Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Functions and Models Explained
Uploaded by
Cristina GomezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Functions and Models Explained
Uploaded by
Cristina GomezCopyright:
Available Formats
1|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
FUNCTION
LESSON 1: Function as Models
LEARNING OUTCOME(S) : At the end of the lesson, the learner is able to represent real life
situation using function, including piece wise function, and solve problem involving functions.
LESSON OUTLINE:
1. Review of relation and function
2. Review the function as machine.
3. Review function and relation as a table of values.
4. Function as representation of real life situation.
5. Piecewise function.
LESSON PROPER
DEVELOPMENT OF THE LESSON
A. Review of the function from Junior High School
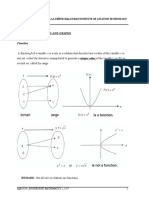
A function is a correspondence (relation) between two sets of elements such that to each element in
the first set there corresponds one and only one element in the second set. The first set is called the
domain and the set of all corresponding elements in the second set is called the range.
A function is a relation where each element in the domain is related to only one value in the range by
the some rule. The elements of the domain can be imagined as input to a machine that applies a rule
so that each input corresponds to only one output. A function is a set of ordered pairs (x,y) such that
no two ordered pairs have the same x – value but different y – values.
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
2|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
A relation is a rule that relates values from a set of values (called the domain) to a second set of
values (called the range). The elements of the domain can be imagined as input to a machine that
applies a rule to these inputs to generate one or more outputs.
The function as a machine
Mention that we will represent mathematical relations as machines with an input and an output and
that the output is related to the input by some rule.
Function Machine Activity
Following guide question about this machine:
a. Which of this machine, if you know that input, can you determine a single or unique output?
Answer: machine (a), (c), (d) and (f)
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
3|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
b. Which of these machine, if the output is known, can you determine a single or unique input?
Answer: machine (d) and (f)
c. Suppose we connect machine (a) to the machine (c) such that the output of (a) becomes the
input of (c)
Answer: A, R, S, U
Function and relation as a table of values
For the following illustrations of the function and relation, we draw from the definition for relation
and function given at the start of the chapter.
Example to illustrate these concept:
EXAMPLE 1. Which of the following relation are function?
a. f = {(1,2),(2.2), (3,5), (4,5)}
b. g = {(1,3),(1.4), (2,5), (2,6), (3,7)}
c. h = {(1,3),(2.6), (3,9), …,(n, 3n),…}
Answer: The relation f and h are function because no two ordered pairs have the same x-value but
different y-value. While g is not function because (1,3) and (1,4) are ordered pairs with the same z-
value but different y-values,
Relation and functions can be represent by mapping diagrams where the elements of the domain are
mapped to the elements of the range using arrow. In this case, the relation or function is represented
by the set of all the connection represented by the arrows.
EXAMPLE 2. Which of the following mapping diagrams represent function?
Answer. The relation f and g are function because each x ϵ X corresponds to a unique y ϵ Y. The
relation h is not a function because there is at least one element in X for which there is more than one
corresponds y-value. For example, c = 7 corresponds to y=11 or 13. Similarly, x=2 correspond to the
both y= 17 or 19.
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
4|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
EXAMPLE 3. Which of the following represents a function?
a. y =2x + 1
b. y =x² - 2x + 2
c. x² + y² =1
d.
e.
f. y = [x] + 1where [x] is the greater integer function.
Answer: All are relations.
Definition. The domain of a relation as the set of all possible values that the variable x can take.
EXAMPLE 5. Identify the domain for each relation above using set builder notation.
Answer: The domain for the relation above are as follows.
a. ℝ
b. ℝ
c. [ - 1, 1]
d. [- 1, + ∞]
e. (-∞,1) ∪ (1, + ∞)
f. ℝ
Function as representation of real-life situation.
Function can often be used to model real situation. Identifying an appropriate functional model will
lead to a better understanding of various phenomena.
EXAMPLE 1. Give a function C that can represent the cost of buying x meals, if one meal cost
₱40.
Answer. Since each meal cost ₱40, then the cost function is C(x) = 40x
Piecewise Functions is a function built from pieces of different functions over different intervals.
Some situations can only be described by more than one formula, depending on the value of the
independent variable.
