Professional Documents
Culture Documents
#1 - Related Terminologies
Uploaded by
Bianca A0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesOriginal Title
#1 - RELATED TERMINOLOGIES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pages#1 - Related Terminologies
Uploaded by
Bianca ACopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
LEC # 1 There are four different nucleotides present in a
DNA molecule. The various sequence
REVIEW OF RELATED combinations of these bases ultimately encode
TERMINOLOGIES genetic information
GENETICS AND GENES
Genetics - the study of inherited traits and their
variation; study of heredity
Heredity - the sum of all biological processes
by which particular characteristics are
transmitted from parents to their offspring.
Adenine-Thymine, Guanine-Cytosine
Genes - the units of heredity, which is the PARTS OF NUCLEOTIDES: Phosphate, Sugar,
transmission of inherited traits. Genes can be N. Bases
found on the nucleic acid DNA; segments of
nucleic acid in DNA that encodes for particular THE RNAs
product: protein Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries the
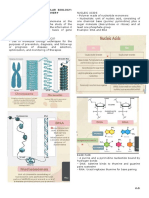
THE NUCLEIC ACIDS instructions for protein synthesis to the sites of
DNA – a molecule whose function is to store protein synthesis; from nucleus to ribosome;
and transfer genetic information; making instruction
protein Ribosome – made up of protein and
RNA – important molecule in protein synthesis rRNA
Both DNA and RNA are polymers of repeating Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – combines with
called nucleotides (nucleic acid monomer) proteins to form ribosomes
Transfer RNA (tRNA) – RNA that delivers
DNA RNA amino acids to the sites of protein synthesis;
Double-stranded Single-stranded amino acids are building blocks of protein
Secured inside nucleus Helps interpret Protein has diverse function.
Instruction instruction to make
Polymers that is made up protein Catalaze – enzymes; structure – collagen
of nucleotides Polymers that is made up It helps us to have certain characteristics.
Blueprint of nucleotides
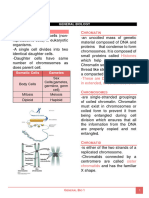
Sugar: Deoxyribose Sugar: Ribose GENES, CHROMOSOMES AND GENOMES
Anti-parallel In & out of nucleus Genome – it is the complete set of genetic
instructions characteristic of an organism,
DNA is transcribed to make mRNA including protein-encoding genes and other
mRNA translated to make proteins DNA sequences; totality
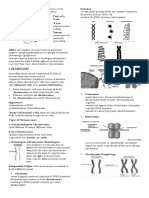
Central Dogma because all living things follow Chromosomes – structures that are a product of
these steps DNA coiling in association with proteins
Genes, the segment of DNA strand that
encodes for the production of different
proteins, may have different variants. These
are called alleles.
**Genes that encodes for eye color have different Chromatid - one of two identical halves of a
variants but same characteristic; people have replicated chromosome
different eye color. Centromere - a constricted region of a
chromosome that
separates it into a
short arm (p) and a
long arm (q).
Centrosome - the
major
microtubule-
organizing centre
(MTOC) in
eukaryotic cells
Centrioles - a barrel-shaped organelle which
lives normally within the centrosome
Genomics - the study of all of a person's
Histoles – circles, proteins that interacts with genes (the genome)
DNA molecules that forms coiling to form Sister chromatids - pairs of identical copies
chromosome (visible in cell division) of DNA joined at a point called the
centromere
MUTATIONS, PHENOTYPE, AND
Non-sister chromatids - chromatids of
GENOTYPE
homologous chromosomes
Alleles are products of mutations. Daughter chromosomes - a chromosome that
Mutations - defined as any heritable change in results from the separation of sister
the DNA sequence and are the source of all chromatids during cell division
genetic variation Spermatogonia - a cell produced at an early
stage in the formation of spermatozoa,
Phenotype – observable traits or features of an formed in the wall of a seminiferous tubule
organism (alleles that are expressed); EX: and giving rise by mitosis to spermatocyte;
color, hair, height Immature
Spermatocyte - a type of male gametocyte in
Genotype – set of alleles for a given trait animals
carried by an organism (alleles that are present) Spermatid - the haploid male gametid that
results from division of secondary
** Not all alleles are expressed spermatocytes
Spermatozoa - the male sex cells that carry a
MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS man's genetic material
Mitosis – a type of cell division in which one
somatic cell give rise to two new ones
Somatic cells – body cells except
gametes (not sperm or egg cell)
Meiosis – cell division involved in the
production of gametes
TERMS IN GENETICS
Chromatin - a complex of DNA and proteins
that forms chromosomes within the nucleus
of eukaryotic cells.
