Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Weak Forms 8 Pages
Weak Forms 8 Pages
Uploaded by
Wendell EspinalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Weak Forms 8 Pages
Weak Forms 8 Pages
Uploaded by
Wendell EspinalCopyright:
Available Formats
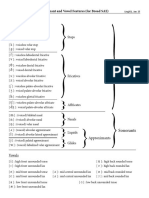
Weak and Strong Forms:
1. The indefinite article: <a>/<an>
a) strong forms: // and //
The strong form is used exclusively in the context of quotation and receives stress in this
context:
You say [] before a consonant but [] before a vowel.
b) weak forms // and //
The weak form is used elsewhere.
[] boy was bitten by [] alligator.
2. The conjunction <and>:
a) strong form: //
Used in the context of quotation, for emphasis and in impatient usually impolite answers
where it receives stress and question-like intonation:
- I love you!
- []...??? (meaning: ‘So what?!?!’)
- Do you have anything apart from cosmetics in your purse?
- Hmmm...I’ve got cosmetics [] cosmetics...
b) weak forms: 1) // or 2) //
1) is used in normal speech:
You will read this again [] again [] again until you remember it!
You use 2) in fast speech before a CONSONANT:
Dumb [] dumber.
3. Comparative particle <as>:
a) strong form: //
The strong form is used sentence finally and optionally between two unstressed syllables. It
is stressed only in the former case:
Such []?
I hate it when he uses her [] his cook and waitress!
b) weak form: //
Weak forms are used elsewhere.
[] drunk [] a lord...
Hard [] I tried, I could not keep up with her.
4. Prepositions: <at, of, for, from>
a) strong forms: /t, (), /
Used sentence finally, for emphasis, quoting, and optionally between two unstressed
syllables. In the first three contexts receive stress.
What are you staring [t]?
b) Weak forms: /t, ()()(), /
Used elsewhere.
I got it [] my father [] my 10th birthday.
I’ll stay [] you [] a week.
That is not my cup [] tea.
THE PREPOSITION LIKE <by, in, with, out, up etc.> THAT CONTAIN (AT LEAST)
ETYMOLOGICALLY HIGH VOWELS DO NOT HAVE SEPARATE WEAK FORMS IN
STANDARD BRITISH ENGLISH!!!!
<on> DOES NOT HAVE A WEAK FORM REDUCED TO SHWA!
5. The verb ‘to be’<be, am, are, is, was, were, been>:
a) strong forms: /()(), /
Used sentence initially in questions, sentence finally, in question tags, for emphasis, quoting.
- [] they playing our favourite song?
- Yes, they [].
He isn’t too eager to help you, [] he?
b) weak forms: /()()()()/
Used in other positions, as an operator in wh-questions.
They [] in China and they [] coming back in January.
I’ve never [] to Ukraine.
6. The verb ‘to have’ <have, has, had>
a) strong forms: //, // and //
Used sentence finally, in question tags, sentence medially as a lexical verb (meaning ‘to
possess sth.’)
- Have you seen his newest movie?
- Yes, I [].
He [] three flats in Manhattan and two in Hollywood.
I [] to stay longer at work.
b) Weak forms: 1) // or 2) // or 3) // and 1) // or 2) // or 3) // and 1) // or 2)
// or 3) //
Used as an auxiliary verb. 1) are used sentence initially or after a word ending in //. 3) are
used after a vowel and 2) are used elsewhere.
She[] made a complaint against you.
John and Peter [] done something terrible.
[~d] you been there before that day?
7. The verb <do, does>
a) strong forms: // and //
Sentence finally, as a lexical verb.
- Yes, I am sure he [].
- We’ll [] plenty of exercises!
b) weak forms: 1) // 2) /d/ and 1) // or 3) //
Used as an auxiliary verb 2) used before vowels, 3) in very fast speech
[] he know what to do?
[d] I look as if I was your twin brother?
8. Conjunction <but>
a) strong form: //
Sentence finally, metaphorically meaning ‘doubts’
There are still some ifs and [].
I think you are right []...
b) weak form: //
Used elsewhere.
I could have tried to help her [] did not have knowledge enough to do that.