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
5|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
EXAMPLE 1 : A user is charged ₱300 monthly for a particular mobile plan, which includes 100
free text messages. Messages in excess of 100 are charged ₱1. Represent the amount a consumer
pays each month as s function of the number of messages m sent in a month.
Answer: Let t(m) represent the amount paid by the consumer each month. It can be expressed by
the piecewise function.
300 if 0 < m ≤ 100
t(m) =
300 + m if m >100
EXAMPLE 2: A jeepney ride costs ₱8.00 for the first 4 kilometers, and each additional integer
kilometer adds ₱1.50 to the fare. Use a piecewise function to represent the jeepney face in terms of
the distance d in kilometers.
Answer: The input value is the distance and the output is the cost of the jeepney fare. If F (d)
represents the fare as a function of distance,the function can be represented as follows.
8 if < d ≤ 4
F(d) =
8 + 1.5 (d) if d > 4
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
6|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
LESSON 2: Evaluates a Function.
LEARNING OUTCOME(S): At the end of the lesson, the learner is able to evaluate functions and
solve problems involving functions.
LESSON OUTLINE:
1. Evaluating of functions
Evaluating a Function
Evaluating a function means replacing the variable in the function, in this case x, with the value
from the functions domain and computing for the result. To denote that we are evaluating f at a for
some a in the domain of f, we write f (a).
If one thinks of the function as a function machine, evaluating a function is analogous to providing
our machines with a valid input.
EXAMPLE 1. Evaluate the following functions at x =1.5:
a. f(x) = 2x + 1
b. q(x) = x² - 2x + 2
Answer: Substituting 1.5 for x in the function above
EXAMPLE 2: Evaluate the following functions, f (x) = (2x + 3) at the given values
a. f (3x – 1)
Answer: To evaluate f (3x – 1), replace all the x in f (x) = 2x + 3 by (3x – 1):
f (3x – 1) = 2(3x – 1) + 3
= 6x – 2 + 3
= 6x + 1
EXAMPLE 3: Evaluate the following function f(x) = x² – 2x + 2 at the given values
a. q(2x + 3)
Answer: To evaluate f(2x + 3), replace all the x in q(x) = x² – 2x + 2 with (2x + 3):
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
7|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
q (2x +3) = (2x +3)² – 2(2x +3) + 2
= (4x² + 12x + 9) – 4x – 6 + 2
= 4x² + 8x + 5
Example 4: Evaluate f (x) = 3x – 1 at the given values
a. f (4)
b. f (2)
c. f (-1)
Answer:
a. f (4) = 3x – 1 = 3(4) – 1 = 11
b. f(2) = 3x – 1 = 3(2) – 1 = 5
c. f(-1) = 3x – 1 = 3(-1) – 1 = -4
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
8|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
LESSON 3: Operations on Functions
LEARNING OUTCOME(S): At the end of the lesson, the learner is able to perform addition,
subtraction, multiplication, division and composition of function.
LESSON OUTLINE:
1. Review addition and subtraction of algebraic expression
2. Review multiplication and division of algebraic expression.
3. Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of function
4. Composition of function
Addition and Subtraction
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
9|Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
EXAMPLE 5: Let f(x) = x – 4 and g(x) = 2x – 3 .
Find the functions
a. f + g,
b. f – g,
c. f∙g,
d. f/g.
Answer:
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
10 | Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
a. (f + g)(x) = f(x)+g(x)
= x – 4 + 2x – 3
= 3x – 7
b. (f – g)(x) = f(x) – g(x)
= (x – 4) – (2x – 3)
= -x – 1
c. (f g)(x) = f(x) g(x)
= (x – 4) (2x – 3)
= 2x² – 11x + 12
d. (f / g)(x) = f(x) / g(x)
= (x – 4) / (2x – 3)
Composition of Function
The Composition of a function f with another function g is denoted by (read “f composed with g”)
and is defined by
(f ◦ g) (x) = f(g(x))
EXAMPLE 1: Find for (f ◦g)(x) for f (x) = x² - x and g(x) = 3 + 2x.
