Professional Documents
Culture Documents
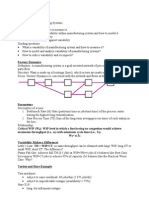
Input Rate (Unit/hr) Throughput Rate Output Rate (Unit/hr) Min (Demand, Capacity)
Input Rate (Unit/hr) Throughput Rate Output Rate (Unit/hr) Min (Demand, Capacity)
Uploaded by
Tanvi S PurohitOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Input Rate (Unit/hr) Throughput Rate Output Rate (Unit/hr) Min (Demand, Capacity)
Input Rate (Unit/hr) Throughput Rate Output Rate (Unit/hr) Min (Demand, Capacity)
Uploaded by
Tanvi S PurohitCopyright:
Available Formats
Demand Rate = Input Rate (Unit/hr)
Flow Rate = Throughput Rate = Output Rate (Unit/hr) = Min (Demand, Capacity)
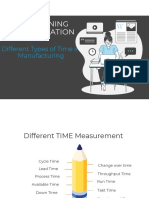
Flow Time
o Total Time of Process
o Time between entry and exit for a unit output
o Also called as Throughput time.
o This is end-to-end time for one unit of output.
Cycle Time
Individual Cycle time = Cycle time between 2 consecutive exits/completion for individual
process.
Process cycle time = Cycle time between 2 consecutive exits/completion of process as a whole
o Inverse of Throughput Rate/Output rate or Capacity
o Time between 2 consecutive departures.
o It can be at individual task level and at process level.
o NOTE:
Cycle time of individual process is Individual cycle time
Cycle time of final output is Cycle time of process.
o Process Cycle Time = Max of all the individual cycle time.
Capacity (Units/hr)
Maximum output rate (It’s not absolute number but rate)
Capacity = Total Time/ Cycle Time
NOTE:
Flow time can be changed by changing any of the process or making processes to run
parallel. But to change the Capacity, we must improve the bottleneck resource only.
Resource with highest cycle time is bottleneck. This is also the one with lowest capacity in
individual tasks.
Implied Utilization (IU)
Implied Utilization = Demand / Capacity * 100
o This can be more than 100%
o Resource with highest implied utilization is a bottleneck
Also, IU = Total Required / Total Available
Actual Utilization (AU)
Actual Utilization = Flow rate / Capacity * 100
= Min (Demand, Capacity) / Capacity.
o This is always <= 100
Utilization Profile:
Utilization calculated for all the resources and all the activities entered in the process diagram.
Little’s Law
Inventory = Flow Rate * Flow Time
Total Time
Total Time = Wait Time + Process Time
Waiting Time
W = V(f) * U(f) * T(f)
o V(f) – Variability Factor
o U(f) – Utilization Factor
o T(f) – Time Factor
Coefficient of Variability
Coefficient of Variability = Standard Deviation (SD) / Mean
Processes for solving any case
1. Identify and Draw the process diagram first.
2. Identify the flow unit
3. Identify resource and its capacity
4. Identify the Input Demand
5. Identify cycle time at each step
6. Calculate IU (Implied Utilization)
a. IU should be calculated based on Demand always assuming theoretically demand
will always be fulfilled.
b. The process with highest IU is the bottleneck.
7. Try to add resource at bottleneck and see the impact of same.
8. Consider the cost associated with adding the resource and see value obtained by adding
more resources is greater than the loss without it. If so, continue else drop that approach.
