Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test 2 Phy
Uploaded by
Hassan KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test 2 Phy
Uploaded by
Hassan KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
2
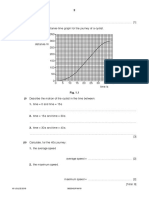
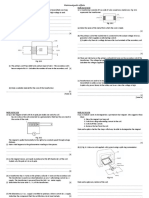
1 Fig. 1.1 shows the speed–time graph for a car travelling on a straight horizontal road.
20
speed
m/s
10
0
0 10 20 30 40 50
time / s
Fig. 1.1
(a) Describe the motion of the car shown in Fig. 1.1.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................. [2]
(b) At time t = 10 s the engine of the car is switched off. The brakes are not applied.
(i) Name two forces that act on the car to cause the change in motion after t = 10 s.
1 ........................................................................................................................................
2 ........................................................................................................................................
[1]
(ii) Suggest why Fig. 1.1 is a curve after t = 10 s.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................... [1]
© UCLES 2023 5054/22/M/J/23
3
(c) Between t = 10 s and t = 20 s the speed of the car changes from 18 m / s to 11 m / s.
The mass of the car is 1200 kg.
(i) Calculate the change in momentum of the car in this time.
Give the unit of your answer
momentum change = ...................................... unit ........... [2]
(ii) Calculate the average resultant force exerted on the car during this time.
average resultant force = ..................................................... N [2]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2023 5054/22/M/J/23 [Turn over
5
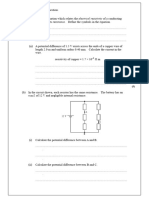
(c) The battery is marked ‘energy capacity 0.35 kilowatt-hour (kW h)’.
(i) Define what is meant by a kilowatt-hour.
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) The scooter stops working because the battery is totally discharged (flat). This means
that there is no more energy stored in the battery.
The battery is then recharged using a 70 W power supply.
Calculate the time taken to fully recharge the battery.
time = ............................................... hours [2]
[Total: 8]
© UCLES 2023 5054/22/M/J/23 [Turn over
10
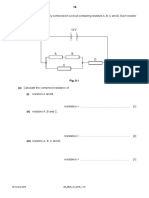
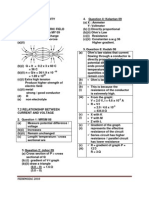
6 Fig. 6.1 shows an electric circuit containing a filament lamp, a resistor R, a 12 V battery and five
meters.
12 V
ammeter ammeter
A A
A1 A3
ammeter
A2
resistor R
A
V V
voltmeter voltmeter
V1 V2
Fig. 6.1
(a) (i) The reading on ammeter A1 is 0.25 A.
The reading on voltmeter V1 is 3.0 V.
Determine the readings on the other meters.
reading on ammeter A2 = ............................................................ A
reading on ammeter A3 = ............................................................ A
reading on voltmeter V2 = ........................................................... V
[2]
(ii) Calculate the resistance of resistor R.
resistance of resistor R = ..................................................... Ω [2]
© UCLES 2023 5054/22/M/J/23
11
(iii) The resistor obeys Ohm’s law.
State Ohm’s law.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [2]
(b) Fig. 6.2 shows the current–voltage graph for the filament lamp.
0.40
0.30
current / A
0.20
0.10
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
voltage / V
Fig. 6.2
The battery in Fig. 6.1 is replaced with a different battery which has a different e.m.f.
(electromotive force).
The voltage across the lamp increases to 6.0 V.
Use data from the graph to determine the e.m.f. of the second battery.
Show your working.
