Professional Documents
Culture Documents
15.1 Scalars & Vectors
Uploaded by
Roan AudieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
15.1 Scalars & Vectors
Uploaded by
Roan AudieCopyright:
Available Formats
1
1 (a) State the factors which completely describe a vector quantity.
...................................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b) An aeroplane is flying towards the east in still air at 92 m / s.
A wind starts to blow at 24 m / s towards the north.
Draw a vector diagram to find the resultant velocity of the aeroplane. Use a scale of
1.0 cm = 10 m / s.
resultant speed = .......................................................
angle between resultant and easterly direction = [5]
15.1 Scalars & Vectors
2
2 (a) Underline the vectors in the following list of quantities.
density energy force mass ve
elocity volume [2]
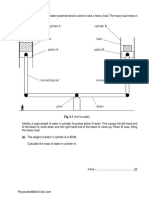
3 On a windy day, a parachutist of mass 85 kg jumps from an aeroplane.
Fig. 3.1 shows the parachutist falling through the air at a constant vertical velocity of 8.4 m / s
downwards.
8.4 m / s
Fig. 3.1
(a) Distinguish between speed and velocity.
..........................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................... [1]
15.1 Scalars & Vectors
3
(b) As the parachutist falls, the wind is moving him towards the right of the diagram, at a
horizontal velocity of 6.3 m / s.
(i) On Fig. 3.1, draw an arrow to show the horizontal velocity of the parachutist. [1]
(ii) On the grid below, draw a vector diagram to determine graphically the size and
direction of the resultant velocity of the parachutist.
size = ........................................................
direction = [4]
15.1 Scalars & Vectors
4
4 (i) State why force is a vector quantity.
............................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) A 20 N force and a 15 N force act at the same time on an object of mass 14 kg.
Calculate
(i) the maximum possible force on the object due to these two forces,
force = .................................................................... [1]
(ii) the acceleration caused by a resultant force equal to this maximum force.
acceleration = ..................................................................... [2]
(c) Fig. 6.1 shows a river in which the velocity of the flowing water is 0.85 m / s parallel to the river
banks.
river bank
velocity of swimmer
velocity relative to water
of water NOT TO
45 1.2 m / s
SCALE
0.85 m / s
Fig. 6.1
15.1 Scalars & Vectors
5
A swimmer sets off from one bank. The velocity of the swimmer relative to the water is 1.2 m / s
at 45° to the river banks, as shown in Fig. 6.1.
In the space below, draw a scale diagram to determine the resultant velocity of the swimmer
relative to the river banks. This velocity is the resultant of the two velocities shown on Fig. 6.1.
Label this resultant on your diagram.
resultant velocity = ........................................................................ [3]
15.1 Scalars & Vectors
You might also like
- General Physics RevisionDocument22 pagesGeneral Physics RevisionJon SnowNo ratings yet
- Force 1Document11 pagesForce 1Peter TaremwaNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPmexicohunt6No ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPItz MeNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPRahat RizwanNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QP-Samra-No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticeDocument27 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticealfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 09 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 09 QPItss TumeloNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument12 pagesMy TestLim Chin YangNo ratings yet
- Class-X Physics Home Work-1B (Theory) : Chapter: Physical Quantity, Kinematics, DynamicsDocument18 pagesClass-X Physics Home Work-1B (Theory) : Chapter: Physical Quantity, Kinematics, DynamicsNuha TasniahNo ratings yet
- Measuring acceleration and speed of a skierDocument9 pagesMeasuring acceleration and speed of a skierTan Chen WuiNo ratings yet
- Forces PracticeDocument6 pagesForces PracticemanlofansotanjoNo ratings yet
