Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Appraisal Exam Dosdos
Uploaded by
Bianca Mikaela DosdosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2nd Appraisal Exam Dosdos
Uploaded by
Bianca Mikaela DosdosCopyright:
Available Formats
Dosdos, Bianca Mikaela F.
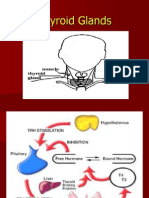
DIABETES
Block CCC 21. C
2nd Appraisal Exam 22. A
23. B
PARATHYROID DISORDERS 24. C
1. D 25. B, E, F
2. D 26. A, B, D
3. C 27. B, D
4. B 28. B.
5. B 29. C.
6. B 30. A.
7. C 31. C
8. A 32. A.
9. A,C,D,E 33. D.
10. A,B,F,G 34. A
11. A. 35. A
12. B. 36. D
13. A 37. D.
14. C 38. B
15. A 39. B
16. A 40. D.
17. B 41. B
18. A 42. A, C, D
19. C 43. C
20. B,C,D 44. B
45. D 20%. Thyroid storm is most commonly
46. A seen in the context of underlying Graves'
47. B, C, E hyperthyroidism but can complicate
48. B thyrotoxicosis of any aetiology. Clinical
49. B features represent manifestations of
50. A organ decompensation, with fever seen
51. D almost universally. Management is
52. ABFG supportive with cooling and fluids,
53. C alongside measures taken to reduce
54. D thyroid hormone synthesis, hormone
55. B release and inhibition of the peripheral
56. C effects of excessive thyroid hormone. In
57. C addition, the management of thyroid
58. B storm should not disregard the search
59. D, E and appropriate treatment of any
60. B precipitating factors.
ESSAY Immediate objectives are
A. reduction of body temperature and heart
Thyroid storm (also known as rate and prevention of vascular collapse.
thyroid or thyrotoxic crisis) is an Measures to accomplish these objectives
uncommon condition reflecting an in objectives include:
extreme physiological state within the A hypothermia mattress or blanket,
spectrum of thyrotoxicosis. The ice packs, a cool environment,
condition is rare, however, mortality hydrocortisone, and acetaminophen
rates are high and may approach 10– (Tylenol).
Salicylates (e.g., aspirin) are not fibrillation, dysrhythmias, and heart
used because they displace thyroid 45 failure, sympatholytic agents
hormone from binding proteins and may be given. Propranolol,
worsen the hypermetabolism. combined with digitalis, has been
Humidified oxygen is given to effective in reducing severe cardiac
improve tissue oxygenation and symptoms.
meet the high metabolic demands. i. Administer dextrose-containing
Arterial blood gas levels or pulse intravenous fluids as ordered to correct
oximetry may be used to monitor fluid and glucose deficits.
respiratory status. ii. Carefully assess the patient for
IV fluids containing dextrose are heart failure or pulmonary edema.
given to replace liver glycogen iii. Dopamine may be used to
stores that have been decreased in support blood pressure.
the patient who is hyperthyroid. iv. Provide supplemental oxygen as
Propylthiouracil (PTU) or ordered to help meet increased
methimazole is given to impede metabolic demands.
formation of thyroid hormone and v. Once the patient is
block conversion of T4 to T3, the hemodynamically stable, provide
more active form of thyroid pulmonary hygiene to reduce pulmonary
hormone. complications.
Hydrocortisone is prescribed to vi. If the patient is in heart failure,
treat shock or adrenal insufficiency. typical pharmacologic agents for
Iodine is given to decrease output treatment of heart failure may also be
of T4 from the thyroid gland. For indicated.
cardiac problems such as atrial
vii. Reduce oxygen demands by approximately 4 to 6 weeks. After the
decreasing anxiety, reduce fever, dose is stabilized, patients can be
decrease pain, and limit visitors if monitored with laboratory measurement
necessary. of TSH annually.
viii. Anticipate aggressive treatment - Levothyroxine sodium a synthetic
of precipitating factor. thyroid hormone replacement is used to
ix. Institute pressure ulcer strategies. returns the patient to the euthyroid
B. (normal) state. Dosage is 1.5–2.5
Nursing Interventions mcg/kg PO daily; (use lowest dose
1. Monitor vital signs, including heart possible because over-replacement of
rate and rhythm. thyroid can cause bone loss or
2. Administer thyroid replacement, cardiovascular complications).
levothyroxine sodium (Synthroid) is 3. Instruct the client about thyroid
most commonly prescribed. replacement therapy.
- Treatment consists of replacing the 4. Instruct the client in low-calorie, low-
deficient hormone with synthetic thyroid cholesterol, low-saturated-fate diet.
hormone; low doses are initially used, 5. Assess the client for constipation;
and the dose is increased every 1 to 2 provide roughage and fluids to prevent
months based on the clinical response constipation.
and serial laboratory measurements that 6. Provide a warm environment for the
show normalization of thyroid- client.
stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in 7. Avoid sedatives and narcotics because
primary hypothyroidism. The patient of increase sensitivity to these
begins to experience clinical benefits in medications.
