Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E.T. - Module - 1.1 Introduction To Information and Communication Technology
E.T. - Module - 1.1 Introduction To Information and Communication Technology
Uploaded by
ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E.T. - Module - 1.1 Introduction To Information and Communication Technology
E.T. - Module - 1.1 Introduction To Information and Communication Technology
Uploaded by
ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIACopyright:
Available Formats
University of Makati
Empowerment Technology Higher School ng UMak
Lesson 1.1
INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION AND
COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ICT)
Time started: ____________
Time Ended: ____________
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lesson, the students should be able to:
1. maximize their knowledge on how ICT affects their lives and nation;
2. compare online platforms, sites, and contents;
3. analyze the different trends in ICT and use them to their advantage; and
4. understanding the world of ICT.
KNOWLEDGE BOOSTER
Information
refers to the knowledge obtained from reading, investigation, study or research. The tools to
transmit information are the telephone, television and radio. We need information to make decisions and
to predict the future.
Communication
is an act of transmitting messages. It is a process whereby information is exchanged between
individuals using symbols, signs or verbal interactions. Previously, people communicated through sign or
symbols, performing drama and poetry. With the advent of technology, these ‘older’ forms of
communication are less utilized as compared to the use of the Internet, e-mail or video conferencing.
Technology
is the use of scientific knowledge, experience and resources to create processes and products that
fulfill human needs.
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT)
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) deals with the use of different communication
technologies such as mobile phones, telephones, the internet, etc. to locate, save, and edit information.
ICT in the Philippines
Several international companies dub the Philippines as the “ICT Hub of Asia”. It is no secret that
there is a huge growth of ICT-related jobs around the country, one of which is the call center or BPO
(Business Process Outsourcing) centers.
According to the 2013 edition of Measuring the Information Society by the International
Telecommunication Union, that are 106.8 cellphones per every 100 Filipinos in the year of 2012. This implies
that for every 100 Filipinos, seven of them own two cellphones.
In the data gathered by the Annual Survey of Philippine Business and Industries and NSO (2010),
the ICT industry shares 19.3% of the total employment population here in the Philippines.
To add to this statistics, Time Magazine declared Makati City, Philippines as Selfie capital of the
world while Cebu City ranks 9.
World Wide Web (WWW)
The World Wide Web, commonly referred to as WWW, W3, or simply the web is an interconnected
system of public web pages accessible through the internet. It was invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989.
When the World Wide Web was invented, most pages were static (also known as Flat page or
Stationary Page) in the sense that the page was "as is" and could not be manipulated by the user. The content
was also the same for all users. This was referred to as Web 1.0
However, the World Wide Web was more than just static pages. Pretty soon, Web 2.0 came to the
picture. Web 2.0 is a term coined by Darcy DiNucci in January 1999.
1|Page Technical-Vocational Department
S/Y 2021-2022
University of Makati
Higher School ng UMak
Web 2.0 is the evolution of Web 1.0 by adding a dynamic web pages-the user can see a website
differently than others. Examples of Web 2.0 include social networking sites, blogs, wikis, video sharing,
hosted services, and web applications. Web 2.0 allows users to interact with the page instead of just reading
it. The user may be able to comment or create a user account. Web 2.0 also allows users to use a web browser
rather than simply using their operating system. Browsers can now be used for their user interface,
application software (or web application), and even for file storage. Most websites that we visit today are
Web 2.0.
Features of Web 2.0
1. Folksonomy – Allows the user to categorize and classify/arrange information using a freely chosen
word (e.g., tagging). Popular social networking sites such as Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, etc. use
tags to start with the pound sign (#). This is also referred to as HASHTAG.
2. Rich User Interface – Content is dynamic and is responsive to the user's input. An example would
be a website that shows local content. In the case of the social networking site, when logged on, your
account is used to modify what you see on their website.
3. User Participation – The owner of the website is not the only one who can put content. Others can
place on their own using comments, reviews, and evaluations. Some websites allow readers to
comment on an article, participate polls, or review a specific product (e.g., Amazon.com, online stores).