Answer: (f ◦g)(x) = f(g(x))
= f(3 + 2x)
= (3 + 2x)² – (3 + 2x)
= 9 + 12x +4x² – 3 – 2x
= 4x² + 10x + 6
EXAMPLE 2: Find for (g ◦f)(x) for f (x) = 2x + 1, and g(x) = √ x+1
Answer:
EXAMPLE 3: : Find for (q ◦f)(x) for q(x) = x² - 2x + 2, and for f (x) = 2x + 1
(q ◦f)(x) = q(f(x))
=[f(x)]² - 2[ f ( x ) ]+2
=(2x + 1)² - 2 (2x + 1) + 2
= (4x² + 4x + 1) – (4x +2) + 2
= 4x² + 1
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
11 | Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
Name:___________________________ Date:_______________
Q1W1 Activity 1 ( 41 PTS)
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
12 | Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
I. Problem Solving
1. Provide a real world example or scenario that can expressed as a realtion that is not a
function.
2. Provide a real world example or scenario that can be modeled by a linear function.
3. A videoke machine can be rented for ₱10,000 for three days, but the forth day onwards, a
additional cost of ₱400 per day is added. Represent the cost of renting a videoke machine as a
piecewise function of the function of the number of days it is rented.
4. The fee for hiring a guide to explore a cave is ₱700. A guide can only take care of a
maximum of 4 persons, and additional guides can be hired as needed. Represent the cost of
hiring guides as a function of the number of the number of tourist who wish to explore the
cave.
5. Define a piecewise function that models this situation by giving a functions equation
6. Find for (q ◦f)(x) for q(x) = x² - 2x + 2, and for f (x) = 2x + 1
Answer
7. Find for (g ◦f)(x) for f (x) = 2x + 1, and g(x) = √ x+1
Answer
8. Find for (f ◦g)(x) for f (x) = x² - x and g(x) = 3 + 2x.
Answer
9. Given f(x) = x – 2, find the following values:
a. f(0)
b. f(3)
c. f( -1)
d. f(ℼ)
e. f(x + 1)
f. f(3x)
10. Given f(x) =√ x+1 , find the following values:
a. f(3)
b. f(4)
c. f(12)
d. f(x – 3)
e. f(x² + 4x + 7)
4
11. Given f(x) = x , find the following values
a. f(1)
b. f(2)
c. f( -1 )
d. f(√2)
e. f(1/x)
f. f(2x)
II. Multiple Choice
12. Express the function f(x) = x² + 3 as the sum or difference of the function ______________.
a. 2x + 1 and x – 1 c. 2x + 1 and x² - 2x + 2
b. x² + 2x + 1 and 2x + 1 d. x² - 2x + 2 and 2x + 2
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
13 | Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
13. Subtract q(x) = (x² - 2x + 2) and f(x) = (2x + 1)
a. x² - 4x + 1 c. x² + 4x + 1
b. x² + 3 d. x² + 4x + 3
14. Evaluate f (x) = 3x – 1 at the given values
a. f (4) 11
b. f(2) 5
c. f(-1) -4
15. A ___________is a correspondence _____________between two sets of elements such that
to each element in the first set there corresponds one and only one element in the second set.
a. function, relation c. relation, range
b. Domain, range d. composition, function
16. Is any set of ordered pairs.
a. Range c. relation
b. piecewise d. function
17. A function built from pieces of different functions over different intervals.
a. Relation c. piecewise
b. composition d. range
18. The composition of a function f with another function g is denoted by
a. (f ◦ g) (x) = f(g(x)) c. (f ◦ g) (-x) = f(g(x))
b. (f ◦ g) (x) = f(g(-x)) d. (f ◦ g) (x) = -f(g(x))
19. Means replacing the variable in the function, in this case x, with the value from the functions
domain and computing for the result.
