Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOL 385 Notes
Uploaded by
Olivia SnyderCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOL 385 Notes
Uploaded by
Olivia SnyderCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOL 385 CH 10-12 NOTES
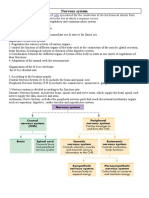
1.Describe the different types of receptors for somatic & special senses.
Chemoreceptors- pH, oxygen, glucose
Thermoreceptors- heat- use cation channels
Mechanoreceptors- baroreceptors, cell stretch, vibration, sound
Photoreceptors- photons of light
Naked/free neural endings
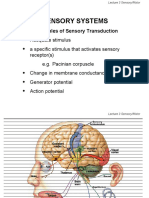
2. Explain how receptors convert physical stimuli into electrical signals using the
following terms: transduction, threshold, adequate stimulus, receptive field, receptor
potential.
Stimulus energy converted into info processed by the nervous system
Threshold is min. stimulus
Form of energy to which a receptor is most responsive
Graded/receptor potential- change in sensory receptor membrane potential
*Sensory transduction converts stimuli into graded potentials
*Sensory neurons have a receptive field- sensitives have smaller area, and less sensitive larger
3.Explain how the central nervous system is able to determine modality, location,
intensity, and duration of a stimulus.
CNS determines modality: which sensory neurons are activated, and where they terminate in the
brain
Location: which receptive fields are activated, and lateral inhibition
Intensity: amount of receptors activated
Duration of stim: receptors adapt with tonic vs. phasic receptors, duration of action potentials
*The brain uses timing differences to localize sound*
-Longer stronger stimulus release more neurotransmitter
-Receptors adapt to a sustained stimulus:
Tonic-slowly adapting receptors that respond for the duration of the stimulus
Phasic- rapidly adapt to a constant stimulus and turn off
5.Trace the pathways for somatic sensation from the receptor to the somatosensory
cortex.
Pthways for somatic perception project to the cortex and cerebellum
•Primary sensory neurons–Synapse in CNS with secondary sensory
neurons •Secondary sensory neurons–Interneurons in the CNS -
synapse with tertiary sensory neurons in thalamus •Tertiary sensory
neurons–Project to somatosensory cortex and many project to
cerebellum Somatosensory cortex
Spinal cord, medulla, thalamus, sensory cortex
6.Describe the different types of somatosensory receptors.
BIOL 385 CH 10-12 NOTES
Touch receptors most common in the body
Skin temp receptors are free nerve endings
7.Explain how the pain and itch are mediated by nociceptors, and describe the neural
pathways for pain.
Nociceptors –Neurons with free nerve endings–Respond to
strong noxious stimulus that may damage tissue–Found in the
skin, joints, muscles, bones, and viscera–Not found in
CNS•Activation initiates adaptive, protective response (reflex) –
Integrated in spinal cord
Initiate protective responses, histamine
CH 11
1.Describe the physiological role of the autonomic division and its
branches.
Autonomic; parasympathetic= “rest and digest”
Sympathetic=”fight or flight”
BIOL 385 CH 10-12 NOTES
-Autonomic division is under antagonistic control
2.Compare and contrast the anatomy and chemical communication of the
sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.