4. Long Tail – Services that are offered on-demand rather than on a one-time purchase. In certain
cases, time-based pricing is better than file size-based pricing or vice versa. This is synonymous with
subscribing to a data plan that charges you for the amount you spend on the internet or data plan
that charges you for the amount of bandwidth you used.
5. Software as a Service – Users will subscribe to software only when needed rather than purchasing
them. This is a cheaper option if you do not always need to use the software. For instance, Google
Docs is a free web-based application that allows the user to create and edit word processing and
spreadsheet documents online. When you need software, like a Word processor, you can purchase it
for a one-time huge amount and install it on your computer and it is yours forever. Software as a
service allows you to "rent" software for a minimal fee.
6. Mass Participation – Diverse information sharing through universal web access. Since most users
can use the internet, Web 2.0's content is based on people from various cultures.
Web 3.0 and the Semantic Web
The Semantic Web is a movement led by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The W3C
standard encourages web developers to include semantic content in their web pages. The term was coined by
the inventor of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee. Lee also noted that the semantic web is a component
of Web 3.0.
According to the W3C, "The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be
shared and reused across application, enterprise, and community boundaries." The aim of Web 3.0 is to have
machines (or servers) understand the user's preferences to be able to deliver web content specifically targeting
users. For example, when doing a web search in Web 2.0, the top most result is based on the preferences of
several users who already searched for the item. The search engine then labels it as the most common answer
to the search query. Though there are instances wherein several preferences are considered like geographic
location., Web 3.0 aims to do better. This is through studying the personal preferences of an individual user
and showing results based on those preferences. The internet can predict the best answer to your questions
by "learning" from your previous choices.
2|Page Technical-Vocational Department
S/Y 2021-2022
University of Makati
Higher School ng UMak
For example, if you search the internet for "Where is the best place to go shopping”, Web 3.0 will aim
to give you a result depending on how you made choices in the past. If you have purchased several shoes
online, the internet will give you a result of the best places with the highest rated shoes around your vicinity.
Web 3.0 is yet to be fully realized because of several problems:
1. Compatibility – HTML files and current web browsers could not support Web 3.0
2. Security – The user's security is also questionable since the machine is saving his or her
preferences
3. Vastness – The World Wide Web already contains billions of web pages.
4. Vagueness – Certain words are imprecise. The word "old" and "small" would depend on the users.
5. Logic – Since machine uses logic, there is a certain limitation for a computer to be able to predict
what the user is referring to at a given time.
Trends in ICT
1. Convergence
Technological Convergence is an evolution of technological developments that merge into new
system bringing together different types of applications and media.
For example, aside from calling and texting using the smartphone, you can also use it for browsing
the internet or creating a word document.
2. Social Media
It is a collection of internet-based communication tools and computer-assisted channels dedicated
to allow users to interact, communicate, and share information in a virtual community and
network.
There are six (6) types of social media:
1. Social Network – These are the sites that allow you to connect with other people with
the same interest or background. Once a user creates his or her account, he or she can set
up a profile, add people, create groups, and share content.
Example: Facebook
2. Bookmarking Sites – These are the sites that allow you to store and manage links to
various websites and resources. Most of these allow you to create a tag that allows you
and others to easily search or share them.
Example: StumbleUpon and Pinterest.
3. Social News – These are sites that allow users to post their news items or links to other
news sources.
Example: Reddit and Digg
4. Media Sharing – These are sites that allow you to upload and share media content like
images, music, and video.
Example: Flickr, YouTube, and Instagram
5. Microblogging - These are sites that allow users to focus on short updates. Those who
subscribed to the user will be able to receive these updates.
Example: Twitter and Plurk
6. Blogs and Forums - These are websites that allow users to post their content. Other
users can comment on the said topic.
Example: Blogger, WordPress, and Tumblr
3|Page Technical-Vocational Department
S/Y 2021-2022
University of Makati
Higher School ng UMak
3. Mobile Technologies - The popularity of smartphones and tablets have taken a major rise over
the years. The devices' large capacity to do tasks that was originally found in PCs.