3 to 5 days, which level off after
8. Monitor for overdose of thyroid function and that the medications may
medications, characterized by lead to hyperthyroidism despite the
tachycardia, restlessness,, nervousness, patient’s underlying hypothyroidism.
and insomnia. 2. Teach the patient about the thyroid
9. Instruct the client to report episodes gland and hypothyroidism, as well as
of chest pain immediately. complications such as heart disease and
10. Document the following: edema. Teach the patient that new
a. Physical findings: Cardiovascular cardiac or hyperthyroidism symptoms
status, bowel activity, edema, condition need to be reported immediately.
of skin, and activity tolerance Explain that the caloric and fiber
b. Response to medications, skin care requirements vary. The patient should
regimen, nutrition report any abnormal weight gain or loss
c. Psychosocial response to changes in or change in bowel elimination.
bodily function, including mental acuity
Health teaching:
1. Explain all medications, including
dosage, potential side effects, and drug
interactions. Instruct the patient to check
the pulse at least twice a week and to
stop the thyroid supplement and notify
the physician if the pulse is greater than
100. Explain that the healthcare
professional should be notified about the
condition. Explain that ongoing medical
assessment is required to check thyroid
You might also like
- Hyperthyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyperthyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- General Surgery MCQDocument190 pagesGeneral Surgery MCQلمسة مصمم100% (1)
- Endocrine: Common Lab Tests For Endocrine and Hormonal DisordersDocument19 pagesEndocrine: Common Lab Tests For Endocrine and Hormonal DisordersPhilip SimanganNo ratings yet
- Addison’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAddison’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Soundarya LahiriDocument50 pagesSoundarya Lahirivsh101No ratings yet
- Arrhythmias Teacher GuideDocument12 pagesArrhythmias Teacher GuideMayer Rosenberg100% (3)
- Peer Support For PeopleDocument120 pagesPeer Support For Peoplebraulio rojasNo ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 1-Module 6Document25 pagesHealth: Quarter 1-Module 6Niko Igie Albino Pujeda0% (1)
- Lecture 6 - 7oct2022 - RDocument22 pagesLecture 6 - 7oct2022 - RAryaNo ratings yet
- Sata EndocrineDocument10 pagesSata EndocrineMaurice Bryan Roslinda100% (1)
- 2nd Sem PHARMA ENDTERMS 1Document11 pages2nd Sem PHARMA ENDTERMS 1Micah Lou Calamba50% (2)
- E - Cart DrugsDocument18 pagesE - Cart Drugs'SheenMarkReal'100% (2)
- Type A Choice Questions (Only One Answer Is Correct) : A. B. C. D. EDocument10 pagesType A Choice Questions (Only One Answer Is Correct) : A. B. C. D. ERAED GhunaimNo ratings yet
- Roubal 2012 Three Perspectives Diagnostic ModelDocument34 pagesRoubal 2012 Three Perspectives Diagnostic ModelGricka DzindzerNo ratings yet
- 1-Deep Breathing and Cough Exercises - DosdosDocument6 pages1-Deep Breathing and Cough Exercises - DosdosBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Tips For Passing NclexDocument2 pagesTips For Passing NclexNimraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Exam 2006 2007Document10 pagesAnesthesia Exam 2006 2007Mysheb SSNo ratings yet
- DM & DI ExamsDocument11 pagesDM & DI ExamsTomzki CornelioNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease Anesthetic ConsiderationsDocument30 pagesThyroid Disease Anesthetic Considerationssachin10dulkarNo ratings yet
- General Surgery MCQDocument249 pagesGeneral Surgery MCQShriyansh Chahar88% (8)
- Thyroid StormDocument16 pagesThyroid StormRaquid MariaNo ratings yet
- Post Test - Pharma (Students Copy)Document5 pagesPost Test - Pharma (Students Copy)irish felix100% (1)
- Pharmacology IIDocument178 pagesPharmacology IIMelanieNo ratings yet
- HYPERTHYROIDISMDocument2 pagesHYPERTHYROIDISMPhilip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- ADDISONIANDocument2 pagesADDISONIANPhilip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Prepared By: Prof. Mike Chavez RN, USRNDocument7 pagesEndocrine System Prepared By: Prof. Mike Chavez RN, USRNMeiJoyFlamianoIINo ratings yet
- Ms-Endocrine Sample QuestionsDocument28 pagesMs-Endocrine Sample QuestionsDanica Alan QuemanNo ratings yet
