Professional Documents
Culture Documents
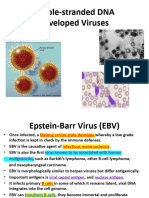
EBV Patho
Uploaded by
Nicole Chloe OcanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EBV Patho
Uploaded by
Nicole Chloe OcanaCopyright:
Available Formats
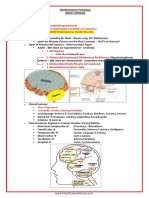
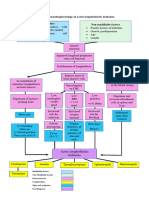
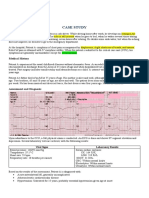
Mechanics Signs and Symptoms exhibited by the patient.
Main Diagnosis Secondary Diagnosis
LEGENDS:
Confirmatory Diagnostic results Predisposing Factors
close contact with an individual • Presence of EBV VCA IgG and IgM
infected with EBV:
EBV transferred through saliva. antibodies
• Presence of atypical lymphocytes
• Kissing
• Pharyngitis
• Sharing drinks and food
• Bilateral orbital edema
• Sharing the same utensils or EBV is exposed to the oral cavity.
toothbrush • Inflammation of liver, spleen, and
• Having contact with toys that or kidneys
EBV+ children drooled on • Petechial rashes
EBV then replicates
Immune response: B lymphocytes in the nasopharynx.
engages with the virus. • hyperemia of pharynx
• fever
• WBC was 17,060/mm3
Inflammation of the nasopharynx SLIGHTLY ELEVATED
11% atypical EBV infects B lymphocytes.
lymphocytes ELEVATED
• Free collections: perihepatic,
peri splenic
Mature CD8+ T cells Development of EBV • mild elevation of
infected B lymphocytes transaminases (aspartate
responds.
aminotransferase: 170 U/L
and alanine
aminotransferase: 79 U/L)
Development of EBV
infected T lymphocytes
• albumin: 2.95 g/dL =
proteinuria
• 7 leucocytes in urine =
EBV infected B and T lymphocytes then infection
spreads toward the entire reticular • 2 erythrocytes in urine =
endothelial system (i.e liver, spleen) hematuria
• potassium: 7.09 mEq/L
ELEVATED
• bicarbonate: 11.5 mEq/L LOW
EBV infected T cells infiltrates into the • urea: 181 mg/dL VERY
renal interstitium of both kidneys. ELEVATED
• creatinine: 4.1 mg/dL
ELAVATED
• calcium: 7.3 mg/dL ELAVATED
• right kidney axes: Presence of EBV infected T cells promotes the • Both kidneys had grades 1-2
82 mm (8.2 cm) BIG parenchymal
secretion of inflammatory cytokines and histiocytes.
• left kidney long axes: hyperechogenicity
83 mm (8.3 cm) BIG •
Inflammatory cytokines Reductions in glomerular
Swelling of the kidneys compromise epithelial barriers. filtration rate (GFR)
Promotes tubular epithelial atypia. Oligoanuria
• renal biopsy material Tubulointerstitial Nephritis (TIN)
showed: intense and mixed
tubulointerstitial • presence of peripheral
inflammatory infiltration rich atypical lymphocytosis and
with T cells and histiocytes. Acute Kidney Injury positive serological tests for
EBV
• bilateral upper lid edema
• some petechial rashes on
Epstein-Barr Viral Infection
lower limbs
• maculopapular rash that blanches under pressure
• low urine output
• bilateral orbital edema
You might also like
- The History of Biological Warfare 1Document4 pagesThe History of Biological Warfare 1Thonieroce Apryle Jey MorelosNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Path (MSN) PDFDocument150 pagesNervous System Path (MSN) PDFRodrigoMendozaNo ratings yet
- Hematology NotesDocument4 pagesHematology NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- WBC Neoplasms Review - PathologyDocument6 pagesWBC Neoplasms Review - Pathologylas100% (6)
- Pediatric LymphomaDocument43 pagesPediatric LymphomaAnsu MaliyakalNo ratings yet
- Micropara Lab NotesDocument34 pagesMicropara Lab NotesShyenNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Ceftriaxone (Forgram)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Ceftriaxone (Forgram)julesubayubay5428100% (8)
- Pathophysiology of Hepatitis B InfectionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hepatitis B InfectionSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Dossier Guide-for-IMPD ATMP - 1.0Document29 pagesDossier Guide-for-IMPD ATMP - 1.0nsk79inNo ratings yet
- CMV & Ebv: A.ChancharoenDocument59 pagesCMV & Ebv: A.ChancharoenRapid MedicineNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Document5 pagesAcute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Kim LompotNo ratings yet
- Liver Disorders: Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders Part 1Document7 pagesLiver Disorders: Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders Part 1Ayessa MoniqueNo ratings yet
- Group 2 HepatitisDocument27 pagesGroup 2 HepatitisMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- AntiviralsDocument6 pagesAntiviralsNur NajminaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis VirusesDocument11 pagesHepatitis VirusesClaraNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Causative DiseasesDocument3 pagesCirrhosis Causative DiseasesMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- SurgPatho WBC 2018Document28 pagesSurgPatho WBC 2018Janella SuerteNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument54 pagesCase StudysHaYnEsEy100% (1)