You might also like
- Matching Supply With Demand Solutions To End of Chapter Problems 4Document6 pagesMatching Supply With Demand Solutions To End of Chapter Problems 4Omar Al-azzawi100% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Production ConceptsDocument16 pagesLecture 3 - Production ConceptsFatimaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Swift Even FlowDocument12 pagesTheory of Swift Even FlowNgiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document11 pagesChapter 4Gabriel Garza100% (4)
- Theory of ConstraintsDocument30 pagesTheory of Constraintsapi-3696776100% (5)
- Chapter 5Document8 pagesChapter 5Gabriel Garza100% (1)
- Fatigue Assessment of Offshore Structures Commentary On The Guide For TheDocument76 pagesFatigue Assessment of Offshore Structures Commentary On The Guide For TheElvis Osorio SantanderNo ratings yet
- OPIM Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesOPIM Cheat Sheet PDFjoe91bmwNo ratings yet
- MGT 3121Document18 pagesMGT 3121Christina RomanoNo ratings yet
- MGT Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMGT Cheat SheetChristina RomanoNo ratings yet
- AutoRecovery Save of Managing Operations - Chapte3Document3 pagesAutoRecovery Save of Managing Operations - Chapte3Aisha Almazrouee92No ratings yet
- Process AnalysisDocument32 pagesProcess Analysisur23095No ratings yet
- OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT EditedDocument12 pagesOPERATIONS MANAGEMENT EditedAnil BallaNo ratings yet
- Process FundamentalsDocument6 pagesProcess Fundamentalsadithi.manjunath1No ratings yet
- Process Analysis 202021 R1Document39 pagesProcess Analysis 202021 R1kamals55No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Flow Rate and Capacity 1-16-10Document27 pagesChapter 5 Flow Rate and Capacity 1-16-10Cucak RowoNo ratings yet
- Short Keys and Formulas of ExcelDocument40 pagesShort Keys and Formulas of ExcelSattar CANo ratings yet
- Module 02 UpdatedDocument51 pagesModule 02 Updatedjano.alamoudiNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Models and MetricsDocument41 pagesManufacturing Models and MetricsHildandi NlgögmhnNo ratings yet
- Flow Concepts: Source: Managing Business Process Flows by Anupindi, Et AlDocument7 pagesFlow Concepts: Source: Managing Business Process Flows by Anupindi, Et AlKausik KskNo ratings yet
- Opim Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesOpim Cheat Sheetjoe91bmwNo ratings yet
- Operation Exam NotesDocument16 pagesOperation Exam NotesZaki KamardinNo ratings yet
- Measuring Performance Metrics For Time, Rate, Cost, Quality, Flexibility, and The Environment Tim Gutowski, July 8, 2002Document10 pagesMeasuring Performance Metrics For Time, Rate, Cost, Quality, Flexibility, and The Environment Tim Gutowski, July 8, 2002ivan morelNo ratings yet
- Note On Process Analysis 2012Document5 pagesNote On Process Analysis 2012Jordan_Fernand_1149No ratings yet
- Process Analysis: By: Dennis Arthur S. LeonorDocument20 pagesProcess Analysis: By: Dennis Arthur S. LeonorKhy Nellas-LeonorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3Gabriel Garza100% (4)
- SDM 5001 Systems Architecture: Production Process AnalysisDocument38 pagesSDM 5001 Systems Architecture: Production Process AnalysisanonNo ratings yet
- Mba 8155 SlidESDocument12 pagesMba 8155 SlidESchethan626No ratings yet
- Process Analysis: Introduction / The Three MeasuresDocument47 pagesProcess Analysis: Introduction / The Three MeasuresRohitNo ratings yet
- Session2 - Slides1 - Evaluating - Process - Capacity, Flow RateDocument14 pagesSession2 - Slides1 - Evaluating - Process - Capacity, Flow RateNikhil ParasharNo ratings yet
- Session 4-5 - Process Management and Process AnalysisDocument31 pagesSession 4-5 - Process Management and Process Analysischandel08No ratings yet
- SCM-MRP-4-Process Analysis & Break Even (REVIEW) - 22 Mar 2019Document30 pagesSCM-MRP-4-Process Analysis & Break Even (REVIEW) - 22 Mar 2019Kelas B Tekdus UPNVJ 2016No ratings yet
