100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views2 pagesMusculoskeletal System Overview
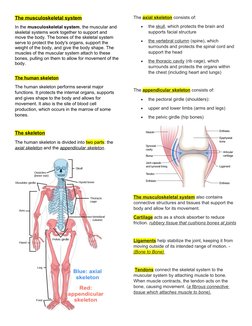
The musculoskeletal system consists of the skeletal and muscular systems. The skeletal system includes the axial skeleton (skull, vertebral column, rib cage) and appendicular skeleton (shoulders, arms, legs, pelvis). Bones provide structure, protect organs, and allow for movement through attachment to muscles via tendons. Muscles contract to pull on bones and enable both voluntary and involuntary motion. Together, the skeleton and muscles support the body, allow movement, and perform critical functions like circulation.
Uploaded by
James Wilstar Delicano SandovalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views2 pagesMusculoskeletal System Overview
The musculoskeletal system consists of the skeletal and muscular systems. The skeletal system includes the axial skeleton (skull, vertebral column, rib cage) and appendicular skeleton (shoulders, arms, legs, pelvis). Bones provide structure, protect organs, and allow for movement through attachment to muscles via tendons. Muscles contract to pull on bones and enable both voluntary and involuntary motion. Together, the skeleton and muscles support the body, allow movement, and perform critical functions like circulation.
Uploaded by
James Wilstar Delicano SandovalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Musculoskeletal System: Describes the structure and functions of the musculoskeletal system including the skeleton, tendons, and ligaments.
- Muscles: Explains different types of muscle tissues including skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, with their specific functions in the body.