Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 3-Unit Weight
Experiment 3-Unit Weight
Uploaded by
AhmedMahirCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 3-Unit Weight
Experiment 3-Unit Weight
Uploaded by
AhmedMahirCopyright:
Available Formats
20
EXPERIMENT 3
DENSITY (UNIT WEIGHT) DETERMINATIOM
Purpose:
This lab is performed to determine the in-place density of undisturbed soil
obtained by pushing or drilling a thin-walled cylinder. The bulk density is the ratio
of mass of moist soil to the volume of the soil sample, and the dry density is the
ratio of the mass of the dry soil to the volume the soil sample.
Standard Reference:
ASTM D 2937-00 – Standard Test for Density of Soil in Place by the Drive-
Cylinder Method
Significance:
This test is used to determine the in-place density of soils. This test can
also be used to determine density of compacted soils used in the construction of
structural fills, highway embankments, or earth dams. This method is not
recommended for organic or friable soils.
Equipment:
Straightedge, Balance, Moisture can, Drying oven, Vernier caliper
Engineering Properties of Soils Based on Laboratory Testing
Prof. Krishna Reddy, UIC
21
Test Procedure:
(1) Extrude the soil sample from the cylinder using the extruder.
(2) Cut a representative soil specimen from the extruded sample.
(3) Determine and record the length (L), diameter (D) and mass (Mt) of
the soil specimen.
(4) Determine and record the moisture content of the soil (w).
(See Experiment 1)
Engineering Properties of Soils Based on Laboratory Testing
Prof. Krishna Reddy, UIC
22
(Note: If the soil is sandy or loose, weigh the cylinder and soil sample
together. Measure dimensions of the soil sample within the cylinder. Extrude and
weigh the soil sample and determine moisture content)
Data Analysis:
(1) Determine the moisture content as in Experiment 1
(2) Determine the volume of the soil sample
πD 2L
V= cm3
4
(3) Calculate bulk density (ρt) of soil
M g
ρ = t
t V
cm3
or unit weight γ t = ρ t g
(4) Calculate dry density (ρd) of soil
ρt g
ρd =
1+ w cm 3
or dry unit weight γ =ρ g
d d
Engineering Properties of Soils Based on Laboratory Testing
Prof. Krishna Reddy, UIC
23
EXAMPLE DATA
Engineering Properties of Soils Based on Laboratory Testing
Prof. Krishna Reddy, UIC
24
DENSITY (UNIT WEIGHT) DETERMINATION
DATA SHEET
Sample number: B-1, ST-1, 10’-12’ Date Tested: September 10, 2002
Soil description: Gray silty clay
Mass of the soil sample (Mt): 125.20 grams
Length of the soil sample (L): 7.26 cm
Diameter of the soil sample (D): 3.41 cm
Moisture content determination:
Specimen number 1
Moisture can and lid number 15
MC = Mass of empty, clean can + lid (grams) 7.83
MCMS = Mass of can, lid, and moist soil (grams) 13.43
MCDS = Mass of can, lid, and dry soil (grams) 12.69
MS = Mass of soil solids (grams) 4.86
MW = Mass of pore water (grams) 0.74
w = Water content, w% 15. 2
Example calculations: w=15.2%, Mt=125.2g, L=7.26cm, D=3.41cm
π(3.41 )2 ( 7.26 )
V= = 66.28 cm 3
4
125.20 g Ib
ρt = = 1.89 or γ = 1.89 × 62.4 = 118
66.28 cm 3 t
ft 3
1.89 g Ib
ρd = = 1.64 or γ = 1.64 × 62.4 = 102.3
d
15.20
1+ cm 3 ft 3
100
(Note: 62.4 is the conversion factor to convert density in g/cm3 to unit weight in
lb/ft3)
Engineering Properties of Soils Based on Laboratory Testing
Prof. Krishna Reddy, UIC
25
BLANK DATA SHEETS
Engineering Properties of Soils Based on Laboratory Testing
Prof. Krishna Reddy, UIC
26
DENSITY (UNIT WEIGHT) DETERMINATION
DATA SHEET
Sample number: Date Tested:
Soil description:
Mass of the soil sample (Mt):
Length of the soil sample (L):
Diameter of the soil sample (D):
Moisture content determination:
Specimen number 1
Moisture can and lid number
MC = Mass of empty, clean can + lid (grams)
MCMS = Mass of can, lid, and moist soil (grams)
MCDS = Mass of can, lid, and dry soil (grams)
MS = Mass of soil solids (grams)
MW = Mass of pore water (grams)
w = Water content, w%
Calculations:
Engineering Properties of Soils Based on Laboratory Testing