9. Modal verbs <must, can, could, shall, should, will, would >:
a) strong forms
VERB/FORMS STRONG FORMS WHERE USED:
Must // Sentence initially, sentence
finally, in question tags, in
the meaning of logical
assumption.
Can // Sentence initially, sentence
finally and in question tags.
Could // as above
Shall // as above
Should // as above
Will // as above
Would // as above
IN NEGATIVE FORMS ALL AUXULLIARY VERBS (ALL MODALS + NON-MODAL
AUXILIARIES i.e. ALL MENTIONED IN 9 + DO, BE AND HAVE) RETAIN THEIR
STRONG FORMS!
REMEMBER THAT SOME OF THE VOWELS IN CONTRACTED NEGATIVE FORMS
ARE DIFFERENT FROM THOSE IN NON-NEGATED FORMS!!!
CONTRACTED NEGATIVE FORMS LOSE ‘T’ BEFORE A CONSONANT:
You [] smoke here!
b) weak forms:
VERB/FORMS WEAK FORMS WHERE USED
Must 1) // or 2) // Elsewhere. 1) before
vowels 2) before
consonants
Can // Elsewhere.
Could // as above
Shall 1) // 2) // or // Elsewhere. 2) used
before consonants
Should // or // Elsewhere.
Will 1) // 2) // As above. 2) used after a
pronoun.
Would // or / / or 3) // Elsewhere. 3) after
pronouns except for ‘it’.
10. Pronouns in nominative <you, he, she, we>
a) strong forms: //
In emphatic contexts, sentence finally.
- So it was really []!?
- If [] can’t, nobody can!
b) weak forms: /1) 2) /
Elsewhere. 1) used sentence initially, 2) used elsewhere.
I bet [] can’t count to 8723680276350287436.
[] was so excited that [] forgot to put on her clothes.
11. Pronouns in accusative <me, you, him, her, us, them>
a) strong forms //
Emphatic context, quoting...
It is [] to whom I wrote the letter....
b) weak forms: /()()() /
Elsewhere, sentence initially only the forms with // are attested. They are not stressed.
I hate []!
12. Pronouns in genitive <your, his, her, their>
a) strong forms: / (), ()/
Sentence finally, for emphasis.
Is this car []?
b) weak forms: /j(), () , ()/
Elsewhere. //-initial forms are used sentence initially and after shwa.
He was doing [] best not to disappoint her but she did not care.
<their> is not reduced to shwa!
13. Pronoun/subject filler <there>
a) strong form: /()/
As a pronoun...
He has hidden it [].
b) weak forms: /()/
Elsewhere: as a subject position filler (dummy subject):
[] has been a terrible misunderstanding.
14. Modifier <some>:
a) strong form: //
before nouns, meaning an unidentified object/person, in the environment of weak syllables,
sentence finally:
[] Mr Smith is waiting for you outside the building.
[] of them may be dangerous.
My mother made a delicious cheesecake, would you like to have []?
b) weak form: //
Before mass nouns to mean an unidentified amount of sth. before a count nouns meaning
several:
I found [] coins.
I need [] water.
15. Conjunction <or>:
a) strong forms: /()/
Two // three people in the company speak French.
b) weak forms (only in fixed phrases) : /(r)/
More // less one big mess.
16. Pronoun <who>:
a) strong form (as an interrogative pronoun): //
// is she?
Do you know // she is?
b) weak form (relative pronoun): //
People // are absent will have to make up for it.
17. Comparative particle <than>:
a) strong form (sentence finally, emphasis): //
What is he bigger than?
b) weak form (elsewhere): //
I’m better [] you.
18. Preposition/particle <to>
a) strong forms //: sentence finally
Where are you going []?
b) weak forms 1) // 2) //
1) before consonants, 2) before vowels
I’m going [] Japan.
I want [] open a shop.
19. Demonstrative/ relative pronoun <that>
a) strong form //: as a demonstrative pronoun
Why did you do []?
b) weak form //: as a relative pronoun
I told you [] I didn’t like you.