- Autonomic pathways have two efferent series
- Preganglionic neurons:
- Postganglionic neurons
- Ganglion- a cluster of neuron cell bodies outside the CNS
You might also like
- CNS 1 - Part 1Document151 pagesCNS 1 - Part 1Qamariah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Dr. Shofa Nur Fauzah Explains the Sensory SystemDocument42 pagesDr. Shofa Nur Fauzah Explains the Sensory SystemHani100% (1)
- Sensory Receptors 2021Document13 pagesSensory Receptors 2021Marvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and Somatic Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 15 - Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and Somatic Nervous Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- 1general SensationDocument141 pages1general SensationAzimuddeen AzeliNo ratings yet
- Ascending SystemDocument104 pagesAscending SystemCharles OkohNo ratings yet
- Sensory ReceptorsDocument26 pagesSensory ReceptorsEmmanuel JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Sensory ReceptorsDocument24 pagesSensory ReceptorsKhateeja Tul KubraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Sensory PhysiologyDocument10 pagesLecture 4 Sensory PhysiologyJanvi MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Sensory System in 40 CharactersDocument10 pagesThe Sensory System in 40 CharactersnabeelNo ratings yet
- BLG600 Week 3a Full SizeDocument35 pagesBLG600 Week 3a Full SizeDineth GunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiology of the Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesNeurophysiology of the Nervous SystemKhalid AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Sensory Process and PerceptionDocument78 pagesSensory Process and Perceptionmedicine lifeNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyNervous Review2Document3 pagesPhysiologyNervous Review2djxela89No ratings yet
- CNS 2Document8 pagesCNS 2Jeff ParkNo ratings yet
- CNS Part 1 (Lec 1-7)Document32 pagesCNS Part 1 (Lec 1-7)ABO ALSOFNo ratings yet
- What Is The Importance of Receptors in Our Sensory System? Give A Detailed Description On Types and Functions of These CategoriesDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Importance of Receptors in Our Sensory System? Give A Detailed Description On Types and Functions of These CategoriesKiran HassanNo ratings yet
- Physiology NotesDocument13 pagesPhysiology NotesGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- BPK 205 Intro To Human Physiology: Lecture 12 - Sensory Physiology I: Intro & The Somatic SensesDocument24 pagesBPK 205 Intro To Human Physiology: Lecture 12 - Sensory Physiology I: Intro & The Somatic SensesnathanNo ratings yet
- Sensory - chap 2Document47 pagesSensory - chap 2Ahmed khanNo ratings yet
- Sonsoryreceptos 141217101431 Conversion Gate01Document68 pagesSonsoryreceptos 141217101431 Conversion Gate01Olaniyi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Group 4 General Biology 2 1Document64 pagesGroup 4 General Biology 2 1orticiojosephinemarialynbayonaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Complete Unit 4 - RemovedDocument25 pagesPsychology Complete Unit 4 - RemovedDivyanshi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Psychology Complete Unit 4Document210 pagesPsychology Complete Unit 4VeekeshGuptaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Skin ReceptorsDocument16 pagesPhysiology of Skin ReceptorsJaynier Jayson JayaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: Recovery Lesson 1Document44 pagesLesson Title: Recovery Lesson 1Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System and SensesDocument33 pagesThe Nervous System and Senses孙美美Ezra Paola TaysonNo ratings yet
- Types and Functions of Sensory ReceptorsDocument20 pagesTypes and Functions of Sensory ReceptorspashaNo ratings yet
- CNS Physiotherapy 2021Document88 pagesCNS Physiotherapy 2021atefmoussaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Saraf SensorikDocument48 pagesFisiologi Saraf SensorikVivie Tirany SoediroNo ratings yet