- الاسئله الوزاريه Thyroid gland by ᴬᴮᴺ ᶠᴬᴸᴵᴴDocument23 pagesالاسئله الوزاريه Thyroid gland by ᴬᴮᴺ ᶠᴬᴸᴵᴴAliHuseiyn HaddieeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Self-Assessment Q&ADocument8 pagesChapter 6 - Self-Assessment Q&AVijay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Errata List-I (1 - 10 Subjects) - Target Jipmer 2 EditionDocument9 pagesErrata List-I (1 - 10 Subjects) - Target Jipmer 2 Editiondhanj1921No ratings yet
- Thyroid Emergencies: Siddharth N ShahDocument1 pageThyroid Emergencies: Siddharth N ShahSubramanian MurugesanNo ratings yet
- External MCQDocument4 pagesExternal MCQFaridOrahaNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument10 pagesHeart FailureAfiya MohammedNo ratings yet
- COMMON MCQ Endo 2017 PDFDocument27 pagesCOMMON MCQ Endo 2017 PDFعلي. احمدNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Drugs For Endocrinologic DisordersDocument4 pagesLong Quiz Drugs For Endocrinologic Disorderspay tinapayNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy (Rai) : GoalsDocument6 pagesRadioactive Iodine Therapy (Rai) : GoalsFirras SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Walter Reed MCHypothermiaprotocolrevised 21 SeptDocument8 pagesWalter Reed MCHypothermiaprotocolrevised 21 SeptBEST OF PAKISTANNo ratings yet
- MyxedemaDocument3 pagesMyxedemaBobet ReñaNo ratings yet
- Legend - Answer - Rationale Hypothyroidism Vs Hyperthyroidism NCLEX QuizDocument8 pagesLegend - Answer - Rationale Hypothyroidism Vs Hyperthyroidism NCLEX QuizSherilNo ratings yet
- Amls Als Pretest Version 1.11Document10 pagesAmls Als Pretest Version 1.11Lancelot LeungNo ratings yet
- Try Out 2 MASTER UKAI JULI 2022Document26 pagesTry Out 2 MASTER UKAI JULI 2022zubaidah zubadahNo ratings yet
- Case IDHDocument6 pagesCase IDHIrma HermaliaNo ratings yet
- Course Task #3: AnswerDocument5 pagesCourse Task #3: AnswerAria100% (3)
- Hormonal RegulationDocument20 pagesHormonal Regulationel shilohNo ratings yet
- CarbimazoleDocument3 pagesCarbimazoleManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- ESSAYDocument2 pagesESSAYBokNo ratings yet
- Kandili Physio ExamDocument17 pagesKandili Physio ExamJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Test 2020 2Document7 pagesEndocrinology Test 2020 2Claudia IrimieNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland McqsDocument6 pagesThyroid Gland Mcqssabreena.samad.ssNo ratings yet
- Answer For Pharma QuizDocument11 pagesAnswer For Pharma Quizzyyw.abello.uiNo ratings yet
- N245 Endocrine PPT NotesDocument9 pagesN245 Endocrine PPT NotesAANo ratings yet
- Myxedema and ComaDocument1 pageMyxedema and ComagoldenslaughtererNo ratings yet
- Exam Key ms3Document33 pagesExam Key ms3joanneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine CasesDocument12 pagesEndocrine Casesعلي. احمدNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: 2015-2016 MED 2 Semester 1 Human Function Mock TestDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: 2015-2016 MED 2 Semester 1 Human Function Mock TestAnonymous w4lLoMd7No ratings yet
- RN101Document40 pagesRN101Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Shock and SIRSDocument85 pagesShock and SIRSBryan Mae H. DegorioNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Endocrine PDocument3 pagesAnaphy Endocrine PArcher RiegoNo ratings yet
- 250 Latest Surgical Background Multiple - HTML PDFDocument32 pages250 Latest Surgical Background Multiple - HTML PDFazizNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CrisisDocument34 pagesThyroid CrisisRidyah Ning TyasNo ratings yet
- Practice ExamDocument15 pagesPractice ExamShay Ann CharltonNo ratings yet
- PhysioDocument6 pagesPhysioabigail corre0% (1)
- Etomidate For Rapid Sequence IntubationDocument19 pagesEtomidate For Rapid Sequence IntubationSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- KMB II Sistem Endokrin PT IIDocument68 pagesKMB II Sistem Endokrin PT IIAngel ChrisNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test 2 On MS 1Document17 pagesMastery Test 2 On MS 1Rika MaeNo ratings yet
- Review ExamDocument5 pagesReview ExamKatNo ratings yet