Prof. Krishna Reddy, UIC
You might also like
- Study of Strength Properties of Polyester Fibre Reinforced ConcreteDocument5 pagesStudy of Strength Properties of Polyester Fibre Reinforced ConcreteJournal 4 ResearchNo ratings yet
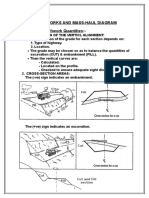
- Lecture 3 EARTH WORKS AND MASS HAUL DIAGRAMDocument18 pagesLecture 3 EARTH WORKS AND MASS HAUL DIAGRAMKadhim Falah100% (1)
- Mahsr GsDocument13 pagesMahsr GsSaifuddinNo ratings yet
- Test For CementDocument9 pagesTest For CementSrinath KamathNo ratings yet
- Application of Prefabricated Vertical Drains To The Changi Land Reclamation Project, SingaporeDocument5 pagesApplication of Prefabricated Vertical Drains To The Changi Land Reclamation Project, SingaporehjmieNo ratings yet
- Material Requirement Planning PresentationDocument26 pagesMaterial Requirement Planning PresentationAshutosh PareekNo ratings yet
- Actros 2035 4x2 5400Document2 pagesActros 2035 4x2 5400v53No ratings yet
- Uber:Jump Report On Shared Ebike PotentialDocument47 pagesUber:Jump Report On Shared Ebike PotentialGersh KuntzmanNo ratings yet
- Geotech Report Jharsuguda Trial Pit Boundry WallDocument24 pagesGeotech Report Jharsuguda Trial Pit Boundry WallRatnakar DashNo ratings yet
- Site InvestigationDocument8 pagesSite Investigation11 Sqn RERNo ratings yet
- 11 Flash and Fire Point of Bitumen - SayeedDocument2 pages11 Flash and Fire Point of Bitumen - Sayeedlm hasnainNo ratings yet
- FM ExercisesDocument5 pagesFM ExercisesanililhanNo ratings yet
- NILOS-Rings SKF PDFDocument54 pagesNILOS-Rings SKF PDFВиталий БобуличNo ratings yet
- AASHTO t99 180Document7 pagesAASHTO t99 180dongpc1No ratings yet
- National Technical Services: F.D.T Test Report by Sand Replacement MethodDocument1 pageNational Technical Services: F.D.T Test Report by Sand Replacement MethodhafizNo ratings yet
- Methods For Determining Affinity BTWN Aggregate and Bitumen - Pavol, Jozef, MarcelaDocument7 pagesMethods For Determining Affinity BTWN Aggregate and Bitumen - Pavol, Jozef, MarcelaJohn Prashanth VadlapatiNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Report - PreliminaryDocument29 pagesGeotechnical Report - PreliminaryAyoola OluwadotunNo ratings yet
- Free Colour Flashcards PDFDocument5 pagesFree Colour Flashcards PDFMarta Escartí CastellNo ratings yet
- Sand Replacement Test Lab ManualDocument3 pagesSand Replacement Test Lab Manualmm100% (1)
- 21 27 Bulk Density Apparatus TMIDocument2 pages21 27 Bulk Density Apparatus TMIMauricio CarestiaNo ratings yet
- Report 2 Water Absorption of BlockDocument8 pagesReport 2 Water Absorption of BlockZhiwar oramariNo ratings yet
- 229 - PadurDocument14 pages229 - PadurpmrameshkumarNo ratings yet
- Soilmech Lab 1Document10 pagesSoilmech Lab 1Kleinne KristenneNo ratings yet
- Moisture Content Astm d2216Document3 pagesMoisture Content Astm d2216Mubashar Islam100% (1)
- Ce511 Tabinas HW02 PDFDocument17 pagesCe511 Tabinas HW02 PDFKathlyn Kit TabinasNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines: 938 Aurora Boulevard Cubao, Quezon CityDocument15 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines: 938 Aurora Boulevard Cubao, Quezon CityJoshua CalaNo ratings yet
- 2015 Estimating MDD and OMCDocument9 pages2015 Estimating MDD and OMCKrmt Goji SamaratunggadewaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual On Geotechnical Engineering/Foundation Engineering/Soil Mechanics:Test of SoilDocument18 pagesLaboratory Manual On Geotechnical Engineering/Foundation Engineering/Soil Mechanics:Test of SoilSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Application of Multilinear Regression Analysis in Modeling of Soil Properties For Geotechnical Civil Engineering Works in Calabar SouthDocument7 pagesApplication of Multilinear Regression Analysis in Modeling of Soil Properties For Geotechnical Civil Engineering Works in Calabar SouthMasood AhmedNo ratings yet
