Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DrugStudy Omeprazole
Uploaded by
Ashknee Khainna AlejoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DrugStudy Omeprazole
Uploaded by
Ashknee Khainna AlejoCopyright:
Available Formats
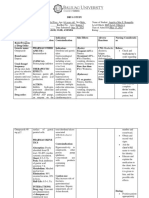
Ateneo de Davao University CRITERIA
E. Jacinto Street, 8016
Content: 35% ____
Davao City
Nursing Responsibilities: 35% ____
Picture: 10% ____
Format: 5% ____
Name of Student: Ashknee Khainna A. Alejo Course/Year/Section: BSN 2B Subject: NCM 2144/ Pharmacology Date: 09-23- 2020 Promptness: 5% ____
Reference: 10% ____
DRUG STUDY FORM
Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Nursing Responsibilities/
Adverse Effects Patient and Family Health Teachings
Generic Name Pharmacotherapeutic Inhibits hydrogen-potassium SE: 1. Perform a physical examination prior to the therapy
Omeprazole Class: adenosine triphosphatase (H+/K+ (Frequent) Headache (Occasional) R: To establish baseline data and to evaluate for the
Benzimidazole ATP pump), an enzyme on the Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea effectiveness and presence of adverse effects of the
surface of gastric parietal cells which (Rare) Dizziness, asthenia, medication.
Clinical Class: results in suppression of gastric basal vomiting, constipation, upper
Brand Name and acid secretion.
Proton pump inhibitor respiratory tract infection, back 2. Assess for presence of liver disease in patients.
Apo-Omeprazole
pain, rash, cough. R: The metabolism of omeprazole is decreased in patients
Losec with hepatic impairment.
PriLOSEC
AE:
Pancreatitis, hepatotoxicity, 3. Assess for history of allergy to a proton pump inhibitor
interstitial nephritis may also occur R: To reduce the risk of hypersensitivity reactions
rarely.
4. Administer omeprazole before breakfast and ensure that the
patient does not chew, or crush capsules.
R: Omeprazole capsules should be swallowed whole to
ensure the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug.
5. Assess for current status of pregnancy or lactation
R: Omeprazole may cause adverse effects on the fetus or
nursing baby.
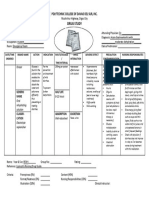
Drawing/ Picture Indication Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamics
6. Monitor the patient’s bowel movement
R: To formulate an appropriate bowel program as needed.
Oral Absorption PO
It is indicated for patients It is rapidly absorbed from the GI tract Onset: 2 hrs
7. Assess the neurological status of the patient, including level of
with esophagitis or following oral intake. Peak: 5 days
orientation, affect and reflexes.
duodenal ulcer. Duration: 1-5 days
R: To evaluate for the effects of the drug in CNS.
Distribution
PB: 95%
8. Evaluate for improvements in gastritis, heartburn, and other GI
symptoms.
Metabolism
R: To help determine if drug therapy is successful.
t ½: 0.5-1 hr
9. Provide comprehensive medical information, including the
Excretion
name of the medication, prescription dose, signs and
It is excreted through urine
symptoms of potential adverse reactions and interventions to
reduce or avoid them.
R: To enhance patient knowledge about his/her medication
10. Arrange for medical follow-up if symptoms are not resolved
after 4 to 8 weeks of therapy
R: To assess for serious underlying conditions that might be
causing the symptoms.
References:
Kee, MS, RN, Hayes, PhD, MPH, FNP-BC; McCuistion PhD, RN, CNS . (2015.). Pharmacology: A Patient-Centered Nursing Process Action (8th ed.).
Kizior, R., BS, RPh, & Hodgson, K., RN, BSN, CCRN. (2019). Saunders Nursing Drug Handbook 2019. Elsevier.
Lilley, RN, PhD, Collins,PharmD & Snyder , MSN, RN-BC. (2007). PHARMACOLOGY AND THE NURSING PROCESS (7th ed.). Elsevier Mosby.
