Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 39 Nhps in DM
Uploaded by
Ahmed Mashaly0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pagePharmacology - DM
Original Title
lecture-39-nhps-in-dm
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPharmacology - DM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageLecture 39 Nhps in DM
Uploaded by
Ahmed MashalyPharmacology - DM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
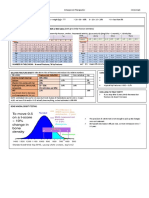
Lecture 39 NHPs in DM Eccott
PRODUCT MOA DOSE AND DURATION EFFICACY SAFETY
HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS
Fenugreek Fibrous seeds may affect GI 2.5 – 15 g daily In combo with sulfonylureas: Well tolerated
transit time, slowing glucose Capsules come in ↓ FBG, HbA1C by 0.5% Diarrhea, flatulence
absorption (bulk laxative) 600 mg – 1 g Systemic review: ↓FBG Contraindicated in pregnancy
4-hydroxy-isoleucine in the Crushing seeds vital to (0.96 mmol/dL) (uterine stimulant)
seed stimulates glucose- release viscous gel Prediabetics: ↓ post- Avoid in thyroid conditions
dependent insulin secretion fiber prandial & fasting BG, ↑ (hypothyroid effects)
(hypoglycemic effects) serum insulin, RRR of Caution with anti-platelet/
developing T2DM 0.6 coagulants (contains coumarin
o Poor study, each was derivative) = ↑ risk of
own control bleeding/bruising
Monitor BG
Gymnema Enhances insulin release from 200 mg bid used for ↓ HbA1c, cholesterol, TGs, Avoid in pregnancy
Sylvestre beta cells up to 20 months dose of hypoglycemic drugs
Decreases intestinal o Poor study (no R, DB)
(Gurmar) absorption of glucose
Use leaves of the plant
Bitter melon Believed to have similar Small studies, mixed results Caution pts taking
(Momordica effects to bovine insulin hypoglycemic drugs who eat
charantia) bitter melon
INSULIN SENSITIZERS:
Chromium Cofactor for insulin function: 200 – 1400 ug used HbA1C ↓ by 0.58% Well tolerated (some GI upset)
o Helps transport glucose for up to 6 months o Picolinate salt: -0.6% SAFE in pregnancy and
(also used in into cell by increasing Use picolinate salt o Brewers yeast: -1.85% breastfeeding
weight loss insulin binding (better absorption and FBG ↓ by 1.13 Contraindicated in renal
products) o Increases number of bioavailability) TG: ↓ by 0.3 disease (excessive Cr may
insulin receptors Food sources: HDL: ↑ by 0.12 damage kidneys)
o May enhance insulin broccoli, grape juice, Space apart from
sensitivity by activating whole wheat muffin, levothyroxine (binding
intracellular signalling red wine, Brewers’ interaction)
pathways yeast
Chromium deficiency has
similar features to diabetes
Cassia cinnamon Promotes insulin release and Up to 6 g/d of cassia Insufficient evidence Very well tolerated
enhances insulin receptor cinnamon o ↓ FBG (-1.36), LDL Contains coumarin
sensitivity (animal studies) NOTE: most stores sell (-0.52), TG (-1.42); constituents (high doses for
cinnamon bark (C. ↑ HDL-C (0.09) – all ss long time = liver damage)
verum) instead but clinical Avoid in pregnancy
significance??
o No improvement in
HbA1C
MISC.