You might also like
- DNA and Gene Expression - G10 (Luke)Document24 pagesDNA and Gene Expression - G10 (Luke)JuliusNo ratings yet
- Unit7 Microbial Genetics 1Document5 pagesUnit7 Microbial Genetics 1Tresha MadroñalNo ratings yet
- TransesDocument3 pagesTransesits mitziNo ratings yet
- Science Exam Preparations - Joel TDocument12 pagesScience Exam Preparations - Joel TvaughanNo ratings yet
- Cyto311 LectureDocument28 pagesCyto311 Lecture2senpaijesse7No ratings yet
- 00 Core Learning Checklist Astrobio Unit 1 23-24Document2 pages00 Core Learning Checklist Astrobio Unit 1 23-24gaoNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Basic Unit of Plant & Animal LifeDocument11 pagesThe Cell: Basic Unit of Plant & Animal Lifepotionyesterday100% (2)
- 456 Mic 1Document2 pages456 Mic 1Margot JonesNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics: The HOW of HeredityDocument49 pagesMolecular Genetics: The HOW of Hereditycorygunther6451No ratings yet
- Cytogenetics ReviewerDocument46 pagesCytogenetics ReviewerSarah EugenioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular BiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Molecular BiologyAda AudreyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HredirtyDocument15 pagesUnit 2 HredirtyMarga AbabaNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDocument37 pagesGenetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Review of Related TerminologiesDocument4 pagesReview of Related TerminologiesJamaica SalvadorNo ratings yet
- ChromosomesDocument4 pagesChromosomesAlliah Angela Soldevilla BasadreNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesChromosomes and Cell DivisionEllaine Larren RazonNo ratings yet
- Microbiology (Chapter 7: Microbial Genetics) : The Structure and Replication of GenomesDocument14 pagesMicrobiology (Chapter 7: Microbial Genetics) : The Structure and Replication of GenomesCarrie ANo ratings yet
- Lect10F1 Cell Nucleus 2011Document9 pagesLect10F1 Cell Nucleus 2011phicho5781No ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle ReviewerDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle ReviewerNcle NaborNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2019Document151 pagesGenetics 2019Joycee Jatulan-EnajeNo ratings yet
- Chromosome StructureDocument14 pagesChromosome Structurehanisakura92No ratings yet
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Document15 pages٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument20 pagesGeneticsMadaNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Control: DNA RNA ProteinDocument9 pagesGene Expression and Control: DNA RNA ProteinChristia Sandee SuanNo ratings yet
- DNA - Genes, Transcription, Translation and InheritanceDocument2 pagesDNA - Genes, Transcription, Translation and InheritanceLouis AmorNo ratings yet
- Genpath 1 5Document26 pagesGenpath 1 5yzzamedina44No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument103 pagesCell DivisionAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 Study Notes P2Document14 pagesLIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 Study Notes P2thatohatsihlohonolofatsoNo ratings yet
- Medical Embryology 1-76Document12 pagesMedical Embryology 1-76Aliya TambacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Cell Division - Part 1Document92 pagesChapter 4 - Cell Division - Part 1happyflowerNo ratings yet
- Chromosome: - To Efficiently Package DNA Into Smaller Volumes ToDocument10 pagesChromosome: - To Efficiently Package DNA Into Smaller Volumes ToCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- #2 - Intro CytogeneticsDocument3 pages#2 - Intro CytogeneticsBianca ANo ratings yet
- 2 NucleusDocument19 pages2 NucleusYuu Ayu'k LifestarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document3 pagesLesson 4Samantha VeraNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Study Notes - Paper 2Document16 pagesLife Sciences Study Notes - Paper 2Aysha MohammadNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - DNA Structure and FunctionDocument47 pagesModule 7 - DNA Structure and FunctionAllan SigangaNo ratings yet