You might also like
- Aromatherapy - 600 Aromatherapy Recipes For Beauty, Health & Home - Plus Advice & Tips On How To Use Essential Oils - Nodrm PDFDocument365 pagesAromatherapy - 600 Aromatherapy Recipes For Beauty, Health & Home - Plus Advice & Tips On How To Use Essential Oils - Nodrm PDFFernanda Rodriguez75% (4)
- DrugStudy MetforminDocument3 pagesDrugStudy MetforminAshknee Khainna AlejoNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy MetforminDocument3 pagesDrugStudy MetforminAshknee Khainna AlejoNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NameMichael PalmaNo ratings yet
- What Are CarbohydratesDocument36 pagesWhat Are CarbohydratesPINNACLE CAFENo ratings yet
- AminoglycosidesDocument20 pagesAminoglycosidesHassan.shehri100% (5)
- DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquilloDocument4 pagesDRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNo ratings yet
- Calvit Tablet/Suspension: Generic Name: Category: CompositionDocument2 pagesCalvit Tablet/Suspension: Generic Name: Category: CompositiondentsavvyNo ratings yet
- TOP 10 WI LD Foods: A Free Download FromDocument12 pagesTOP 10 WI LD Foods: A Free Download Fromlifelonglearner1100% (3)
- Ultimate Guide To Surviving in The WildDocument175 pagesUltimate Guide To Surviving in The WildSal Ot100% (1)
- Carboprost Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCarboprost Drug StudyAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Eye LubricantDocument9 pagesEye LubricantbuddhahandNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy PotassiumchlorideDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Potassiumchloridetrina412No ratings yet
- Drug Study: D IphenhydramineDocument5 pagesDrug Study: D IphenhydramineAnthonette DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Dr. Huang's 10 Relieving ProtocolsDocument5 pagesDr. Huang's 10 Relieving ProtocolsCarissa Nichols86% (7)
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document2 pagesDrug Study 2Kirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Sodium ChlorideDocument1 pageSodium ChlorideMark Christian M. GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - FractureDocument58 pagesCase Study - FractureChristian97% (31)
- Drug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Lactulose (Duphalac, Lilac)AgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductDocument3 pagesMyasthenia Gravis, Megacolon and Narrow Angle Glaucoma, Hypersensitivity To HNBB and Other Components of The ProductGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOmeprazole Drug StudyMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Ds OresolDocument1 pageDs OresolShannie Padilla100% (1)
- Article and Journal in Delivery RoomDocument3 pagesArticle and Journal in Delivery Roomcutei_annNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibility BetahistineDocument16 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibility Betahistineclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide DSDocument1 pageMetoclopramide DSAngelica Idio0% (1)
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument1 pageOMEPRAZOLERheza0% (1)
- Drug Study Cefazolin Module 13Document1 pageDrug Study Cefazolin Module 13Daryl Joy Cortez100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan Practical Research 2Document29 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan Practical Research 2Erica CanonNo ratings yet
- AllopurinolDocument1 pageAllopurinolRachel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- ParecoxibDocument2 pagesParecoxibPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Butorphanol Tartrate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesButorphanol Tartrate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (2)
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Nursing Departmentrica sebabillones100% (1)
- Drug Study OmeprazoleDocument3 pagesDrug Study OmeprazoleSandeepNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - BisacodylDocument4 pagesDrug Study - BisacodylKyla CastroNo ratings yet
- OmeprazoleDocument1 pageOmeprazoleFritz JanobasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study inDocument1 pageDrug Study inElcid PimentelNo ratings yet
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Focus Diagnosis Action ResponseDocument2 pagesFocus Diagnosis Action ResponseGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii ErcefloraDocument1 pageBacillus Clausii ErcefloraCezhille BattadNo ratings yet
- DS - ColchicineDocument2 pagesDS - ColchicineMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document1 pageDrug Study 2Blitz KriegNo ratings yet
- Tramadol UltramDocument2 pagesTramadol UltramatchiekNo ratings yet
- Kremil S CsDocument2 pagesKremil S Csunkown userNo ratings yet
- Exit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseDocument2 pagesExit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseGayle RavanchoNo ratings yet
- DRUG LactuloseDocument1 pageDRUG LactuloseJona Phie Domingo MonteroNo ratings yet