- Afolayan2021 Article CharacterizationOfBariteReservDocument22 pagesAfolayan2021 Article CharacterizationOfBariteReservUtibe EdemNo ratings yet
- 4 Flexure PDFDocument48 pages4 Flexure PDFKetanNo ratings yet
- CBR Test Procedure Determination of California Bearing Ratio For Road Design PDFDocument5 pagesCBR Test Procedure Determination of California Bearing Ratio For Road Design PDFMohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- 057A - Quotation - SOIL INVESTIGATION - ORANGE - GUJRAT - 04.08.16 PDFDocument3 pages057A - Quotation - SOIL INVESTIGATION - ORANGE - GUJRAT - 04.08.16 PDFDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- LAB 3 - Traffic Volume (Method 1) OEL 1Document5 pagesLAB 3 - Traffic Volume (Method 1) OEL 1saraa sharanNo ratings yet
- KIRK - Falling Head Permeability Test (100%)Document16 pagesKIRK - Falling Head Permeability Test (100%)Kirk Woo ChongNo ratings yet
- Ece 2303 Soil Mechanics I-PrintreadyDocument3 pagesEce 2303 Soil Mechanics I-PrintreadyJoe NjoreNo ratings yet
- Benefits of The Dilatometer TestDocument5 pagesBenefits of The Dilatometer Testkaleswara_tellakulaNo ratings yet
- Bitumen ExtractorDocument7 pagesBitumen ExtractorNirmal NayakNo ratings yet
- Determination of Field Density of Soil by Core Cutter MethodDocument3 pagesDetermination of Field Density of Soil by Core Cutter MethodsiddiqueakbarNo ratings yet
- Presentable Industrial Training Experience GabrielDocument15 pagesPresentable Industrial Training Experience GabrielOkortnne AyibaNo ratings yet
- Construction Material Lab Manual2Document44 pagesConstruction Material Lab Manual2VitoPascasioNo ratings yet
- Highway RehabilitationDocument31 pagesHighway Rehabilitationketh patrickNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Standard Proctor Test and Modified Proctor Test.Document7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Standard Proctor Test and Modified Proctor Test.Asif RajaNo ratings yet
- Nishane Khola Landslide PDFDocument10 pagesNishane Khola Landslide PDFGeology CCT DharanNo ratings yet
- Beneficiation of Azara Barite Ore Using A Combination of Jigging, Froth Flotation and LeachingDocument6 pagesBeneficiation of Azara Barite Ore Using A Combination of Jigging, Froth Flotation and LeachingPhilips UchennaNo ratings yet
- To Determine Specific Gravity of Solids by Pycnometer MethodDocument3 pagesTo Determine Specific Gravity of Solids by Pycnometer MethodRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Cement Using AlccofineDocument8 pagesExperimental Study On Partial Replacement of Cement Using AlccofineNavik BhandariNo ratings yet
- of Standard Penetration TestDocument19 pagesof Standard Penetration Testrishav baishyaNo ratings yet
- 3 Constant HeadDocument12 pages3 Constant HeadWHfamilyNo ratings yet
- ProctorDocument1 pageProctorMohammed SalhinNo ratings yet
- PWD UPDATdEDocument41 pagesPWD UPDATdEmukeshNo ratings yet
- U2 Direct Shear Test Unconfined Compression TestDocument35 pagesU2 Direct Shear Test Unconfined Compression TestazmieNo ratings yet
- To Find The Moisture Content in A SoilDocument4 pagesTo Find The Moisture Content in A Soilliaqt zaib khanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Partial Replacement of Sharp Sand With Stone Dust On Mechanical Properties of ConcreteDocument105 pagesThe Effect of Partial Replacement of Sharp Sand With Stone Dust On Mechanical Properties of ConcreteNwigwe Promise ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Soil Test Report KhagariaDocument28 pagesSoil Test Report KhagariaSajan SinghNo ratings yet
- ASD Specification (Volumn 1 Corrigendum)Document0 pagesASD Specification (Volumn 1 Corrigendum)Agnon FungNo ratings yet
- Soil ReportDocument9 pagesSoil ReportHabib Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Exp-4 GrainSizeDistribution PDFDocument14 pagesExp-4 GrainSizeDistribution PDFsriknta sahuNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization by Using: Fly AshDocument12 pagesSoil Stabilization by Using: Fly AshRavi HirulkarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Compaction Assignment-3Document1 pageDynamic Compaction Assignment-3Riyad ArafatNo ratings yet