a. Evaluation a function c. value a function
b. Evaluating a function d. extracting a function
20. Evaluate the following functions, f (x) = (2x + 3) at the given values f (3x – 1)
a. 6x + 1 c. 3x – 1
b. 6x – 1 d. -6x + 2
21. Quotient denote as _________
a. f*g c. f–g
b. f/g d. f+g
22. Sum denote as ___________
a. f*g c. f–g
b. f/g d. f+g
23. ______________________of a function f with another function g is denoted by (read “f composed with
g”)
a. Relation c. composition
b. Domain d. range
24. Product denote as ___________
a. f*g c. f–g
b. f/g d. f+g
25. Difference denote as ___________
a. f*g c. f–g
b. f/g d. f+g
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
14 | Q u a r t e r 1 (Week 1 Module)
ACEBA Systems Technology Institute, Inc. CFGC
Rex Tower Building, Poblacion 1, Tiaong, Quezon
C O D E : M11GM-Ia-1 to M11GM-Ia-4
You might also like
- Bond NVRDocument28 pagesBond NVRTadmore Tutors TuitonNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - General MathematicsDocument40 pagesWeek 1 - General MathematicsSirr AustriaNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics: Module 1: Introduction To FunctionsDocument17 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Module 1: Introduction To FunctionsPinky PardilladaNo ratings yet
- GenMath PPT - Relations and Functions (Wk1&2) - 2005Document42 pagesGenMath PPT - Relations and Functions (Wk1&2) - 2005SpedsijedNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Module Number 1: Review On Functions ObjectivesDocument53 pagesGeneral Mathematics Module Number 1: Review On Functions ObjectivesGolda Crizelle NoquiaoNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Functions and Piecewise FunctionsDocument48 pagesLesson 1 Functions and Piecewise FunctionsGeraldine ElisanNo ratings yet
- Functions As Models (General Mathematics)Document8 pagesFunctions As Models (General Mathematics)Myrhelle Grecia100% (1)
- Topic:: Understanding Function and RelationDocument28 pagesTopic:: Understanding Function and RelationCarlos Enriquez IVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Functions 2Document25 pagesChapter 1. Functions 2Cassy RabangNo ratings yet
- LP-GenMath - Week1Document10 pagesLP-GenMath - Week1Cry BeroNo ratings yet
- Einstein 1950 Generalized Theory of Relativity Sci AmDocument5 pagesEinstein 1950 Generalized Theory of Relativity Sci AmbeemitsuNo ratings yet
- Math 11-CORE Gen Math-Q1-Week-1Document14 pagesMath 11-CORE Gen Math-Q1-Week-1SeMi NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Functions As Model: Review of Functions From Junior High SchoolDocument1 pageFunctions As Model: Review of Functions From Junior High SchoolMaiChard MoonNo ratings yet
- Module 1 and 2 - General MathematicsDocument6 pagesModule 1 and 2 - General MathematicsMillet PañoNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Q1 Mod 1Document21 pagesGen Math Q1 Mod 1Joselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Mod 1Document21 pagesGen Math Mod 1Joselito Ubaldo100% (1)
- General Mathematics: Grade 11 Quarter 1 Module 1 - Week 1Document18 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Grade 11 Quarter 1 Module 1 - Week 1Joanna Marie RamosNo ratings yet
- Genmath 11 q1 Week 1Document18 pagesGenmath 11 q1 Week 1Joanna Marie RamosNo ratings yet
- General-Mathematics_Q1_Module-1Document19 pagesGeneral-Mathematics_Q1_Module-1Malen GallegosNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Week 1 - Quarter 1 - Gen MathDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Week 1 - Quarter 1 - Gen MathKaru GreyNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics - Q1 - Week 1-3Document20 pagesGeneral Mathematics - Q1 - Week 1-3Rayezeus Jaiden Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Week 1 - Gen.-Math-2-FINALDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Week 1 - Gen.-Math-2-FINALKenneth IbarraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Functions and GraphsDocument39 pagesChapter 3 Functions and Graphssyamim ikram bin mohd zamriNo ratings yet
- SHS Lesson 1Document11 pagesSHS Lesson 1Tisha Galolo100% (1)
- Intro To FunctionDocument32 pagesIntro To FunctionMark Kirby De Las LlagasNo ratings yet
- Welcome General Mathematics For Grade 11: Mr. Adonis C. Honasan Teacher IIIDocument21 pagesWelcome General Mathematics For Grade 11: Mr. Adonis C. Honasan Teacher IIIRyan Joseph HernoNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS pptx1Document57 pagesFUNCTIONS pptx1Manuela Kassandra TribianaNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument47 pagesRelations and FunctionsCarleen VillamilNo ratings yet
