessels that branch off the ileocolic artery. The submucosa contains rich lymphoid tissue. Acute appendicitis is the most common cause of acute abdomen and can be difficult to diagnose due to the variable positioning of the appendix.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesAnatomy of Large Intestine - 041020094918
Uploaded by
flickers xxxThe vermiform appendix is a narrow tube located in the right iliac fossa attached to the back of the cecum. It varies in length from 2-20 cm on average. The appendix has a complete peritoneal covering and receives its blood supply from appendicular vessels that branch off the ileocolic artery. The submucosa contains rich lymphoid tissue. Acute appendicitis is the most common cause of acute abdomen and can be difficult to diagnose due to the variable positioning of the appendix.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
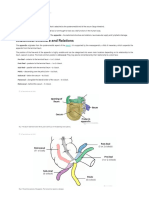
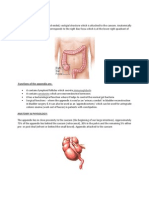
VERMIFORM APPENDIX
* Site: Right iliac fossa , attached to the postero-medial aspect of caecum , 1 cm
below the ileocaecal junction.
* Size: 2-20 cm (average 10 cm). It is the narrowest part of gut.
* Shape: A uniform narrow tube which having an attached end to the caecum
(base) and a free end (tip).
* Surface anatomy of base : McBurny's point ( junction between the lat. 1/3 &
med. 2/3 of a line extending between A.S.I.S. & the umbilicus).
* Peritoneal covering: Completely covered, having a triangular meso-appendix
with its base attached to the back of terminal ileum, contains appendix in its free
right border & appendicular vessels in its free left border.
* Blood supply: Appendicular vessels (from ilio-colic which is from superior
mesenteric vessels) .
* Position: Variable.
1. Retrocaecal (75%) behind the caecum and may be related to right proas
major, quadratus lumborum, lower pole of kidney & ureter.
2. Pelvic (20%): related to uterine tube, ovary, rectum & obturator internus
muscle.
3. Pre-ileal: in the front of terminal ileum.
4. Post-ileal: behind teminal ileum & related to ileo-colic vessels.
5. Paracaecal: On the right side of caecum .
6. Subcaecal : below the caecum .
7. Subhepatic (a congenital anomaly due to failure of descent of the caecum).
8. Pregnancy displaces the caecum & appendix towards the right hypochondrium .
9 . Subserous appendix : Meso-appendix may be abscent and the appendix lies beneath the
serosa of caecum .
* The submucosa of the appendix is rich in lymphoid tissue ( tonsil of abdomen )
which progressively atrophies with age .
* Nerve supply: TI0 supply the peritoneal covering of appendix (as well as the
umbilicus).
Applied Anatomy:
1) Acute appendicitis is the commonest cause for acute abdomen.
2) Narrow lumen and rich lymphoid follicles in the appendix leading to high
incidence of appendicitis.
3) The clinical picture of appendicitis varies according to the position of the
appendix. Therefore, diagnosis of appendicitis may be difficult.
4) Pain of appendicitis is felt in the right iliac fossa and may be referred to
the umbilicus (T10 nerve supply the appendix and umbilicus).
5) Appendicular pain is early visceral ( generalized abdominal pain
specially around umbilicus ) and later on somatic ( localized in right iliac
fossa ).
6) Acute appendicitis may result in thrombosis of the appendicular artery
(only arterial supply to appendix) causing gangrene and perforation of the
appendix, leading to fatal peritonitis.
7) Appendicular vessels are distally closely applied to the wall , therefore in
acute appendicitis thrombosis and gangrene usually affect the distal part of
the appendix .
8) Post-ileal appendix is closely related to ileocolic vein and appendicitis may
result in its thrombosis leading to portal vein thrombosis and portal pyemia
leading to jaundice and later on portal hypertension.
9) At operation the appendix is identified by the 3 taeniae coli which meet at
its base.