Mobile devices use a different operating system:
1. iOS – is used in apple devices such as the iPhone and iPad.
2. Android - an open-source OS developed by Google.
3. Blackberry OS – is used in blackberry devices.
4. Symbian - the original smartphone OS used by Nokia devices.
5. WebOS (Palm/HP) - The WebOS is a mobile operating system that was developed by Palm.
It based on the Linux Kernel. The HP uses this operating system in its mobile and touchpads.
6. Windows Mobile - developed by Microsoft for smartphones and pocket PCs.
7. Harmony OS - he harmony operating system is the latest mobile operating system that was
developed by Huawei for the use of its devices. It is designed primarily for IoT devices.
8. Palm OS - The palm operating system is a mobile operating system that was developed by
Palm Ltd for use on personal digital assistants (PADs). It was introduced in 1996. Palm OS
is also known as the Garnet OS.
4. Assistive Media - is a non-profit service designed to help people who have visual and reading
impairments. A database of audio recording is used to read the user.
Assignment
1. What is Netiquette?
2. Identify the rules of netiquette.
3. What is the internet?
4. What are Internet threats?
5. What are the types of Malware?
References
1. Lara, M. B. (2016, November 03). Lesson 1 Empowerment Technology. Retrieved from
https://www.slideshare.net/maricelbaldomerodelara/lesson-1-empowerment-technology
2. (Nerval, Lesson 1: Empowerment Technology Information and Communication Technology
2018)https://www.academia.edu/36905646/Lesson_1_Empowerment_Technology_Information_and_
Communication_Technology
3. (n.d.). Retrieved June 09, 2020, from https://www.armoredpenguin.com/crossword/
4. Bookstore, R. (2016). RBS Empowerment Technologies. Manila, Luzon: Rex Bookstore.
4|Page Technical-Vocational Department
S/Y 2021-2022
You might also like
- Case Study Report On MaerskDocument2 pagesCase Study Report On MaerskGabriel de VeraNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDocument18 pagesL1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyIct GothongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologiesDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Information and Communication TechnologiesGlydelle Sarita CasaNo ratings yet
- Etech Module Q3Document23 pagesEtech Module Q3hi022885No ratings yet
- Empowerment TechnologyDocument43 pagesEmpowerment TechnologyBryan GianganNo ratings yet
- #1 Handout ICT (W1-W2)Document5 pages#1 Handout ICT (W1-W2)Coleen Alezandra SabungeyNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 WEEK 1Document37 pagesPresentation1 WEEK 1Vincent AcapenNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies Lesson 1Document45 pagesEmpowerment Technologies Lesson 1marissa.ramos007No ratings yet
- Empowerment Tech.-Lesson-1-3Document123 pagesEmpowerment Tech.-Lesson-1-3rodel megollasNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies: Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Deals With The Use of DifferentDocument5 pagesEmpowerment Technologies: Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Deals With The Use of DifferentAnonymous oVIEi4FxQyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1riazamaximojrNo ratings yet
- EmTech Module Lesson 1 2Document19 pagesEmTech Module Lesson 1 2RHYNALYN UNTARANNo ratings yet
- Ict Lesson 1Document17 pagesIct Lesson 1Yi Shien VirayNo ratings yet
- q1 EmptechDocument91 pagesq1 EmptechKrizford CervantesNo ratings yet
- E-Tech Module (F.A.R.D)Document27 pagesE-Tech Module (F.A.R.D)fe airam dakig100% (1)
- 2g2rff6f5 Module-1-E.T.-intro. To ICTDocument10 pages2g2rff6f5 Module-1-E.T.-intro. To ICTAnnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ICT Class Lesson & Study GuideDocument56 pagesIntroduction To ICT Class Lesson & Study GuideYraNo ratings yet
- CT5 Empowerment TechnologiesDocument34 pagesCT5 Empowerment TechnologiesVeco CastilloNo ratings yet
- Activity: Form The Class Into Group of 5 Members. Take Turns Answering The Questions. Share by GroupDocument35 pagesActivity: Form The Class Into Group of 5 Members. Take Turns Answering The Questions. Share by GroupalbertNo ratings yet