- FunctionDocument17 pagesFunctionAc CruzNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Q1 WEEK 1-2Document7 pagesGen Math Q1 WEEK 1-2ronilynn veranoNo ratings yet
- Calculus with Transcendental FunctionsDocument32 pagesCalculus with Transcendental FunctionsHarrdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture Transcript 1 Introduction To Functions and Piecewise Functions7Document14 pagesLecture Transcript 1 Introduction To Functions and Piecewise Functions7eve lopezNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics - M01 - L01 - WEEK 1Document4 pagesGeneral Mathematics - M01 - L01 - WEEK 1Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 GMDocument41 pagesWeek 1 GMJhanjhan BoniNo ratings yet
- GenMath W1 Q1Document18 pagesGenMath W1 Q1JohnNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHSDocument48 pagesFUNCTIONS AND GRAPHSKarina FerrerNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Functions: Lesson DescriptionDocument11 pagesRevisiting Functions: Lesson DescriptionPrincess Joie RamosNo ratings yet
- Learn Functions & Piecewise ModelsDocument25 pagesLearn Functions & Piecewise ModelsRex FajardoNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet In: General MathematicsDocument12 pagesActivity Sheet In: General MathematicsRevanVilladozNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Week 1 PDFDocument17 pagesGeneral Mathematics Week 1 PDFRussiel DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Mimaropa RegionDocument24 pagesDepartment of Education: Mimaropa RegionEinjhel Gaverielle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Study Guide # 2024 - 1Document2 pagesStudy Guide # 2024 - 1ingridgiselavNo ratings yet
- Met 1 Q1 PDFDocument8 pagesMet 1 Q1 PDFShannen MonteroNo ratings yet
- Gen MathDocument8 pagesGen MathHershell ContaNo ratings yet
- Functions As ModelsDocument88 pagesFunctions As ModelsMii Chel50% (2)
- JIM101 Learning Material (Lecture Note) - CHAPTER 1Document50 pagesJIM101 Learning Material (Lecture Note) - CHAPTER 1visionisolnNo ratings yet
- Bellman, Lee - Functional Equations in Dynamic ProgrammingDocument18 pagesBellman, Lee - Functional Equations in Dynamic ProgrammingYermakov Vadim IvanovichNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 FunctionsDocument365 pagesGrade 11 FunctionsMrBigbozz21No ratings yet
- General Mathematics Dcsa ModuleDocument38 pagesGeneral Mathematics Dcsa ModuleJessel HaveriaNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Q1W01Document11 pagesGeneral Mathematics Q1W01Loren Kingston MelendezNo ratings yet
- 1 2 - Represent Real Life Situations - Evaluating - FunctionsDocument29 pages1 2 - Represent Real Life Situations - Evaluating - FunctionsryanneNo ratings yet
- Language 0f MathDocument57 pagesLanguage 0f MathChristian Dave Balasa100% (1)
- Week1 Gen - Math ModuleDocument26 pagesWeek1 Gen - Math ModuleAshrel Rasonable NuynayNo ratings yet
- R1 - FunctionsDocument77 pagesR1 - FunctionsAdrian Perolino MonillaNo ratings yet
- Module 1. Functions and Their GraphsDocument7 pagesModule 1. Functions and Their GraphsMori OugaiNo ratings yet
- Survey of Trust-Region Derivative Free Optimization MethodsDocument12 pagesSurvey of Trust-Region Derivative Free Optimization MethodsMariangela PintoNo ratings yet
- CS-2012 (Daa) - CS End Nov 2023Document21 pagesCS-2012 (Daa) - CS End Nov 2023bojat18440No ratings yet
- Share CHAPTER QUIZDocument2 pagesShare CHAPTER QUIZJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS FUNCTIONSDocument11 pagesMATHEMATICS FUNCTIONSLea Grace GulengNo ratings yet