You might also like
- Autoimmune Matrix DR Peter Osborne EbookDocument68 pagesAutoimmune Matrix DR Peter Osborne EbookSoftMan100% (1)
- Columbine High School DeceasedDocument4 pagesColumbine High School DeceasedpaccolleNo ratings yet
- UW Notes - 9 - Gastero-Intestinal ArrangedDocument61 pagesUW Notes - 9 - Gastero-Intestinal ArrangedMohammed SadoonNo ratings yet
- Irfan Mir Anatomy Usmle Step 1Document8 pagesIrfan Mir Anatomy Usmle Step 1sammieahemd100% (1)
- Abdomen - FRCEM SuccessDocument275 pagesAbdomen - FRCEM SuccessAbin ThomasNo ratings yet
- ABG - Acid Base BalanceDocument4 pagesABG - Acid Base BalanceTingCheungNo ratings yet
- Ana Print 3Document12 pagesAna Print 3Ade AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Visceral RenalDocument120 pagesVisceral RenalShivik PatelNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum and Peritoneal CavityDocument26 pagesPeritoneum and Peritoneal CavitytuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Clinical Embriology and Anatomy of Gi Tract Part1Document44 pagesClinical Embriology and Anatomy of Gi Tract Part1trianaamalia100% (1)
- Rectum & Anal CanalDocument14 pagesRectum & Anal CanalLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- IRMA - Inkontinensia Urine Dan GinekologiDocument31 pagesIRMA - Inkontinensia Urine Dan GinekologisitirahmaNo ratings yet
- Lipoma: General Dr. El-MataryDocument7 pagesLipoma: General Dr. El-Mataryflickers xxxNo ratings yet
- Hemicolectomy 1Document40 pagesHemicolectomy 1Preethi GudipalliNo ratings yet
- Health DLPDocument2 pagesHealth DLPGavinKarl Mianabanatao100% (3)
- SURGERY - 1.5 Colon, Rectum, and Anus (Lecture)Document8 pagesSURGERY - 1.5 Colon, Rectum, and Anus (Lecture)Bianca Jane Maaliw100% (1)
- Birads PosterDocument1 pageBirads PosterGopalarathnam BalachandranNo ratings yet
- Anatomia de Vesicula BiliarDocument5 pagesAnatomia de Vesicula BiliarHumberto CamposNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic ENT sLE MCQDocument10 pagesOphthalmic ENT sLE MCQAsif Newaz100% (4)
- Large Intestine Extends: The Intestine Is Divided Into TWO Main Parts: From TheDocument16 pagesLarge Intestine Extends: The Intestine Is Divided Into TWO Main Parts: From ThePriya GKNo ratings yet
- Caecum and Vermiform Appendix 1Document42 pagesCaecum and Vermiform Appendix 1Sohail SinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Caecum, Appendix and Colon: Basic ScienceDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Caecum, Appendix and Colon: Basic ScienceMirza RisqaNo ratings yet
- Chapter I-V-1-Anatomy-Dr-Mark-MakaryDocument17 pagesChapter I-V-1-Anatomy-Dr-Mark-MakaryMark MakaryNo ratings yet
- IntestinesDocument56 pagesIntestinesShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- The Appendix - Retrocecal - Arterial Supply - Appendicitis - TeachMeAnatomy PDFDocument2 pagesThe Appendix - Retrocecal - Arterial Supply - Appendicitis - TeachMeAnatomy PDFUsama KhawajaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Gross Prelims 2ndsemDocument13 pages2020 Gross Prelims 2ndsemChristian TayagNo ratings yet
- 062012SCNADocument11 pages062012SCNAMc KobaNo ratings yet
- Abiola Seminar in SpleenDocument23 pagesAbiola Seminar in SpleenBamgbose OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- The Vermiform Appendix: AnatomyDocument10 pagesThe Vermiform Appendix: AnatomyBereket temesgenNo ratings yet
- Referat PeritonitisDocument18 pagesReferat PeritonitisWilliam Grandinata Soeseno100% (2)
- Liver:: Anatomy The Abdomen Liver and Gall BladderDocument5 pagesLiver:: Anatomy The Abdomen Liver and Gall BladderWaeel AbdullatifNo ratings yet
- Jejunal and Ileal AtresiasDocument37 pagesJejunal and Ileal AtresiasABDUL RAHIM UMAR FAROUKNo ratings yet