- Notes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesDocument6 pagesNotes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesamberNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters: A. Paracrine Regulators (Tissue Hormones)Document11 pagesNeurotransmitters: A. Paracrine Regulators (Tissue Hormones)Prasana100% (1)
- Chapter 14 - The Somatic Nervous SystemDocument55 pagesChapter 14 - The Somatic Nervous SystemTH TNo ratings yet
- ANP PHYSIOLOGYDocument8 pagesANP PHYSIOLOGYElijah KamaniNo ratings yet
- Ch. 15 Sensory SystemDocument23 pagesCh. 15 Sensory SystemJackieFernandezNo ratings yet
- KP 1.3.2.3 Fisiologi Sistem Saraf PeriferDocument50 pagesKP 1.3.2.3 Fisiologi Sistem Saraf PeriferShintia Surya PutriNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9Th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9Th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcleopatrabanhft1vh7100% (9)
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manualoraliemaximusp474w3100% (32)
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument39 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manualbufochauswu2w100% (17)
- 1 Cns 1 Receptor 1 1Document95 pages1 Cns 1 Receptor 1 1SanketNandaniNo ratings yet
- Sensory Receptors WorksheetDocument12 pagesSensory Receptors WorksheetAlexis CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Modalities of SensationDocument16 pagesModalities of SensationKELVINNo ratings yet
- Coordination HDocument9 pagesCoordination HmatinNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord MechanismesDocument9 pagesSpinal Cord Mechanismesmarina rodriguezNo ratings yet
- 1.response To StimuliDocument20 pages1.response To StimuliRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Dept Fisiologi FKIK UnsoedDocument69 pagesDept Fisiologi FKIK UnsoedMellyNo ratings yet
- Sci-Hub - Anatomía Básica y Fisiología de Las Vías Del Dolor - 10.1016:j.nec.2014.06Document10 pagesSci-Hub - Anatomía Básica y Fisiología de Las Vías Del Dolor - 10.1016:j.nec.2014.06Lucero DiazNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument69 pagesCoordination and ResponseRegis WachenukaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF SENSORY SYSTEMS cM7srPXDocument72 pagesGENERAL PRINCIPLES OF SENSORY SYSTEMS cM7srPXAtefeh AhangarNo ratings yet
- Sensory Systems: 1. General Principles of Sensory TransductionDocument26 pagesSensory Systems: 1. General Principles of Sensory TransductionMsKizzyNo ratings yet
- Basicanatomyand Physiologyofpain Pathways: Sarah Bourne,, Andre G. Machado,, Sean J. NagelDocument10 pagesBasicanatomyand Physiologyofpain Pathways: Sarah Bourne,, Andre G. Machado,, Sean J. NagelarlinieNo ratings yet
- Somatosensory System OverviewDocument16 pagesSomatosensory System OverviewRamadhan OdiestaNo ratings yet
- Nerve SystemDocument5 pagesNerve SystemRekesh SaeedNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous System Part 1 Study GuideDocument4 pagesHuman Nervous System Part 1 Study Guidevanessa solanoNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument3 pagesCoordination and ResponseclintonbogololephojaneNo ratings yet
- WEEK 8 LAB EXERCISE - Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesWEEK 8 LAB EXERCISE - Nervous SystemMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manual 1barrywilliamsgedyaqspcfNo ratings yet
- PL-10 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesPL-10 Autonomic Nervous SystemFoong Zhen HinNo ratings yet
- Ceballos, Mary Kate L. (BSN 1-Ya-18) - Week 7 - Laboratory Exercise - The Nervous System Cns and PnsDocument9 pagesCeballos, Mary Kate L. (BSN 1-Ya-18) - Week 7 - Laboratory Exercise - The Nervous System Cns and PnsKay ChoiNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument7 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentOlivia SnyderNo ratings yet
- HLTH 380 Website ReviewsDocument2 pagesHLTH 380 Website ReviewsOlivia SnyderNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Study GuideDocument6 pagesExam 3 Study GuideOlivia SnyderNo ratings yet
- HLTH 420 GoalDocument1 pageHLTH 420 GoalOlivia SnyderNo ratings yet
- Cultural Interview Survey Document-1Document2 pagesCultural Interview Survey Document-1Olivia SnyderNo ratings yet
