Professional Documents
Culture Documents
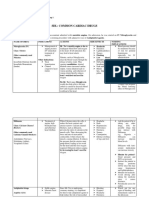
Medications and Antidotes Chart
Uploaded by
k0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
237 views2 pagesThis document provides information on medications and their antidotes, types of insulin and their properties, intravenous cardiac drips and their uses and dosages, common medications classified by type including nursing considerations, medications used in obstetrics, and antifungal amphotericin B administration.
Original Description:
Original Title
2 Pharmacy Cheat Sheets Nurse Nation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on medications and their antidotes, types of insulin and their properties, intravenous cardiac drips and their uses and dosages, common medications classified by type including nursing considerations, medications used in obstetrics, and antifungal amphotericin B administration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
237 views2 pagesMedications and Antidotes Chart
Uploaded by
kThis document provides information on medications and their antidotes, types of insulin and their properties, intravenous cardiac drips and their uses and dosages, common medications classified by type including nursing considerations, medications used in obstetrics, and antifungal amphotericin B administration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
PHARMACY
Medications With Antidotes Insulin Chart
Medication Antidote Insulin Name (U-100,
Onset Peak Duration
Acetaminophen Acetylcysteine or Mucomyst except where noted)
Anticholinesterase Atropine or Pralidoxime Rapid Acting
Anticholinergic Physostigmine 30-90
Antifreeze Fomepizole, Ethanol insulin aspart 10-20 minutes 3-5 hours
minutes
Benzodiazepines Romazicon (Flumazenil) 12-15
insulin human 10-20 minutes 3 hours
Beta- Blocking Agents Mesna minutes
Calcium Channel 30-90
Calcium Chloride, Glucagon insulin glulisine 10-20 minutes 3-5 hours
Blockers minutes
Carbon Monoxide Hyperbaric, Oxygen 30-90
Coumadin Phytonadione or Vitamin K insulin lispro 10-20 minutes 3-5 hours
minutes
Cyclophosphamide Mesna Regular
Digibind or Digoxin Immune Regular 30-60 minutes 2-4 hours 5-8 hours
Digoxin
Fab Regular 30-60 minutes 2-4 hours 5-8 hours
Dopamine Rigitidine Intermediate Acting
Fluorouacil Leucovorin Calcium NPH 1-3 hours 8 hours 12-16 hours
Heparin Protamine SO4
Long Acting
Insulin Reaction IV Glucose (D50)
insulin detemir 1 hour No peak 20-26 hours
Iron Deferoxamine
insulin glargine 1 hour No peak 20-26 hours
Methotrexate Leucovorin Calcium
Narcan ( Naloxone) or Ultra Long Acting
Narcotics insulin glargine U-300 6 hours No peak 36 hours
Nalmefene
Narcan ( Naloxone) or Mixtures
Opiod Analgesics 50% lispro protamine/50%
Nalmefene 10-15 minutes Varies 10-16 hours
Organophosphate Atroppine, Pralidoxime insulin lispro
Insulin and Glucose, NaHCO3, 75% lispro protamine/25%
Potassium 10-15 minutes Varies 10-16 hours
Albuterol inhaler insulin lispro
Succinylcholine Respiratory support 70% aspart protamine/30%
5-15 minutes Varies 10-16hours
Tensilon Atropine Sulfate insulin aspart
Tylenol Acetylcysteine 70% NPH/30% Regular 30-60 minutes Varies 10-16 hours
Warfarin Phytonadione or Vitamin K 70% NPH/30% Regular 30-60 minutes Varies 10-16 hours
Cardiac Drips
Drug Dosage Use
Load: 4-5 gm/1 hour, Then 1 gm/hour for 8 hours. • Don’t
Amicar Inhibit fibronolysis • Reduce post op bleeding
exceed 30 gm/day
150 mg bolus over 10 min • 1mg/min for 6 hours • 0.5 mg/min
Amiodarone Treatment for VF/VT, antiarrhythmic
for 18 hours • Don’t exceed 2.2gm/24 hours
Diltiazem 2.5-15mg/hr • Don’t exceed 24 hours Decrease HR & BP, Antiarrhythmic
Dobutamine 0.5-20/mcg/kg/min Increase CO, Increase BP
Low: Increased renal blood flow, increased UOP
1-5 mcg/kg/min for low dose
Med: May increase renal blood flow, CO, HR, and contractility
Dopamine 5-15mcg/kg/min for med dose
High: May increase BP and stimulate vasoconstriction, may not
20-150 mcg/kg/min for high dose
increase BP, may increase risk of tachyarrhythmias
2-20 mg/min
Epinephrine Increase HR and BP
0.01-0.5 mg/kg/min
Load: 250-500 mcg/kg over 1 min
Esmolol Decrease HR & BP, Antiarrhythmic, Treat SVT
50-300 mcg/kg/min
Labetalol 1-8 mg/min Treat hypertensive emergency
Load: 50 mcg/kg over 10-30 min
Milrinone Vasodilator, Increase HR & CO
0.375-0.75 mcg/kg/min
Nicardipine 2.5 mg/hr Decrease BP
Nitroglycerine 10-400 mcg/min • 0.2-5mcg/kg/min Vasodilator, Decreases BP
Norepinephrine 5-30 mcg/min • 0.01-0.5 mcg/kg/min Increase BP
Bolus: 5-20 mcg/kg IV Q10-15 min • 40-300 mcg/min • 0.1-0.5
Phenylphrine Increase BP
mcg/kg/min
Vasopressin 0.01-0.04 units/min Increase BP
www.NurseNation.net • These charts are for reference only.