Alpha lipoic acid Coenzyme involved in carb 600 mg (divided Improved nerve conduction Higher doses more likely to
metabolism (naturally doses) up to 2 years velocity & diabetic produce AEs (vertigo, NV)
synthesized in mitochondria) May take 3-5 weeks peripheral neuropathy sx Avoid in pregnancy
Antioxidant properties for symptom relief (pain, burning)
(regenerate other Doesn’t lower HbA1C
antioxidants like Vit E and C)
Improves insulin sensitivity
(conflicting)
White mulberry Leaf extract inhibits alpha- 1g powdered leaf Limited Avoid in pregnancy
glucoside in gut, preventing before a meal o No change in HbA1C Well tolerated
(also used in absorption of carbs lower o ↓ post-prandial BG Monitor glucose & A1C
weight loss post-prandial BG
products)
Glucomannan or Root of elephant yam ↓ in FBG May reduce drug absorption
PGX Highly viscous soluble fiber o Poor methods (space drugs)
that absorbs water slows Some cases of GI obstruction
(also used in absorption of carbs slows o Take with LOTS of water
weight loss down release of sugars in gut o Don’t use if difficulty
products) swallowing
Avoid in pregnancy
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Connexus SigcodesDocument8 pagesConnexus SigcodesAhmed Mashaly100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Key Answers and Medical Surgical Nursing 1 - FINALS ExaminatiDocument11 pagesKey Answers and Medical Surgical Nursing 1 - FINALS ExaminatiJune Dumdumaya100% (1)
- FDRM's Shopping Guide V1.7.4Document42 pagesFDRM's Shopping Guide V1.7.4universalhealthproject100% (2)
- هام -Clinical & Chemical Pathology MCQsDocument68 pagesهام -Clinical & Chemical Pathology MCQsnarendrakumar9463% (8)
- Sample Letter To Consular Section, Us Embassy/Consulate Supporting Application For Visa (Or Renewal/Extension) by Foreign IndividualDocument1 pageSample Letter To Consular Section, Us Embassy/Consulate Supporting Application For Visa (Or Renewal/Extension) by Foreign IndividualZodin100% (3)
- David Sinclair's Supplement Regimen - NMN, Resveratrol, Metformin, Vitamin D, Vitamin K and The Science of Longevity - Podcast NotesDocument5 pagesDavid Sinclair's Supplement Regimen - NMN, Resveratrol, Metformin, Vitamin D, Vitamin K and The Science of Longevity - Podcast NotesEvariste Galois92% (13)
- Nine Simple Ways To Make It Easier To (Re) Use Your Data Vol 6 No 2 (2013) : Special Issue - Data Sharing in Ecology and EvolutionDocument10 pagesNine Simple Ways To Make It Easier To (Re) Use Your Data Vol 6 No 2 (2013) : Special Issue - Data Sharing in Ecology and EvolutionalbgomezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsDocument3 pagesLecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31 Osteoporosis Pathophys FlattenedDocument3 pagesLecture 31 Osteoporosis Pathophys FlattenedAhmed Mashaly100% (1)
- Osteoporosis Pharmacology Drugs Bone Remodeling BisphosphonatesDocument4 pagesOsteoporosis Pharmacology Drugs Bone Remodeling BisphosphonatesAhmed Mashaly100% (1)
- Lecture 33 Osteoporosis TherapeuticsDocument1 pageLecture 33 Osteoporosis TherapeuticsAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Ontario COVID-19 Vaccination ServiceDocument4 pagesOntario COVID-19 Vaccination ServiceAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Legal Issues in Clinical ResearchDocument48 pagesLegal Issues in Clinical ResearchAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- 4 Joneckis, Chris-02-16-16Document62 pages4 Joneckis, Chris-02-16-16OstazNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 Thyroid PathophysDocument2 pagesLecture 28 Thyroid PathophysAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Research EthicsDocument114 pagesResearch EthicsAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Ethical Principles in Clinical ResearchDocument46 pagesEthical Principles in Clinical ResearchAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- An Overview of File Formats JsonDocument3 pagesAn Overview of File Formats JsonAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Manual-2016 4Document257 pagesManual-2016 4Ahmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Research EthicsDocument114 pagesResearch EthicsAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Amber 14Document826 pagesAmber 14Ahmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Journal of The Taiwan Institute of Chemical EngineersDocument13 pagesJournal of The Taiwan Institute of Chemical EngineersAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Medical - Chemestry Q&ADocument13 pagesMedical - Chemestry Q&AAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- 1 Gallin, John-10-13-15-Handouts-Color-1Document29 pages1 Gallin, John-10-13-15-Handouts-Color-1OstazNo ratings yet