- Safari PDFDocument13 pagesSafari PDFHussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Motion - Mass and WeightDocument23 pagesEffect of Motion - Mass and WeightkhalidNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities, Units and MeasurementDocument8 pagesPhysical Quantities, Units and Measurementmanya mustafaNo ratings yet
- Energy Work and Power QP 9Document11 pagesEnergy Work and Power QP 9Haleema GulNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector DiagramDocument2 pagesPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector Diagramlelon ongNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties 3 QPDocument8 pagesGeneral Wave Properties 3 QPAli SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Waves and Interference Worksheet 2Document14 pagesWaves and Interference Worksheet 2Freya SawNo ratings yet
- Mobile bird sculpture physics problemDocument9 pagesMobile bird sculpture physics problemGiorgioNo ratings yet
- Effects of Force 1Document27 pagesEffects of Force 1Peter TaremwaNo ratings yet
- Scalar and vector quantities in physicsDocument9 pagesScalar and vector quantities in physicsAndrei FloreaNo ratings yet
- Forces on a tipped floorboardDocument7 pagesForces on a tipped floorboardItz MeNo ratings yet
- A - Forces Revision QuestionsDocument6 pagesA - Forces Revision Questionsdeivid floreaNo ratings yet
- AS Level WorksheetDocument10 pagesAS Level WorksheetVivehaNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion TestBoockletDocument13 pagesCircular Motion TestBoockletpeaceomoregbee837No ratings yet
- Length & Time 1 QPDocument9 pagesLength & Time 1 QPpkrajenpillaygmailcomNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument2 pagesMy TestLim Chin YangNo ratings yet
- Expr Waves TidyDocument34 pagesExpr Waves TidyMohamed ElaminNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/41Document18 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/41KirubhashiniNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion P2 Set-ADocument21 pagesForces and Motion P2 Set-AAnonymous jwdY0VNo ratings yet
- Forces QPDocument10 pagesForces QPZahra SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics 5054 - 22 Paper 2 Theory Oct - Nov 2023Document8 pagesO Level Physics 5054 - 22 Paper 2 Theory Oct - Nov 2023ayeshaNo ratings yet
- 11.2-Length Time-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-qpDocument10 pages11.2-Length Time-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-qpAbian Arshil AzadNo ratings yet
- P2 Qs (Wave - Sound Wave)Document13 pagesP2 Qs (Wave - Sound Wave)kingsarim006No ratings yet
- Physics Yr 11 Revision QsDocument14 pagesPhysics Yr 11 Revision QsPunitha PanchaNo ratings yet
- Momentum QPDocument16 pagesMomentum QPHimanshu BhandariNo ratings yet
- 46.2-Electromagnetic Effects-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpDocument13 pages46.2-Electromagnetic Effects-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpNurul FadhilahNo ratings yet
- Full Mock - 1 Paper-2Document16 pagesFull Mock - 1 Paper-2Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Vector diagram analysisDocument11 pagesVector diagram analysisAden FatimaNo ratings yet
- Forces 1 QPDocument11 pagesForces 1 QPkhalil rehman100% (1)
- Physics Mock Exam 1: Mrs - Sara Salah +2/01020088624Document12 pagesPhysics Mock Exam 1: Mrs - Sara Salah +2/01020088624Yousef Abdel HamidNo ratings yet
- 1foundation Forces and Their Effects Self Study QuestionsDocument44 pages1foundation Forces and Their Effects Self Study QuestionsGame HubNo ratings yet
- Y11 Revision QuestionsDocument13 pagesY11 Revision QuestionsKwang yuan HiiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Descriptive PaperDocument12 pagesIGCSE Physics Descriptive PaperSriram ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work & Power 04 QPDocument10 pagesEnergy, Work & Power 04 QPTran Phuong LinhNo ratings yet
- 60 SETS PhysicsDocument8 pages60 SETS PhysicsAhmed Hossain100% (1)
- Set 61 - Chapter 1Document25 pagesSet 61 - Chapter 1lelon81No ratings yet
- A&O Centre of Excellence Term 2 Examination 2013 Physics Paper 2 Year 10 (40 marksDocument5 pagesA&O Centre of Excellence Term 2 Examination 2013 Physics Paper 2 Year 10 (40 marksEzra Loganathan MuniandiNo ratings yet
- Updated Kinematics PastpapersDocument14 pagesUpdated Kinematics Pastpapersbilal8910aliNo ratings yet