- MCQ GitDocument19 pagesMCQ Gitvideoediting77No ratings yet
- Appendicitis Method EngDocument10 pagesAppendicitis Method EngMohammad AyoubNo ratings yet
- 18 IntestinesDocument28 pages18 Intestinesafzal sulemaniNo ratings yet
- Appendix MooreDocument2 pagesAppendix Moorebrett andrea aliaNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine AnatomyDocument4 pagesSmall Intestine AnatomyMaria Natalie IrwandaNo ratings yet
- Abdomen CAP Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesAbdomen CAP Questions and AnswersRathnaNo ratings yet
- Referat AppendicitisDocument21 pagesReferat Appendicitisyaspie100% (2)
- The Jejunoileum: Anatomy The Abdomen Small and Large IntestineDocument7 pagesThe Jejunoileum: Anatomy The Abdomen Small and Large IntestineWaeel AbdullatifNo ratings yet
- Anatomia Laparoscopica A Ficatului - Jurnalul de ChirurgieDocument11 pagesAnatomia Laparoscopica A Ficatului - Jurnalul de ChirurgieDan PintilescuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of LiverDocument11 pagesAnatomy of LiverSyed NusrathNo ratings yet
- Background: Pediatric AppendicitisDocument15 pagesBackground: Pediatric AppendicitisnikkitaihsanNo ratings yet
- Problem 2.03Document12 pagesProblem 2.03DeirdreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document14 pagesLecture 4X RamboNo ratings yet
- Journal AslinyaDocument11 pagesJournal AslinyainNo ratings yet
- PeritoneumDocument53 pagesPeritoneumtuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- LI, Pancreas, Liver, GallbladderDocument106 pagesLI, Pancreas, Liver, GallbladderSuhayb CumarNo ratings yet
- Large Intestine PIMSR-Dr - Gosai 2022Document40 pagesLarge Intestine PIMSR-Dr - Gosai 2022Dr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis: Michael Alan Cole Robert David HuangDocument10 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Michael Alan Cole Robert David HuangandreaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Abdominal Wall ThorekDocument26 pagesAnatomy Abdominal Wall ThorekAlna Shelah IbañezNo ratings yet
- ABDOMEN Understanding ConceptsDocument5 pagesABDOMEN Understanding ConceptsAdnan MusaNo ratings yet
- Anat 221-Large IntestineDocument21 pagesAnat 221-Large IntestineWisdom IkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Checklist 2Document7 pagesChecklist 2FranklinSappNo ratings yet
- Abdominal HerniasDocument38 pagesAbdominal HerniasHafizah HoshniNo ratings yet
- Apendicitis Aguda1Document4 pagesApendicitis Aguda1Montserrat CandiaNo ratings yet
- My Rectum Anal CanalDocument21 pagesMy Rectum Anal CanalPriya GKNo ratings yet
- Large IntestineDocument29 pagesLarge IntestineHamza SultanNo ratings yet
- Colon Benign Conditions - Surgery NotesDocument85 pagesColon Benign Conditions - Surgery NotesNagulan ChanemougameNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument2 pagesAppendixKatey Silverio UmaliNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Large Intestine PDFDocument7 pagesThe Anatomy, Histology and Development of The Large Intestine PDFredderdatNo ratings yet
- APOSTLE JOHN'S ABDOMEN NOTE - WPS OfficeDocument19 pagesAPOSTLE JOHN'S ABDOMEN NOTE - WPS OfficeOROKE JOHN EJENo ratings yet
- Large IntestineDocument50 pagesLarge Intestinemex Gbrekorkos100% (1)
- Anatomy of ColonDocument19 pagesAnatomy of ColonIshNo ratings yet
- A Manual of the Operations of Surgery: For the Use of Senior Students, House Surgeons, and Junior PractitionersFrom EverandA Manual of the Operations of Surgery: For the Use of Senior Students, House Surgeons, and Junior PractitionersNo ratings yet
