Professional Documents
Culture Documents
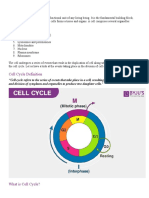
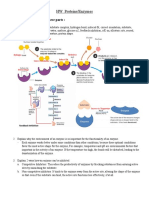
Interphase G Phase S Phase G Phase Mitotic Phase
Uploaded by
Chie ValdezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
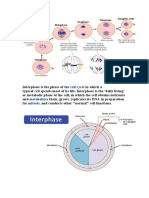
Interphase G Phase S Phase G Phase Mitotic Phase
Uploaded by
Chie ValdezCopyright:
Available Formats
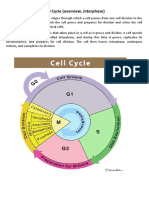
INTERPHASE G1 PHASE S PHASE G2PHASE MITOTIC PHASE G0PHAS
Write on the table the processes involved on the cell cycle
● In this phase, the cell replenishes its energy stores and synthesizes proteins necessary for
chromosome manipulation. Some cell organelles are duplicated, and the cytoskeleton is
dismantled to provide resources for the mitotic phase. There may be additional cell growth
during this phase. The final preparations for the mitotic phase must be completed before the
cell is able to enter the first stage of mitosis.
● This phase is a multistep process during which the duplicated chromosomes are condensed,
aligned, separated, and moved to opposite poles of the cell, and then are divided into two new
identical daughter cells.
● This phase technically refers to the division of a parental cell into two which entails the
cytoplasm of a cell into two is distinct from nuclear division. More cytoplasmic division as well.
● During this phase, cell grows and more organelles are produced, increasing the volume of the
cytoplasm.
● The cell is quite active at the biochemical level.
● Not all cells adhere to the classic cell cycle pattern in which a newly formed daughter cell
immediately enters the preparatory phases of inter- phase, closely followed by the mitotic
phase. Cells in G0 phase are not actively preparing to divide. The cell is in quiescent (inactive)
state that occurs when cells exit the cell cycle. Some cells enter this phase temporarily until an
external signal triggers the onset of G1. Other cells that never or rarely divide, such as mature
cardiac muscle and nerve cells, permanently remain in this phase.
● The cell is accumulating the building blocks of chromosomal DNA and the associated proteins as
well as accumulating sufficient energy reserves to complete the task of replicating each
chromosome in the nucleus.
● The centrosome is duplicated during this phase. The two centrosomes will give rise to the
mitotic spindle, the apparatus that orchestrates the movement of chromosomes during this
phase. At the center of each animal cell, the centrosomes of animal cells are associated with a
pair of rod-like objects, the centrioles, which are at right angles to each other. Centrioles help
organize cell division. Centrioles are not present in the centrosomes of other eukaryotic species,
such as plants and most fungi.
● The first stage of interphase is called the ________.
● Throughout interphase, nuclear DNA remains in a semi-condensed chromatin configuration.
● In this phase, DNA replication can proceed through the mechanisms that result in the formation
of identical DNA molecules. Sister chromatids—that are joined at a point by the centromeric
region.
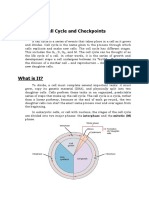
● During this stage, the cell undergoes normal growth processes while also preparing for cell
division. In order for a cell to move from interphase into the mitotic phase, many internal and
external conditions must be met.