- Friedel CraftsDocument8 pagesFriedel CraftsAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Total Quality Management in HospitalsDocument6 pagesImplementation of Total Quality Management in HospitalsAhmed Mashaly100% (1)
- Integrated modeling system for structural biologyDocument10 pagesIntegrated modeling system for structural biologyAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Medical - Chemestry Q&ADocument13 pagesMedical - Chemestry Q&AAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- General Information On Medical Certificates and List of Accredited Clinics of The Embassy of BelgiumDocument4 pagesGeneral Information On Medical Certificates and List of Accredited Clinics of The Embassy of BelgiumAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Conversion of GradesDocument61 pagesConversion of GradesAhmed Mashaly0% (1)
- Student Cover LetterDocument1 pageStudent Cover LetterAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Master's Degree CourseDocument2 pagesPharmaceutical Biotechnology: Master's Degree CourseAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhythmiaDocument1 pageCardiac DysrhythmiaAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyKyla CalzadoNo ratings yet
- Thiamazole PretreatmentDocument7 pagesThiamazole PretreatmentWendy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet drugs mechanisms and clinical usesDocument31 pagesAntiplatelet drugs mechanisms and clinical usesPaul Behring ManurungNo ratings yet
- Naturally-Occurring Neoplasms in The Mongolian GerbilDocument4 pagesNaturally-Occurring Neoplasms in The Mongolian GerbilAna Julia Tonetti ClaroNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer Imaging July, 2020 - ICI 01Document42 pagesProstate Cancer Imaging July, 2020 - ICI 01madvincyNo ratings yet
- Dance - Health and Wellness - Acosta - Bgo - v3Document24 pagesDance - Health and Wellness - Acosta - Bgo - v3abba may dennisNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Gallstones Case FileDocument2 pagesBiochemistry Gallstones Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- Roche Chemstrip 5 Ob 7 Insert Data SheetDocument2 pagesRoche Chemstrip 5 Ob 7 Insert Data SheetJames Anthony ParasNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Parathyroid DiseaseDocument3 pagesThyroid and Parathyroid DiseaselalamNo ratings yet
- Female Genital Tuberculosis-PatelDocument37 pagesFemale Genital Tuberculosis-PatelRoxana Ioana DumitriuNo ratings yet
- Antioxidative Potential of Cynodon DactyloDocument5 pagesAntioxidative Potential of Cynodon Dactylochaitanya gNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesEndocrine SystemNick Bantolo100% (1)
- Clinical Evidence Lantus XR PDFDocument85 pagesClinical Evidence Lantus XR PDFPeter HoNo ratings yet
- 3 X 3 Faster Fat Loss DietDocument23 pages3 X 3 Faster Fat Loss DietShoaib MansuriNo ratings yet
- Catalogue: Oem/OdmDocument14 pagesCatalogue: Oem/OdmCarlito RiccyNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Raghav Dogra M.Pharm (Analysis) 2016-2017Document38 pagesPresented By: Raghav Dogra M.Pharm (Analysis) 2016-2017gggNo ratings yet
- Spec Modified Whey (Permeate) 13-0919Document2 pagesSpec Modified Whey (Permeate) 13-0919Adi TAM SBYNo ratings yet
- Individualization of Drug Dosage RegimenDocument34 pagesIndividualization of Drug Dosage RegimenPreethi Iyengar86% (7)
- ProteinsDocument64 pagesProteinsCHALIE MEQUNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Board ReviewDocument599 pagesPharmacology Board ReviewMelbhon Fabro RamosNo ratings yet
- History of Blood Banking Anticoagulants and PreservativesDocument27 pagesHistory of Blood Banking Anticoagulants and Preservativeslovi bahunNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Gland Disorders: Addison's DiseaseDocument4 pagesAdrenal Gland Disorders: Addison's DiseaseyoussraselimNo ratings yet
- Pathology 1016-Test 2 - Path 1Document3 pagesPathology 1016-Test 2 - Path 1Nicholas ObasiNo ratings yet
- Bedah 21 Nov 2022 + FU 19 Nov 22 + Patof.Document28 pagesBedah 21 Nov 2022 + FU 19 Nov 22 + Patof.maya_rosmariaNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Miscarriages Due to Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome (APSDocument83 pagesRecurrent Miscarriages Due to Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome (APSOmar Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals Toxicity and Deficiency GuideDocument3 pagesVitamins and Minerals Toxicity and Deficiency GuideRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet