Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 7 Math Teaching Guide Lesson 25: Special Products Time: 3.5 Hours Pre-Requisite Concepts: Addition and Multiplication of Polynomials Objectives
Uploaded by
Kez MaxOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 7 Math Teaching Guide Lesson 25: Special Products Time: 3.5 Hours Pre-Requisite Concepts: Addition and Multiplication of Polynomials Objectives
Uploaded by
Kez MaxCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
GRADE 7 MATH TEACHING GUIDE
Lesson 25: Special Products Time: 3.5 hours
Pre-requisite Concepts: Addition and Multiplication of Polynomials
Objectives:
In this lesson, you are expected to:
find (a) inductively, using models and (b) algebraically the
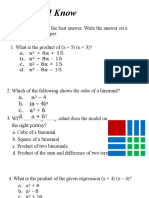
1. product of two binomials
2. product of a sum and difference of two terms
3. square of a binomial
4. cube of a binomial
5. product of a binomial and a trinomial
Lesson Proper:
A. Product of two binomials
I. Activity
Prepare three sets of algebra tiles by cutting them out from a page of newspaper or art paper. If you are using newspaper, color
the tiles from the first set black, the second set red and the third set yellow.
This activity uses algebra tiles to find a general formula for the product of two binomials. Have the students bring several
pages of newspaper and a pair of scissors in class. Ask them to cut at least 3 sheets of paper in the following pattern. Have them color
the pieces from one sheet black, the second red and the last one yellow.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 1
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
Problem:
1. What is the area of a square whose sides are 2cm?
2. What is the area of a rectangle with a length of 3cm and a width of 2cm?
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 2
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
3. Demonstrate the area of the figures using algebra tiles.
Solution:
1. 2cm x 2cm = 4cm2
2. 3cm x 2cm = 6cm2
3.
Tell the students that the large squares have dimensions of x units, the rectangles are x units by 1 unit and the small squares have a
side length of 1 unit.
Review with the students the area of a square and a rectangle. Have them determine the area of the large square, the rectangle
and the small square.
Problem:
1. What are the areas of the different kinds of algebra tiles?
2. Form a rectangle with a length of x + 2 and a width of x + 1 using the algebra tiles. What is the area of the rectangle?
Solution:
1. x2, x and 1 square units.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 3
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
2.
The area is the sum of all the areas of the algebra tiles.
Area = x2 + x + x + x + 1 + 1 = x2 + 3x + 2
Ask the students what the product of x + 1 and x + 2 is. Once they answer x2 + 3x + 2, ask them again, why is it the same as the
area of the rectangle. Explain that the area of a rectangle is the product of its length and its width and if the dimensions are represented
by binomials, then the area of the rectangle is equivalent to the product of the two binomials.
Problem:
1. Use algebra tiles to find the product of the following:
a.
b.
c.
2. How can you represent the difference x – 1 using algebra tiles?
Solution:
1.
a.
b.
c.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 4
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
2. You should use black colored tiles to denote addition and red colored tiles to denote subtraction.
Problem:
1. Use algebra tiles to find the product of the following:
a.
b.
c.
d.
Solution:
1.
The students should realize that the yellow squares indicate that they have subtracted that area twice using the red figures and
they should “add them” back again to get the product.
2.
3.
4.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 5
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
II. Questions to Ponder
1. Using the concept learned in algebra tiles what is the area of the rectangle shown below?
2. Derive a general formula for the product of two binomials .
The area of the rectangle is equivalent to the product of which is . This is the general formula for
the product of two binomials . This general form is sometimes called the FOIL method where the letters of FOIL stand
for first, outside, inside, and last.
Example: Find the product of (x + 3) (x + 5)
First: x . x = x2
Outside: x . 5 = 5x
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 6
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
Inside: 3 . x = 3x
Last: 3 . 5 = 15
(x + 3) (x + 5) = x2 + 5x + 3x + 15 = x2 + 8x + 15
III. Exercises
Find the product using the FOIL method. Write your answers on the spaces provided:
1. (x + 2) (x + 7) x2 + 9x + 14
2. (x + 4) (x + 8) x2 + 12x + 32
3. (x – 2) (x – 4) x2 – 6x + 24
4. (x – 5) (x + 1) x2 – 4x - 5
5. (2x + 3) (x + 5) 2x2 + 13x + 15
6. (3x – 2) (4x + 1) 12x2 – 5x - 2
7. (x2 + 4) (2x – 1) 2x3 – x2 + 8x - 4
8. (5x3 + 2x) (x2 – 5) 5x5 -23x3 – 10x
9. (4x + 3y) (2x + y) 8x2 + 10xy + 3y2
10. (7x – 8y) (3x + 5y) 21x2 + 11xy – 40y2
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 7
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
B. product of a sum and difference of two terms
I. Activity
1. Use algebra tiles to find the product of the following:
a. (x + 1) (x – 1)
b. (x + 3) (x – 3)
c. (2x – 1) (2x + 1)
d. (2x – 3) (2x + 3)
2. Use the FOIL method to find the products of the above numbers.
The algebra tiles should be arranged in this form.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 8
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 9
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
The students should notice that for each multiplication there are an equal number of black and red rectangles. This means that
they “cancel” out each other. Also, the red small squares form a bigger square whose dimensions are equal to the last term in the
factors.
Answers
1. x2 + x – x – 1 = x2 – 1
2. x2 + 3x – 3x – 9 = x2 – 9
3. 4x2 + 2x – 2x – 1 = 4x2 – 1
4. 4x2 + 6x – 6x – 9 = 4x2 – 9
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 10
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
II. Questions to Ponder
1. What are the products?
2. What is the common characteristic of the factors in the activity?
3. Is there a pattern for the products for these kinds of factors? Give the rule.
Concepts to Remember
The factors in the activity are called the sum and difference of two terms. Each binomial factor is made up of two terms. One
factor is the sum of the terms and the other factor being their difference. The general form is (a + b) (a – b).
The product of the sum and difference of two terms is given by the general formula
(a + b) (a – b) = a2 – b2.
III. Exercises
Find the product of each of the following:
1. (x – 5) (x + 5) x2 - 25
2. (x + 2) (x – 2) x2 - 4
3. (3x – 1) (3x + 1) 9x2 - 1
4. (2x + 3) (2x – 3) 4x2 - 9
5. (x + y2) (x – y2) x2 – y4
6. (x2 – 10)(x2 + 10) x4 - 100
7. (4xy + 3z3) (4xy – 3z3) 16x2y2 – 9z6
8. (3x3 – 4)(3x3 + 4) 9x6 - 16
9. [(x + y) - 1] [(x + y) + 1] (x + y)2 – 1 = x2 + 2xy + y2 - 1
10. (2x + y – z) (2x + y + z) (2x + y)2 – z2 = 4x2 + 4xy + y2 – z2
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 11
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
C. square of a binomial
I. Activity
1. Using algebra tiles, find the product of the following:
a. (x + 3) (x + 3)
b. (x – 2) (x – 2)
c. (2x + 1) (2x + 1)
d. (2x – 1) (2x – 1)
2. Use the FOIL method to find their products.
Answers:
1. x2 + 6x + 9
2. x2 – 4x + 4
3. 4x2 + 4x + 1
4. 4x2 - 4x + 1
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 12
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 13
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
II. Questions to Ponder
1. Find another method of expressing the product of the given binomials.
2. What is the general formula for the square of a binomial?
3. How many terms are there? Will this be the case for all squares of binomials? Why?
4. What is the difference between the square of the sum of two terms from the square of the difference of the same two terms?
Concepts to Remember
The square of a binomial is the product of a binomial when multiplied to itself. The square of a binomial has a
general formula, .
The students should know that the outer and inner terms using the FOIL method will be identical and can be combined to form
one term. This means that the square of a binomial will always have three terms. Furthermore, they should realize that the term b2 is
always positive while the sign of the middle term 2ab depends on whether the binomials are sums or differences.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 14
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
III. Exercises
Find the squares of the following binomials.
