Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Cycle, Mitosis & Cancer Review
Uploaded by
33 NICASA, DENDEN S.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Cycle, Mitosis & Cancer Review
Uploaded by
33 NICASA, DENDEN S.Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: ____Nicasa Denden S.
_________________________________________Date: _________________
Period: _____
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, & Cancer Review
Due Date: _________________
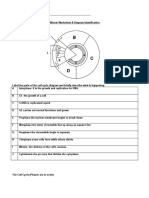
Using the labeled Cell Cycle diagram to the right do the
following:
Left column: place the corresponding letter for the correct stage
Right column: Complete the description of the stage in the
_______interphase_____________: Consists of G1, S
1. A
and G2 phases in the Cell Cycle.
Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm resulting in two
2. _J__
identical d the rest of the cell divides cells.
G1 – growth phase: Makes organelles and proteins needed for replication of DNA. Also contains a G 1
3. _B__
checkpoint. If everything is correct, cell will proceed to S phase.
4. _C__ S phase: DNA is replicated or synthesized.
G2 - growth phase: Cell gets ready to undergo Mitosis___________. Also contains a G 2 checkpoint. If
5. D
DNA replication is correct, checkpoint allows cell to enter M phase.
Prophase: chromatin condenses to become chromatin, nuclear envelopes breaks down, and
6. _E__
centrioles migrate to opposite poles in animal cells. Nucleolus disappears.
Metaphase: sister chromatids line up along the metaphase plate in the middle. Spindle apparatus
7. _F__
attaches at the centromere of the chromosomes.
Anaphase____________: sister chromatids separate and move to opposite sides of the cell. The
8. G separate__________ aoppasite of the cell pulls them apart. This phase ends when the chromatids
stop moving.
Telophase: two nuclear envelopes begin reforming. Chromatids relax, uncoil & are now chromatin.
Cytokinesis is occurring during Telophase but it is NOT considered a part of mitosis because it does
9. H
not involve the nucleus of the cell. In plant cells, a cell plate begins to form while a Cleavage furror
is visible in animal cells.
Mitosis: division of a cell’s nucleus. Occurs in this order: prophase, metaphase,
10. _I__
______anaphase_________, and telophase.
Label the phases of Mitosis below:
11. Prophase 12. Metaphase 13. Anaphase 14. Telophase 15. Cytokinesis
Complete the table by checking the correct column for each statement.
Statement Interphase Mitosis
16. Cell growth occurs ✓
17. Nuclear division occurs ✓
18. Chromosomes are finishing moving into separate daughter cells. ✓
19. Chromosomes are duplicated ✓
20. DNA synthesis occurs ✓
21. Where cells spend most of their life ✓
22. Mitochondria and other organelles are made. ✓
Use the following illustrations for questions 23 - 32
23. In cell A, what is the structure labeled X? _____Centriole______________
24. In cell F, what is the structure labeled Y? ________spinale fibers__________
25. Which cell is not in a phase of mitosis? ____________D__________
26. New nuclear membranes are forming in B. What is this phase called? ________telophase_____________
27. Sequence the six diagrams in chronological order from first to last. ___D_, __A__, __f__, ___c_, __E__, __D_
28. Chromosomes move to the middle of the cell during?_______Metaphase__________
29. When do the sister chromatids separate?_____________anaphase____________
30. During which phase do chromosomes first become visible? _______________prophase_________________
31. During which phase does the cleavage furrow start forming on animal cells? ___________Anaphase_____________
32. If a cell has 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after mitosis?
______chromosomes_____
Identify the stage of mitosis each A E
lettered plant cell is in:
B
33. A Prophase
34. B Metaphase
35. C Anaphase D
C F
36. D Metaphase
37. E Prophase
Regulation of the cell cycle
38. A mass of cancerous cells is called a tumor_____________________.
39. What is the purpose of checkpoints in the cell cycle?Cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor
the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell cycle
40. What is a carcinogen? A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis, the
formation of cancer
Give 2 examples of carcinogens: ________Radon___________ and _________Tobacco___________
41. Cancer is defined as uncontrolled growth and division of cells due to a failure in the regulation of the cell cycle. Do
cancerous cells spend much of their time in G o, the resting period of the cell cycle? Explain why or why not.
-Cancer is the result of unchecked cell division caused by a breakdown of the mechanisms that regulate the cell
cycle. The loss of control begins with a change in the DNA sequence of a gene that codes for one of the regulatory
molecules. Faulty instructions lead to a protein that does not function as it should
Apoptosis Chromosome Develop Grow
Daughter Chromatin Divide Repair
Use the word box below to answer questions 42- 44
42. Programmed cell death is called _______________________ and is often trigged by cells that are damaged beyond
repair. This process can help protect against cancerous growth.
Big Ideas
43. What are reasons EUKARYOTIC cells divide?
a. To _____mitosis_____& ______meosis__________.
b. To organism, reproduction and tissues.
44. What is the relationship between chromatin and chromosomes?
- chromatin undergoes further condensation to form the chromosome.