- Module 01 NumericalsDocument12 pagesModule 01 NumericalsRahulNo ratings yet
- ASM-Chapter 3 With NotesDocument15 pagesASM-Chapter 3 With NotessmritiNo ratings yet
- Stanley 2Document30 pagesStanley 2Deepak PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Process Analysis IIDocument22 pagesProcess Analysis IITianzhu Sylvia LeiNo ratings yet
- Process AnalysisDocument4 pagesProcess AnalysisAgemo MicksNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 ReviewDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 ReviewAndrew PhilipsNo ratings yet
- ASM-Chapter 04 With NotesDocument28 pagesASM-Chapter 04 With NotessmritiNo ratings yet
- 20 Produccion MetricsDocument12 pages20 Produccion MetricsCristopher Jimenez JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Design of Operations Services P2 VEDocument27 pagesDesign of Operations Services P2 VEAbdelhak OuanzouguiNo ratings yet
- 7th Sem Cim Module-III 3.2Document19 pages7th Sem Cim Module-III 3.2Abdul GaffarNo ratings yet
- Basic Process Analysis ConceptsDocument7 pagesBasic Process Analysis ConceptsJoseAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Process AnalysisDocument26 pagesProcess AnalysisSankha BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Process AnalysisDocument39 pagesProcess AnalysisShatrujit GurayaNo ratings yet
- MPC 5 2003Document35 pagesMPC 5 2003pinakindpatelNo ratings yet
- 3 Process AnalysisDocument25 pages3 Process Analysisvlvllxxvii6677No ratings yet
- Formulas PDFDocument4 pagesFormulas PDFRj KumarNo ratings yet
- Variable Loads: Von Eric Damirez, Me, MSCDocument14 pagesVariable Loads: Von Eric Damirez, Me, MSCAnonymous cuVSFiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Cycle Time and ProductivityDocument2 pagesLesson 8 Cycle Time and ProductivityrosarionaritNo ratings yet
- 02b. Manufacturing OperationsDocument27 pages02b. Manufacturing OperationsUnmesh UnnikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Time in ManufacturingDocument15 pagesDifferent Types of Time in ManufacturingkazuNo ratings yet
- Opm 4Document26 pagesOpm 4satyam mehrotraNo ratings yet
- Capacity Planning The First Encounter With The Bottleneck The Achilles' Heel in The Business ProcessesDocument22 pagesCapacity Planning The First Encounter With The Bottleneck The Achilles' Heel in The Business Processesglen_beckNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Numerical Analysis For Productivity ImprovementDocument34 pagesWeek 11 - Numerical Analysis For Productivity ImprovementNguyễn Ngọc Minh QuânNo ratings yet
- Lean Production: Week 4: StandardizationDocument34 pagesLean Production: Week 4: StandardizationQuynh Chau TranNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Manufacturing Operations: SectionsDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Manufacturing Operations: SectionsSaeed AlshamsiNo ratings yet
- Prof. Arun MishraDocument21 pagesProf. Arun MishraArun MishraNo ratings yet
- " " by Eliyahu Goldratt: The GoalDocument50 pages" " by Eliyahu Goldratt: The GoalpeanutsmonkeyNo ratings yet
- Takt Time: A Guide to the Very Basic Lean CalculationFrom EverandTakt Time: A Guide to the Very Basic Lean CalculationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Computers UnlimitedDocument8 pagesComputers UnlimitedTanvi S PurohitNo ratings yet
- Exer 4 QDMDocument5 pagesExer 4 QDMTanvi S PurohitNo ratings yet
- Description Remark Actuator Sensor: Cycle Time: 135Document6 pagesDescription Remark Actuator Sensor: Cycle Time: 135Tanvi S PurohitNo ratings yet
- Some Problems With SolutionsDocument16 pagesSome Problems With SolutionsTanvi S PurohitNo ratings yet
- Input Data in Only Purple Cells: Graphical Representation With Intersection PointsDocument4 pagesInput Data in Only Purple Cells: Graphical Representation With Intersection PointsTanvi S PurohitNo ratings yet
- First Read The Case Completely. PL Do Not Use Pencil To Write Final AnswersDocument3 pagesFirst Read The Case Completely. PL Do Not Use Pencil To Write Final AnswersTanvi S PurohitNo ratings yet