You might also like
- Cell Cycle Pre Act 1Document2 pagesCell Cycle Pre Act 1Kristhel SahagunNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument5 pagesCell CycleJeanelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleAnahita SuriNo ratings yet
- Lab11 The Cell Cycle PDFDocument32 pagesLab11 The Cell Cycle PDFعبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاحNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument46 pagesCell Cycleatnasiya2026No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument4 pagesCell CycleRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Cellcycle-190703053908Document68 pagesCellcycle-190703053908AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1Document13 pagesBio 1Mary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NotesDocument12 pagesCell Cycle NotesMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: - Dr. Ishita SinghalDocument69 pagesCell Cycle: - Dr. Ishita SinghalDR. ISHITA SINGHAL100% (1)
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument22 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint Presentationsaramaktoof2No ratings yet
- Biology Test 3Document8 pagesBiology Test 3Patricia Sofia De LeonNo ratings yet
- BIO12 - Lesson 5-6Document8 pagesBIO12 - Lesson 5-6Atarax iaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Cell Cycle and Cell Division For NEET 2023 - Free PDF DownloadDocument10 pagesRevision Notes On Cell Cycle and Cell Division For NEET 2023 - Free PDF Downloadtswrs jaffargadhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: A. G1 PhaseDocument17 pagesChapter 2: Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: A. G1 PhaseIrish GatpoNo ratings yet
- PACKET Cell Cycle - MitosisDocument7 pagesPACKET Cell Cycle - MitosisSawin HainiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document48 pagesModule 1Saalif RahmanNo ratings yet
- InterphaseDocument5 pagesInterphaseChool Cydrick B. BascosNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Gen Bio 1 - MidtermAngel Cuacko GacmatanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & DivisionDocument28 pagesCell Cycle & DivisionThelma SimonNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument19 pagesThe Cell CycleShiba ShirzadNo ratings yet
- Class Notes: Cell CycleDocument9 pagesClass Notes: Cell CycleWhyNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology and HSB Cell Divsion NotesDocument10 pagesCSEC Biology and HSB Cell Divsion NotesAnasha Éttienne-Taylor100% (2)
- L 11 MeiosisDocument39 pagesL 11 MeiosissNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NewDocument11 pagesCell Cycle NewOlogunja PaulNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument2 pagesThe Cell CycleJoyzeannNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument39 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionSayantan SethNo ratings yet
- GENBIO1MOD3Document11 pagesGENBIO1MOD3Renzsoc JalmascoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division: Chapte r10Document17 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division: Chapte r10RitajNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle (Rubina)Document35 pagesCell Cycle (Rubina)RubinaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument4 pagesCell CycleSujith KuttanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument45 pagesCell Cycle & Cell DivisionAdyasha mishraNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument10 pagesCell CycleDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: (Fundamental Process)Document8 pagesCell Cycle: (Fundamental Process)r_borresNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument9 pagesThe Cell CycleChidera EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument120 pagesCell Cycle & Cell DivisionGanesh Patil100% (1)
- Cell Cycle CheckpointsDocument6 pagesCell Cycle CheckpointsJoyce NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument20 pagesCell CycleShelrenNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionHajie RosarioNo ratings yet
- Name - Period - The Cell Cycle & Mitosis Learning QuestDocument9 pagesName - Period - The Cell Cycle & Mitosis Learning QuestZayden SexyNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GDocument15 pagesOverview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GJavali.GNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment PDFDocument13 pagesBiology Assignment PDFmohd mehartaj100% (1)
- CDVDDocument16 pagesCDVDmuchi muchoNo ratings yet
- Phases of The Cell CycleDocument6 pagesPhases of The Cell CyclejayweinxNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Cell Division (Mitosis)Document79 pagesWeek 8 - Cell Division (Mitosis)KENT GARCIANo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument12 pagesCell CycleVega, Charles Gabriel G.No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Cell Cycle and CheckpointsDocument6 pagesLesson 6 - Cell Cycle and CheckpointsReuben Al'jaldi100% (1)
- GNBIO1 - Module 5-wk7Document57 pagesGNBIO1 - Module 5-wk7Julius Vincent YapsangcoNo ratings yet