45. What chromosome is thread-like DNA and is the form usually found in a cell that is not dividing. When a cell
is going to divide, chromatin coils up to form a(n) Visible Chromosome Condensing and packaging DNA this way
makes it much more manageable and easier to divede DNA evenly among the 2 new IDENTICAL
____daughter___ cells.
You might also like
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheetAngelic ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Cancer ReviewDocument3 pagesCell Cycle, Mitosis and Cancer ReviewAnicia Toscano100% (3)
- 2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewDocument3 pages2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewAnne Romo50% (8)
- Mitosis - Worksheet KEYDocument4 pagesMitosis - Worksheet KEYGeorgia0% (1)
- The-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersDocument3 pagesThe-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersHiezel Dapat100% (1)
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheetLaarni Faye Sarmiento100% (1)
- Cell Cycle and Division: Phases, Significance of Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesCell Cycle and Division: Phases, Significance of Mitosis and MeiosisAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Quiz: Answers Each Question. Write The Answer On The Sheet ProvidedDocument5 pagesMitosis Quiz: Answers Each Question. Write The Answer On The Sheet ProvidedJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument2 pagesMitosis Worksheetkatherine corvera100% (2)
- Cellular Reproduction and GeneticsDocument47 pagesCellular Reproduction and GeneticsJean Marie Macadaeg OrdinarioNo ratings yet
- Pre Test AnswersDocument3 pagesPre Test AnswersJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- 15 The Cell Cycle-S PDFDocument6 pages15 The Cell Cycle-S PDFAml Aml0% (1)
- DNA Replication Practice WKSH Blank PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Replication Practice WKSH Blank PDFKim100% (2)
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Problems KEYDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Problems KEYnona wayne dela peña100% (1)
- Mitosis Quiz 17 04 2015Document6 pagesMitosis Quiz 17 04 2015api-296545639100% (1)
- Cell ModificationsDocument38 pagesCell ModificationsMarlennete Urbano Ligas100% (1)
- Biology Test Cell StructureDocument7 pagesBiology Test Cell Structuredee.aira29550% (1)
- Study Guide Protein Synthesis (KEY)Document2 pagesStudy Guide Protein Synthesis (KEY)owls_1102No ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Cell CycleDocument3 pagesActivity 2 - Cell CycleNick Andrew boholNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cell Cycle ReviewDocument3 pagesKami Export - Cell Cycle ReviewAchionta Nandy100% (3)
- Summative Test Genbio 1 Q1Document26 pagesSummative Test Genbio 1 Q1Duane0% (1)
- Gen Physics 1 ExamDocument8 pagesGen Physics 1 ExamArvinNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Worksheet - CompletedDocument4 pagesMitosis Worksheet - CompletedAbel100% (1)
- Meiosis Worksheet 13 KeyDocument2 pagesMeiosis Worksheet 13 KeyFarhan Pranadarmesta Merch100% (1)
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells AnswersDocument3 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Answersboney67% (3)
- Biology M15 EvolutionDocument25 pagesBiology M15 EvolutionDiana Dealino-Sabandal0% (2)
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Followingapi-39708077950% (2)
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocument19 pagesCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (2)
- Multiple Choice Review – Mitosis & MeiosisDocument12 pagesMultiple Choice Review – Mitosis & MeiosisyoumasankarNo ratings yet
- Biology I-Mitosis Test BankDocument9 pagesBiology I-Mitosis Test BankAmos Josephat100% (2)
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument1 pageMitosis WorksheetFrician Bernadette Muyco100% (1)
- Meiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inDocument29 pagesMeiosis: Chromatids (The Two Halves of A Duplicated Chromosome), As inyamamaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetMaktoumNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter Exam in General Biology 1Document3 pages1ST Quarter Exam in General Biology 1KatherineNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 3.2 The Structure of The Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 3.2 The Structure of The Plasma MembraneRosmainah Osman40% (5)
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education: St. Joseph Village, Cogon, Bogo City, CebuDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education: St. Joseph Village, Cogon, Bogo City, CebuSaiza BarrientosNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY Midterm Exams FinalDocument8 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY Midterm Exams FinalCrismar Takinan100% (1)
- Cell Division Worksheet Chapter SummaryDocument18 pagesCell Division Worksheet Chapter SummaryEma Fatimah0% (1)
- MeiosisDocument55 pagesMeiosisasuncionjarquioNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMitosis WorksheetAmna Jamshed67% (3)
- p3 - Cellular Transport MechanismDocument53 pagesp3 - Cellular Transport MechanismJudithNo ratings yet
- Biology2 Q3 Module 3 Evolution and - Origin of BiodiversityDocument15 pagesBiology2 Q3 Module 3 Evolution and - Origin of BiodiversityDrew MalubagNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleDocument3 pagesWorksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis WorksheetsDocument3 pagesMitosis and Meiosis WorksheetsVinson Eric50% (2)