- LESSON 9: One-to-One Functions: Learning Outcome (S) : Lesson OutlineDocument6 pagesLESSON 9: One-to-One Functions: Learning Outcome (S) : Lesson OutlineCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making: Laguna State Polytechnic UniversityDocument6 pagesDecision-Making: Laguna State Polytechnic UniversityCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Improving Student Achievement with a Problem-Solving ModelDocument6 pagesImproving Student Achievement with a Problem-Solving ModelCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Improving Student Achievement with a Problem-Solving ModelDocument6 pagesImproving Student Achievement with a Problem-Solving ModelCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Model - 207Document6 pagesProblem Solving Model - 207Cristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument10 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Q1W1 PHILO Doing PhilosopyDocument13 pagesQ1W1 PHILO Doing PhilosopyCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument10 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Q1W2 PHILO - Methods of PhilosphizingDocument15 pagesQ1W2 PHILO - Methods of PhilosphizingCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Q1W2 PHILO - Methods of PhilosphizingDocument15 pagesQ1W2 PHILO - Methods of PhilosphizingCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Philo Online ActivityDocument1 pagePhilo Online ActivityCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument10 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Q1W1 PHILO Doing PhilosopyDocument13 pagesQ1W1 PHILO Doing PhilosopyCristina GomezNo ratings yet
- ISC Computer Science - 2015Document17 pagesISC Computer Science - 2015Bimal Roy MehtaNo ratings yet
- Tycssem5aiunit12345 (Munotes - In)Document55 pagesTycssem5aiunit12345 (Munotes - In)Chirag MummadiNo ratings yet
- FAQs in C LanguageDocument256 pagesFAQs in C LanguageShrinivas A B0% (2)
- Chapter IV - Space SyntaxDocument18 pagesChapter IV - Space SyntaxVương Đình Huy100% (1)
- Measurement Error: What Is Random Error?Document3 pagesMeasurement Error: What Is Random Error?Fatin Amni MnkNo ratings yet
- Seminar Topics Fall 10Document2 pagesSeminar Topics Fall 10Jimada AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Core Java Ex 1Document157 pagesCore Java Ex 1lcbkraj2133No ratings yet
- Database Mba NOTESDocument35 pagesDatabase Mba NOTESWasim Ahamad KhanNo ratings yet
- Line, Circle, EllipseDocument8 pagesLine, Circle, Ellipsepriskilla SelvinNo ratings yet
- Transportation ModelsDocument9 pagesTransportation ModelsAllonah G. de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Quality) Terhadap Keputusan Pembelian (Purchase Decision) MelaluiDocument12 pagesQuality) Terhadap Keputusan Pembelian (Purchase Decision) MelaluiSatria WijayaNo ratings yet
- Math Operation Table TarpDocument5 pagesMath Operation Table TarpAna Mirata DumaogNo ratings yet
- A4 - G10 - Q3 - Module 2 - MELC 3&4Document12 pagesA4 - G10 - Q3 - Module 2 - MELC 3&4Jayzi VicenteNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis of VarianceDocument62 pagesMultivariate Analysis of VarianceRyan Mohammad Macaradi HadjinasserNo ratings yet
- Bill Gaede: Science 341 (2014) What Is Physics?Document13 pagesBill Gaede: Science 341 (2014) What Is Physics?Herczegh TamasNo ratings yet
- Design of High Speed Carry Select Adder Using Brent Kung AdderDocument4 pagesDesign of High Speed Carry Select Adder Using Brent Kung AdderAngel ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Reliability of Gait Performance Tests in Men and Women With Hemiparesis After StrokeDocument8 pagesReliability of Gait Performance Tests in Men and Women With Hemiparesis After StrokeKaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Scalars and VectorsDocument5 pagesChapter One: Scalars and VectorszinabuNo ratings yet
- Iready-Using-Iready-As-A-Student-Growth-Measure-2017-2018 DraggedDocument2 pagesIready-Using-Iready-As-A-Student-Growth-Measure-2017-2018 Draggedapi-301365542No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1robert_tanNo ratings yet
- 15th IAHR Ice Symp Poland 2000 AllDocument553 pages15th IAHR Ice Symp Poland 2000 AllAnonymous ZO1piE3VNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Math Lesson on Factors, Fractions and Word ProblemsDocument44 pagesGrade 4 Math Lesson on Factors, Fractions and Word ProblemsFUMIKO SOPHIANo ratings yet
- Beam Analysis2dDocument80 pagesBeam Analysis2dMSNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument100 pagesObject Oriented ProgrammingPrasanna KSNo ratings yet
- Understanding Probability ConceptsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Probability ConceptsAngelo Delos CentesNo ratings yet
- Fractionally Spaced Adaptive Equalizer A ReviewDocument3 pagesFractionally Spaced Adaptive Equalizer A ReviewEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Co Math6025 PDFDocument9 pagesCo Math6025 PDFikmalNo ratings yet
- Aqa 43602h QP Jun15Document20 pagesAqa 43602h QP Jun15Milla Savova0% (1)