- General Biology I Long Test ReviewerDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology I Long Test ReviewerJillian GarcilanNo ratings yet
- Cycle: Radiation Biology HVB32103Document24 pagesCycle: Radiation Biology HVB32103Sya WalNo ratings yet
- 1cell CycleDocument19 pages1cell CycleUrdu KahaniNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument63 pagesCell CycleLovely PeñaredondoNo ratings yet
- Module in EnglishDocument28 pagesModule in EnglishIannNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument26 pagesCell CycleMa. Theresa AgsaoayNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Regulation - Control Points (Part I)Document24 pagesCell Cycle Regulation - Control Points (Part I)Amara TargaryenNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell Cyclewebpixel servicesNo ratings yet
- Article 1Document11 pagesArticle 1UMESH RAJ25No ratings yet
- Final Evaluation in Entrepreneurship (Output)Document6 pagesFinal Evaluation in Entrepreneurship (Output)Chie ValdezNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Quarter 1Document5 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Quarter 1Chie ValdezNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY - Mitosis and Meiosis ComparisonDocument4 pagesACTIVITY - Mitosis and Meiosis ComparisonChie Valdez100% (3)
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 1Document13 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 1Chie ValdezNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Submitted byDocument12 pagesBusiness Plan: Submitted byChie ValdezNo ratings yet
- Jules Arnel M. Valdez. 12 Stem-C Ma'am Mary Rose Rueda. General Biology 2 Exam: Part 2Document4 pagesJules Arnel M. Valdez. 12 Stem-C Ma'am Mary Rose Rueda. General Biology 2 Exam: Part 2Chie ValdezNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Submitted byDocument12 pagesBusiness Plan: Submitted byChie ValdezNo ratings yet
- Genetics MCQDocument19 pagesGenetics MCQSonam RanaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesCellular RespirationegeniasaljonnielpNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Neuronal Communication POWERPOINTDocument58 pages5.3 Neuronal Communication POWERPOINTLisa MillardNo ratings yet
- Cell-Structure and Functions - Class 8 - NCERT Exercise Questions - PANTOMATHDocument4 pagesCell-Structure and Functions - Class 8 - NCERT Exercise Questions - PANTOMATHsourav9823No ratings yet
- Meiosis ReportDocument6 pagesMeiosis ReportDaizLee Ahmad71% (7)
- rDNA 3Document33 pagesrDNA 3Šhââń RøýNo ratings yet
- Formulation of The Cell TheoryDocument4 pagesFormulation of The Cell Theoryapi-345209915No ratings yet
- 2020 - Prac 1 - Sds-page+Westernblotting - Bmol3201 - 6231 - FinalDocument40 pages2020 - Prac 1 - Sds-page+Westernblotting - Bmol3201 - 6231 - FinalshaheenNo ratings yet
- 126 NotesDocument44 pages126 Notesammsantos300No ratings yet
- Clinical Application of PharmacodynamicDocument2 pagesClinical Application of PharmacodynamicSyed Shafiq Syed ZainiNo ratings yet
- Junctional Epithelium: Dr. Ishita Singhal Mds First YearDocument54 pagesJunctional Epithelium: Dr. Ishita Singhal Mds First YearDR. ISHITA SINGHALNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Exam IDocument7 pagesBacteriology Exam ITorillo KimNo ratings yet
- Oet Reading Part 1Document5 pagesOet Reading Part 1AparnnaNo ratings yet
- Integration of MetabolismDocument40 pagesIntegration of MetabolismIrfanArifZulfikar100% (1)
- Cell Structure Practice QuizDocument3 pagesCell Structure Practice QuizkishoreddiNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Cornell Notes TeacherDocument5 pagesCell Respiration Cornell Notes TeacherErik Artur100% (1)
- Exam 3 Term 6 PDFDocument3 pagesExam 3 Term 6 PDFThomas Santiago Torres CastroNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Amino AcidsDocument31 pagesBiosynthesis of Amino AcidsEvaNo ratings yet
- Science - Cell SpecializationDocument4 pagesScience - Cell SpecializationAvila VarshiniNo ratings yet
- HW Proteins EnzymesDocument2 pagesHW Proteins Enzymesapi-524061079No ratings yet
- Term Paper General Biology 1 Final DraftDocument18 pagesTerm Paper General Biology 1 Final DraftEstelleNerieLamsinNo ratings yet
- Sandip BambhaniyaDocument13 pagesSandip BambhaniyaAnyone Can CookNo ratings yet
- Protein MicroarrayDocument5 pagesProtein Microarraysudhu sudsNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingDocument64 pagesLecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingDiabyNo ratings yet
- Almeida 2023 - Molecular Approaches For Spinal Cord Injury TreatmentDocument8 pagesAlmeida 2023 - Molecular Approaches For Spinal Cord Injury TreatmentSuelen Adriani MarquesNo ratings yet
- 1 B. Teknologi Sel Punca Terapi HatiDocument12 pages1 B. Teknologi Sel Punca Terapi HatiarisNo ratings yet
- Normal Oral Flora 9Document95 pagesNormal Oral Flora 9adi raghav50% (2)
- D652-Kowshik Kumar MDocument89 pagesD652-Kowshik Kumar MDr osama khamisNo ratings yet
- Effects and Mechanisms of Resveratrol On Aging and Age - Related DiseasesDocument15 pagesEffects and Mechanisms of Resveratrol On Aging and Age - Related DiseasesAna MariaNo ratings yet