Nurse Nation is not responsible for decisions made based on this information. • Local policy should supersede. • COPYRIGHT NURSE NATION 2020
PHARMACY
Common Medications with OBSTETRICS
Classifications Oxytocin
Assess uterus for tetanic contraction
Classification / Monitor fetal heart rate
Nursing Considerations Tocolytic (stop contractions)
Example
ANALGETICS Terbutaline Don’t give before 20 weeks
Monitor fetal heart rate
Do not give with other anticoagulants
ANTIFUNGAL
Aspirin Don’t take before surgery
Don’t give to children with viral infections IVPB Slow
Monitor for renal damage
NSAIDs (Ibuprofen) Contraindicated with GI ulcers Amphotericin B
Increase fluid intake
Opioids (Morphine) Respiratory depressant Assess hearing
ANTICONVULSANTS ANTICHOLINERGICS
Gum hyperplasia - Regular dental check-ups GI - slows motility
Dilantin
Monitor therapeutic levels Eyes - dilates pupils
Atropine
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY Cardiac - increase heart rate
Immunosuppression Respiratory - bronchodilation
Cushing-like symptoms ONCOLOGICAL MEDICATIONS
Prednisone Use extreme caution
Hyperglycemia
Osteoporosis Chemotherapy Wear gloves and mask while mixing and
ANTICOAGULANT administering
Heparin aPTT ANTI-GOUT
Increase fluid intake
Warfarin PT / INR Allopurinol
Increased urine output
ANTI-PARKINSONIAN Colchicine May cause bloody diarrhea if toxicity occurs
Benztropine Treats extrapyramidal symptoms
Carbidopa/Levodopa Effective in the absence of tremors
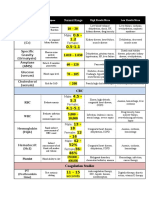
Therapeutic Drug Levels
Drug Therapeutic Level
BETA BLOCKERS
Do not stop abruptly Acetaminophen (Tylenol) 10 - 20 mcg/mL
Propranolol Carbamazepine (Tegretol) 4 - 10 mcg/mL
Masks signs of hypoglycemia
POTASSIUM SUPPLEMENTS Digoxin (Lanoxin) 0.5 - 2.0 ng/mL
Check labs prior to administration Gentamycin (Garamycin) 5 - 10 mcg/mL
Potassium Chloride Never give IV push Lithium (Eskalith) 0.5 - 1.2 mEq/L
Do not give with renal failure Magnesium Sulfate 4 - 7 mg/dL
BRONCHODILATOR Phenobarbital (Solfoton) 15 - 40 mcg/mL
Theophylline Monitor therapeutic levels Phenytoin (Dilantin) 10 - 20 mcg/dL
Monitor for tachycardia and tremors Salicylate 15 - 30 mg/dL
Albuterol Theophylline (Aminophylline) 10 - 20 mcg/dL
May also decrease potassium levels
CARDIAC GLYCO SIDE Tobramycin (Tobrex) 5 - 10 mcg/mL
Toxicity - Visual changes, loss of appetite Valproic Acid (Depaken) 50 - 100 mcg/mL
Digoxin Assess apical pulse for a minute prior to Vancomycin (Vancocin) 20 - 40 mcg/mL
administering Drug Schedule
ANTI-ECLAMPTIC Schedule Description Examples
Used in Preeclampsia High potential for abuse. No currently MDMA, LSD,
Monitor deep tendon reflexes I
Magnesium Sulfate accepted medical use. GHB
Assess for respiratory depression High potential for abuse, but with
Seizure precations Morphine,
II some accepted medical uses in the
cocaine, Opium
DIURETICS US. Requires written prescription
Potassium wasting Potential for abuse, but lower than Ketamine,
Furosemide previous categories. Requires new codeine,
Monitor Potassium levels III
Potassium sparing prescription after 6 months or five anabolic
Spironolactone refills steroids
Monitor Potassium Levels
Relatively low potential for abuse.