- EmpowermentDocument24 pagesEmpowermentThea Aaliyah Cruz ShalimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Empowerment Technology InformatDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Empowerment Technology InformatRaul MIRALNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies - Lesson 1Document4 pagesEmpowerment Technologies - Lesson 1Bridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Information and Communication Technology PDFDocument18 pagesL1 Introduction To Information and Communication Technology PDFCriza Laureano SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Emp Tech 1Document30 pagesEmp Tech 1BRENDEL SACARISNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologiesDocument17 pagesEmpowerment Technologies Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologiesNeil DojetaNo ratings yet
- ICT Deals With The Use of Different Communication Technologies Such As Mobile PhonesDocument1 pageICT Deals With The Use of Different Communication Technologies Such As Mobile PhonesAllen AllenNo ratings yet
- What Is Information and Communication Technology?Document48 pagesWhat Is Information and Communication Technology?Jerilou EstradaNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDocument28 pagesL1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyArianne CantreNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies - IctDocument53 pagesEmpowerment Technologies - IctChristian Oliver BernabeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologiesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Information and Communication TechnologiesKeon Clark GarlejoNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDocument44 pagesL1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyFelipe Cariño Lucena Jr.No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Emp TechDocument7 pagesModule 1 - Emp TechRose Kimberly Bagtas Lucban-CarlonNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies Topic 1Document31 pagesEmpowerment Technologies Topic 1erianmondido.officialNo ratings yet
- Living in IT EraDocument12 pagesLiving in IT EraBaby Jane LugasNo ratings yet
- QTR 3 - Learning Activity Sheets - Week 1Document6 pagesQTR 3 - Learning Activity Sheets - Week 1Ginevieve GibertasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document31 pagesLesson 1erichanne marcelinoNo ratings yet
- Empowerment TechnologiesDocument28 pagesEmpowerment Technologiesmacy kang (maceeeeh)No ratings yet
- EMP - TECH 1st Sem 1 Lesson 1 by J.A AuxteroDocument28 pagesEMP - TECH 1st Sem 1 Lesson 1 by J.A AuxteroJhay RomNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Empowerment TechnologyDocument43 pagesLesson 1 Empowerment TechnologyAngelica Manalo PerezNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies Module1 1 3Document48 pagesEmpowerment Technologies Module1 1 3chwe sevenith100% (1)
- Q1 Emtech Lessons 1 and 2Document6 pagesQ1 Emtech Lessons 1 and 2Ruviannemay MayNo ratings yet
- Holy Child'S Academy: Self-Paced Learning Module in Empowerment Technologies 11Document4 pagesHoly Child'S Academy: Self-Paced Learning Module in Empowerment Technologies 11Jengol MadriñanNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technology SHS - Q1 - Mod1 - ICT in The Context of Global Communication PDFDocument36 pagesEmpowerment Technology SHS - Q1 - Mod1 - ICT in The Context of Global Communication PDFPacho JudeNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Empowerment TechnologyDocument4 pagesLecture On Empowerment TechnologyChem Scie100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Current State of IctDocument58 pagesLesson 1 Current State of Ictgelmar clementeNo ratings yet
- EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY ReviewerDocument5 pagesEMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY ReviewerKim Charlotte Balicat-Rojo ManzoriNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies: Prepared: Subject TeacherDocument41 pagesEmpowerment Technologies: Prepared: Subject TeacherJason Roger TacataNo ratings yet
- ICT in Our Everyday LivesDocument20 pagesICT in Our Everyday LivesdrewNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDocument22 pagesL1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyRenz OrlidoNo ratings yet
- Cisco Module 1Document33 pagesCisco Module 1Alfredo VergaraNo ratings yet