1. (x + 5)2 x2 + 10x + 25
2. (x - 5)2 x2 – 10x + 25
3. (x + 4)2 x2 + 8x + 16
4. (x – 4)2 x2 – 8x + 16
5. (2x + 3)2 4x2 + 12x + 9
6. (3x - 2)2 9x2 – 12x + 4
7. (4 – 5x)2 16 – 40x + 25x2
8. (1 + 9x)2 1 + 18x + 81x2
9. (x2 + 3y)2 x4 + 6x2y + 9y2
10. (3x3 – 4y2)2 9x6 – 24x6y4 + 16y4
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 15
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
D. Cube of a binomial
I. Activity
A. The cube of the binomial (x + 1) can be expressed as (x + 1)3. This is equivalent to
(x + 1)(x + 1)(x + 1).
1. Show that (x + 1)2 = x2 + 2x + 1.
2. How are you going to use the above expression to find (x + 1)3?
3. What is the expanded form of (x + 1)3?
Answers:
1. By using special products for the square of a binomial, we can show that (x + 1)2 = x2 + 2x + 1.
2. (x + 1)3 = (x + 1)2(x + 1) = (x2 + 2x + 1)(x + 1)
3. (x + 1)3 = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1
B. Use the techniques outlined above, to find the following:
1. (x + 2)2
2. (x – 1)2
3. (x – 2)2
Answers:
1. x3 + 6x2 + 12x + 8
2. x3 – 3x2 + 3x – 1
3. x3 – 6x2 + 12x – 8
This activity is meant to present the students with several simple examples of finding the cube of a binomial. They should then
analyze the answers to identify the pattern and the general rule in finding the cube of a binomial.
II. Questions to Ponder
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 16
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
1. How many terms are there in each of the cubes of binomials?
2. Compare your answers in numbers 1 and 2?
a. What are similar with the first term? How are they different?
b. What are similar with the second terms? How are they different?
c. What are similar with the third terms? How are they different?
d. What are similar with the fourth terms? How are they different?
3. Craft a rule for finding the cube of the binomial in the form (x + a)3. Use this rule to find (x + 3)3. Check by using the method
outlined in the activity.
4. Compare numbers 1 and 3 and numbers 2 and 4.
a. What are the similarities for each of these pairs?
b. What are their differences?
5. Craft a rule for finding the cube of a binomial in the form (x –a )3. Use this rule to find (x – 4)3.
6. Use the method outlined in the activity to find (2x + 5)3. Can you apply the rule you made in number 3 for getting the cube of
this binomial? If not, modify your rule and use it to find
(4x + 1)3.
Answers:
1. The cube of a binomial has four terms.
2. First, make sure that the students write the expanded form in standard form.
a. The first terms are the same. They are both x3.
b. The second terms have the same degree, x2. Their coefficients are different. (3 and 6).
c. The third terms have the same degree, x. Their coefficients are 3 and 12.
d. The fourth terms are both constants. The coefficients are 1 and 8.
Make sure that the students notice that the ratio of the coefficients of the terms are 1, 2, 4 and 8. These correspond to the
powers of the second term 20, 21, 22, and 23.
3. . Thus,
4. The pairs have similar terms, except that the second and fourth terms of (x-a)3 are negative while those of (x+a)3 are positive.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 17
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
5. . Thus, .
6. From numbers, 3 and 5, we can generalize the formula to . In (2x + 5)3, a = 2x and b = 5. Thus,
Concepts to Remember
The cube of a binomial has the general form, .
III. Exercises
Expand.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Answers
1.
2.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 18
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 19
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
D. Product of a binomial and a trinomial
I. Activity
In the previous activity, we have tried multiplying a trinomial with a binomial. The resulting product then had four terms. But,
the product of a trinomial and a binomial does not always give a product of four terms.
1. Find the product of and .
2. How many terms are in the product?
Answers:
The product is x3 + 1 and it has two terms. Tell the students that the product is a sum of two cubes and can be written as x3 +
13.
3. What trinomial should be multiplied to to get ?
Answers
The other factor should be x2 + x + 1. This question can be done step-by-step analytically. First, ask the students what the first
term should be and why. They should realize that the first term can only be x2, since multiplying it by x from (x – 1) is the only way to
get x3. Then, ask them what the last term should be and why. The only possible answer is 1, since that is the only way to get -1 in (x3 –
1) by multiplying by -1 in (x – 1). They should then be able to get that the middle term should be +x.