e.m.f. = ...................................................... V [3]
[Total: 9]
© UCLES 2023 5054/22/M/J/23 [Turn over
You might also like
- Safari PDFDocument13 pagesSafari PDFHussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/22Ved P4h PratapNo ratings yet
- 13 7 Fig. 7.1 Shows A Circuit That Contains A Battery, A Switch, A Voltmeter and Three 40 Resistors, RDocument2 pages13 7 Fig. 7.1 Shows A Circuit That Contains A Battery, A Switch, A Voltmeter and Three 40 Resistors, RDaniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Igcse Physics c9 Prac QuesDocument6 pagesIgcse Physics c9 Prac QueshuxxiNo ratings yet
- Energy, Power & Resistance 5 QPDocument6 pagesEnergy, Power & Resistance 5 QPXhoniNo ratings yet
- ST Edward'S Oxford: Lower Sixth Entrance Assessment November 2013 Physics 1 HourDocument13 pagesST Edward'S Oxford: Lower Sixth Entrance Assessment November 2013 Physics 1 HourDarren ContrerasNo ratings yet
- March 2020 P4Document15 pagesMarch 2020 P4Rohim FirdausNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits 3 QPDocument7 pagesElectrical Circuits 3 QParmaanb617No ratings yet
- Revision Paper 1Document14 pagesRevision Paper 1AvehiNo ratings yet
- 46.2-Electromagnetic Effects-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpDocument13 pages46.2-Electromagnetic Effects-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpNurul FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Mechanics Part 1Document4 pagesAssessment 1 Mechanics Part 1Nirmani RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 12 8 (A) (I) State What Is Meant by A Magnetic Field.: 0625/42/M/J/23 © UCLES 2023Document2 pages12 8 (A) (I) State What Is Meant by A Magnetic Field.: 0625/42/M/J/23 © UCLES 2023Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- Potential Divider QDocument9 pagesPotential Divider QJellyfishNo ratings yet
- P 1Document10 pagesP 1ayeshaNo ratings yet
- Binder1 - Py5Document27 pagesBinder1 - Py5lelon81No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effects 2 QPDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 2 QPValerine Victoria100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Effects 2 QPDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 2 QPVyom agarwalNo ratings yet
- Y11 Revision QuestionsDocument13 pagesY11 Revision QuestionsKwang yuan HiiNo ratings yet
- Set 61 - Chapter 1Document25 pagesSet 61 - Chapter 1lelon81No ratings yet
- 46.4 Electromagnetic EffectsDocument11 pages46.4 Electromagnetic Effectskatise1794No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 4 QPDocument7 pagesDigital Electronics 4 QPCatherine Dharshini LabrooyNo ratings yet
- Section BDocument8 pagesSection BDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- R Power Supply: Fig. 10.1 (A)Document7 pagesR Power Supply: Fig. 10.1 (A)huxxiNo ratings yet
- 12 Work, Energy&PowerDocument9 pages12 Work, Energy&PowersyedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effects 2 QPDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 2 QPA ordinary civilian zengNo ratings yet
- 12 7 (A) Define Potential Difference (P.D.) .: 0625/42/F/M/23 © UCLES 2023Document3 pages12 7 (A) Define Potential Difference (P.D.) .: 0625/42/F/M/23 © UCLES 2023Daniel CannywoodNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticeDocument27 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticealfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- GertDocument20 pagesGertSuvdaa SanjaanyamNo ratings yet
- Electricity WS2Document3 pagesElectricity WS2visit.rgNo ratings yet
- RWS 1Document5 pagesRWS 1Mahendra CSA CBENo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power P2Document69 pagesWork, Energy and Power P2carbohemoglobinNo ratings yet
- 1-6 Testyr11Document7 pages1-6 Testyr11kingmannan2008No ratings yet
- 0625/42/M/J/18 © Ucles 2018Document5 pages0625/42/M/J/18 © Ucles 2018Yakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A CarDocument5 pages2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A CarYakshrajsinh JadejaNo ratings yet
- Q2,3Document3 pagesQ2,3PC AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Motion 2 QPDocument14 pagesMotion 2 QPUddin AimanNo ratings yet
- Physics 5054 P2 Complete Electricity Topical Past Paper (Only Questions)Document183 pagesPhysics 5054 P2 Complete Electricity Topical Past Paper (Only Questions)Manthan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- OL Basic Electrical Physics WS 2 PDFDocument6 pagesOL Basic Electrical Physics WS 2 PDFFatima ShahNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument6 pagesPhysicswabumundupallaso076No ratings yet
- Electricity p4 s17-18Document5 pagesElectricity p4 s17-18Austin RexNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits 7 QPDocument16 pagesElectric Circuits 7 QPChong Xue ErNo ratings yet
- Magnets Test 1Document4 pagesMagnets Test 1sniperpandabNo ratings yet
- 15.1 Scalars & VectorsDocument5 pages15.1 Scalars & VectorsRoan AudieNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Desire KandawasvikaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics P-4Document307 pagesIGCSE Physics P-4Belal GTNo ratings yet
