Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 12 Pages From 0625 - s16 - QP - 43
Uploaded by
Nicole NicoleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 12 Pages From 0625 - s16 - QP - 43
Uploaded by
Nicole NicoleCopyright:
Available Formats
4
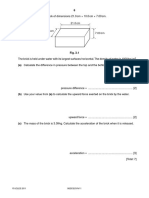
2 Fig. 2.1 shows two cars, A and B, before they collide.
18 m / s
stationary
car B car A
Fig. 2.1
Car B, of mass 1200 kg, is stationary. Car A, of mass 2000 kg, is travelling towards car B at 18 m / s.
(a) Calculate the momentum of car A.
momentum = ................................................................. [2]
(b) The cars collide and car B experiences an impulse. Car A continues to move in the same
direction, with a momentum of 21 000 kg m / s.
(i) Calculate the momentum of car B immediately after the collision.
momentum = ................................................................. [1]
(ii) Determine the average impulse experienced by car B during the collision.
impulse = ................................................................. [1]
© UCLES 2016 06_0625_43_2016_1.8
5
(iii) The cars are in contact for 0.20 s.
Calculate the average resultant force experienced by car B during the collision.
force = ................................................................. [2]
(c) A modern car is designed so that, during a collision, the front section of the car is crushed and
the time of contact increases.
Explain the benefit of increasing the time of contact for the people in the car.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................................... [2]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2016 06_0625_43_2016_1.8 [Turn over
You might also like
- Hammer HeadDocument23 pagesHammer Headhuzaifa mobusherNo ratings yet
- Mometum New Worksheet 2023Document5 pagesMometum New Worksheet 2023Chelsea OkoroigweNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 For MomentumDocument1 pageWorksheet 2 For Momentumsaarahatif88No ratings yet
- 1 2-QPDocument7 pages1 2-QPPC AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For A Vehicle Accelerating From RestDocument3 pages2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For A Vehicle Accelerating From RestYakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument17 pagesMomentumSamar GoelNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - s16 - QP - 41-02Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - s16 - QP - 41-02lelon ongNo ratings yet
- Q2,3Document3 pagesQ2,3PC AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- 1 1-QPDocument8 pages1 1-QPQasim BilalNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument3 pagesMomentumGoogle Drive shahNo ratings yet
- Vectors UpdatedDocument16 pagesVectors UpdatedppsppcyhbsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: 0625/42 PhysicsDocument24 pagesCambridge International Examinations: 0625/42 Physics...No ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity and Acceleration QnsDocument29 pagesSpeed, Velocity and Acceleration Qnsimaanzuberi123No ratings yet
- 30th May - Phy TestDocument28 pages30th May - Phy TestMuhammad Annas AsimNo ratings yet
- 0625 Igcse Physics 42Document233 pages0625 Igcse Physics 42Vinod RNo ratings yet
- Last Minute HWDocument2 pagesLast Minute HWMfanafuthiNo ratings yet
- Motion With ForcesDocument6 pagesMotion With ForcesRuhaifa AsaliNo ratings yet
- Forces & Braking 1 QPDocument23 pagesForces & Braking 1 QPLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Momentum 1 QPDocument18 pagesMomentum 1 QPtechnical videosNo ratings yet
- 03 0625 42 7RP AfpDocument16 pages03 0625 42 7RP AfpAnonymous oYtCFVNV0% (1)
- Mixed Oned QuestionsDocument4 pagesMixed Oned QuestionsHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Motion Worksheet2Document15 pagesMotion Worksheet2Faizan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Test 2 PhyDocument5 pagesTest 2 PhyHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - s15 - QP - 33-01Document1 pagePages From 0625 - s15 - QP - 33-01lelon81No ratings yet
- 2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A CarDocument5 pages2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A CarYakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- Momentum QPDocument6 pagesMomentum QPXandws -IOS tips and trick and gamingNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument243 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationAnu DamdintsogtNo ratings yet
- 18 9 Car A and Car B Take Part in A Race Around A Circular TrackDocument1 page18 9 Car A and Car B Take Part in A Race Around A Circular TrackYoussef YasserNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Dynamics)Document6 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (Dynamics)Syed Jawwad JD JamaliNo ratings yet