- K PotaDocument2 pagesK PotaJustine May GervacioNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Bearse Tablet InsertDocument2 pagesBearse Tablet InsertLeonard ByunNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFADocument3 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Metoclopramide Brand Name: Reglan and Metozolv ODTJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument18 pagesDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesDocument2 pagesWesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesShane Aileen AngelesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- XtendaDocument2 pagesXtendaAlexis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJ.r. MercadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FADocument3 pagesDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FAKristine ChampnessNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesKetorolac DRUG STUDYA.No ratings yet
- Drug Study - OB WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study - OB WardCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayNo ratings yet
- CoamoxiclavDocument1 pageCoamoxiclavBbhie AntiguaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Pletal: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacokinetics General Indications Contraindications BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Pletal: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacokinetics General Indications Contraindications Beforeart_mutantNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy MetoclopramideDocument2 pagesDrugStudy MetoclopramideAshknee Khainna AlejoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument4 pagesDrug Study FormKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy MetoclopramideDocument2 pagesDrugStudy MetoclopramideAshknee Khainna AlejoNo ratings yet
- Self Care Theory: Dorothea OremDocument42 pagesSelf Care Theory: Dorothea OremFelica Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- TFN Jean WatsonsDocument27 pagesTFN Jean Watsonschryss advinculaNo ratings yet
- STS CRFDocument38 pagesSTS CRFYosoy LomasNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Iron MetabolismDocument21 pagesRegulation of Iron MetabolismElita Maritan SNo ratings yet
- Conversion of ASTM To TBP and EFVDocument111 pagesConversion of ASTM To TBP and EFVsyedmuhammadtariqueNo ratings yet
- Left Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDocument9 pagesLeft Thigh Pain: I. Chief Complaint/ Other ComplaintsDominic BristolNo ratings yet
- Low Platelet CountDocument9 pagesLow Platelet Countfatimah_zkhanNo ratings yet
- FM - Hse.020 Statistik HSE TahunanDocument2 pagesFM - Hse.020 Statistik HSE TahunanEka Nanda HermarianyNo ratings yet
- Disability EssayDocument7 pagesDisability Essayapi-459529771No ratings yet
- P.E 3A Learning Activity Sheet WEEK 5 6Document7 pagesP.E 3A Learning Activity Sheet WEEK 5 6Ris CorreaNo ratings yet
- Semmelweis' Handwashing & Lister's Antiseptic TechniqueDocument22 pagesSemmelweis' Handwashing & Lister's Antiseptic TechniqueNewNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of BacteriaDocument57 pagesMolecular Biology of BacteriaSean ArifinNo ratings yet
- Is Fast Food The New Tobacco PDFDocument6 pagesIs Fast Food The New Tobacco PDFCustom Writing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Myths PDFDocument8 pagesMyths PDFLuisa Elena HernandezNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Kirandul: Investigatory Project of BiologyDocument10 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Kirandul: Investigatory Project of BiologyAachal GayreNo ratings yet
- The Nurse Leader's Role: Crisis ManagementDocument3 pagesThe Nurse Leader's Role: Crisis Managementravsab GaikwadNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On PrednisoneDocument5 pagesA Drug Study On PrednisonePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Regarding Immunization Among Mothers of Under Five ChildrenDocument3 pagesKnowledge Regarding Immunization Among Mothers of Under Five ChildrenEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis, Quality and Conformity: Certified: ISO 9001:2008, ISO 13485-2003 and WHO GMPDocument3 pagesCertificate of Analysis, Quality and Conformity: Certified: ISO 9001:2008, ISO 13485-2003 and WHO GMPMitha AriantiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Insensitivity To Pain With Anhidrosis (CIPA) : A Case ReportDocument5 pagesCongenital Insensitivity To Pain With Anhidrosis (CIPA) : A Case ReportAhmad DiazNo ratings yet
- CALGB Schema FinalDocument1 pageCALGB Schema FinalMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Curs 1 Introducere EndodontieDocument24 pagesCurs 1 Introducere EndodontieVlahul VladNo ratings yet
- Semey State Medical University: Department of Psychiatry Topic Schizophrenia Raja Ali HassanDocument45 pagesSemey State Medical University: Department of Psychiatry Topic Schizophrenia Raja Ali HassanRaja HassanNo ratings yet