- Physic AssignmentDocument9 pagesPhysic AssignmentAlex jamesNo ratings yet
- Current Elec Test and MSDocument14 pagesCurrent Elec Test and MSsmarts1lrealNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument7 pagesMy TestJacked CapyNo ratings yet
- 46.2-Electromagnetic EffectsDocument14 pages46.2-Electromagnetic Effectskatise1794No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effect (Motor Generator Transformer)Document6 pagesElectromagnetic Effect (Motor Generator Transformer)FN LowNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Electricity)Document8 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Electricity)Kiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- PphhyyDocument6 pagesPphhyysangita bediyaNo ratings yet
- 1dXWounKcsaOnaWfBjPrfe YvjlTYlJveDocument11 pages1dXWounKcsaOnaWfBjPrfe YvjlTYlJvePradeepa SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 5054 s13 QP 21Document16 pages5054 s13 QP 21Farhad AliNo ratings yet
- Electricity Qs 2Document13 pagesElectricity Qs 2sydneysmith713No ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 SLDocument16 pagesPhysics Paper 2 SLAbdul RaqeebNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationcamaralckinNo ratings yet
- Full Mock-3 Olevel-Paper-4 Final SourceDocument10 pagesFull Mock-3 Olevel-Paper-4 Final SourceDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Design: A Practitioner's GuideFrom EverandPower Electronics Design: A Practitioner's GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Activity 1.2 Familiarization of Components and EquipmentsDocument7 pagesActivity 1.2 Familiarization of Components and EquipmentsMALAKIPWETKONo ratings yet
- LG 50PT85Document53 pagesLG 50PT85videosonNo ratings yet
- CP Training Maual-Module 8-Field Measurement and Testing of CP Sys...Document38 pagesCP Training Maual-Module 8-Field Measurement and Testing of CP Sys...Emre Erdem100% (1)
- Sony dsr-40 Ver1.0Document205 pagesSony dsr-40 Ver1.0saul64No ratings yet
- Sverker-900 Ug en V12a - User ManualDocument56 pagesSverker-900 Ug en V12a - User ManualManjithaGeethadharaGunarathneNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Test ReportDocument3 pagesSaudi Aramco Test Reportkarthi51289No ratings yet
- M. Statment Lines - OHL Instal & TestingDocument27 pagesM. Statment Lines - OHL Instal & Testingahmedshah512100% (1)
- Hfe Marantz Pm4001 Ose 4001f ServiceDocument48 pagesHfe Marantz Pm4001 Ose 4001f Servicetml3nrNo ratings yet
- Lab ActivityDocument9 pagesLab ActivityAnvi MantriNo ratings yet
- Mathematical EconomicsDocument4 pagesMathematical EconomicsSayyid JifriNo ratings yet
- Elmeasure All Product Catalog PDFDocument40 pagesElmeasure All Product Catalog PDFSunitha PNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 Direct Current CircuitssssssssDocument19 pagesChapter15 Direct Current CircuitssssssssAnn Shen ThianNo ratings yet
- 2004 Legacy Service Manual Quick Reference Index Wiring System SectionDocument116 pages2004 Legacy Service Manual Quick Reference Index Wiring System SectionspelectronNo ratings yet
- Double Frequency Meters and Double Voltmeters Data Sheet 4921240005 UKDocument4 pagesDouble Frequency Meters and Double Voltmeters Data Sheet 4921240005 UKDario GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current & Mechanical Effct of Electric CurrentDocument41 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current & Mechanical Effct of Electric CurrentShweta Y KNo ratings yet
- 1949 - Service Manual For The National NC-TV7W and M Television RecieverDocument36 pages1949 - Service Manual For The National NC-TV7W and M Television RecieverKenneth LeakeNo ratings yet
- PAG 03.3 - Determining Internal Resistance and Maximum Power of A CellDocument3 pagesPAG 03.3 - Determining Internal Resistance and Maximum Power of A CelljmsonlNo ratings yet
- MV Switchgear Inspection and Test Procedure: October 2019Document21 pagesMV Switchgear Inspection and Test Procedure: October 2019sabamalarNo ratings yet
- Guide To Low-Voltage Motor Testing - MeggerDocument44 pagesGuide To Low-Voltage Motor Testing - MeggerJustine Joshua DagondonNo ratings yet
- R 508 HsDocument27 pagesR 508 HsCarlos Toledo FreitasNo ratings yet
- Sanyo Ds13320 Service ManualDocument26 pagesSanyo Ds13320 Service ManualMauricio SolanoNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Energy Student BookDocument76 pagesElectricity and Energy Student BookNebyu GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 P2 AnswerDocument10 pagesChapter 7 P2 AnswerLee Hue Kean100% (1)
- PTG Chapter 12 Asal PhysicsDocument9 pagesPTG Chapter 12 Asal Physicszzrnwdzpsmhs951003No ratings yet
- JVC mx-gt88Document81 pagesJVC mx-gt88Diego VilchezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Electrical Theory and CircuitsDocument142 pagesUnit 1 - Electrical Theory and CircuitsBinodSah100% (1)
- 570 Portable Oxygen Analyser: Instruction ManualDocument61 pages570 Portable Oxygen Analyser: Instruction ManualJennie CardozoNo ratings yet
- Listrik Dinamis TranslationDocument27 pagesListrik Dinamis TranslationDimas ApriliyantoNo ratings yet
- Zapi FC2125 CodesDocument9 pagesZapi FC2125 CodesDaniel PopescuNo ratings yet