Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment No-3 (Optical Fibre Lab)
Uploaded by
EC-007-18 AhmadRazaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment No-3 (Optical Fibre Lab)
Uploaded by
EC-007-18 AhmadRazaCopyright:
Available Formats
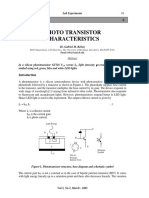
OBJECT 03: TO STUDY THE CHARACTERTSTTCS OF A PHOTO TRANSTSTOR
THEORY
Photo Transistor
A bipolar photo transistor (also known as a photo diode is a threeJayer device having its
base region exposed to illumination. Both n-p-n and p-n-p devices are manufactured. They
are usually connected in the common emitter conflguration, and may either have the base
connection open-circuit or be connected through a resistance to the common line. ln some
cases it is possible to forward bias the transistor. ln a basic circuit incorporating an n-p-n
photo transistor the collector current in the absence of illumination is, Ig (hpE + 1) ICBO
=
when illuminated, electron hole pairs are generated in the base region and by transistor
action the new value of collector current
Ic = (hEF + 1) (IcBo + Ip)
where Ip = photo current component of base current. The characteristics of a photo
transistor are as shown in Fig 5(a).
COLLECTOR
CURRENT
+v (voLTS)
COLLECTOR VOLTACE
FlG.5 (a) OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS OF A PHOTO TRANSTSTOR
Note : Photo transistor is provided on the panel.
PROCEDURE FOR THE EXPERIMENT
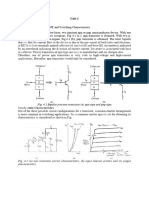
01 Assemble the circuit as shown in Fig.S(b). Check for circuit assembled, and switch ON
the supply to the ETB.
S.N. Voltage Current (uA)
(v)
Lrl Lt2 Lt3
01
02
PHOTO
03
04
05
FrG. 5 (b) C|RCU|T FOR CHARACTERTSTTCS OF A PHOTO TRANSTSTOR
02 Repeat the STEP no. (2) of experiment no. 2.
03 Place the ETB under a table lamp so that the light falls directly on the face of the photo
transistor fitted on the panel. Switch on the table lamp.
04 Take readings of collector voltage (Vc) & corresponding collector current (lc).
05 Plot the above readings on the graph paper.
06 Now change the light intensity falling on the photo transistor by varying the voltage of
table lamp with the help of variac and again take readings of Vc & lc. Plot different sets
of readings on the same graph. The graph will be (approx.) similar to as shown in Fig
5(a).
You might also like
- Opto Electronic Devices Characteristic - IDocument6 pagesOpto Electronic Devices Characteristic - IPatel ParthNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor Characteristics EELE101 LaboratoryDocument11 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor Characteristics EELE101 LaboratoryHanieft NdNo ratings yet
- Photo TransistorDocument8 pagesPhoto TransistorCk LNo ratings yet
- Unijunction Transistor: by Matthew H. Williams Back To TheDocument6 pagesUnijunction Transistor: by Matthew H. Williams Back To TheRachmat Guntur Dwi PutraNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices - Part2Document12 pagesSemiconductor Devices - Part2Venugopal kulkarniNo ratings yet
- Lab 08Document3 pagesLab 08Juan TarquiNo ratings yet
- Lab 09FDocument5 pagesLab 09FUmar AyubNo ratings yet
- Find UJT Static Emitter Characteristics and Study The Variation in Peak Point and Valley PointDocument4 pagesFind UJT Static Emitter Characteristics and Study The Variation in Peak Point and Valley PointNikhil BindalNo ratings yet
- Simulation of BJT Amplifier: Course - Section: ECE20L-E06 Group NumberDocument10 pagesSimulation of BJT Amplifier: Course - Section: ECE20L-E06 Group NumberLuch ÜNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment # 05: To Study The Characteristics of UJT Relaxation OscillatorDocument5 pagesLab Assignment # 05: To Study The Characteristics of UJT Relaxation OscillatorintelsarNo ratings yet
- L-3 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 5Document5 pagesL-3 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 5GagneNo ratings yet
- EEC201L Circuits 2 (Lab) : ExerciseDocument6 pagesEEC201L Circuits 2 (Lab) : ExerciseNicoNo ratings yet
- Edc Lab Manuals Third SemesterDocument56 pagesEdc Lab Manuals Third SemesterSprout GigsNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 01: To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law ForDocument56 pagesExperiment No. 01: To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law ForKaushik NNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 BJT SwitchDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 BJT Switchprop_kcp50% (2)