- The Growth of Tomato Seedlings Inoculated With Co-Cultivated Piriformospora Indica and Bacillus PumilusDocument8 pagesThe Growth of Tomato Seedlings Inoculated With Co-Cultivated Piriformospora Indica and Bacillus PumilusNayo PalomequeNo ratings yet
- Tití BebelecheDocument19 pagesTití BebelecheJaime MoralesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 1&2 (Part 1)Document117 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 1&2 (Part 1)Kleindyn Joy PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual and Workbook For Biological Anthropology 1st Edition Soluri Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesLaboratory Manual and Workbook For Biological Anthropology 1st Edition Soluri Solutions ManualAlexMartinxfgr100% (57)
- Artigo OncoDocument14 pagesArtigo OncoCatarina LuísNo ratings yet
- EXCI 202 Review Questions 2014: Answer: FalseDocument25 pagesEXCI 202 Review Questions 2014: Answer: FalseChrisNo ratings yet
- NemoDocument333 pagesNemoash krisNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Mitosis and Meiosis Pre LabDocument1 pageLab 3 Mitosis and Meiosis Pre LabS. Spencer0% (2)
- Test Bank For Family Therapy History Theory and Practice 6th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Family Therapy History Theory and Practice 6th EditionKaraKentygbc100% (51)
- Sistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)Document38 pagesSistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaNo ratings yet
- Drosophila Lab Write UpDocument13 pagesDrosophila Lab Write Upapi-585837255No ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument22 pagesControl and CoordinationMozibor RahmanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Sexuality 6th Edition Hyde Test BankDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Human Sexuality 6th Edition Hyde Test BankMichaelFletcheroiqr100% (27)
- Latihan PKP Bahasa Inggeris TAHUN 4Document2 pagesLatihan PKP Bahasa Inggeris TAHUN 4XzuLLXNo ratings yet
- Toothpickase Activity - Modeling Enzyme ActionDocument7 pagesToothpickase Activity - Modeling Enzyme ActionJSM320No ratings yet
- New Insights Into The Function and Global Distribution ofDocument34 pagesNew Insights Into The Function and Global Distribution ofWi FuentesNo ratings yet
- Life Science: Keanekaragaman Spesies Mangrove Dan Zonasi Di Wilayah Kelurahan Mangunharjo Kecamatan Tugu Kota SemarangDocument13 pagesLife Science: Keanekaragaman Spesies Mangrove Dan Zonasi Di Wilayah Kelurahan Mangunharjo Kecamatan Tugu Kota SemarangSandy Wahyu DNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.2.2: The Secret To SignalsDocument2 pagesActivity 2.2.2: The Secret To SignalsSelma SabriNo ratings yet
- Regional Map Wide Bay Burnett Ed 8 Front 2009Document1 pageRegional Map Wide Bay Burnett Ed 8 Front 2009linNo ratings yet
- Unusual Looking Pentatomids: Reassessing The Taxonomy of Braunus Distant and Lojus McDonald (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae)Document19 pagesUnusual Looking Pentatomids: Reassessing The Taxonomy of Braunus Distant and Lojus McDonald (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae)bolosphex1634No ratings yet
- Pub Quick Amp Easy Decorative PaintingDocument74 pagesPub Quick Amp Easy Decorative PaintingEtab BarakatNo ratings yet
- 3C Development of Organisms PDFDocument74 pages3C Development of Organisms PDFBryan YeohNo ratings yet
- The true origins of Fulton's condition factorDocument4 pagesThe true origins of Fulton's condition factorjoebiolmarNo ratings yet
- Insect Collection Project & RubricDocument5 pagesInsect Collection Project & Rubricbasketball7878100% (1)
- Activity 4 Systematics LabNotSoFinal.1Document15 pagesActivity 4 Systematics LabNotSoFinal.1EPHRAIM JOASH ABEJO GAGANTINGNo ratings yet
- Lrdi 100 PDFDocument101 pagesLrdi 100 PDFPuneet MalhotraNo ratings yet
- 3is Q2 MODULE 2.1Document10 pages3is Q2 MODULE 2.1dfgerbrcNo ratings yet
- Reading Exercises 0627Document22 pagesReading Exercises 0627lydianDNo ratings yet
- Senior High School - Year 1: Section 1: Introducing BiologyDocument72 pagesSenior High School - Year 1: Section 1: Introducing BiologySharifNo ratings yet
- Rhodococcus EquiDocument15 pagesRhodococcus EquiAdriana Montaña100% (1)