- Foz Lab M3Document7 pagesFoz Lab M3jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Holmesan123 GeneticsDocument2 pagesHolmesan123 GeneticsdanishNo ratings yet
- Unit 4, Topic 1 (ATAR NOTES)Document10 pagesUnit 4, Topic 1 (ATAR NOTES)lilyNo ratings yet
- Cyto Trans PrelimDocument12 pagesCyto Trans PrelimSarah EugenioNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument9 pagesInheritanceFalak FathimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Genetics (Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology For Nursing and Healthcare Students)Document87 pagesChapter 3 - Genetics (Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology For Nursing and Healthcare Students)Mary Grace MartinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologySJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit 3Document27 pagesBiology Notes Unit 3Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control of Cell Function PDFDocument14 pagesGenetic Control of Cell Function PDFEDGAR A. SERVINNo ratings yet
- X Bio Masterkey Differences 22 - 234Document40 pagesX Bio Masterkey Differences 22 - 234Varenayam editzNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionChristina DaligconNo ratings yet
- Bio Chap 5 and 6Document19 pagesBio Chap 5 and 6mjNo ratings yet
- Human Genetic Mo - AliDocument15 pagesHuman Genetic Mo - AliSnowNo ratings yet
- The Genetic CodeDocument67 pagesThe Genetic CodeRhea SharmaNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument3 pagesMITOSISDaphne Ezra F. OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Gr12 PAPER 2 Bio TERMSDocument13 pagesGr12 PAPER 2 Bio TERMSMmabatho VilakaziNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Human Genetics JassimDocument16 pagesAn Introduction To Human Genetics Jassimdr_47839666No ratings yet
- The Cell:: Fundamental Medical Science 1 CytologyDocument16 pagesThe Cell:: Fundamental Medical Science 1 CytologyezebelluciNo ratings yet
- Genetics Year 10 NSW 2022Document10 pagesGenetics Year 10 NSW 2022Rachel QuahNo ratings yet
- Structure of Eukaryotic Chromosomes. Karyotype. Methods of Cytogenetic AnalysisDocument4 pagesStructure of Eukaryotic Chromosomes. Karyotype. Methods of Cytogenetic Analysiscarlottabovi28No ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsDocument4 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- Cellular Division Reviewer PDFDocument16 pagesCellular Division Reviewer PDFBrylle Angelo PolintanNo ratings yet
- L1 Gene ExpressionDocument5 pagesL1 Gene Expressiontowalovesports920No ratings yet
- #4 - Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument4 pages#4 - Cell Cycle and MitosisBianca ANo ratings yet
- #2 - Intro CytogeneticsDocument3 pages#2 - Intro CytogeneticsBianca ANo ratings yet
- #7 - Model OrganismsDocument2 pages#7 - Model OrganismsBianca ANo ratings yet
- Cells: Somatic Cells Body CellsDocument2 pagesCells: Somatic Cells Body CellsBianca ANo ratings yet
- 2lab - Lab SafetyDocument5 pages2lab - Lab SafetyBianca ANo ratings yet
- 5lab - Serial DilutionDocument3 pages5lab - Serial DilutionBianca ANo ratings yet
- 4lec - CytokinesDocument4 pages4lec - CytokinesBianca ANo ratings yet
- Screening Test For Phagocytic Engulfment: DiapedesisDocument2 pagesScreening Test For Phagocytic Engulfment: DiapedesisBianca ANo ratings yet
- 4lec - CytokinesDocument4 pages4lec - CytokinesBianca ANo ratings yet
- Agglutination Reaction: Sensitization Lattice FormationDocument2 pagesAgglutination Reaction: Sensitization Lattice FormationBianca ANo ratings yet
- Screening Test For Phagocytic Engulfment: DiapedesisDocument2 pagesScreening Test For Phagocytic Engulfment: DiapedesisBianca ANo ratings yet
- Agglutination Reaction: Sensitization Lattice FormationDocument2 pagesAgglutination Reaction: Sensitization Lattice FormationBianca ANo ratings yet
- COURSE WORK MOLECULAR BIOLOGY & GeneticsDocument3 pagesCOURSE WORK MOLECULAR BIOLOGY & Geneticsusaeed00000No ratings yet
