Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 5
Uploaded by
Hazim Izzat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views1 pageForced convection is caused by winds blowing across a transmission line at 40 km / h. In which mode of heat transfer is the convection heat transfer coefficient usually higher? What is the physical significance of the Nusselt number?
Original Description:
Original Title
TUTORIAL 5
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentForced convection is caused by winds blowing across a transmission line at 40 km / h. In which mode of heat transfer is the convection heat transfer coefficient usually higher? What is the physical significance of the Nusselt number?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views1 pageTutorial 5
Uploaded by
Hazim IzzatForced convection is caused by winds blowing across a transmission line at 40 km / h. In which mode of heat transfer is the convection heat transfer coefficient usually higher? What is the physical significance of the Nusselt number?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
THERMAL ENGINEERING( MEC 551)
TUTORIAL 5: CONVECTION
1. What is forced convection? How does it differ from natural convection?
Is convection caused by winds forced or natural convection?
2. In which mode of heat transfer is the convection heat transfer
coefficient usually higher, natural convection or forced convection?
Why?
3. What is the physical significance of the Nusselt number? How is it
defined?
4. The local atmospheric pressure in Denver, Colorado (elevation 1610
m), is 83.4 kPa. Air at this pressure and at 30°C flows with a velocity of
6 m/s over a 2.5-m X 8-m flat plate whose temperature is 120°C.
Determine the rate of heat transfer from the plate if the air flows
parallel to the (a) 8-m-long side and (b) the 2.5-m side.
5. Air at 25°C and 1 atm is flowing over a long flat plate with a velocity of
8 m/s. Determine the distance from the leading edge of the plate
where the flow becomes turbulent, and the thickness of the boundary
layer at that location.
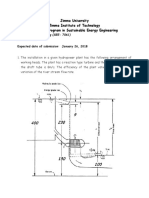
6. In a geothermal power plant, the used geothermal water at 80°C
enters a 15-cm-diameter and 400-m-long uninsulated pipe at a rate of
8.5 kg/s and leaves at 70°C before being reinjected back to the
ground. Windy air at 15°C flows normal to the pipe. Disregarding
radiation, determine the average wind velocity in km/h.
7. A 6-mm-diameter electrical transmission line carries an electric current
of 50 A and has a resistance of 0.002 ohm per meter length. Determine
the surface temperature of the wire during a windy day when the air
temperature is 10°C and the wind is blowing across the transmission
line at 40 km/h.
You might also like
- Laying Out Arnold Palmer Hospital-Assignment OM2Document2 pagesLaying Out Arnold Palmer Hospital-Assignment OM2Hazim Izzat100% (2)
- CH 11Document72 pagesCH 11cameronsidwell0% (2)
- Total Quality Management Short NoteDocument4 pagesTotal Quality Management Short NoteHazim IzzatNo ratings yet
- Flow in Pipes and Channels - Solved ExamplesDocument6 pagesFlow in Pipes and Channels - Solved ExamplesEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Orifice, Nozzle and Venturi Flow Rate Meters: Water & Air FlowmetersDocument4 pagesOrifice, Nozzle and Venturi Flow Rate Meters: Water & Air Flowmeterssiva_nagesh_2No ratings yet
- Chte3 Fluidproperties Examples 1Document4 pagesChte3 Fluidproperties Examples 1Sphe DlomoNo ratings yet
- Best dimensions for open channel flowDocument4 pagesBest dimensions for open channel flowSarah HarunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document21 pagesLecture 3alyssaNo ratings yet
- Bloque 6 Op Unit 1-2Document2 pagesBloque 6 Op Unit 1-2Luis Ramirez0% (1)
- Chapter Summary and Study Guide for Control Volume Analysis Using EnergyDocument24 pagesChapter Summary and Study Guide for Control Volume Analysis Using Energykrntomboy25% (4)
- Solucionario Ingenieria Economica Blank Tarquin 7ma EdicionDocument4 pagesSolucionario Ingenieria Economica Blank Tarquin 7ma EdicionHugo Enrique Ramirez Patiño33% (3)
- Solutions From OnlineDocument36 pagesSolutions From OnlineNiniGooseNo ratings yet
- AHMT Assignment 01Document2 pagesAHMT Assignment 01shubhamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Andrew0% (1)
- SUEZ CANAL University Fluid Mechanics AssignmentDocument3 pagesSUEZ CANAL University Fluid Mechanics Assignmentmahmoud EissaNo ratings yet
- Power Generation PDFDocument59 pagesPower Generation PDFyasinNo ratings yet
- War 2103 PrecipitationDocument52 pagesWar 2103 PrecipitationEgana IsaacNo ratings yet
- Sheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevDocument2 pagesSheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevBibaswan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Steel Structure AssignmentDocument11 pagesSteel Structure AssignmentGetaneh HailuNo ratings yet
- HW 12 Solutions Spring 2012Document4 pagesHW 12 Solutions Spring 2012Pravallika KolliparaNo ratings yet