PSYCHOTROPICS Benzodia-
Accepted medical uses in the US.
Therapeutic range 0.8 - 1.2 IV zepines,
Lithium Requires new prescription after 6
Increase fluid intake phenobarbital
months.
MAOI’s Avoid foods with Tyramine Low potential for abuse. Accepted Pyrovalerone,
V
Disulfiram Avoid alcohol intake of any kind medical uses in the US retigabine
www.NurseNation.net • These charts are for reference only.
Nurse Nation is not responsible for decisions made based on this information. • Local policy should supersede. • COPYRIGHT NURSE NATION 2020
You might also like
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- Type Drug ChartDocument3 pagesType Drug ChartKarina Rodriguez100% (3)
- Nursing Cheat LabValuesDocument4 pagesNursing Cheat LabValuessasukenoneko100% (5)
- Pharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetSanobar Charania100% (1)
- NCLEX Drug CardsDocument136 pagesNCLEX Drug CardsC Johnson100% (44)
- OTM 101 Nursing MnemonicsDocument2 pagesOTM 101 Nursing MnemonicsMarlena Nicole100% (6)
- Cardiac Drugs Study Guide CourseDocument19 pagesCardiac Drugs Study Guide CourseAmanda Brittain100% (6)
- Nursing Study SitesDocument16 pagesNursing Study Sitesspartacuslives100% (3)
- Pharm PhalshDocument206 pagesPharm PhalshJohn MichealNo ratings yet
- 76 Cheat Sheets For Nursing StudentsDocument95 pages76 Cheat Sheets For Nursing StudentsIly Lagoniya100% (14)
- Entire Medication BundleDocument22 pagesEntire Medication BundleKarina Castillo100% (1)
- 1430 Drug CardsfinalDocument7 pages1430 Drug CardsfinalLizSherman100% (1)
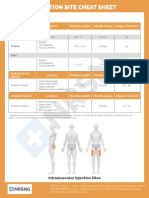
- Cs Pharm 022 Injection Site Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCs Pharm 022 Injection Site Cheat SheetEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Nursing School Drug ChartDocument13 pagesNursing School Drug ChartEve Lester100% (3)
- Disease Cheat SheetDocument393 pagesDisease Cheat Sheetsurviving nursing school50% (2)
- ATI Pharm TIPSDocument17 pagesATI Pharm TIPSmike Gee100% (3)
- Nursing School Necessities Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesNursing School Necessities Cheat SheetRevNo ratings yet
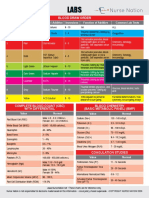
- 2 Labs Cheat Sheets Nurse NationDocument2 pages2 Labs Cheat Sheets Nurse NationkNo ratings yet
- Quick Nursing Student Notes 2Document1 pageQuick Nursing Student Notes 2Frank KimNo ratings yet
- Patho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept MapsDocument139 pagesPatho Physiology Bible: Over 70 Concept Mapslauramphs79100% (5)
- Cardiac DrugsDocument10 pagesCardiac Drugssurviving nursing school100% (3)
- Template For NURSING NotesDocument2 pagesTemplate For NURSING Notesbngraham4No ratings yet
- Med BundleDocument36 pagesMed Bundlejamie sealNo ratings yet
- Injection Site Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesInjection Site Cheat Sheet PDFjustin_sane100% (2)
- Common Cardiac Drugs for Angina and StentingDocument13 pagesCommon Cardiac Drugs for Angina and StentingDonna Deala100% (2)
- Basic Drug Cards 3Document14 pagesBasic Drug Cards 3Karima Jones100% (1)
- Med Surg Study Guide 41 PagesDocument42 pagesMed Surg Study Guide 41 PagesVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (2)
- Test InformationDocument5 pagesTest InformationCatalina BorquezNo ratings yet
- Memory Notebook of Nursing VolDocument170 pagesMemory Notebook of Nursing Voleric100% (1)
- Heart Blocks: "The Heart Block Poem"Document18 pagesHeart Blocks: "The Heart Block Poem"Bijay Kumar Mahato100% (1)
- NURSING PHARMACOLOGY TIPSDocument19 pagesNURSING PHARMACOLOGY TIPSmaniz442100% (2)