- Enterobacteriaceace Part 2Document37 pagesEnterobacteriaceace Part 2Krenz CatiboNo ratings yet
- MID 4 BACTE EnterobacteriaceaeDocument6 pagesMID 4 BACTE EnterobacteriaceaePotenciano MaricarNo ratings yet
- Microbio Lec 11 - Ecoli, Klebsiella Proteus, Citrobacter AnDocument3 pagesMicrobio Lec 11 - Ecoli, Klebsiella Proteus, Citrobacter Anapi-374321750% (2)
- RETROVIRIDAEDocument1 pageRETROVIRIDAEjcpacate1178qcNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology ReviewDocument11 pagesClinical Pathology Reviewrob hNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis VirusDocument83 pagesHepatitis VirusRudresh Shoorashetty ManoharNo ratings yet
- Infectious MononucleosisDocument26 pagesInfectious MononucleosisAkshan SentinelNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis - Ferri's Clinical AdvisorDocument2 pagesLeptospirosis - Ferri's Clinical AdvisorAndika GhifariNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart Disease - Patho - DiagramDocument10 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease - Patho - DiagramJoann100% (12)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYAngela Jane MadristaNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument22 pagesInfectious DiseasesMrgNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - 01. LY - EBV Biology in Nasopharyngeal CancerDocument5 pagesDay 1 - 01. LY - EBV Biology in Nasopharyngeal CancerHari PranotoNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis RevDocument83 pagesVirus Hepatitis RevSukma WinahyuNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument18 pagesIlovepdf MergedAnita Paredes VillegasNo ratings yet
- 2-Viral GatroenteritisDocument16 pages2-Viral Gatroenteritisademabdella38No ratings yet
- Muhammad Asaad Maidin Departement Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument54 pagesMuhammad Asaad Maidin Departement Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin University, MakassarPratiwi PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Heaptobiliary Disease by Lecturio.Document106 pagesHeaptobiliary Disease by Lecturio.louisegantierNo ratings yet
- Dengue-Malaria TOT For Doctors 2022 District Dengue PPTDocument88 pagesDengue-Malaria TOT For Doctors 2022 District Dengue PPTRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Oncological DisordersDocument7 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Oncological DisordersLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- Complement System: DR Shamaila Saleem PHD PhysiologyDocument10 pagesComplement System: DR Shamaila Saleem PHD PhysiologyAfnankh698No ratings yet
- Diseases of The Newborn Part2Document6 pagesDiseases of The Newborn Part2sarguss14100% (1)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid - AUBFDocument9 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid - AUBFMitch IbayNo ratings yet
- Rotation5 SIC LarceñaDocument10 pagesRotation5 SIC LarceñanoemilauNo ratings yet
- Lab Results Odontogenic Infection 1Document4 pagesLab Results Odontogenic Infection 1Jamie HaravataNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument408 pagesIlovepdf MergedSAKSHI DUBEYNo ratings yet
- Diff DiagnDocument3 pagesDiff DiagnАбдул Насер МохаммадізмаелNo ratings yet
- Herpes 4Document17 pagesHerpes 4Charles SainzNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: Prepared By: Mina Zana Nozhin Ahmed Hoshyar Omer Hawkar IsmailDocument19 pagesHepatitis B: Prepared By: Mina Zana Nozhin Ahmed Hoshyar Omer Hawkar Ismailraman saeedNo ratings yet
- CARE OF THE CHILD WITH CANCER HandoutDocument3 pagesCARE OF THE CHILD WITH CANCER HandoutMatt Andrei P. SongcuanNo ratings yet
- Part2 OncologyDocument39 pagesPart2 OncologySamah AlshamiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen 2222Document75 pagesOxygen 2222Salim AlmetewtyNo ratings yet
- 11 23 2006 Oncology EBV PHDDocument35 pages11 23 2006 Oncology EBV PHDapi-3696530No ratings yet
- Togaviruses: FindingsDocument4 pagesTogaviruses: Findingsحسين محمد مطرود كاظمNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Bacterial Meningitis Case PresentationDocument22 pagesPediatric Bacterial Meningitis Case Presentationapi-602288180No ratings yet
- Kemia: Reported byDocument49 pagesKemia: Reported bykris_ocio963No ratings yet
- 6 Adaptive ImmunityDocument4 pages6 Adaptive ImmunityanonymousNo ratings yet