4. Is there a trinomial that can be multiplied to x – 1 to get x3 + 1?
Answers
There is none. To get the sum of two cubes, one of the factors should be the sum of the terms. Similarly, explain that to get the
difference of two cubes, one of the factors should be the difference of the terms.
5. Using the methods outlined in the previous problems, what should be multiplied to x + 2 to get
x3 + 8? Multiplied to x – 3 to get x3 – 27?
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 20
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
II. Questions to Ponder
Answers
(x2 – 2x + 4)(x + 2) = x3 + 8 and (x2 + 3x + 9)(x - 3) = x3 – 27
1. What factors should be multiplied to get the product x3 + a3? x3 – a3?
Answers
2. What factors should be multiplied to get 27x3 + 8?
Answers
Make the students discover that the previous formula can be generalized to . 27x3 + 8 = (3x)3 + 23;
a = 3x and b = 2. Thus,
[(3x)2 – (3x)(2) + 22](3x + 2) = (9x2 – 6x + 4)(3x + 2) = 27x3 + 8
Concepts to Remember
The product of a trinomial and a binomial can be expressed as the sum or difference of two cubes if they are in the following
form.
III. Exercises
A. Find the product.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 21
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
B. What should be multiplied to the following to get a sum/difference of two cubes? Give the product.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Answers
A.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 22
Grade 7 Math LESSON 25: SPECIAL PRODUCTS TEACHING GUIDE
6.
B.
1. ;
2. ;
3. ;
4. ;
5. ;
6. ;
7. ;
8. ;
Summary: You learned plenty of special products and techniques in solving problems that require special products.
AUTHOR: Rechilda Villame 23
You might also like
- Lesson Plan Factoring Quadratic TrinomialDocument10 pagesLesson Plan Factoring Quadratic TrinomialArjune Tadique Gajeto50% (2)
- Human CapitalDocument31 pagesHuman CapitalAmit Sharma100% (1)
- Different Types of Film AnalysisDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Film AnalysisKez MaxNo ratings yet
- 1920 - 0725 DEMO LESSON PLAN Problem Solving FactoringDocument4 pages1920 - 0725 DEMO LESSON PLAN Problem Solving FactoringEy Sy100% (1)
- Difference of Two Squares - Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesDifference of Two Squares - Lesson PlanMaria Nerissa Gomop-as100% (2)
- Accounts Receivable and Receivable FinancingDocument4 pagesAccounts Receivable and Receivable FinancingLui50% (2)
- Corporate LiquidationDocument2 pagesCorporate LiquidationKristienalyn De Asis33% (3)
- Notes-Full-Set-Slides Stock Market PDFDocument185 pagesNotes-Full-Set-Slides Stock Market PDFbijayrNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Lesson 25: Special Products Learning GuideDocument7 pagesGrade 7 Math Lesson 25: Special Products Learning GuideKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet in Mathematics 7 Quarter 2-Week 6: A. Product of Two BinomialsDocument8 pagesActivity Sheet in Mathematics 7 Quarter 2-Week 6: A. Product of Two BinomialsXyla Joy Perez100% (1)
- Unit 1: Module 1: SPECIAL PRODUCTS and FactorsDocument25 pagesUnit 1: Module 1: SPECIAL PRODUCTS and FactorsShirley Dela Cueva GolezNo ratings yet
- Dlplesson 2Document4 pagesDlplesson 2Ami RANo ratings yet
- g7 q2 Week6Document3 pagesg7 q2 Week6Michelle NavaNo ratings yet
- DLP-Math - Oct 2Document2 pagesDLP-Math - Oct 2Ma. Teresa SolivenNo ratings yet
- Recall: Perfect Squares Are Numbers or Expressions That Can Be ExpressedDocument5 pagesRecall: Perfect Squares Are Numbers or Expressions That Can Be ExpressedVijenne IsraelNo ratings yet
- Special Product Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSpecial Product Lesson PlanUmmo Labeebah BintKhosaynNo ratings yet
- Math7 Q2 Weeks5to8 Binded Ver1.0Document41 pagesMath7 Q2 Weeks5to8 Binded Ver1.0peachgirlgamersNo ratings yet
- Special ProductDocument18 pagesSpecial Productcyrose50% (2)
