Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology, Surat Electrical Engineering Department
Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology, Surat Electrical Engineering Department
Uploaded by
ja ck0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesThis document contains assignments related to fundamentals of power system protection from Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology's Electrical Engineering department. It includes definitions of key terms like reliability, selectivity, and discrimination. It also defines requirements of a protective system like selectivity and reliability. Percentage differential relays are described as including restraining coils to overcome issues with simple differential relays under external faults or current imbalances. Drawbacks of simple differential relays for transmission lines are addressed by the percentage differential relay which restricts unwanted tripping due to imbalance currents.
Original Description:
Original Title
sgp q with ans
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains assignments related to fundamentals of power system protection from Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology's Electrical Engineering department. It includes definitions of key terms like reliability, selectivity, and discrimination. It also defines requirements of a protective system like selectivity and reliability. Percentage differential relays are described as including restraining coils to overcome issues with simple differential relays under external faults or current imbalances. Drawbacks of simple differential relays for transmission lines are addressed by the percentage differential relay which restricts unwanted tripping due to imbalance currents.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesMahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology, Surat Electrical Engineering Department
Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology, Surat Electrical Engineering Department
Uploaded by
ja ckThis document contains assignments related to fundamentals of power system protection from Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology's Electrical Engineering department. It includes definitions of key terms like reliability, selectivity, and discrimination. It also defines requirements of a protective system like selectivity and reliability. Percentage differential relays are described as including restraining coils to overcome issues with simple differential relays under external faults or current imbalances. Drawbacks of simple differential relays for transmission lines are addressed by the percentage differential relay which restricts unwanted tripping due to imbalance currents.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology, Surat
Electrical Engineering Department
Assignments-1:Fundamentals of Power System Protection
1. Define following terms in context to protective relay (i) Reliability (ii) Selectivity (iii)
Discrimination =page no 10
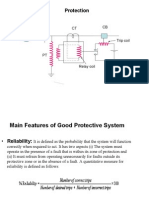
2. Explain the following requirements of protection system. (i) Selectivity (ii) Reliability
=page no 10
(iii) Security = On the other hand, security is a property used to characterize false tripping
on the relays. A relay is said to be secure if it does not trip when it is not expected to trip.
It is the degree of certainty that the relay will not operate incorrectly:
%security=number of correct /total number of trip ×100
3. Clearly distinguish the terms “Overload” and “Overcurrent”=.page no 23
4. Explain, what are the basic requirements of a protective System=.page no 6
5. Define: i) P.S.M.=page no14 ii) Restraining Torque=The restraining coils produce
torque opposite to the operating torque. Under normal and through fault
conditions, restraining torque is greater than operating torque. Thereby relay
remains inactive. When internal fault occurs, the operating force exceeds the
bias force and hence the relay is operated. iii) Burden=page no15
6. Define the following term:
(I) Relay pick up= When a relay operates to open a “b” contact or to close an “a”
contact, we say that it "picks up," and the smallest value of the actuating
quantity that will cause such operation, as the quantity is slowly increased
from zero, is called the "pickup" value.
(II) Fault clearing time= Clearing time is the amount of time it takes a circuit
protection device to clear a fault. An arc flash occurs when a short circuit
(fault) takes place inside of equipment.
(III) Reach of the relay= Reach of distance relay is defined as line protection
covered by relay in terms of line length or impedance. In the example,
the reach of relay is Z as it is expected to protect the entire line.
7. Define reach, under reach= A distance relay is said to under reach when the
impedance seen by relay due to fault is more than the relay setting value even
though the fault point is within the protected zone of line. This means that reach
of relay has decreased from the setting value., and over reach=14 of the relay.
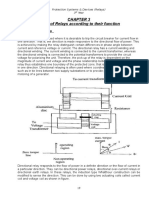
8. Draw and explain basic trip circuit=12
Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology, Surat
Electrical Engineering Department
9.What are the drawbacks of a simple differential scheme? Explain how the percentage
differential relay overcomes the drawbacks of simple differential relay.
The percentage differential relay consists restraining coil for overcoming the
trouble arising out of differences in the current ratio for the high value of an
external short circuit current. ... It restricts the unwanted tripping of the
transformer due to the imbalance current.
10.What problems, if any, do you anticipate in applying conventional differential protection
to a transmission line?
11.Explain simple differential relay. Ans =The relays used in power system protection are
of different types. Among them differential relay is very commonly used relay for
protecting transformers and generators from localised faults.
Differential relays are very sensitive to the faults occurred within the zone of protection but
they are least sensitive to the faults that occur outside the protected zone. Most of the relays
operate when any quantity exceeds beyond a predetermined value for example over current
relay operates when current through it exceeds predetermined value. But the principle of
differential relay is somewhat different. It operates depending upon the difference between
two or more similar electrical quantities.