- 0625 m16 QP 42 RemovedDocument3 pages0625 m16 QP 42 Removeddjwwwaaa123No ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power PDFDocument11 pagesEnergy, Work & Power PDFyolanda gaoliNo ratings yet
- Y11 Revision QuestionsDocument13 pagesY11 Revision QuestionsKwang yuan HiiNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis International School - Pune: NAME: - CLASS: - GROUP: - DATEDocument4 pagesSymbiosis International School - Pune: NAME: - CLASS: - GROUP: - DATEAbhigyan SinhaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument11 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationKabir MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: 0625/41 PhysicsDocument20 pagesCambridge International Examinations: 0625/41 PhysicsAlexander JayadassNo ratings yet
- The City School: University Road Campus Physics Worksheet, Topic: MomentmDocument3 pagesThe City School: University Road Campus Physics Worksheet, Topic: MomentmZeeshan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Motion Review ExamDocument32 pagesMotion Review ExamNadia SasmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Forces and Motion Exam Pack and MarkschemeDocument86 pagesChapter 10 - Forces and Motion Exam Pack and MarkschemeCraftyZaidNo ratings yet
- 0625 s18 QP 41Document16 pages0625 s18 QP 41iSean1337No ratings yet
- 0625/s 19/qp/42Document16 pages0625/s 19/qp/42n.No ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-04Document2 pagesPages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 32-04lelon ongNo ratings yet
- IAS Physics SB1 Assessment 1ADocument5 pagesIAS Physics SB1 Assessment 1ALiang LuNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument5 pagesCircular MotionsurabhiNo ratings yet
- Motion 2 QPDocument14 pagesMotion 2 QPUddin AimanNo ratings yet
- GertDocument20 pagesGertSuvdaa SanjaanyamNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - s15 - QP - 33-02Document1 pagePages From 0625 - s15 - QP - 33-02lelon81No ratings yet
- 1.5 Momentum Set 1 QP MsDocument9 pages1.5 Momentum Set 1 QP Msrakeshreddy12poliNo ratings yet
- Phy Motion 2 Theory QPDocument15 pagesPhy Motion 2 Theory QPAyaan KachwalaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42MariNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDimuthu ShiranNo ratings yet
- 5 - Questions On Motion - 2Document7 pages5 - Questions On Motion - 2John ChiltonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledBobby AzadNo ratings yet
- Assessment April 18Document7 pagesAssessment April 18wajeehmohsin96No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42ProBro Rock 2No ratings yet
- Form 3 21. Linear Motion QDocument23 pagesForm 3 21. Linear Motion Qjohnn1.jrugunaNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Linear Motion: (Question B4 Continued)Document2 pagesPart 2 Linear Motion: (Question B4 Continued)Ahmad OmarNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument29 pagesMomentumemaantejani10No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 P2 IntensiveDocument66 pagesChapter 3 P2 IntensiveyuskazaitieNo ratings yet
- High Speed Off-Road Vehicles: Suspensions, Tracks, Wheels and DynamicsFrom EverandHigh Speed Off-Road Vehicles: Suspensions, Tracks, Wheels and DynamicsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Work Power Efficiency AnswerDocument4 pagesTutorial Work Power Efficiency AnswerNicole Nicole100% (1)
- Pages From 0625 - s17 - QP - 42Document1 pagePages From 0625 - s17 - QP - 42Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 Pages From 0625 - w13 - QP - 33Document1 pageUnit 14 Pages From 0625 - w13 - QP - 33Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w11 - QP - 32Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w11 - QP - 32Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w08 - QP - 03Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w08 - QP - 03Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 w20 QP 42Document1 pagePages From 0625 w20 QP 42Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Physics 0625 - s09 - QP - 3Document1 pagePhysics 0625 - s09 - QP - 3Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Pendulum 0625 - w09 - QP - 32Document1 pagePendulum 0625 - w09 - QP - 32Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Practical Pendulum 0625 - w15 - QP - 61Document2 pagesPractical Pendulum 0625 - w15 - QP - 61Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Micrometer 0625 - w09 - QP - 31Document1 pageMicrometer 0625 - w09 - QP - 31Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Measurement 0625 - s17 - QP - 33Document2 pagesMeasurement 0625 - s17 - QP - 33Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Pemdulum 0625 - w15 - QP - 51Document3 pagesPemdulum 0625 - w15 - QP - 51Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Measurement 0625 - s12 - QP - 31Document1 pageMeasurement 0625 - s12 - QP - 31Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion 0625 - w01 - QP - 3-2Document2 pagesCircular Motion 0625 - w01 - QP - 3-2Nicole NicoleNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Force From 0625 - w09 - QP - 32Document1 pageCentripetal Force From 0625 - w09 - QP - 32Nicole Nicole100% (1)
