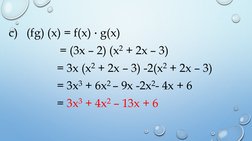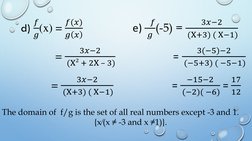0% found this document useful (0 votes)
872 views17 pagesLesson 4 Operations On Functions
The document discusses operations on functions including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition of functions. It provides examples of performing these operations on specific functions and simplifying the results. These operations include finding the sum, difference, product, and quotient of two functions f(x) and g(x), as well as the composition of functions f(g(x)) and g(f(x)). Practice problems are provided to apply these operations on given functions.
Uploaded by
Celestine LunaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
872 views17 pagesLesson 4 Operations On Functions
The document discusses operations on functions including addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition of functions. It provides examples of performing these operations on specific functions and simplifying the results. These operations include finding the sum, difference, product, and quotient of two functions f(x) and g(x), as well as the composition of functions f(g(x)) and g(f(x)). Practice problems are provided to apply these operations on given functions.
Uploaded by
Celestine LunaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Operations on Functions: Introduces the main topic of the document, focusing on mathematical operations involving functions, acting as an entry title with no additional text.
- Objectives: Outlines the learning goals, including performing operations on functions and active participation in discussions.
- Sum, Difference, Product and Quotient of Functions: Explains basic operations on two functions including their sum, difference, product, and quotient with definitions and formulae.
- Composition of Functions: Discusses the concept of function composition and how one function acts within another, using notation and a definition.
- Activity 4: Activity designed to reinforce learning by having students perform operations on functions and simplify answers with a given set of problems.
- Practice: Provides links to online practice resources for additional exercises and tests on the topic.
- Synthesis: Summarizes key concepts of operations on functions, including sum, difference, product, quotient, and composition, providing important formulas.
- Valuing: Encourages active participation and sharing among students during class discussions to enhance learning experience.