- Year-7-Science-revision 2Document17 pagesYear-7-Science-revision 2Cally ChewNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics exam questionsDocument86 pagesA-level Physics exam questionsMoses Junior100% (1)
- Form 3 21. Linear Motion qDocument23 pagesForm 3 21. Linear Motion qjohnn1.jrugunaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Powers Hydroelectric StationDocument9 pagesSolar Energy Powers Hydroelectric StationRahat RizwanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Power Needed to Transport Passengers in a LiftDocument8 pagesCalculating Power Needed to Transport Passengers in a LiftSalman Farsi TaharatNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - s15 - QP - 21-7 - Chapter KinematicDocument3 pagesPages From 5054 - s15 - QP - 21-7 - Chapter Kinematiclelon81No ratings yet
- 1Document7 pages1zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Phys p2Document16 pagesPhys p2Kalana GamageNo ratings yet
- Elah'Im CultureDocument60 pagesElah'Im CultureRichard David DellermanNo ratings yet
- Oil Well Drilling Methods: University of Karbala College of Engineering Petroleum Eng. DepDocument8 pagesOil Well Drilling Methods: University of Karbala College of Engineering Petroleum Eng. DepAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Basics of ECG Recording GuideDocument21 pagesBasics of ECG Recording GuideghoziNo ratings yet
- The Vatican As A World Power (1939)Document481 pagesThe Vatican As A World Power (1939)sexylove1477No ratings yet
- Monitoring Rock and Soil Mass Performance: To The ConferenceDocument1 pageMonitoring Rock and Soil Mass Performance: To The ConferenceÉrica GuedesNo ratings yet
- Customer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourDocument20 pagesCustomer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourmaryNo ratings yet
- L&T Type 2 Co-Ordination Selection ChartsDocument48 pagesL&T Type 2 Co-Ordination Selection Chartsrdeepak99100% (7)
- GROWTH ASSESSMENT FOR 10-YEAR-OLD SCHOOLERDocument4 pagesGROWTH ASSESSMENT FOR 10-YEAR-OLD SCHOOLERYashoda SatputeNo ratings yet
- Solution Map For Mining ppt3952 PDFDocument29 pagesSolution Map For Mining ppt3952 PDFHans AcainNo ratings yet
- Perspective Homework RubricDocument2 pagesPerspective Homework Rubricapi-244578825No ratings yet
- Underwater vessels, sensors, weapons and control systemsDocument1 pageUnderwater vessels, sensors, weapons and control systemsNguyễn ThaoNo ratings yet
- Haven, Quantum Social ScienceDocument306 pagesHaven, Quantum Social ScienceMichael H. HejaziNo ratings yet
- Effect of Grain Boundary Thermal Expansion on Silicon Nitride Fracture ToughnessDocument8 pagesEffect of Grain Boundary Thermal Expansion on Silicon Nitride Fracture Toughnessbrijesh kinkhabNo ratings yet
- IGO Operations Manual PDFDocument2,251 pagesIGO Operations Manual PDFMardi Wirengkoso100% (1)
- MATH 499 Homework 2Document2 pagesMATH 499 Homework 2QuinnNgo100% (3)
- MC61ADocument5 pagesMC61AAlison Foster100% (1)
- Lesson 1 G8Document11 pagesLesson 1 G8Malorie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ancient South Arabian TradeDocument16 pagesAncient South Arabian TradeAbo AliNo ratings yet
- Preschool ADHD QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesPreschool ADHD QuestionnaireAnnaNo ratings yet
- Kanak Dhara StottramDocument9 pagesKanak Dhara Stottramdd bohraNo ratings yet
- Slings CatalogDocument152 pagesSlings CatalogtaNNertaroNo ratings yet
- Carco h90vsDocument9 pagesCarco h90vsRoxana Elizabeth Valencia NavarrteNo ratings yet
- Lucky TextileDocument5 pagesLucky TextileSaim Bin RashidNo ratings yet
- Important Characteristics of an Ideal InductorDocument4 pagesImportant Characteristics of an Ideal Inductorsreekantha reddyNo ratings yet
- Stem 006 Day 9Document6 pagesStem 006 Day 9Jayzl Lastrella CastanedaNo ratings yet
- Peter Linz An Introduction To Formal Languages and Automata Solution ManualDocument4 pagesPeter Linz An Introduction To Formal Languages and Automata Solution ManualEvelyn RM0% (2)
- Manual THT70 PDFDocument54 pagesManual THT70 PDFwerterNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of CopperDocument21 pagesOxidation of CopperAmeen ShahidNo ratings yet
- Wilkinson 2001Document44 pagesWilkinson 2001Toño Gaspar MuñozNo ratings yet
- Herbivoría y Cristales de CaOxDocument33 pagesHerbivoría y Cristales de CaOxBrain LongwoodNo ratings yet