- 3-01 Sample Bid Recommendation Letter - 2016 VerDocument1 page3-01 Sample Bid Recommendation Letter - 2016 VerAnonymous 7FRAZ9hGNo ratings yet
- MPOB Assignment 2 - Group PresentationsDocument4 pagesMPOB Assignment 2 - Group PresentationsSonalika BhambiNo ratings yet
- Fred Hymans and The Theory of Rope Traction, Part Two: HistoryDocument15 pagesFred Hymans and The Theory of Rope Traction, Part Two: Historyاحمد المقرميNo ratings yet
- Design and Fluid Structural Interface Analysis of Marine PropellerDocument67 pagesDesign and Fluid Structural Interface Analysis of Marine PropellerPavaniNo ratings yet
- The Strange Life of Nikola TeslaDocument8 pagesThe Strange Life of Nikola TeslaMohammad MetlejNo ratings yet
- Human Eye WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Eye Worksheetcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- 1969 Book InternationalCompendiumOfNumerDocument316 pages1969 Book InternationalCompendiumOfNumerRemigiusz DąbrowskiNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument12 pagesProject ReportMuhammad SulemanNo ratings yet
- 2 TLE-CSS - SOP FinalDocument4 pages2 TLE-CSS - SOP FinalMam Lorna Es GeeNo ratings yet
- Issue: 3D at Depth: The Future Is GreenDocument72 pagesIssue: 3D at Depth: The Future Is GreenPepeNo ratings yet
- Raju ComparativePhilosophySpiritual 1963Document16 pagesRaju ComparativePhilosophySpiritual 1963Kent Jerson CasianoNo ratings yet
- Importance of ICT in The Teaching and Learning of ChemistryDocument5 pagesImportance of ICT in The Teaching and Learning of ChemistryBOLD BEAUTIFULNo ratings yet
- Valuasi Ekonomi Taman Wisata Alam Punti Kayu Palembang PDFDocument11 pagesValuasi Ekonomi Taman Wisata Alam Punti Kayu Palembang PDFVictorNo ratings yet
- MC 14510B Contador Ascendente Descendente BCDDocument10 pagesMC 14510B Contador Ascendente Descendente BCDmenu1973No ratings yet
- Amperometric Titrations: Principle, Instrumentation and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesAmperometric Titrations: Principle, Instrumentation and ApplicationsNandhanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Story The AwakeningDocument7 pagesAnalysis of The Story The AwakeningAary Rathod100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Cognitive Psychology NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Cognitive Psychology NotesShekinah Pearl NiogNo ratings yet
- At 14 2Document7 pagesAt 14 2Icz Fuentes100% (1)
- Đề HSG Tiếng Anh 11 - 2021Document7 pagesĐề HSG Tiếng Anh 11 - 2021Vân Anh OnceNo ratings yet
- A Blessing and A Curse CEO Empathy by Andreas Konig - Case DownloadedDocument25 pagesA Blessing and A Curse CEO Empathy by Andreas Konig - Case Downloadedsarthak sethNo ratings yet
- Resume and AppDocument3 pagesResume and AppLORNA GUIWANNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Page ! - The Art of Storytelling: Your Hero's Journey 1 Sunyi - CoDocument35 pagesUnit 1: Page ! - The Art of Storytelling: Your Hero's Journey 1 Sunyi - CoKevin SmithNo ratings yet
- Automatic Design of Compliant Surgical Forceps With Adaptive Grasping FunctionsDocument9 pagesAutomatic Design of Compliant Surgical Forceps With Adaptive Grasping FunctionsFarjad KhanNo ratings yet
- Resonance UnlockedDocument5 pagesResonance UnlockedgjjgNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocument74 pagesForm 1 Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceGooi Kee Win91% (43)
- Abs 0678Document11 pagesAbs 0678Jorge OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Richard Heck in MemoriamDocument24 pagesRichard Heck in MemoriamTonie Jane SabadoNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Service Delivery in Panchayat - Experience From ManipurDocument12 pagesEffectiveness of Service Delivery in Panchayat - Experience From Manipurlhingneinemhaokip_38No ratings yet
- Course Information Booklet: FIRST SEMESTER (A.Y 2020-2021) Ged0113: The Filipino in The Contemporary WorldDocument48 pagesCourse Information Booklet: FIRST SEMESTER (A.Y 2020-2021) Ged0113: The Filipino in The Contemporary WorldcasperNo ratings yet
- Development of The Indirect-Drive Approach To Inertial Confinement Fusion and The Target Physics Basis For Ignition and Gain - REVIEW ARTICLE PDFDocument92 pagesDevelopment of The Indirect-Drive Approach To Inertial Confinement Fusion and The Target Physics Basis For Ignition and Gain - REVIEW ARTICLE PDFAjit UpadhyayNo ratings yet