- Current Mirrors: Basic BJT Current MirrorDocument8 pagesCurrent Mirrors: Basic BJT Current MirrorjagruthimsNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 1 - Diode v2021Document4 pagesPre-Lab 1 - Diode v2021محمد ابو جرادNo ratings yet
- Lab ExperimentDocument7 pagesLab ExperimentBryan Owen Salcedo SantosNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Part-3Document11 pagesUnit-2 Part-3rogithprathapNo ratings yet
- (Ce) Transistor Characteristics in Common Emitter ConfigurationDocument7 pages(Ce) Transistor Characteristics in Common Emitter Configurationjassisc100% (1)
- Impedance of RL Circuits: Series RL Circuits: Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesImpedance of RL Circuits: Series RL Circuits: Experiment No. 2NicoNo ratings yet
- Viitanen 2003Document6 pagesViitanen 2003gerson gomesNo ratings yet
- Uni-Junction Transistor (UJT), Lecture - 3, TDC Part - I, Paper - I, (Group - B), Chapter - 8, by - Dr. Niraj KumarDocument19 pagesUni-Junction Transistor (UJT), Lecture - 3, TDC Part - I, Paper - I, (Group - B), Chapter - 8, by - Dr. Niraj Kumaranshulsrh5656No ratings yet
- Properties of The Feedback Loop: Technical University of Gdańsk Department of Medical and Ecological ElectronicsDocument14 pagesProperties of The Feedback Loop: Technical University of Gdańsk Department of Medical and Ecological ElectronicsValentin ValoNo ratings yet
- Unit 12Document23 pagesUnit 12Hello worldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - BJTDocument102 pagesChapter 3 - BJTFarish IskandarNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Differentiator & IntegratorDocument14 pagesLab 4 - Differentiator & IntegratorVickneswaran KalerwananNo ratings yet
- Untitled PDFDocument10 pagesUntitled PDFmukeshNo ratings yet
- Wat MetersDocument13 pagesWat MetersKornepati SureshNo ratings yet
- 301 Lab 4Document17 pages301 Lab 4dkishoreNo ratings yet
- BMEN 3120 Transistor Circuits: Ami Shah 9/29/2015Document11 pagesBMEN 3120 Transistor Circuits: Ami Shah 9/29/2015Ami ShahNo ratings yet
- Transistors: K. Branzuela, E. Ocaba, G.L. PeigDocument6 pagesTransistors: K. Branzuela, E. Ocaba, G.L. PeigAmiyah GlorielleNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Introduction of BJTDocument56 pagesUnit-I: Introduction of BJThodeegits9526No ratings yet
- EEC ActivityDocument19 pagesEEC ActivityKerwin James AustriaNo ratings yet
- VCO AnalysisDocument14 pagesVCO Analysiskok6100% (2)
- Power Electronics محاضراتDocument159 pagesPower Electronics محاضراتHasan Al-asadiNo ratings yet
- Lab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Document11 pagesLab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Ece KayaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Lab No: 1: ExperimentDocument4 pagesLab No: 1: Experimentkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT NO. 1: Verification of The Integrity of The Junctions of A BJT Transistor I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT NO. 1: Verification of The Integrity of The Junctions of A BJT Transistor I. ObjectivesschoolNo ratings yet
- EE Lab ManualDocument23 pagesEE Lab ManualMoordhan SongadeNo ratings yet
- Itmf 2013-07-1 Freiburg EnuDocument6 pagesItmf 2013-07-1 Freiburg EnubcqbaoNo ratings yet
- Ec2155 Lab ManualDocument32 pagesEc2155 Lab ManualSuresh Ponnusamy50% (2)
- Module 4 NotesDocument19 pagesModule 4 Notes4JN20ME039 - Sindhu H KNo ratings yet
- EXP7Document12 pagesEXP7Hero CourseNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab ManualDocument46 pagesEDC Lab ManualMOUNIRAGESHNo ratings yet
- Figure 1a Figure 1bDocument33 pagesFigure 1a Figure 1bKarimovaRaikhanovnaNo ratings yet
- Lab 07Document3 pagesLab 07Juan TarquiNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 TransistorDocument8 pagesLab 9 TransistorChing Wai YongNo ratings yet
- Single-Stage BJT Amplifiers: Experiment-2Document19 pagesSingle-Stage BJT Amplifiers: Experiment-2karan007_mNo ratings yet
- Open Ended 1Document12 pagesOpen Ended 1AneeshaNo ratings yet