20. Pronoun <any>
a) strong form //: when emphasised, used sentence initially, sentence finally, in complex
pronouns like anyone, anyhow, anything etc.
She was surprised because she did not expect anyone.
b) weak form //: used elsewhere
I didn’t expect you to do // better.
You might also like
- Trabajo Final de Ingles TerminadoDocument5 pagesTrabajo Final de Ingles Terminadoelvis espinoza33% (6)
- Weak and Strong Forms + Rules PhoneticsDocument5 pagesWeak and Strong Forms + Rules PhoneticsJohny Be Good100% (3)
- Tenses Notes PDFDocument21 pagesTenses Notes PDFMohd Fahim87% (15)
- Final Exam LinguisticsDocument5 pagesFinal Exam Linguisticsdomonique tameronNo ratings yet
- HO (5) Vowels - Monophthongs and DiphthongsDocument4 pagesHO (5) Vowels - Monophthongs and DiphthongsAnikaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives (CRP 2016)Document26 pagesAdjectives (CRP 2016)maneaxNo ratings yet
- Syntax ExerciseDocument1 pageSyntax ExerciseOanh Nguyễn0% (1)
- Mahasri SobahiyaDocument2 pagesMahasri Sobahiyamahasri sobahiya0% (1)
- ACFrOgC5h2q2QLtVjtFAXdEy 7EJoUy2kUQojIFYei56L31tCWFS6Nqj7IdR-6ZZSUJgFOLu3pAILzk8XXqqbvv7FoJYX6BP8HfBmDns1YK1OG4g76Qqc92SX5Tv2p8qyISmLbMQi9p1yUpPv8hJ PDFDocument9 pagesACFrOgC5h2q2QLtVjtFAXdEy 7EJoUy2kUQojIFYei56L31tCWFS6Nqj7IdR-6ZZSUJgFOLu3pAILzk8XXqqbvv7FoJYX6BP8HfBmDns1YK1OG4g76Qqc92SX5Tv2p8qyISmLbMQi9p1yUpPv8hJ PDFRonaNGusrimaNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument28 pagesTranscriptionDejana VučinićNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - Pronunciation Problem ReportDocument11 pagesTask 1 - Pronunciation Problem ReportLookAtTheMan 2002No ratings yet
- Listening-Lesson-Plan FeedbackDocument23 pagesListening-Lesson-Plan FeedbackHuỳnh Lê Hương KiềuNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercise: I-Multiple Choice: Choose The Best AnswerDocument4 pagesExtra Exercise: I-Multiple Choice: Choose The Best AnswerHương Nguyễn Hồng Sông100% (1)
- Sound Assimilation in English and Arabic A Contrastive Study PDFDocument12 pagesSound Assimilation in English and Arabic A Contrastive Study PDFTaha TmaNo ratings yet
- Averil Coxhead - Pat Byrd - 2007Document19 pagesAveril Coxhead - Pat Byrd - 2007mjoferNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected Speech 968Document25 pagesAspects of Connected Speech 968Đinh Thế TrungNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Introduction To PhonologyDocument16 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Introduction To PhonologyGiang Nguyet MinhNo ratings yet
- Semester Phonetics and Phonology 2021Document3 pagesSemester Phonetics and Phonology 2021Aci Sulthanal KhairatiNo ratings yet
- VowelsDocument18 pagesVowelstiendanghia18101992No ratings yet
- PhonologyDocument26 pagesPhonologyLee Ayn PoncardasNo ratings yet
- 13 - FricativesDocument15 pages13 - FricativesMitzie CañoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PragmaticsDocument16 pagesChapter 10 PragmaticsSadafz channelNo ratings yet
- Linguistics 1Document29 pagesLinguistics 1Hakkuo AmeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Translation 11-2021 - Sample Test Paper - OnlineDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Translation 11-2021 - Sample Test Paper - OnlineNghi PhuongNo ratings yet
- Lectures 7, 8 - Word Classes + ExercisesDocument28 pagesLectures 7, 8 - Word Classes + ExercisestbericaNo ratings yet
- Analyze The Characteristics of English Grammar During The Middle English Period.Document3 pagesAnalyze The Characteristics of English Grammar During The Middle English Period.KAKON AKTER RINKOU Fall 18100% (1)