- Emtech Lesson 1Document35 pagesEmtech Lesson 1Princes Jane BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Nformation and Ommunication: EchnologyDocument38 pagesNformation and Ommunication: EchnologychrismaineNo ratings yet
- LP Emptech Lesson 1Document10 pagesLP Emptech Lesson 1Maria Aurea BorjaNo ratings yet
- L1a Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDocument65 pagesL1a Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDaniel Fancis Amabran Barrientos100% (1)
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Deals With The Use of Different Communication Technologies Such AsDocument2 pagesInformation and Communication Technology (ICT) Deals With The Use of Different Communication Technologies Such AsVince Brave CatinanNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDocument19 pagesL1 Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyClarissa MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 1 UploadedDocument18 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 1 UploadedRose Kimberly Bagtas Lucban-CarlonNo ratings yet
- Ict IntroDocument46 pagesIct Introgemarie malapiraNo ratings yet
- Empotech Lesson 1Document43 pagesEmpotech Lesson 1Juvie Ann BayotNo ratings yet
- The Metaverse : Gain Insight Into The Exciting Future of the Internet: The Exciting World of Web 3.0: The Future of Internet, #1From EverandThe Metaverse : Gain Insight Into The Exciting Future of the Internet: The Exciting World of Web 3.0: The Future of Internet, #1No ratings yet
- Intro To Operations ManagementDocument11 pagesIntro To Operations ManagementALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Mathematics in NatureDocument23 pagesMODULE 1 - Mathematics in NatureALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Palomaria - Module 3Document9 pagesPalomaria - Module 3ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 - Introductory Coding TheoryDocument16 pagesMODULE 5 - Introductory Coding TheoryALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Palomaria - Fitness Plan - Week 1Document2 pagesPalomaria - Fitness Plan - Week 1ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
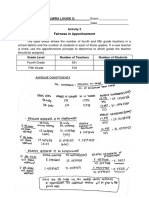
- PALOMARIA - MODULE 6 - ApportionmentDocument1 pagePALOMARIA - MODULE 6 - ApportionmentALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Palomaria - Fitness Plan - Week 2Document3 pagesPalomaria - Fitness Plan - Week 2ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- PALOMARIA-MODULE 4 - Consumer MathDocument16 pagesPALOMARIA-MODULE 4 - Consumer MathALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Nature: Activity 1Document1 pageMathematics in Nature: Activity 1ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- UNIVERSITY OF MAKATIJ.P. Rizal Ext. West Rembo, Makati CityDocument3 pagesUNIVERSITY OF MAKATIJ.P. Rizal Ext. West Rembo, Makati CityALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Palomaria-Activity 2 - Module 1 Mathematics in Modern WorldDocument1 pagePalomaria-Activity 2 - Module 1 Mathematics in Modern WorldALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Statistical Straight Line Method of ProjectionDocument4 pagesStatistical Straight Line Method of ProjectionALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Battle of ManilaDocument8 pagesBattle of ManilaALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Palomaria G12-05ABM Act#1Document3 pagesPalomaria G12-05ABM Act#1ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Aliceplate4 ModelDocument1 pageAliceplate4 ModelALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Understanding The Concepts of Anthropology, Sociology, and Political Science Understanding The Concepts of andDocument37 pagesUnderstanding The Concepts of Anthropology, Sociology, and Political Science Understanding The Concepts of andALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Statement of Changes in Equity - SHS Module 3Document14 pagesStatement of Changes in Equity - SHS Module 3ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Internship Endorsement Letter 2021Document1 pageInternship Endorsement Letter 2021ALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Business Finance MODULE 1 EdDocument8 pagesBusiness Finance MODULE 1 EdALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - UcspDocument37 pagesLesson 2 - UcspALMIRA LOUISE PALOMARIANo ratings yet