- Lab ValuesDocument3 pagesLab Valuessurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Med Surg Cheat Sheet 1Document1 pageMed Surg Cheat Sheet 1Figmentum FigmentumNo ratings yet
- Med Surg BibleDocument502 pagesMed Surg BibleNicole Ahmed100% (4)
- Pharm 1.13 Antidepressant Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharm 1.13 Antidepressant Cheat SheetEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes - 24 Hours or Less To Absolutely Crush The NCLEX Exam!Document45 pagesFluid and Electrolytes - 24 Hours or Less To Absolutely Crush The NCLEX Exam!KingBlack Canarsie100% (2)
- Endocrine NursingDocument2 pagesEndocrine NursingUnclePorkchop94% (34)
- Drug Cards PDFDocument136 pagesDrug Cards PDFTasha100% (3)
- Pulmonary Drugs For Nursing PharmacologyDocument1 pagePulmonary Drugs For Nursing Pharmacologylhayes123475% (4)
- Critical Care Notes Clinical Pocket Guide - (Gastro-Urinary)Document1 pageCritical Care Notes Clinical Pocket Guide - (Gastro-Urinary)Britanny Nelson100% (1)
- NURV 456 Telemetry Interpretation StudentDocument56 pagesNURV 456 Telemetry Interpretation StudentMarie Yi100% (2)
- Commonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1Document9 pagesCommonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1annatw100% (10)
- Critical Care Cheat Sheet FreebieDocument2 pagesCritical Care Cheat Sheet FreebieJeshan Yanong Beltran100% (1)
- Freebie Bundle-50 Pages. PDFDocument63 pagesFreebie Bundle-50 Pages. PDFMaria Conchita Traya100% (1)
- 63 Must Know Lab Values Cheat Sheet - NCLEX (Caribbean Nurses of Puerto Rico and Latin America) PDFDocument4 pages63 Must Know Lab Values Cheat Sheet - NCLEX (Caribbean Nurses of Puerto Rico and Latin America) PDFChristineBiankii100% (1)
- Chart of Neuro DisordersDocument1 pageChart of Neuro DisordersNursingSchoolNotes100% (2)
- Anti-Infectives Course #25Document18 pagesAnti-Infectives Course #25Gina Giammalvo100% (2)
- 1.4 Blood Types & RH FactorDocument1 page1.4 Blood Types & RH FactorTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Fluid and Electrolytes ChartsDocument7 pagesChapter 14 Fluid and Electrolytes ChartsBNA_RN100% (3)
- Drug CardsDocument10 pagesDrug CardsMaria Robustelli100% (3)
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- 50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know NowDocument29 pages50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know Nowtandz100% (19)
- Nursing Fundamentals DeMYSTiFieD, Second EditionFrom EverandNursing Fundamentals DeMYSTiFieD, Second EditionRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- CRITICAL THINKING IN CLINICAL NURSING PRACTICE (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCRITICAL THINKING IN CLINICAL NURSING PRACTICE (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Maternal-Newborn Nursing DeMYSTiFieD: A Self-Teaching GuideFrom EverandMaternal-Newborn Nursing DeMYSTiFieD: A Self-Teaching GuideNo ratings yet
- 2 Labs Cheat Sheets Nurse NationDocument2 pages2 Labs Cheat Sheets Nurse NationkNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MnemonicsDocument91 pagesPharmacology MnemonicsKnizhonki Knizhonki96% (72)
- Chilton & Bain (2018) A Textbook of Community Nursing-RoutledgeDocument405 pagesChilton & Bain (2018) A Textbook of Community Nursing-RoutledgeAsri ApriliantiNo ratings yet
- 2 Labs Cheat Sheets Nurse NationDocument2 pages2 Labs Cheat Sheets Nurse NationkNo ratings yet
- Anti-Manic Drugs: Lithium, Haloperidol, Carbamazepine & Valproic AcidDocument19 pagesAnti-Manic Drugs: Lithium, Haloperidol, Carbamazepine & Valproic AcidVickyEliseFinandaNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin PAR 45Document65 pagesPhenytoin PAR 45Lourdes VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Emrcp CNS 1-37Document34 pagesEmrcp CNS 1-37dryusufsNo ratings yet