- Nasals and Other ConsonantsDocument13 pagesNasals and Other ConsonantsMercedes GalayNo ratings yet
- Advanced Syntax NotesDocument3 pagesAdvanced Syntax NotesMahnur Naqvi0% (1)
- Velarization - Mohammed MasoudDocument6 pagesVelarization - Mohammed MasoudMohammed MasoudNo ratings yet
- Phonology - Session 3 2-1112 English VowelsDocument30 pagesPhonology - Session 3 2-1112 English VowelsSuong Trong Mai HoangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Phonological Units Of: LanguageDocument2 pagesChapter 3: The Phonological Units Of: LanguageDung ThùyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Writing Skills October Exam, S 2nd Sem 2017-2018Document1 pageAdvanced Writing Skills October Exam, S 2nd Sem 2017-2018Dr. Abdullah ShaghiNo ratings yet
- NHA2 - Derivational and Inflectional MorphemesDocument12 pagesNHA2 - Derivational and Inflectional Morphemes08AV2D50% (2)
- Tugas Uas PhonologyDocument86 pagesTugas Uas PhonologySofi Mina NurrohmanNo ratings yet
- A Brief Study On Syllable DivisionDocument5 pagesA Brief Study On Syllable Divisionisraramone0% (1)
- Giáo Trình Hình Thái HọcDocument63 pagesGiáo Trình Hình Thái Họcthao4557010120No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 PhonologyDocument23 pagesChapter 9 PhonologyNie Luh Ayu100% (1)
- Weak and Strong FormsDocument2 pagesWeak and Strong Formsvalex8No ratings yet
- Syntax: Adverbials and Other Matters RevDocument31 pagesSyntax: Adverbials and Other Matters RevMaulana MualimNo ratings yet
- ElisionDocument3 pagesElisionramy bnmNo ratings yet
- Bài Tập Ở Nhà Môn Morpho-SyntaxDocument12 pagesBài Tập Ở Nhà Môn Morpho-SyntaxTran Duc HuyNo ratings yet
- English and Arabic Derivation For Translation StudentsDocument17 pagesEnglish and Arabic Derivation For Translation StudentsMuhammad El-Fiky100% (1)
- The Phonology of Pashto - Henderson 1998Document4 pagesThe Phonology of Pashto - Henderson 1998Donna HallNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument31 pagesAspects of Connected Speecharcher70100% (1)
- Cardinal Vowel TheoryDocument14 pagesCardinal Vowel TheoryAhmed Shojib50% (2)
- Syllabic Consonant, Clusters of S With PlosiveDocument8 pagesSyllabic Consonant, Clusters of S With PlosiveSabrina Kang100% (1)
- The Phoneme. Consonants. VowelsDocument54 pagesThe Phoneme. Consonants. VowelsДарья БелкинаNo ratings yet
- Sound Features For English PDFDocument1 pageSound Features For English PDFMuhammad SaeedNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Skill Focus: ReadingDocument13 pagesLesson Plan: Skill Focus: ReadingHuỳnh Lê Hương KiềuNo ratings yet
- Phonology.1 PHONEMEDocument16 pagesPhonology.1 PHONEMEMOHAMMAD AGUS SALIM EL BAHRI100% (3)
- Traditional GrammarDocument20 pagesTraditional GrammarMessatsu DZNo ratings yet
- Minimal Pairs Exercises IDocument2 pagesMinimal Pairs Exercises IMiguel Perez100% (2)
- Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument13 pagesUniversitas Sumatera Utarahety hidayahNo ratings yet
- Without Slang and IdiomsDocument6 pagesWithout Slang and Idiomsluciferinchaos0% (1)
- Assessing PronunciationDocument28 pagesAssessing PronunciationAlexis Martinez ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers Chapter 8: Q/Define A Morpheme With Reference To Its Three CriteriaDocument34 pagesQuestions and Answers Chapter 8: Q/Define A Morpheme With Reference To Its Three CriteriaNaba MajedNo ratings yet