- Te Old&newDocument1,051 pagesTe Old&newSmith KashidNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Document7 pagesExam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Zaki Smn100% (1)
- Calculating water pressure and turbine selectionDocument7 pagesCalculating water pressure and turbine selectionMaulidNo ratings yet
- IBCASTDocument10 pagesIBCASTKhalil ShadNo ratings yet
- Annular Condensation CFD Models For The Water-Steam in The Heat Pipe SystemsDocument9 pagesAnnular Condensation CFD Models For The Water-Steam in The Heat Pipe SystemsRashed KaiserNo ratings yet
- MI-106 Tut ThermoDocument37 pagesMI-106 Tut ThermoDhananjayLekshmiNarayan100% (7)
- Conceptual Questions: Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 10: Direct-Current CircuitsDocument25 pagesConceptual Questions: Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 10: Direct-Current CircuitsDaniel AntonioNo ratings yet
- PDF Compiled DLDocument477 pagesPDF Compiled DLrickyNo ratings yet
- Tshoga Lo PDFDocument11 pagesTshoga Lo PDFlehlabileNo ratings yet
- 14 2042015Assignment14SolutionDocument5 pages14 2042015Assignment14SolutionInfo Esocket100% (1)
- Finals Ice FormatDocument15 pagesFinals Ice FormatBong PadillaNo ratings yet
- Thermo HW Solution3Document6 pagesThermo HW Solution3Elijah ParkNo ratings yet
- HW 31 Solutions Spring 2012Document9 pagesHW 31 Solutions Spring 2012rameshaarya99No ratings yet
- LTpart 2Document7 pagesLTpart 2Lin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- MIN-305 Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial - 1Document2 pagesMIN-305 Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial - 1Ayush JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-24.02Document68 pagesChapter 2-24.02Vishnu PradeepNo ratings yet
- Solution: First, Convert Co: 3 SpeciesDocument2 pagesSolution: First, Convert Co: 3 Speciesdgdf awerNo ratings yet
- Jimma University Hydropower Engineering AssignmentDocument4 pagesJimma University Hydropower Engineering AssignmentAmexTesfayeKoraNo ratings yet
- Time of Setting of Hydraulic-Cement Paste by Gillmore NeedlesDocument4 pagesTime of Setting of Hydraulic-Cement Paste by Gillmore NeedlesINARQ1979No ratings yet
- GVF Model Question Solved PDFDocument34 pagesGVF Model Question Solved PDFJeewan75% (4)
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Philipp Louis D#2docxDocument8 pagesPhilipp Louis D#2docxEymann Jala100% (3)
- MecFlu 7ed ch07-13Document1,079 pagesMecFlu 7ed ch07-13Gerson Santos - PolamaluNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 - finaFPP L - Fluid - & - Particle - FinalDocument24 pagesAssignment - 1 - finaFPP L - Fluid - & - Particle - FinalKharkhodaNo ratings yet
- 8.4 Continuous Reactors: 8.4.1 Steady-State Chemostat (CHEMOSTA)Document33 pages8.4 Continuous Reactors: 8.4.1 Steady-State Chemostat (CHEMOSTA)Hana HamidNo ratings yet
- Agrohydrology ManualDocument113 pagesAgrohydrology Manualjoverevocal50% (2)
- Ejemplo DTML Crossflow PDFDocument2 pagesEjemplo DTML Crossflow PDFDaniel González Juárez100% (1)
- Sheet 2 - Solution - EE218Document10 pagesSheet 2 - Solution - EE218NouraNo ratings yet
- Rotación de PavimentoDocument7 pagesRotación de PavimentoIván Pimentel OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document26 pagesChapter 1Sohail SakhaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 03Document5 pagesExperiment No. 03saad arslan100% (1)
- Lecture 3 BernoulliDocument27 pagesLecture 3 BernoulliChristal PabalanNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Curves of Centrifugal CompressorDocument26 pagesCharacteristic Curves of Centrifugal CompressorNadiene Salleha100% (1)
- CH 12Document120 pagesCH 12PhimjunkieNo ratings yet
- Mott 4e Applied Strength of Materials Solutions Chapter 13Document20 pagesMott 4e Applied Strength of Materials Solutions Chapter 13kmantillaNo ratings yet
- FM Minor Losses 1Document14 pagesFM Minor Losses 1mahesh100% (1)
- Dry Centrifugal Col Lector - PPT by Hitarth MIHS-IsTARDocument25 pagesDry Centrifugal Col Lector - PPT by Hitarth MIHS-IsTARHM04100% (1)
- ABE 3612C Extra Credit Due Nov 14Document2 pagesABE 3612C Extra Credit Due Nov 14sam9montgomery0% (1)
- Tutorial 2 (B)Document3 pagesTutorial 2 (B)Damien MarleyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ConvectionDocument4 pagesTutorial 5 ConvectionFikri RahimNo ratings yet
- Tut 6Document3 pagesTut 6Jesús Alejandro SantillánNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 (B)Document2 pagesTutorial 2 (B)Suraya JohariNo ratings yet
- Mohd Fadzli Bin Abdul Samad (2008282038) Results Spring ConstantDocument6 pagesMohd Fadzli Bin Abdul Samad (2008282038) Results Spring ConstantHazim IzzatNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls of Elimination MethodsDocument11 pagesPitfalls of Elimination MethodsHazim IzzatNo ratings yet
- Two Stroke EngineDocument7 pagesTwo Stroke EngineHazim IzzatNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara: Applied Mechanics Lab (MEC424) Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument19 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara: Applied Mechanics Lab (MEC424) Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringHazim IzzatNo ratings yet