- M8 Q1W1D4 Contextualized-LP1Document3 pagesM8 Q1W1D4 Contextualized-LP1John Ray MacaspagNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document7 pagesWeek 8Luisa GarcillanNo ratings yet
- Math 8 1 - 31Document29 pagesMath 8 1 - 31Emvie Loyd Pagunsan-ItableNo ratings yet
- November 22, 2018Document2 pagesNovember 22, 2018Melanie PicaNo ratings yet
- 2Q Week 6Document31 pages2Q Week 6Jackie Claire GuiraNo ratings yet
- Take Note:: Miracle Light Christian Academy Casilagan, City of Ilagan, Isabela Mathematics 8Document4 pagesTake Note:: Miracle Light Christian Academy Casilagan, City of Ilagan, Isabela Mathematics 8Dennis PacursaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 in Math 8Document15 pagesModule 1 in Math 8Dexter CarpioNo ratings yet
- Math 7Document48 pagesMath 7Christine BalladNo ratings yet
- Grade 9-Completing The Square (J. Muyco)Document8 pagesGrade 9-Completing The Square (J. Muyco)CRISTOPHER BRYAN N. MAGAT100% (1)
- Mathlearnermodule 130708064103 Phpapp02 PDFDocument112 pagesMathlearnermodule 130708064103 Phpapp02 PDFnel baradiNo ratings yet
- Square of BinomialDocument7 pagesSquare of BinomialRosenia Santiago Pascual67% (6)
- I. Readings/Discussions:: Task 1: Product of Two BinomialsDocument6 pagesI. Readings/Discussions:: Task 1: Product of Two BinomialsSimple as thatNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1 (Grade 7 - Q3)Document4 pagesSummative Test 1 (Grade 7 - Q3)Aljohn Beltran NerzaNo ratings yet
- Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Math - 7 - Special Products - of - PolynomialsDocument6 pagesDetailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Math - 7 - Special Products - of - PolynomialsAiver BelgaNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Surigao: Key QuestionsDocument8 pagesSt. Paul University Surigao: Key QuestionsJen RonNo ratings yet
- DLP August 31, 2022Document3 pagesDLP August 31, 2022John leo ClausNo ratings yet
- DLL Demo TeachingDocument4 pagesDLL Demo TeachingAngelo Morcilla TiquioNo ratings yet
- Math8-Activity Worksheet-Week1Document10 pagesMath8-Activity Worksheet-Week1kiezelNo ratings yet
- Q1 L2 - Solving Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square RootsDocument5 pagesQ1 L2 - Solving Quadratic Equation by Extracting Square Rootseaster florenda buenaflorNo ratings yet
- 1-A. Special ProductDocument23 pages1-A. Special ProductAryne Luzano0% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan No. 1 Learning Area: Mathematics Quarter: Second Quarter Week: Grade Level: 7 Duration: 3 HoursDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan No. 1 Learning Area: Mathematics Quarter: Second Quarter Week: Grade Level: 7 Duration: 3 HoursJohn Eric TorinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in General MathematicsDerren Nierras Gaylo100% (1)
- Q1W2D1 From Sept 8 To 18Document7 pagesQ1W2D1 From Sept 8 To 18JacquelineNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7 LAS Q2 WEEK 6Document3 pagesMathematics 7 LAS Q2 WEEK 6arjo17122No ratings yet
- Special Products and Factors: I. Introduction and Focus QuestionsDocument121 pagesSpecial Products and Factors: I. Introduction and Focus QuestionsDexter CarpioNo ratings yet
- Math9 DLL Sep 11Document5 pagesMath9 DLL Sep 11Ace LagnitonNo ratings yet
- Revalidated - MATH - GR8 - QTR1-MODULE-3 - (28 Pages)Document28 pagesRevalidated - MATH - GR8 - QTR1-MODULE-3 - (28 Pages)Andrei MemanNo ratings yet
- Q1W2D2 From Sept 11 To 19Document8 pagesQ1W2D2 From Sept 11 To 19JacquelineNo ratings yet
- DLL-8 (WEEK 1, Day 2)Document6 pagesDLL-8 (WEEK 1, Day 2)Joyce NolosNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 8 Q1 W1 D2Document4 pagesDLL Math 8 Q1 W1 D2Domilyn ArienzaNo ratings yet
- DLL-8 (WEEK 1, Day 2)Document6 pagesDLL-8 (WEEK 1, Day 2)MARISSA CUIZONNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Math Mis G8Document24 pagesWeek 5 Math Mis G8Joseff Rey PizonNo ratings yet
- Product of The Sum and Difference of Two TermsDocument9 pagesProduct of The Sum and Difference of Two TermsLuffy Leyga100% (1)