- Principles of E Phonetics and PhonologyDocument74 pagesPrinciples of E Phonetics and PhonologyDuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Developing Plans From TitleDocument15 pagesDeveloping Plans From TitleMau LydiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Classifying Speech SoundsDocument5 pagesChapter 2: Classifying Speech SoundsDung ThùyNo ratings yet
- NHA2 - IC - AllomorphsDocument17 pagesNHA2 - IC - Allomorphs08AV2D100% (3)
- Test Fall2021 KEYSDocument4 pagesTest Fall2021 KEYSPhuong BuiNo ratings yet
- English OrthographyDocument31 pagesEnglish Orthographyseanwindow5961No ratings yet
- Lexicology Course Description BujaDocument2 pagesLexicology Course Description BujaIoana Alexandra100% (1)
- Irreguler VerbsDocument5 pagesIrreguler VerbsWind AivatcoNo ratings yet
- Review of TensesDocument4 pagesReview of TensesGeorgia KleoudiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 3Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 3Hope Espiritu VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Rank, Pull Your Weight, Pull A Face, Pull Someone/something To Pieces, Pull Someone's LegDocument36 pagesRank, Pull Your Weight, Pull A Face, Pull Someone/something To Pieces, Pull Someone's LegAndreea ChipailaNo ratings yet
- Common Mistakes in EnglishDocument211 pagesCommon Mistakes in EnglishAymane Salim100% (2)
- English (US) 2Document130 pagesEnglish (US) 2zlatanmesiNo ratings yet
- Libro de Ingles BachilleratoDocument96 pagesLibro de Ingles BachilleratoPerez SuceNo ratings yet
- Let's Identify The Personal Pronouns: Teacher: Sandra J. Carpio Romero 1Document11 pagesLet's Identify The Personal Pronouns: Teacher: Sandra J. Carpio Romero 1Ruben ChiroqueNo ratings yet
- Spelling MatrixDocument1 pageSpelling Matrixapi-51462131No ratings yet
- Colour Coded WritingDocument2 pagesColour Coded Writingapi-252796813No ratings yet
- 11-Foundations of GMAT VerbalDocument35 pages11-Foundations of GMAT VerbalDroea Intimates100% (1)
- Questions Without AuxiliaresDocument10 pagesQuestions Without AuxiliaresNazly MauroNo ratings yet
- Common Noun and Proper Noun PracticeDocument2 pagesCommon Noun and Proper Noun PracticeSumi MajumderNo ratings yet
- Preposition ReportDocument13 pagesPreposition ReportMaria Gerelyn Leray100% (1)
- Japanese ParticlesDocument15 pagesJapanese ParticlesREA002100% (3)
- Kannada HistoryDocument5 pagesKannada HistoryRedfm MangaloreNo ratings yet
- 1 SYLLABUS INGLÉS 1 Descripción Gran Tarea y ContenidosDocument7 pages1 SYLLABUS INGLÉS 1 Descripción Gran Tarea y ContenidosCindy CobosNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument17 pagesActive and Passive VoiceNhung HồngNo ratings yet
- English 1week 1Document4 pagesEnglish 1week 1marisol corpuzNo ratings yet
- Test Zero and First Conditional 2Document1 pageTest Zero and First Conditional 2Ingles Noveno Campo SerranoNo ratings yet
- Tomáš Suchomel - Lukáš ZiebikerDocument2 pagesTomáš Suchomel - Lukáš ZiebikerTomáš SuchomelNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence & SubjunctiveDocument3 pagesConditional Sentence & SubjunctiveFitri ThreeanNo ratings yet
- Verbals Week 8 Flinguis 3Document18 pagesVerbals Week 8 Flinguis 3Shane Mendoza BSED ENGLISHNo ratings yet
- The Alphabet Maltese Letter Approximate Pronunciation Symbol ExamplesDocument20 pagesThe Alphabet Maltese Letter Approximate Pronunciation Symbol Examplesirena34No ratings yet
- Do Make TakeDocument15 pagesDo Make TakeJairo LopezNo ratings yet
- Grammar Games Like Ing Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesGrammar Games Like Ing Worksheet PDFpavel100% (1)