- Linder 2016Document7 pagesLinder 2016Bagus SetiawanNo ratings yet
- CIDPDocument21 pagesCIDPidno1008No ratings yet
- Integrated Therapeutics IiiDocument82 pagesIntegrated Therapeutics IiiSalahadinNo ratings yet
- Drug Interaction SaDocument3 pagesDrug Interaction SaShahabWassiNo ratings yet
- Neurological MCQDocument4 pagesNeurological MCQAnonymous hF5zAdvwCC100% (1)
- Students August SeminarDocument12 pagesStudents August SeminarjjjkkNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument25 pagesQuestionsHanan Qasim100% (1)
- Actinic keratosis to idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura medical signs and diagnosesDocument272 pagesActinic keratosis to idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura medical signs and diagnosesMarie SantoroNo ratings yet
- Case #1: Current Visit: 23 Year Old Man Returns For Follow Up Having Been Last Seen Six Months Ago. He Reports No ChangeDocument11 pagesCase #1: Current Visit: 23 Year Old Man Returns For Follow Up Having Been Last Seen Six Months Ago. He Reports No ChangeRehan SaleemNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Guideline in AdultsDocument131 pagesEpilepsy Guideline in AdultsNEuRoLoGisT CoFFeeCuP100% (3)
- Ms 1 Pat Marline FaustinDocument18 pagesMs 1 Pat Marline Faustinapi-365764138No ratings yet
- Medications and Antidotes ChartDocument2 pagesMedications and Antidotes ChartkNo ratings yet
- Nimotop en PiDocument8 pagesNimotop en PiDonia ShadyNo ratings yet
- ANTICONVULSANTSDocument1 pageANTICONVULSANTSPadmavathi CNo ratings yet
- American Board of Family MedicineDocument71 pagesAmerican Board of Family MedicineMohamed Elmasry100% (4)
- Rogawski 2004Document8 pagesRogawski 2004Dr. Kaushal Kishor SharmaNo ratings yet
- Carbamazepine May Impair Cognition Due to Increased Oxidative StressDocument6 pagesCarbamazepine May Impair Cognition Due to Increased Oxidative Stressece142No ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorders and Carbamazepine PharmacokinetiDocument5 pagesBipolar Disorders and Carbamazepine PharmacokinetiAgr YuroNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Handout Dr. Ann SpolarichDocument16 pagesPharmacology Handout Dr. Ann SpolarichMina Lotfallah ShenoudaNo ratings yet
- University of Hargeisa GIT Pharmacology Review Questions: Name:aniisa Muse Ahmed Faculty:midwifery ID:1716642 Class:3ADocument4 pagesUniversity of Hargeisa GIT Pharmacology Review Questions: Name:aniisa Muse Ahmed Faculty:midwifery ID:1716642 Class:3AAniza Mouse100% (1)
- اسئلة مفيدة ل المجلس الطبي والهيئةDocument37 pagesاسئلة مفيدة ل المجلس الطبي والهيئةتعلم فالعلم حياةNo ratings yet
- The Epilepsy Prescriber's Guide To Antiepileptic Drugs 2010Document333 pagesThe Epilepsy Prescriber's Guide To Antiepileptic Drugs 2010Andi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Lamotrigine and Other Antiepileptics On Sleep Architecture - No Effect PDFDocument5 pagesLamotrigine and Other Antiepileptics On Sleep Architecture - No Effect PDFNones NoneachNo ratings yet
- P2 (1) - Kowski AB, Et Al. Epilepsy Behav - 2016 Jan 54150-7.Document8 pagesP2 (1) - Kowski AB, Et Al. Epilepsy Behav - 2016 Jan 54150-7.li chenNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide For The Pharmacy Licensing Exam - Questions and AnswersDocument81 pagesReference Guide For The Pharmacy Licensing Exam - Questions and AnswersNikka LaborteNo ratings yet
- High Yield PsychiatryDocument44 pagesHigh Yield PsychiatryAntony Awad100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Funds 2Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan Funds 2Yash RamawatNo ratings yet