- Biology Model Examination For Grade 12 in The Year 2007 E.CDocument15 pagesBiology Model Examination For Grade 12 in The Year 2007 E.CDanielNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Chapter 23 PresentationDocument18 pagesAP Biology Chapter 23 PresentationHayleeNo ratings yet
- Developmental GeneticsDocument20 pagesDevelopmental GeneticsabhishekNo ratings yet
- STAAR EOC 2017 Test Biology PDFDocument48 pagesSTAAR EOC 2017 Test Biology PDFAnonymous WZXek8GNo ratings yet
- Melvin L. Moss: Key Words: Causation, Epigenetics, Genetics, Craniofacial GrowthDocument10 pagesMelvin L. Moss: Key Words: Causation, Epigenetics, Genetics, Craniofacial GrowthCony Del CidNo ratings yet
- Chapter Vocabulary Review: Name Class DateDocument1 pageChapter Vocabulary Review: Name Class Datesamixox singsNo ratings yet
- What Is The Human Genome?Document13 pagesWhat Is The Human Genome?Rahul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Genomics and Bioinformatics: Peter Gregory and Senthil NatesanDocument22 pagesGenomics and Bioinformatics: Peter Gregory and Senthil NatesanajaybioinfoNo ratings yet
- Pierce - Genetics - A Conceptual Approach CH 16Document33 pagesPierce - Genetics - A Conceptual Approach CH 16gustavoNo ratings yet
- Biopsych Trans Chap 2Document13 pagesBiopsych Trans Chap 2Chantelle SiyNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - 2ndqtrexamDocument6 pagesEarth and Life Science - 2ndqtrexamMa. Lourdes LazaroNo ratings yet
- Cumming School of Medicine Graduate Course Outline MDSC 641.03 Advanced Genetics II (Advanced Molecular Genetics) Winter 2018Document6 pagesCumming School of Medicine Graduate Course Outline MDSC 641.03 Advanced Genetics II (Advanced Molecular Genetics) Winter 2018achinatbiotechNo ratings yet
- Transposable Genetic ElementDocument60 pagesTransposable Genetic ElementabimubNo ratings yet
- A Study On Tongue Rolling, Tongue Folding and Cerumen Type in A Nigeria PopulationDocument4 pagesA Study On Tongue Rolling, Tongue Folding and Cerumen Type in A Nigeria PopulationJada HartNo ratings yet
- 202 07 BioinformaticsDocument14 pages202 07 BioinformaticsroliepolieolieNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam Notes by ConstantinDocument120 pagesBiology Exam Notes by ConstantinbnvjNo ratings yet
- PRODUCCIÓN FUMARATO (1) GgyDocument7 pagesPRODUCCIÓN FUMARATO (1) GgyERICK GARCIA LAGUNANo ratings yet
- Dna VaccineDocument2 pagesDna VaccinesauravsarkarNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Reflection: Members: Boh Guias Mangubat Oñate Tayko VerdonDocument3 pagesGroup 1 Reflection: Members: Boh Guias Mangubat Oñate Tayko VerdonTonette Hatamosa VerdonNo ratings yet
- HAYATI Journal of Biosciences: Fenny M. Dwivany, Rizkita Rahmi Esyanti, Aksarani 'Sa Pratiwi, Hera Fi ZaskiaDocument4 pagesHAYATI Journal of Biosciences: Fenny M. Dwivany, Rizkita Rahmi Esyanti, Aksarani 'Sa Pratiwi, Hera Fi ZaskiaCherylou CamusNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Buah Naga PDFDocument7 pagesJurnal Buah Naga PDFAmelia GustinNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Foods - Boon or BaneDocument6 pagesGenetically Modified Foods - Boon or BaneushapvermaNo ratings yet
- Digital Portfolio 5Document3 pagesDigital Portfolio 5api-264713930No ratings yet
- A Time and A Tide: Kao, Charles KDocument23 pagesA Time and A Tide: Kao, Charles KrlNo ratings yet
- Molbio HandoutDocument29 pagesMolbio HandoutHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- 1 Examen 2 Trimestre BiologiaDocument3 pages1 Examen 2 Trimestre Biologianacho urbina rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cancer Cytopathology - 2022 - Gokozan - Combining Molecular Testing and The Bethesda Category III VI Ratio For ThyroidDocument16 pagesCancer Cytopathology - 2022 - Gokozan - Combining Molecular Testing and The Bethesda Category III VI Ratio For ThyroidMariana UsatiiNo ratings yet
- L27 What Is Genetic Engineering 1Document37 pagesL27 What Is Genetic Engineering 1Kent Gabriel DumendenNo ratings yet
- CrisprDocument6 pagesCrispranuradhaclNo ratings yet