- Practical Class 2: ImmunologyDocument41 pagesPractical Class 2: ImmunologyLorena DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Viruses KMCDocument29 pagesHepatitis Viruses KMCmaregnrodiNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis Hepatis 1Document48 pagesCirrhosis Hepatis 1Muhammad RivaileNo ratings yet
- MYCOVIRO LECLAB 5 Other Viruses and PrionsDocument3 pagesMYCOVIRO LECLAB 5 Other Viruses and PrionsMarcus Dave MendozaNo ratings yet
- Problems in Oxygenation Transport Med Surg TransesDocument6 pagesProblems in Oxygenation Transport Med Surg TransestrashhhtineNo ratings yet
- Patient Based Patho ALL Super Final Pro MaxDocument1 pagePatient Based Patho ALL Super Final Pro MaxMarc SorianoNo ratings yet
- High-Resolution Electrophoresis and Immunofixation: Techniques and InterpretationFrom EverandHigh-Resolution Electrophoresis and Immunofixation: Techniques and InterpretationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sustainability EssayDocument1 pageSustainability EssayNicole Chloe OcanaNo ratings yet
- Case Study With ECG Reading OcañaDocument3 pagesCase Study With ECG Reading OcañaNicole Chloe OcanaNo ratings yet
- Classification 2018-2020, 11 Edition. "Insomnia" Is An Approved Nursing Diagnosis Under Domain 4, Class 1, Diagnosis Code 00095Document4 pagesClassification 2018-2020, 11 Edition. "Insomnia" Is An Approved Nursing Diagnosis Under Domain 4, Class 1, Diagnosis Code 00095Nicole Chloe OcanaNo ratings yet
- ABG Analysis OcanaDocument2 pagesABG Analysis OcanaNicole Chloe OcanaNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy - Asynchronous ActivityDocument2 pagesIV Therapy - Asynchronous ActivityNicole Chloe OcanaNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Assessment OcañaDocument10 pagesGeriatric Assessment OcañaNicole Chloe OcanaNo ratings yet
- Biofirm BacteriaDocument87 pagesBiofirm BacteriaThuý SmilerNo ratings yet
- Circular Medical (Dec2020)Document2 pagesCircular Medical (Dec2020)Radison sierraNo ratings yet
- Hematology PCIDocument50 pagesHematology PCIandebetgetnet78100% (2)
- Influenza (Flu) VirusDocument8 pagesInfluenza (Flu) VirusEric EpahNo ratings yet
- Disinfection GatewayDocument6 pagesDisinfection GatewaylynnNo ratings yet
- Immunological Changes With Age and Innovative Approaches To Bolster Immune Function in Older AdultsDocument11 pagesImmunological Changes With Age and Innovative Approaches To Bolster Immune Function in Older AdultsKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Albert Camus (Citate)Document3 pagesAlbert Camus (Citate)Amos AndreicaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document2 pagesActivity 1Annicoldjohn LariozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Um E AbdulSaboorNo ratings yet
- Why Smart People Believe Coronavirus MythsDocument3 pagesWhy Smart People Believe Coronavirus MythsBeatriz Soares SeborroNo ratings yet
- The Potential Benefits of Bloodletting. Yes, BloodlettingDocument12 pagesThe Potential Benefits of Bloodletting. Yes, BloodlettingJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Thesis MouthwashDocument5 pagesThesis MouthwashPayToDoMyPaperSingapore100% (3)
- The Event 201: October 2019Document5 pagesThe Event 201: October 2019Chloe WrightNo ratings yet
- Revision For The Mid-Term Test - Grade 12Document4 pagesRevision For The Mid-Term Test - Grade 12LinhLyNo ratings yet
- 200 Sre PortionDocument2 pages200 Sre PortionJobinNo ratings yet
- Describing Peracetic Acid Vapor SterilizationDocument2 pagesDescribing Peracetic Acid Vapor SterilizationsovalaxNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa2022483 AppendixDocument34 pagesNejmoa2022483 AppendixPaulo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Lactic 1Document4 pagesLactic 1Chaina EuniceNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Mechanisms of HIV Transcription Regulation by Drugs of AbuseDocument29 pagesHHS Public Access: Mechanisms of HIV Transcription Regulation by Drugs of AbusemikiNo ratings yet
- Saliva - A Diagnostic ToolDocument30 pagesSaliva - A Diagnostic ToolPrathusha UmakhanthNo ratings yet
- Mumps VirusDocument13 pagesMumps VirusLara MasriNo ratings yet
- QC in Clinical Microbiology RevDocument48 pagesQC in Clinical Microbiology RevPearl Kinasih2No ratings yet
- Gen. SuhaibManual of PCR in Diagnostic PathologyDocument155 pagesGen. SuhaibManual of PCR in Diagnostic PathologyHUS ALI74No ratings yet
- Viral Transport Media (VTM) - Principle, Preparation, Uses, LimitationsDocument10 pagesViral Transport Media (VTM) - Principle, Preparation, Uses, Limitationsgembul31No ratings yet
- Mahon CompileDocument13 pagesMahon CompileSheinor Fae GalzoteNo ratings yet
- HES 032 BSN - Lecture Long Quiz 3 FINALDocument24 pagesHES 032 BSN - Lecture Long Quiz 3 FINALGem HimenaceNo ratings yet