Mahavir Swami College of Engineering & Technology, Surat
Electrical Engineering Department
12.Write and explain drawbacks of simple differential relay.=same q 11
13.Explain construction, working and operating characteristics of percentage differential
relay.= same q 9
You might also like
- Controller Diagram KLEEMANNDocument16 pagesController Diagram KLEEMANNSrgjan Dimitrieski100% (2)
- Over Cureent and EfDocument7 pagesOver Cureent and EfBasudev Patra100% (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- As Student WorksheetsDocument54 pagesAs Student WorksheetsHiyahiyahiya HuhahuhahuhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 RQDocument3 pagesChapter 1 RQAb C100% (2)
- Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearDocument12 pagesEe2402 Protection and SwitchgearVasudha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1chintuchetan123No ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Question Bank Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearDocument16 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Question Bank Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearSweqZNo ratings yet
- PSG Two Marks With AnswersDocument21 pagesPSG Two Marks With AnswersKRCT EEE HODNo ratings yet
- PSG Two Marks Q and A PDFDocument21 pagesPSG Two Marks Q and A PDFKRCT EEE HODNo ratings yet
- Protection and Switchgear Important QuestionsDocument38 pagesProtection and Switchgear Important QuestionsAkhil Surya0% (1)
- Distribution OverDocument3 pagesDistribution OverPaolo CasungcadNo ratings yet
- QB 105722Document7 pagesQB 105722Nuha Al awaisiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report2Document5 pagesLab Report2Tanzidul AzizNo ratings yet
- Relay Coordination Chapter3Document13 pagesRelay Coordination Chapter3Chân Gà NướngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3nassim.1979No ratings yet
- Protection PhilosophyDocument50 pagesProtection Philosophyrohan sainiNo ratings yet
- UniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eDocument60 pagesUniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eBala MNo ratings yet
- Psps Unit 1 QBDocument9 pagesPsps Unit 1 QBNaveen RajNo ratings yet
- Types of ProtectionDocument9 pagesTypes of Protectionkxalxo7637No ratings yet
- Trafo 3 AsdDocument4 pagesTrafo 3 AsdAchyar Maulana PratamaNo ratings yet
- EE6702 2marksDocument21 pagesEE6702 2marksVISWA VikNo ratings yet
- Over MatlabDocument8 pagesOver MatlabPriyesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- PSP Unit1 MaterialDocument103 pagesPSP Unit1 MaterialMerugu JyothiNo ratings yet
- B) Non-Unit Scheme:: Over Current Relay and Its CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesB) Non-Unit Scheme:: Over Current Relay and Its CharacteristicskarthikNo ratings yet
- Electrical NotesDocument22 pagesElectrical NotesJamil AhmadNo ratings yet
- Report On Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument20 pagesReport On Radial Feeder ProtectionSubhamGangdeb78% (9)
- Relays: The Function of Protective RelaysDocument14 pagesRelays: The Function of Protective RelayswazedbiplobNo ratings yet
- Zone of ProtectionDocument17 pagesZone of ProtectionAkimeNo ratings yet
- Lec # 23 Over Current ProtectionDocument51 pagesLec # 23 Over Current ProtectionAnamika Khan100% (1)
- Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument6 pagesRadial Feeder ProtectionSrivalli ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Electrical Protection SystemDocument101 pagesChapter-3 Electrical Protection Systemgerrzen64No ratings yet
- Over Current Relay Types and ApplicationsDocument11 pagesOver Current Relay Types and ApplicationskishansaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction ProtectionDocument15 pagesIntroduction ProtectionAyushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Ee1302 Protection and SwitchgearDocument12 pagesEe1302 Protection and SwitchgearMukesh Kumar0% (1)
- Assignment of System Protection Eeg 806Document24 pagesAssignment of System Protection Eeg 806emechetasamuel27No ratings yet
- Overcurrent ProtectionDocument3 pagesOvercurrent ProtectionZafiy LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Basic Power Protection Relaying Manual PDFDocument407 pagesBasic Power Protection Relaying Manual PDFmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- The Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocument13 pagesThe Philosophy of Protective RelayingrajeshNo ratings yet
- PSGDocument13 pagesPSGya vikaNo ratings yet
- Protective RelaysDocument79 pagesProtective RelaysMd Saif AliNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Protection Assignment (EEG 806)Document27 pagesPower Systems Protection Assignment (EEG 806)control roomNo ratings yet
- The Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocument14 pagesThe Philosophy of Protective RelayingDev SwainNo ratings yet
- Time Coordination Method For Power System Protection by Evolutionary AlgorithmDocument6 pagesTime Coordination Method For Power System Protection by Evolutionary AlgorithmrockNo ratings yet
- 3898-Article Text-10434-1-10-20180426Document8 pages3898-Article Text-10434-1-10-20180426robier raoufNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PSP PDFDocument8 pagesModule 1 PSP PDFMukund KumarNo ratings yet