- Determination of Moisture ContentDocument21 pagesDetermination of Moisture ContentasadaltafgillNo ratings yet
- 2-Moisture Content - Specific GravityDocument32 pages2-Moisture Content - Specific GravityHidayat 'yayat' HaRaaNo ratings yet
- Improving The Capacity of Bored Piles by Shaft Grouting Shaft GroutingDocument29 pagesImproving The Capacity of Bored Piles by Shaft Grouting Shaft GroutingAnshuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Gawar-Singh (J.V) : Report On Geotechnical Investigation WorkDocument22 pagesGawar-Singh (J.V) : Report On Geotechnical Investigation WorkEr navneet jassiNo ratings yet
- Axially Loaded Pile SpreadsheetDocument12 pagesAxially Loaded Pile SpreadsheetleodegarioporralNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. Name of The Experiment: Aggregate Impact Test AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To Determine The Aggregate Impact Value ofDocument4 pagesExperiment No. Name of The Experiment: Aggregate Impact Test AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: To Determine The Aggregate Impact Value ofBibhuti B. BhardwajNo ratings yet
- What Is Soil Bearing CapacityDocument3 pagesWhat Is Soil Bearing CapacityArly Tolentino100% (1)
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985From EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985No ratings yet
- Mainframe BrochureDocument13 pagesMainframe BrochurearulbenjaminchandruNo ratings yet
- BMFE-04-03e (F) Smokes Extraction PrincipleDocument12 pagesBMFE-04-03e (F) Smokes Extraction PrincipleJustine Mernald ManiquisNo ratings yet
- Pipe Network AnalysisDocument8 pagesPipe Network AnalysisAhmedNo ratings yet
- The Computer Aided System For Planning Efficient Routes: Purdue E-PubsDocument61 pagesThe Computer Aided System For Planning Efficient Routes: Purdue E-PubsMadhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Karaoke/Surround Digital Echo: BU9253AS/FS, BU9262AFSDocument17 pagesKaraoke/Surround Digital Echo: BU9253AS/FS, BU9262AFSRodrigo Augusto SantosNo ratings yet
- E Vison2009Document118 pagesE Vison2009shakyasujaNo ratings yet
- PBL Casting 1Document8 pagesPBL Casting 1Fu AdNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Year 6 2013Document11 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 6 2013Shahrul Ikram Md ShariffNo ratings yet
- CGDocument40 pagesCGbijju007No ratings yet
- Peake "N Series" Highwall Air Conditioning Units: BrandDocument1 pagePeake "N Series" Highwall Air Conditioning Units: BrandAkeel ClarkeNo ratings yet
- Csound ManualDocument287 pagesCsound ManualАлександр ЗемцовNo ratings yet
- Simulations of A Cavity Based Two-Dimensional Scramjet ModelDocument4 pagesSimulations of A Cavity Based Two-Dimensional Scramjet ModelKummitha Obula ReddyNo ratings yet
- Scenario: Replacing Two Omua or Omub Boards With Two Omuc BoardsDocument6 pagesScenario: Replacing Two Omua or Omub Boards With Two Omuc BoardsducnamdtvtNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument52 pagesREPORTزين ال عابدينNo ratings yet
- 1 Winch Control - Jul2015 - JFEDocument40 pages1 Winch Control - Jul2015 - JFEmortizNo ratings yet
- Guitar CompressorDocument2 pagesGuitar Compressoroverdrive0No ratings yet
- Oracle® Fusion MiddlewareDocument174 pagesOracle® Fusion MiddlewaredeartestNo ratings yet
- Chartek 1709 SDSDocument2 pagesChartek 1709 SDSJOHN100% (1)
- Washing Machines Series Gewa Plus & EcoDocument12 pagesWashing Machines Series Gewa Plus & EcoFederico VillagranNo ratings yet
- Major Players of Fuel Oil in The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesMajor Players of Fuel Oil in The PhilippinesFranco Fuderanan0% (1)
- A.P.J.Abdul KalamDocument10 pagesA.P.J.Abdul Kalamrajanjain63No ratings yet
- Walmart Value Chain AnalysisDocument21 pagesWalmart Value Chain AnalysisAnonymous lSeU8v2vQJ100% (2)