Professional Documents
Culture Documents
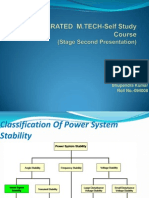
Control System Important
Control System Important
Uploaded by
ankit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesControl loop bandwidth is an important specification in controller design and is related to converter dynamic response. The higher the loop bandwidth, the faster disturbances will be rejected and the less time needed to regulate load voltage. Generally, the loop gain crossover frequency ranges from one-twenty-fifth to one-fifth the switching frequency.
A control system is robust if it is insensitive to differences between the actual system and the model used for controller design. Robuststab computes the stability robustness margin to determine if a system is robustly stable for all modeled uncertainties or if certain uncertainty values could lead to instability.
The theory of robust control defines indices like nominal performance, robust stability, and robust performance to quantify controller robustness under system uncertainties
Original Description:
Control System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentControl loop bandwidth is an important specification in controller design and is related to converter dynamic response. The higher the loop bandwidth, the faster disturbances will be rejected and the less time needed to regulate load voltage. Generally, the loop gain crossover frequency ranges from one-twenty-fifth to one-fifth the switching frequency.
A control system is robust if it is insensitive to differences between the actual system and the model used for controller design. Robuststab computes the stability robustness margin to determine if a system is robustly stable for all modeled uncertainties or if certain uncertainty values could lead to instability.
The theory of robust control defines indices like nominal performance, robust stability, and robust performance to quantify controller robustness under system uncertainties
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesControl System Important
Control System Important
Uploaded by
ankitControl loop bandwidth is an important specification in controller design and is related to converter dynamic response. The higher the loop bandwidth, the faster disturbances will be rejected and the less time needed to regulate load voltage. Generally, the loop gain crossover frequency ranges from one-twenty-fifth to one-fifth the switching frequency.
A control system is robust if it is insensitive to differences between the actual system and the model used for controller design. Robuststab computes the stability robustness margin to determine if a system is robustly stable for all modeled uncertainties or if certain uncertainty values could lead to instability.
The theory of robust control defines indices like nominal performance, robust stability, and robust performance to quantify controller robustness under system uncertainties
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Control system important
Control loop BW is an important specification in the controller design and is
related to the converter dynamic response. The higher the loop gain BW is,
the faster will be the rejection in disturbances, and the lesser will be the time
taken to regulate load voltage. Generally, the loop gain crossover frequency is
in the range (fs/25 < fc <fs/5), where “fs” is the switching frequency and “fc” is
the loop gain crossover frequency. However, in converter systems having real
or complex zeros outside the unit circle, the control.
The digital controller is designed such that the closed-loop system is stable
and the gain-margin must be at least 6 dB and the phase margin is between
45º to 75º.
Robust Stability
A control system is robust if it is insensitive to difference between actual
system and the model of the system which was used to design the controller.
These differences are referred to as model/plant mismatch or simply model
uncertainty. The key idea in the H∞ robust control paradigm we use to check
whether the design specifications are satisfied even for worst case uncertainty.
A nominally stable uncertain system is generally unstable for specific values of
its uncertain elements. Determining the values of the uncertain elements
closest to their nominal values for which instability occurs is a robust stability
calculation.
If the uncertain system is stable for all values of uncertain elements within
their allowable ranges the uncertain system is robustly stable Conversely, if
there is a combination of element values that cause instability, and all lie
within their allowable ranges, then the uncertain system is not robustly stable.
Robuststab computes the margin of stability robustness for an uncertain
system. A stability robustness margin greater than 1 means that the uncertain
system is stable for all values of its modeled uncertainty. A stability robustness
margin less than 1 implies that certain allowable values of the uncertain
elements, within their specified ranges, lead to instability.
The theory of robust control defines a set of performance indices to quantify
controller robustness, these are: (i) Nominal Performance (NP), (ii) Robust
Stability (RS), and (iii) Robust Performance (RP). System uncertainties.