- Experiment in Basics of Electronic TechnologyDocument9 pagesExperiment in Basics of Electronic TechnologyMahedi HassanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 10 Verifying Characteristics of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) ObjectiveDocument10 pagesExperiment No 10 Verifying Characteristics of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) ObjectiveMuhammad Arslan AfzalNo ratings yet
- AQRspicemodelDocument13 pagesAQRspicemodelRakesh SandarativjuNo ratings yet
- A6 Relleta JamesDocument13 pagesA6 Relleta JamesLorenzo AbolarNo ratings yet
- To Study The Operation of UJT As A Pulse Generation CircuitDocument5 pagesTo Study The Operation of UJT As A Pulse Generation CircuitkashishlalaNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- THEM Edieval Science o F Weights: (Scientia de Ponderibus)Document224 pagesTHEM Edieval Science o F Weights: (Scientia de Ponderibus)Mónica MondragónNo ratings yet
- Section A-A: Details of Column Details of FootingDocument1 pageSection A-A: Details of Column Details of Footingom RakseNo ratings yet
- 176 Index Operating InstructionDocument3 pages176 Index Operating InstructionLuận NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Types of Welding ElectrodesDocument2 pagesTypes of Welding ElectrodeschittineniNo ratings yet
- Continuous R. C. Beams: Idealizations in Structural AnalysisDocument45 pagesContinuous R. C. Beams: Idealizations in Structural AnalysisPranav GairolaNo ratings yet
- 3.4.THERMODYNAMICS OF SOLUTIONS - SOME BASIC CONCEPTS - BusmeonDocument5 pages3.4.THERMODYNAMICS OF SOLUTIONS - SOME BASIC CONCEPTS - BusmeonAJ Kent Ray BusmeonNo ratings yet
- Aviation Info BankDocument1,025 pagesAviation Info BankHI HILLSNo ratings yet
- Crane Wheels-General InformationDocument3 pagesCrane Wheels-General InformationArvind VaishNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Velocity AnalysisDocument57 pagesChapter Three Velocity Analysismekete mulualemNo ratings yet
- Downflo Workstation: Installation and Operation ManualDocument48 pagesDownflo Workstation: Installation and Operation ManualMaintenanceNo ratings yet
- Mall Installation PlanningDocument7 pagesMall Installation PlanningDirrty ClubNo ratings yet
- Review of Tribological Characteristics of Modified PEEK CompositesDocument6 pagesReview of Tribological Characteristics of Modified PEEK CompositesVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- Bong Xcs Fidr Eb01Document30 pagesBong Xcs Fidr Eb01selvaortonNo ratings yet
- GROWATT MIN 2500-5000 TL-XA DatasheetDocument2 pagesGROWATT MIN 2500-5000 TL-XA DatasheetErlangga SatyawanNo ratings yet
- Seca1505 Cae 2Document2 pagesSeca1505 Cae 2sada mutyamNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Physics.soeDocument20 pagesLab Manual - Physics.soejhoyvanNo ratings yet
- RPT Form 4 Physics 2022Document30 pagesRPT Form 4 Physics 2022NoorNo ratings yet
- Master Jee Classes: Kukatpally, HyderabadDocument42 pagesMaster Jee Classes: Kukatpally, HyderabadVLSISD23 KORRA NIKHILNo ratings yet
- Mechanical SpringDocument49 pagesMechanical SpringYeamlak SisayNo ratings yet
- Conditions And/or Factors Affecting Echo-SoundingDocument2 pagesConditions And/or Factors Affecting Echo-Soundingarjay AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Notes PDFDocument123 pagesThermodynamics Notes PDFsubhash chandraNo ratings yet
- Irl 6342 PBFDocument8 pagesIrl 6342 PBFonafetsNo ratings yet
- Piping QC Guide (For Saudi Aramco Project)Document11 pagesPiping QC Guide (For Saudi Aramco Project)Heng100% (1)
- 2016 NCSE Math Paper IIDocument15 pages2016 NCSE Math Paper IIDarryan Dhanpat0% (1)
- Answer Keys: NCERT Booster Programme For NEET-2024 (XII Studying) - Physics - Poll-08Document14 pagesAnswer Keys: NCERT Booster Programme For NEET-2024 (XII Studying) - Physics - Poll-08Rohit LokvaniNo ratings yet
- Manual Espectro N4SDocument49 pagesManual Espectro N4SAvril PacioNo ratings yet
- Malabou-The Future of HegelDocument26 pagesMalabou-The Future of HegelJane Blough100% (3)
- Grammar Friends 3 MoversDocument78 pagesGrammar Friends 3 MoversCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Type Tests On Disc Insulator Units & StringsDocument33 pagesType Tests On Disc Insulator Units & Stringssalsa222100% (8)
- TDS ATLANTIC CHT81Ni1Document1 pageTDS ATLANTIC CHT81Ni1Andi Baso Temalala STNo ratings yet