- 2 Assisting Clients To Use Incentive Spirometer DosdosDocument3 pages2 Assisting Clients To Use Incentive Spirometer DosdosBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Endorsement NotesDocument2 pagesEndorsement NotesBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- 1ST SceneSpanish Tried To Get St. Michael To OzamisDocument2 pages1ST SceneSpanish Tried To Get St. Michael To OzamisBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Summative Assessment Answer SheetDocument1 page1st Quarter Summative Assessment Answer SheetBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- 1 Quarter Reflection and 2 Quarter GoalsDocument2 pages1 Quarter Reflection and 2 Quarter GoalsBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Patient's Name / Room No. - 1Document3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Patient's Name / Room No. - 1Bianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeDocument7 pagesName: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IDocument2 pagesMSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Wound Irrigation DefinitionDocument3 pagesWound Irrigation DefinitionBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Changing A Dry Sterile DressingDocument6 pagesChanging A Dry Sterile DressingBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeDocument3 pagesName: - Date: - Evaluator/Signature: - GradeBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Module 3: The Web and The Internet: College of Computer and Information SciencesDocument9 pagesModule 3: The Web and The Internet: College of Computer and Information SciencesBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Applying A Wet-To-dry DressingDocument4 pagesApplying A Wet-To-dry DressingBianca Mikaela Dosdos0% (1)
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementBianca Mikaela DosdosNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Jameel BBA, 6 Semester Sociology (Anum Kamal) Assignment No 1Document3 pagesMuhammad Jameel BBA, 6 Semester Sociology (Anum Kamal) Assignment No 1Mohammad JamilNo ratings yet
- Hospital Health Services AdministrationDocument2 pagesHospital Health Services Administrationmalleshwari athramNo ratings yet
- Unilever Sri LankaDocument4 pagesUnilever Sri LankaAnushka GunasingheNo ratings yet
- No Pain No GainDocument3 pagesNo Pain No GainKADREY BIN LAMJAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) - DHT Stimulates Cell Growth in The Tissue That Lines The Prostate GlandDocument7 pagesDihydrotestosterone (DHT) - DHT Stimulates Cell Growth in The Tissue That Lines The Prostate GlandPeter Kenneth LampitocNo ratings yet
- Crime Preventive MeasuresDocument3 pagesCrime Preventive MeasuresNumra AttiqNo ratings yet
- (123doc) - Opthalmic-Microsurgical-Suturing-Techniques-Part-3-PpsxDocument15 pages(123doc) - Opthalmic-Microsurgical-Suturing-Techniques-Part-3-PpsxTEODORA MIHAELA PELEASANo ratings yet
- Plants Used in Veterinary MedicineDocument297 pagesPlants Used in Veterinary MedicinefdfdfdfNo ratings yet
- Painless Diabetic Motor NeuropathyDocument12 pagesPainless Diabetic Motor NeuropathyHamza JubranNo ratings yet
- Journal ListDocument522 pagesJournal ListalkshobaNo ratings yet
- India's 1 Health Management LabDocument14 pagesIndia's 1 Health Management LabAjay Kumar dasNo ratings yet
- Effect of SnailDocument13 pagesEffect of SnailElvy ChardilaNo ratings yet
- 6 Learning and Memory: Consumer Behavior, 11EDocument35 pages6 Learning and Memory: Consumer Behavior, 11EFatima Tul ZahraNo ratings yet
- MetotrexatDocument6 pagesMetotrexatMuhamad Rizqy MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Las Peh 2Document3 pagesLas Peh 2Paul Vincent LauretaNo ratings yet
- Karl Storz VAAFTDocument35 pagesKarl Storz VAAFTSalam KamilNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Test Success An Unfolding Case Study Review Innovative Nursing Test Success 1st Edition Ebook PDFDocument58 pagesPediatric Nursing Test Success An Unfolding Case Study Review Innovative Nursing Test Success 1st Edition Ebook PDFedith.beltran702100% (45)
- Template PLANNING YOUR CAREER MODULE Cohort 2 V3 3Document15 pagesTemplate PLANNING YOUR CAREER MODULE Cohort 2 V3 3Alvi SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Orum, A.M. and Aliste, E. (2023) - Urban Liveability.Document3 pagesOrum, A.M. and Aliste, E. (2023) - Urban Liveability.Marcelo adsdasNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 9 PE9 Q1 Module 1 v.01 CCDocument16 pagesMAPEH 9 PE9 Q1 Module 1 v.01 CCAngelica Dyan MendozaNo ratings yet
- MTADocument48 pagesMTAMalaquias Varavatché100% (2)
- Svu Area SeatsDocument26 pagesSvu Area SeatsDevi VaraNo ratings yet
- The Dose-Response Relationship Between Interval-Training and VO in Well-Trained Endurance Runners: A Systematic ReviewDocument19 pagesThe Dose-Response Relationship Between Interval-Training and VO in Well-Trained Endurance Runners: A Systematic Reviewok okNo ratings yet
- Disaster Nursing SAS Session 21Document10 pagesDisaster Nursing SAS Session 21Niceniadas CaraballeNo ratings yet