You might also like
- Understand Advanced Process Control: Back To BasicsDocument4 pagesUnderstand Advanced Process Control: Back To BasicsJohn AnthoniNo ratings yet
- Types of Controllers - Proportional Integral and Derivative Controllers - Electrical4UDocument13 pagesTypes of Controllers - Proportional Integral and Derivative Controllers - Electrical4UHasan Qayyum ChohanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control, An Overview On Robust ControlDocument31 pagesAdvanced Control, An Overview On Robust Controlgerty1100% (1)
- Biomedical Control SystemsDocument3 pagesBiomedical Control SystemsNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- EmediKarimi FirstSubmissionACC2012Document6 pagesEmediKarimi FirstSubmissionACC2012zlatko22225No ratings yet
- Brief Papers: Robust Tuning of Power System Stabilizers Using QFTDocument9 pagesBrief Papers: Robust Tuning of Power System Stabilizers Using QFTAhmed HussainNo ratings yet
- Chap 8: Robust Control Part I: Uncertainty and RobustnessDocument7 pagesChap 8: Robust Control Part I: Uncertainty and RobustnessranaateeqNo ratings yet
- TA CONTROL-LOOP v1Document5 pagesTA CONTROL-LOOP v1Jorge Garcia AbadNo ratings yet
- Stability of Digital Control SystemsDocument77 pagesStability of Digital Control SystemsRonald George100% (8)
- Establishing Basis in Instrumentation EngineeringDocument5 pagesEstablishing Basis in Instrumentation EngineeringAgbim MartinsNo ratings yet
- Untitled 96aug97pd2Document5 pagesUntitled 96aug97pd2CharlesNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument29 pagesControl SystemsBrenton DahlNo ratings yet
- Scilab Ninja: Module 3: Classical Loopshaping DesignDocument12 pagesScilab Ninja: Module 3: Classical Loopshaping Designorg25grNo ratings yet
- Report SeminarDocument23 pagesReport SeminarpradnyaekadNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Impact-FisherDocument16 pagesControl Valve Impact-FisherCarlos de la TorreNo ratings yet
- The University of MindanaoDocument8 pagesThe University of MindanaoGrazel MDNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control Chapter 1Document19 pagesIndustrial Control Chapter 1Qayyum AqasyahNo ratings yet
- Conditional and Marginal StabilityDocument7 pagesConditional and Marginal StabilitySarthak GautamNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - StabilityDocument2 pagesControl Systems - StabilitySc RayaNo ratings yet
- Marlin Ch13Document44 pagesMarlin Ch13Ashwin Kumar SabatNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop ResponseDocument8 pagesClosed Loop ResponseJoydeep Choudhury 20UCH030No ratings yet
- Neural Nett HybridDocument13 pagesNeural Nett HybridrahulsundaresanNo ratings yet
- Wide-Area Robust H /H Control With Pole Placement For Damping Inter-Area OscillationsDocument7 pagesWide-Area Robust H /H Control With Pole Placement For Damping Inter-Area OscillationssunitharajababuNo ratings yet
- Question BANKDocument15 pagesQuestion BANKAyush MandhareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document22 pagesChapter 1Guido Wilder Algarañaz MonteroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 1 NotesSouvik DasNo ratings yet
- Huawei HO Parameter OptimizeDocument24 pagesHuawei HO Parameter Optimizerizal0111884120% (2)
- Task 4 PDFDocument48 pagesTask 4 PDFFathihah AnuarNo ratings yet
- Use These Methods Synthesis of Damp-: Try ForDocument5 pagesUse These Methods Synthesis of Damp-: Try ForFelix GamarraNo ratings yet
- Ipc PPT 7thDocument25 pagesIpc PPT 7thChemical engrNo ratings yet
- ChE170 Lecture 9 (Control Tuning) PDFDocument27 pagesChE170 Lecture 9 (Control Tuning) PDFRowieNo ratings yet
- Dhan Kumar Rai 0701CM171013 Vi Sem Assignment 1 On Chemical Process ControlDocument4 pagesDhan Kumar Rai 0701CM171013 Vi Sem Assignment 1 On Chemical Process ControlYng Dmb Broke GuyNo ratings yet
- 2Document25 pages2aashish meenaNo ratings yet
- HCHE 322 Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument8 pagesHCHE 322 Lecture 1 - IntroductionBrian MasauliNo ratings yet
- Pod Using HVDCDocument31 pagesPod Using HVDCRajeev JhaNo ratings yet
- Convergence CriteriaDocument9 pagesConvergence Criteriaajota_7No ratings yet
- Improved System OperationDocument6 pagesImproved System OperationRafi MuhammedNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument13 pagesFinallalit chola100% (1)
- Topic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignDocument14 pagesTopic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignxREDCivicCometxNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1. Control Systems Engineering - MEB 4101-1Document44 pagesLECTURE 1. Control Systems Engineering - MEB 4101-1nickokinyunyu11No ratings yet
- Bhupendra Kumar Roll No.-094008: Submitted byDocument36 pagesBhupendra Kumar Roll No.-094008: Submitted bytarnedo1No ratings yet
- Robust Control: Saba RezvanianDocument44 pagesRobust Control: Saba RezvanianTatić ArnelaNo ratings yet
- Control Valves 1678169882Document22 pagesControl Valves 1678169882Myo Myint MaungNo ratings yet
- Denavit Hartenberg MethodsDocument42 pagesDenavit Hartenberg MethodsShyamalNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Overview Professor GopalankrishnaDocument23 pagesControl Systems Overview Professor GopalankrishnaJameNo ratings yet
- Reliability Guideline: Primary Frequency ControlDocument14 pagesReliability Guideline: Primary Frequency ControlAnonymous AOsAXgNo ratings yet
- Bsic of ControlDocument12 pagesBsic of ControlSreekanth RaveendranNo ratings yet
- 22 Buckboost Converter Control With Fuzzy Logic ApproachDocument8 pages22 Buckboost Converter Control With Fuzzy Logic Approachapi-19508046No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ControlDocument44 pagesChapter 4 ControlFootball HDNo ratings yet
- Controls YsDocument17 pagesControls Ysbamboo shackNo ratings yet
- Controller ExperimentDocument11 pagesController ExperimentHira ShariqNo ratings yet
- University of Khartoum Faculty of Engineering Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument27 pagesUniversity of Khartoum Faculty of Engineering Chemical Engineering DepartmentmurtadaNo ratings yet
- CS Lecture Notes Units 1 2 3Document88 pagesCS Lecture Notes Units 1 2 3sushinkNo ratings yet
- 04 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument17 pages04 - Chapter 1 PDFAnonymous KhhapQJVYtNo ratings yet
- Homework 6 TCDocument17 pagesHomework 6 TCSebastián TorresNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument49 pagesControl SystemYashwant ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- PSOC Module 1Document40 pagesPSOC Module 1Priyadarshi MNo ratings yet
- General Decoupling Theory 2Document54 pagesGeneral Decoupling Theory 2Nguyen Thu HaNo ratings yet