- EE1302 Protection and Switchgear-SignedDocument12 pagesEE1302 Protection and Switchgear-SignedarivurpNo ratings yet
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent Relay 1Document10 pagesTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relay 1Alfredo RamirezNo ratings yet
- قسم الوقاية - الجزء الثانيDocument14 pagesقسم الوقاية - الجزء الثانيوليد موسىNo ratings yet
- Protection Schemes For Electrical Power SystemDocument10 pagesProtection Schemes For Electrical Power SystemAous HNo ratings yet
- PSP ImpDocument36 pagesPSP ImpHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Principle of Power SystemDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Principle of Power SystemSurendra PanditNo ratings yet
- Ee2402 - Protection and Switchgear Seventh Semester Two Marks Question &answers Unit IDocument38 pagesEe2402 - Protection and Switchgear Seventh Semester Two Marks Question &answers Unit INavneethNo ratings yet
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent Relay Part 1Document10 pagesTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relay Part 1carlos vidalNo ratings yet
- Relay Coordination StudiesDocument23 pagesRelay Coordination StudiesRonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Electrical Protection System PDFDocument101 pagesChapter-3 Electrical Protection System PDFBalachandra MallyaNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- The IEE Wiring Regulations Explained and IllustratedFrom EverandThe IEE Wiring Regulations Explained and IllustratedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Overcurrent Relay Advances for Modern Electricity NetworksFrom EverandOvercurrent Relay Advances for Modern Electricity NetworksNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Practice MSDocument88 pagesTopic 2 Practice MSAmina RakhaNo ratings yet
- Bay Wise Equpiment Information of 220 KV G.S.S., Bali Location of Equipment Sl. No. Name of Equipment Equipment IdDocument7 pagesBay Wise Equpiment Information of 220 KV G.S.S., Bali Location of Equipment Sl. No. Name of Equipment Equipment IdPrashant SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Electromagnetic Waves (Griffiths - ch9)Document95 pages04 - Electromagnetic Waves (Griffiths - ch9)JL1206No ratings yet
- Digital Measurement of Electrical Quantities Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDocument65 pagesDigital Measurement of Electrical Quantities Cathode Ray OscilloscopekrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- 3D Modelling of Rock Mass Falls Using The Particle Flow Code PFC3DDocument6 pages3D Modelling of Rock Mass Falls Using The Particle Flow Code PFC3DahsanNo ratings yet
- What Is ForceDocument5 pagesWhat Is ForceCherry Mobile SpinNo ratings yet
- 43 PDFDocument10 pages43 PDFeli700No ratings yet
- Spring Mass DamperDocument15 pagesSpring Mass DamperAeitesham Ul Huq SubedarNo ratings yet
- Alternators and Starter Motors 2003 PDFDocument106 pagesAlternators and Starter Motors 2003 PDFjovopavlovic100% (14)
- Mechanics Lab 2Document4 pagesMechanics Lab 2yogendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Architectural Acoustics 2Document12 pagesArchitectural Acoustics 2Leonoralynn SapunganNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Rotational MotionDocument5 pagesTutorial Rotational Motioneyfa firdausNo ratings yet
- Relais Bistable, 3 RT / 25 A: Relay Latch, 3 PDT / 25 AmpDocument4 pagesRelais Bistable, 3 RT / 25 A: Relay Latch, 3 PDT / 25 AmpXavier DevauxNo ratings yet
- Motions in One Dimension: Example 1Document3 pagesMotions in One Dimension: Example 1Angelo DumaopNo ratings yet
- Cusat Btech SyllabusDocument43 pagesCusat Btech SyllabusSteve ShivaNo ratings yet
- Power Factor ImprovementDocument9 pagesPower Factor ImprovementAnonymous 31rCP6OaNo ratings yet
- MECH223 - Prelim Lecture 1 (Introduction To Dynamics)Document10 pagesMECH223 - Prelim Lecture 1 (Introduction To Dynamics)Jomare RiveraNo ratings yet
- WaterwheelDocument10 pagesWaterwheelHermawan Mulyono100% (1)
- JC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1Document13 pagesJC2 (05/06) Physics Common Test 2006 Suggested Answers: Paper 1wangks1980No ratings yet
- Final Review ProblemsDocument9 pagesFinal Review ProblemsthomasNo ratings yet
- 060 Electric Current WorksheetDocument3 pages060 Electric Current WorksheetAbdullah SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Mixed CapacitorDocument10 pagesMixed CapacitorMr SonuNo ratings yet
- Technical Help: Ecodial Advance Calculation 4.2Document44 pagesTechnical Help: Ecodial Advance Calculation 4.2mumi87No ratings yet
- 004 Pwm-OcxiDocument7 pages004 Pwm-OcxiNeodymeNo ratings yet
- EN - ACS880-01-11-31 - P940 - P944 - Suppl - D - A5Document100 pagesEN - ACS880-01-11-31 - P940 - P944 - Suppl - D - A5Sambasivarao GoriparthiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rotating Machines: M.I. Friswell, J.E.T. Penny, S.D. Garvey and A.W. Lees Cambridge University Press, 2010Document19 pagesDynamics of Rotating Machines: M.I. Friswell, J.E.T. Penny, S.D. Garvey and A.W. Lees Cambridge University Press, 2010Bernardo ForestiNo ratings yet