- Service Marketing: How Does Nykaa India, Listen To Their Customers?Document7 pagesService Marketing: How Does Nykaa India, Listen To Their Customers?GHARAT BHAVESHNo ratings yet
- Social Bookmarking For DummiesDocument13 pagesSocial Bookmarking For DummiesKaneNo ratings yet
- Social Media Live Project Submission: Facebook CampaignDocument8 pagesSocial Media Live Project Submission: Facebook CampaignGaurav ChhabriaNo ratings yet
- Sonatina y Variacion by - Torroba Fredrico Moreno - Fingered-Andres SegoviaDocument10 pagesSonatina y Variacion by - Torroba Fredrico Moreno - Fingered-Andres SegoviaKeith Rhodes0% (1)
- Google Ads + Conversion TrackingDocument8 pagesGoogle Ads + Conversion Trackingraphael.gagnon9No ratings yet
- Using Del - Icio.us in EducationDocument11 pagesUsing Del - Icio.us in EducationGabriela Grosseck100% (35)
- Chapter One - Understanding The Digital WorldDocument8 pagesChapter One - Understanding The Digital Worldlaith alakelNo ratings yet
- Cases & ReadingsDocument2 pagesCases & ReadingsShubham BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Flux-Zone - Details For Thor1234Document1 pageFlux-Zone - Details For Thor1234Gabriel CaraolaniNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Teaching With VineDocument37 pagesDokumen - Tips - Teaching With VineafiqahNo ratings yet
- Cool About It - Boygenius - Piano TutorialDocument1 pageCool About It - Boygenius - Piano TutorialtesswyniaNo ratings yet
- SEO Proposal - Qloud SolutionsDocument8 pagesSEO Proposal - Qloud Solutionsashwini sharmaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Calendar TemplateDocument39 pagesMarketing Calendar TemplateFadiNo ratings yet
- Uno Module 1 Lesson 1&2Document2 pagesUno Module 1 Lesson 1&2Christea Marie UnoNo ratings yet
- A Social Media Plan For The Ultimate Fighting ChampionshipDocument36 pagesA Social Media Plan For The Ultimate Fighting Championshiplwalker1545No ratings yet
- Unit 4, Pharmaceutical Engineering, B Pharmacy 3rd Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument20 pagesUnit 4, Pharmaceutical Engineering, B Pharmacy 3rd Sem, Carewell Pharmaohayo3590No ratings yet
- Search Engine OptimizationDocument17 pagesSearch Engine Optimization18BCS4038- KAVYADHARSINI PNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart 123Document2 pagesFlow Chart 123Uma Mahesh100% (1)
- Living in IT EraDocument12 pagesLiving in IT EraBaby Jane LugasNo ratings yet
- SEO and Snapchat, Digital C, Assign 1Document27 pagesSEO and Snapchat, Digital C, Assign 1Raja AsadNo ratings yet
- Understanding Off-Page Search Engine OptimizationDocument32 pagesUnderstanding Off-Page Search Engine OptimizationThayananth100% (2)
- Lesson 1 What Is ICT and Online Platfors and SitesDocument5 pagesLesson 1 What Is ICT and Online Platfors and Sitesjeremie mesinaNo ratings yet
- Practical 5: Identify The Business Opportunity Suitable For You. Digital Marketing: A Right Business For Youngster'sDocument5 pagesPractical 5: Identify The Business Opportunity Suitable For You. Digital Marketing: A Right Business For Youngster's02 - CM Ankita AdamNo ratings yet
- How To Limit The Number of Posts in Label Pages On BloggerDocument2 pagesHow To Limit The Number of Posts in Label Pages On BloggerRabail KhalidNo ratings yet
- Сувилахуйн ур чадвар тестDocument199 pagesСувилахуйн ур чадвар тестnanodo7004No ratings yet
- WileyPlus Integrated Into FOL Fall 2021 You Got This!Document18 pagesWileyPlus Integrated Into FOL Fall 2021 You Got This!Saroz ParajuliNo ratings yet
- Get Unlimited Downloads With A 30 Day Free Trial: Download Piaget Jean La Equilibracion de Las Estructuras CognitivasDocument3 pagesGet Unlimited Downloads With A 30 Day Free Trial: Download Piaget Jean La Equilibracion de Las Estructuras CognitivasmauchmichelNo ratings yet
- Emp Tech Q2 Module-1-2Document28 pagesEmp Tech Q2 Module-1-2LorielNo ratings yet
- 4 - How To Develop Discipline To Become A More Successful Investor by Dr. Van TharpDocument158 pages4 - How To Develop Discipline To Become A More Successful Investor by Dr. Van TharpYashkumar JainNo ratings yet