- A New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasFrom EverandA New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasNo ratings yet
- Scalp Injuries: Neurosurgery Dr. El - MataryDocument5 pagesScalp Injuries: Neurosurgery Dr. El - Mataryflickers xxxNo ratings yet
- Revision Tables - 270820162807Document105 pagesRevision Tables - 270820162807flickers xxxNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Materials Breaking New Grounds in Dentistry - 110621210536Document5 pagesIntelligent Materials Breaking New Grounds in Dentistry - 110621210536flickers xxxNo ratings yet
- DENTISTERY 3rd - 020218173609Document17 pagesDENTISTERY 3rd - 020218173609flickers xxxNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Headache in AdultsDocument21 pagesEvaluation of Headache in AdultsMaicon RamosNo ratings yet
- ContusionsDocument35 pagesContusionsSARVESH MAWALE100% (1)
- Red Beetroot: Health Benefits, Production Techniques and Quality Maintaining For Food IndustryDocument15 pagesRed Beetroot: Health Benefits, Production Techniques and Quality Maintaining For Food Industrygodson ifeanyiNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument56 pagesAnswer KeyRivy Valen PabesakNo ratings yet
- Kti Siti Rahmi FebrianiDocument43 pagesKti Siti Rahmi FebrianiPipit DelfiNo ratings yet
- HLTC 24Document5 pagesHLTC 24elmaNo ratings yet
- Flashcard Questions: Compilation of Chemical Connections From Lemay, Brown, & BettelheimDocument42 pagesFlashcard Questions: Compilation of Chemical Connections From Lemay, Brown, & Bettelheimtina pixieNo ratings yet
- D S T E I B D B V: Esirable Pecifications For Otal Rror, Mprecision, and Ias, Erived From Iologic AriationDocument14 pagesD S T E I B D B V: Esirable Pecifications For Otal Rror, Mprecision, and Ias, Erived From Iologic Ariationlaboratorium rsud jatipadangNo ratings yet
- Banana - Recommendations For Maintaining Postharvest Quality - Postharvest Technology Center - UC Davis PDFDocument3 pagesBanana - Recommendations For Maintaining Postharvest Quality - Postharvest Technology Center - UC Davis PDFFernando SanchezNo ratings yet
- МартDocument55 pagesМартLuisAngelPonceTorresNo ratings yet
- Ashtasthana ParikshaDocument17 pagesAshtasthana Parikshanarayana asso100% (1)
- GROUP 3 - Biocon PresentationDocument7 pagesGROUP 3 - Biocon PresentationAditya VatsNo ratings yet
- Sudan IMCI 2.pptx ccDocument55 pagesSudan IMCI 2.pptx ccabdiqadir ali adanNo ratings yet
- Influence of Preprocessing Methods and Fermentation of Adzu 2013 Journal ofDocument8 pagesInfluence of Preprocessing Methods and Fermentation of Adzu 2013 Journal ofEmerald Falah BrayogaNo ratings yet
- Celgene January 2019 Investor-PresentationDocument26 pagesCelgene January 2019 Investor-PresentationmedtechyNo ratings yet
- Nutrigenomics and Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument19 pagesNutrigenomics and Cardiovascular DiseaseAssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- Clinical Evaluation of Corneal Ulcer Among Patients Attending Teaching Hospital PDFDocument4 pagesClinical Evaluation of Corneal Ulcer Among Patients Attending Teaching Hospital PDFYosiita KartinaaNo ratings yet
- FijiTimes Aug 12 2016 PDFDocument20 pagesFijiTimes Aug 12 2016 PDFfijitimescanadaNo ratings yet
- Daftar ICD Bedah Mulut Orif Diagnosa ICDDocument3 pagesDaftar ICD Bedah Mulut Orif Diagnosa ICDTitoNo ratings yet
- Martin Lobatos Grand Jury IndictmentDocument14 pagesMartin Lobatos Grand Jury IndictmentNickNo ratings yet
- AmitriptylineDocument13 pagesAmitriptylineاحمد محسنNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual - Field Diagnosis in AgricultureDocument127 pagesPractical Manual - Field Diagnosis in AgriculturePrakash Kumar KumarNo ratings yet