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument78 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFJoni AboboNo ratings yet
- Q1W2D1 Sept 8Document11 pagesQ1W2D1 Sept 8JacquelineNo ratings yet
- DLP (Assessment and Learning 2)Document7 pagesDLP (Assessment and Learning 2)joniel ajeroNo ratings yet
- I-Objectives: Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument3 pagesI-Objectives: Lesson Plan in MathematicsCharlene RiveraNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment 7.2.3 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Directions: Choose The Correct Answer by Writing The Letter of Your ChoiceDocument4 pagesSummative Assessment 7.2.3 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Directions: Choose The Correct Answer by Writing The Letter of Your ChoiceGen-GenAlcantaraBaldadoNo ratings yet
- DLLromelyn 004Document3 pagesDLLromelyn 004Rey Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Week 4Document11 pagesMath 9 Week 48DG01Angeles, Anika EuniceNo ratings yet
- Special Products On Factoring PDFDocument26 pagesSpecial Products On Factoring PDFnel baradiNo ratings yet
- AA SL Topic 9 Exponential and LogarithmnsDocument19 pagesAA SL Topic 9 Exponential and LogarithmnsPaco WongNo ratings yet
- TEST I. Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer. NO ERASUREDocument1 pageTEST I. Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer. NO ERASUREJennyzylNo ratings yet
- Let's Review Regents: Algebra II Revised EditionFrom EverandLet's Review Regents: Algebra II Revised EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Internet AdvertisingDocument6 pagesInternet AdvertisingKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning, Strategic Leadership, Challenges To Strategic Decision MakingDocument13 pagesStrategic Planning, Strategic Leadership, Challenges To Strategic Decision MakingKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: StramanDocument14 pagesStrategic Management: StramanKez MaxNo ratings yet
- A Schema TheoryDocument15 pagesA Schema TheoryKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Cheryle Harrington Baker College BUS 3710 Maximizing Shareholder Value EssayDocument5 pagesCheryle Harrington Baker College BUS 3710 Maximizing Shareholder Value EssayKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes Midterm 1Document2 pagesChapter 1 Notes Midterm 1Kez MaxNo ratings yet
- Compound Prepositions: Aside From Singing, She Also Plays The Piano at The BarDocument2 pagesCompound Prepositions: Aside From Singing, She Also Plays The Piano at The BarKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Theory of Multimedia LearningDocument5 pagesCognitive Theory of Multimedia LearningKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Albert Bandura's Social Learning TheoryDocument9 pagesAlbert Bandura's Social Learning TheoryKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Preposition Basics: Prepositions of DirectionDocument3 pagesPreposition Basics: Prepositions of DirectionKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Ending A Sentence With A PrepositionDocument2 pagesEnding A Sentence With A PrepositionKez MaxNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument9 pagesDocxKez MaxNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Partnership LiquidationDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Partnership LiquidationKez MaxNo ratings yet
- National Mock Board Examination 2017 Auditing: A. Consolidated Net Profit After Tax Attributable To ParentDocument13 pagesNational Mock Board Examination 2017 Auditing: A. Consolidated Net Profit After Tax Attributable To ParentKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Business TransactionsDocument8 pagesAccounting For Business TransactionsKez Max100% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: Consignment SalesDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Consignment SalesKez MaxNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Quiz On Receivable FinancingDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Quiz On Receivable FinancingKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Total Assets 937,500 Total Liab &she 937,500Document14 pagesProblem 1: Total Assets 937,500 Total Liab &she 937,500Kez MaxNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Assets Liabilities and CapitalDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Assets Liabilities and CapitalKez MaxNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods .PPT by AnindyaDocument49 pagesBusiness Research Methods .PPT by Anindyaanindya_kundu87% (23)