- Interviewing CandidatesDocument9 pagesInterviewing CandidatesTanvi S PurohitNo ratings yet
- Session # 3 and 4Document11 pagesSession # 3 and 4ajith vNo ratings yet
- Ranking Resistance of Materials To Sliding Wear Using Block-on-Ring Wear TestDocument11 pagesRanking Resistance of Materials To Sliding Wear Using Block-on-Ring Wear TestNav Talukdar100% (1)
- 7 B Content Quant QC PDFDocument13 pages7 B Content Quant QC PDFFarhan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Safety InventoryDocument4 pagesSafety InventoryShivraj GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Limitations in Analytical AccuracyDocument6 pagesLimitations in Analytical AccuracyImmerNo ratings yet
- Assessment For Learning Unit 10: Technological Based Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Learning OutcomesDocument56 pagesAssessment For Learning Unit 10: Technological Based Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Learning OutcomesPriyaNo ratings yet
- Mean, Mode, Median, and Standard DeviationDocument17 pagesMean, Mode, Median, and Standard DeviationBryan BaraNo ratings yet
- Brochure Microlab 300Document6 pagesBrochure Microlab 300Shaheen Tabbassum0% (1)
- Kelompok 5 - Biostatistik IntermedietDocument8 pagesKelompok 5 - Biostatistik Intermedietaisya maulianaNo ratings yet
- 11 Economics - Measures of Dispersion - Notes and Video LinksDocument8 pages11 Economics - Measures of Dispersion - Notes and Video LinksNIMMANAGANTI RAMAKRISHNANo ratings yet
- ASTM D5199 Nominal ThicknessDocument4 pagesASTM D5199 Nominal ThicknessCharleneTaneoNo ratings yet
- 2-Analysis of Risk Among AgribusnessDocument8 pages2-Analysis of Risk Among AgribusnessHilda Anugrah PutriNo ratings yet
- 2 Despersion NewDocument2 pages2 Despersion NewABINAYA BNo ratings yet
- Multi XL Sop em 360 NDocument68 pagesMulti XL Sop em 360 NSowji PNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics PrinceDocument33 pagesDescriptive Statistics PrincepRiNcE DuDhAtRa100% (1)
- Workshop 3Document30 pagesWorkshop 3Jeevika BasnetNo ratings yet
- Parameters of Quality ControlDocument42 pagesParameters of Quality ControlKathlyn GraceNo ratings yet
- RCBDDocument55 pagesRCBDHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of BanksDocument60 pagesComparative Study of BanksBaidyanath Kumar47% (15)
- The Correlation Between Age and MemoryDocument10 pagesThe Correlation Between Age and MemoryCamille LuceloNo ratings yet
- Mann Kendall Statistic and COVDocument11 pagesMann Kendall Statistic and COVMayankNo ratings yet
- Conducting An Interlaboratory Study To Determine Precision Estimates For A Fire Test Method With Fewer Than Six Participating LaboratoriesDocument6 pagesConducting An Interlaboratory Study To Determine Precision Estimates For A Fire Test Method With Fewer Than Six Participating LaboratoriesAhmad Zubair Rasuly100% (1)
- Statistics w1Document43 pagesStatistics w1Muhammad Saddam SofyandiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Risk and Return: Prof. Dr. Tamer Mohamed ShahwanDocument24 pagesChapter 6: Risk and Return: Prof. Dr. Tamer Mohamed ShahwanDalia ElarabyNo ratings yet
- Advance Monthly Sales For Retail and Food Services, January 2023Document7 pagesAdvance Monthly Sales For Retail and Food Services, January 2023dali layouniNo ratings yet
- Market Price Index - Q2 2023 04.04.2023-Lstone Final 09.39cDocument107 pagesMarket Price Index - Q2 2023 04.04.2023-Lstone Final 09.39cMazubaNo ratings yet
- Ch26 Tool KitADocument21 pagesCh26 Tool KitARoy HemenwayNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Sampling Error and Sampling Precision in Resource Estimation - A DiscussionDocument24 pagesFundamental Sampling Error and Sampling Precision in Resource Estimation - A DiscussionMega Putri ArisandaNo ratings yet
- Normas ASTM G 57 - 06Document5 pagesNormas ASTM G 57 - 06Andrés Leonardo García MuñozNo ratings yet