- Cell Exam Practice Multiple ChoiceDocument46 pagesCell Exam Practice Multiple ChoiceVulneraSanentur67% (3)
- BIOTECH Q3.Week 3-4 - Science 8Document15 pagesBIOTECH Q3.Week 3-4 - Science 8Clark BautistaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis WorksheetDocument2 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis WorksheetFabian Andres Paez Velandia100% (1)
- Handout - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHandout - Cell Transport Review Worksheetapi-502781581No ratings yet
- Cell Division and the Cell Cycle ExplainedDocument25 pagesCell Division and the Cell Cycle ExplainedZamantha Zaynn100% (1)
- DNA replication stepsDocument3 pagesDNA replication stepsKimNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 2 BiotechDocument14 pagesQ3 Module 2 Biotechaizellehahahaha100% (1)
- General Biology 1 (BIO01) Reviewer 2017Document30 pagesGeneral Biology 1 (BIO01) Reviewer 2017Adonis AdornadoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division Practice TestDocument12 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division Practice TestIndu Yadav100% (1)
- General Biology 1 Summative TestDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Summative TestAnna Liza CarrascalNo ratings yet
- General Biology Midterm Exam: Chapter 1: Introduction - Themes in The Study of LifeDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology Midterm Exam: Chapter 1: Introduction - Themes in The Study of LifeNermaDžaferovićNo ratings yet
- GENBIO 1 Q1 Periodic TestDocument6 pagesGENBIO 1 Q1 Periodic TestCelsa ChicoNo ratings yet
- MITOSIS vs MEIOSISDocument5 pagesMITOSIS vs MEIOSISJohanna GultianoNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam Quarter 1 Students PDFDocument7 pagesBiology Exam Quarter 1 Students PDFGellie Mae Badilla DacayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 The Cell CycleDocument8 pagesChapter 12 The Cell CycleMicky Bandera100% (2)
- Cell Cycle, mitosis worksheetDocument3 pagesCell Cycle, mitosis worksheetrosellevalerio2014No ratings yet
- Solid State Device Analysis ApproximationsDocument34 pagesSolid State Device Analysis Approximationsmrd9991No ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Pharmacy, LucknowDocument1 pageMahatma Gandhi Institute of Pharmacy, LucknowMukesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan in English by Laurence MercadoDocument7 pagesA Lesson Plan in English by Laurence Mercadoapi-251199697No ratings yet
- Week 1-12 strength and conditioning programDocument6 pagesWeek 1-12 strength and conditioning programBrian Michael CarrollNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical and Software Development ProjectsDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical and Software Development ProjectsAlexandar123No ratings yet
- Me f215 Mel Lab ManualDocument105 pagesMe f215 Mel Lab ManualpankazspamNo ratings yet
- ACHD 07 The Innsmouth ConspiracyDocument6 pagesACHD 07 The Innsmouth ConspiracyJNo ratings yet
- Superb Estate: PricesDocument10 pagesSuperb Estate: PricesReal GandeaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Annual Report - Printer-ReadyDocument35 pages2016 Annual Report - Printer-ReadyDonna BrodberNo ratings yet
- Detailed CET ListDocument11 pagesDetailed CET ListBhagya H SNo ratings yet
- Pages From Civil EngineeringDocument50 pagesPages From Civil EngineeringRagavanNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocument30 pagesElectric Potential and CapacitanceRachita PatangiNo ratings yet
- German UnificationDocument40 pagesGerman UnificationJosephlangeloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document42 pagesChapter 5Hong AnhNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of CopperDocument21 pagesOxidation of CopperAmeen ShahidNo ratings yet
- Sap GlossaryDocument324 pagesSap GlossaryNikos TataliasNo ratings yet
- Dialogo Ingles 4 FinalDocument3 pagesDialogo Ingles 4 FinalJoae KsnsnsNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds ExplainedDocument37 pagesOrganic Compounds ExplainedAlejandro VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast History EssayDocument9 pagesCompare and Contrast History EssayGiselle PosadaNo ratings yet
- Ancient South Arabian TradeDocument16 pagesAncient South Arabian TradeAbo AliNo ratings yet
- Criminal VIIIDocument31 pagesCriminal VIIIAnantHimanshuEkkaNo ratings yet
- Mystic Mystique Face Reading-IIDocument10 pagesMystic Mystique Face Reading-IIVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- ClinicalOpiateWithdrawalScale PDFDocument2 pagesClinicalOpiateWithdrawalScale PDFRajamanitiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2023/B: International OrganisationsDocument15 pagesTutorial Letter 101/3/2023/B: International OrganisationslesegononNo ratings yet
- 202-Nido 2024Document27 pages202-Nido 2024tabhonor69No ratings yet
- Southwest Globe Times - Sep 8, 2011Document16 pagesSouthwest Globe Times - Sep 8, 2011swglobetimesNo ratings yet
- Manual THT70 PDFDocument54 pagesManual THT70 PDFwerterNo ratings yet
- AMS 2750 E Heat Treatment Standards ComplianceDocument3 pagesAMS 2750 E Heat Treatment Standards ComplianceQualidadeTFNo ratings yet
- Energy Performance of Hot, DryDocument128 pagesEnergy Performance of Hot, DrySrinu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy Services Brochure 4696 3 Da en PDFDocument62 pagesWind Energy Services Brochure 4696 3 Da en PDFghadasaudiNo ratings yet