- HEAT TRANSFER - Chapter 2Document2 pagesHEAT TRANSFER - Chapter 2ghostlenyNo ratings yet
- More Types, Methods, ConditionalsDocument43 pagesMore Types, Methods, ConditionalsFrancene AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Assignment I OS II AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesAssignment I OS II AlgorithmsBca bcaNo ratings yet
- A Multiservice Traffic Allocation Model For LEO Satellite Communication NetworksDocument7 pagesA Multiservice Traffic Allocation Model For LEO Satellite Communication NetworksYounis AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01: Basic Mathematics and Logarithm - ModuleDocument24 pagesChapter 01: Basic Mathematics and Logarithm - ModuleSuraj100% (1)
- Pre Calculus Week 1 9Document75 pagesPre Calculus Week 1 9Lukas AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional Nonlinear Seismic Ground Motion Modeling in BasinsDocument15 pagesThree-Dimensional Nonlinear Seismic Ground Motion Modeling in BasinsPCPCNo ratings yet
- Yuri Abramovich Je Ffrey Banks Taesung Kim Richard Mckelvey: in MemoriamDocument4 pagesYuri Abramovich Je Ffrey Banks Taesung Kim Richard Mckelvey: in Memoriamtodur ganartNo ratings yet
- Goh Et Al-2017-Journal of Computational ChemistryDocument17 pagesGoh Et Al-2017-Journal of Computational ChemistryiplabaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Through Porous MediaDocument28 pagesFluid Flow Through Porous MediadebNo ratings yet
- ENEE 660 HW Sol #3Document13 pagesENEE 660 HW Sol #3PeacefulLion100% (1)
- Astro CyclesDocument5 pagesAstro Cyclespaparock34100% (1)
- Using Cost-Time Profile For Value Stream OptimizationDocument9 pagesUsing Cost-Time Profile For Value Stream OptimizationBagas KaraNo ratings yet
- DEF2 - Directional Earth-Fault Protection Low-Set Stage (DEF2Low) High-Set Stage (DEF2High) Instantaneous Stage (DEF2Inst)Document32 pagesDEF2 - Directional Earth-Fault Protection Low-Set Stage (DEF2Low) High-Set Stage (DEF2High) Instantaneous Stage (DEF2Inst)rajeshNo ratings yet
- CAISSON VHM LateralDocument6 pagesCAISSON VHM LateralgarysootetNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Q2-Week 5-8Document23 pagesMath 6 Q2-Week 5-8REYNALDO PACLETANo ratings yet
- SIP Action Plan OverviewDocument2 pagesSIP Action Plan OverviewfionaphimisterNo ratings yet
- PHYTECH124 Week10-11Document12 pagesPHYTECH124 Week10-11May Ann RiveraNo ratings yet
- Matlab Module 1Document264 pagesMatlab Module 1Mohammed MansoorNo ratings yet
- STPDF2 - Descriptive StatisticsDocument74 pagesSTPDF2 - Descriptive StatisticsEunnicePanaligan100% (1)
- Quantum Field Theory: HistoryDocument22 pagesQuantum Field Theory: HistoryAtikshaNo ratings yet
- 0012 MACH-Pro SeriesDocument2 pages0012 MACH-Pro SeriesLê Quốc KhánhNo ratings yet
- Amagat's Law: Ideal Gas MixtureDocument2 pagesAmagat's Law: Ideal Gas MixtureAar AeyNo ratings yet
- Operations On Large Numbers - Part 9Document11 pagesOperations On Large Numbers - Part 9Sunil NagarNo ratings yet
- Class Presentation 1Document112 pagesClass Presentation 1Nirai MathiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document31 pagesModule 1Aldrin CruzNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - IETE AMIETE ET-CS-IT (Old Scheme) Signals and Systems Sample Paper 1Document4 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - IETE AMIETE ET-CS-IT (Old Scheme) Signals and Systems Sample Paper 1Jonas ParreñoNo ratings yet