Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homeostatic Imbalance 7-10
Uploaded by
enewaw sabaw0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views4 pagesThe document discusses several conditions that can affect the nervous system and special senses. It describes meningitis as an inflammation of the meninges that can spread to the brain, while encephalitis is an inflammation of brain tissue usually caused by a virus. Hydrocephalus is when excess cerebrospinal fluid builds up in the brain, enlarging the head of infants. Damage to nerves can cause flaccid or spastic paralysis depending on the location of damage.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several conditions that can affect the nervous system and special senses. It describes meningitis as an inflammation of the meninges that can spread to the brain, while encephalitis is an inflammation of brain tissue usually caused by a virus. Hydrocephalus is when excess cerebrospinal fluid builds up in the brain, enlarging the head of infants. Damage to nerves can cause flaccid or spastic paralysis depending on the location of damage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views4 pagesHomeostatic Imbalance 7-10
Uploaded by
enewaw sabawThe document discusses several conditions that can affect the nervous system and special senses. It describes meningitis as an inflammation of the meninges that can spread to the brain, while encephalitis is an inflammation of brain tissue usually caused by a virus. Hydrocephalus is when excess cerebrospinal fluid builds up in the brain, enlarging the head of infants. Damage to nerves can cause flaccid or spastic paralysis depending on the location of damage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
the CNS.
This condition of brain inflammation is
Homeostatic Imbalance called encephalitis (en-sef-ah-li′tis). Meningitis is
Nervous System usually diagnosed by taking a sample of cerebro-
spinal fluid from the subarachnoid space
surrounding the spinal cord.
A number of factors can impair the conduction of
impulses. For example, sedatives and anaesthetics Hydro-cephalus (hi-dro-sef′ah-lus) if something
block nerve impulses by altering membrane obstructs its drainage (for example, a tumor), CSF
permeability to ions, mainly sodium ions. As we begins to accumulate and exert pressure on the
have seen, no sodium entry = no action potential. brain. Literally means, “water on the brain.”
Cold and continuous pressure hinder impulse Hydrocephalus in a newborn baby causes the head
conduction because they interrupt blood circulation to enlarge as the brain increases in size. This is
(and hence the delivery of oxygen and nutrients) to possible in an infant because the skull bones have
the neurons. For example, your fingers get numb not yet fused.
when you hold an ice cube for more than a few
seconds. Likewise, when you sit on your foot, it Damage to the ventral root results in flaccid
“goes to sleep.” When you warm your fingers or paralysis of the muscles served. In flaccid
remove the pressure from your foot, the impulses paralysis, nerve impulses do not reach the muscles
begin to be transmitted again, leading to an affected; thus, no voluntary movement of those
unpleasant prickly feeling. _ muscles is possible. The muscles begin to atrophy
because they are no longer stimulated.
Individuals who have problems with their basal
nuclei are often unable to walk normally or carry Spastic paralysis involuntary muscles are not
out other voluntary movements in a normal way. controlled. If the spinal cord is transected (cut
Huntington’s disease and Parkinson’s disease are crosswise) or crushed
two examples of such syndromes.
Alzheimer’s ease (AD) is (altz′hi-merz) a Cerebral palsy is a neuromuscular disability in
progressive dis-degenerative disease of the which the voluntary muscles are poorly controlled
and spastic because of brain damage.
brain that ultimately results in dementia
(mental deterioration).
ENCEPHALITIS – an inflammation of brain
Parkinson’s disease, an example of a
tissue usually caused by a virus transmitted by the
basal nuclei problem, It results from a
bite of a mosquito. It is manifested by a wide
degeneration of specific neurons in the
variety of symptoms, including coma, fever, and
substantia nigra of the midbrain, which
convulsions and could result in death.
normally supply dopamine to the basal
nuclei.
TETANUS – is caused by the introduction of the
Huntington’s disease is a genetic disease
bacterium Clostridium tetani into an open wound.
that strikes during middle age and leads to
The bacterium produces a neurotoxin that affects
massive degeneration of the basal nuclei
motor neurons in the spinal cord and brain stem. It
and later of the cerebral cortex.
also blocks inhibitory neurotransmitters , resulting
in muscle contractions. The jaw muscles are
Ataxia (uh tax′e uh If the cerebellum is damaged affected earliest, locking the jaw in a closed
(for example, by a blow to the head, a tumor, or a position, hence the common name lockjaw. Death
stroke), movements become clumsy and can result from spasms of the respiratory muscles
disorganized). Victims cannot keep their balance and the diaphragm.
and may appear drunk because of the loss of
muscle coordination. They are no longer able to
touch their finger to their nose with eyes closed—a
feat that healthy individuals accomplish easily. Homeostatic Imbalance
Meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, is a Special Senses
serious threat to the brain because bacterial or viral
meningitis may spread into the nervous tissue of
“Watery-Eyes”- Because the nasal cavity mucosa Astigmatism (ah-stig¿mah-tizm), unequal
is continuous with that of the lacrimal duct system, curvatures in different parts of the cornea or lens.
a cold or nasal inflammation often causes the In this condition, blurry images occur because
lacrimal mucosa to become inflamed and swell. points of light are focused not as points on the
This impairs the drainage of tears from the eye retina but as lines (astigma = not a point). Special
surface. cylindrically ground lenses or contacts are used to
correct a stigmatism.
Conjunctivitis, Inflammation of the conjunctiva
results in reddened, irritated eyes. Pinkeye, its
infectious form caused by bacteria or viruses, is otitis media (o-ti¿tis me¿de-ah), inflammation of
highly contagious. the middle ear, is a fairly common result of a sore
throat, especially in children, whose pharyn-
Night Blindness- Its most common cause is gotympanic tubes run more horizontally.
prolonged vitamin A deficiency, which eventually
causes the neural retina to deteriorate. Anything Deafness is defined as hearing loss of any degree
that interferes with rod function hinders our ability —from a slight loss to a total inability to hear
to see at night. sound. Generally speaking, there are two kinds of
deafness, conduction and sensorineural
Color blindness -Lack of all three cone types Conduction deafness results when
whereas lack of one cone type leads to partial color something interferes with the conduction of
blindness. sound vibrations to the fluids of the inner
ear.
Sensorineural deafness occurs when there
Cataracts, the loss of lens transparency, cause is degeneration or damage to the receptor
vision to become hazy and distorted and can cells in the spiral organ of Corti, to the
eventually cause blindness. cochlear nerve, or to neurons of the
auditory cortex. This often results from
extended listening to excessively loud
Glaucoma, if drainage of aqueous humor is sounds.
blocked, fluid backs up like a clogged sink.
Pressure within the eye may increase to dangerous Anosmias, although it is possible to have either
levels and com- press the delicate retina and optic taste or smell deficits, most people seeking
nerve. medical help for loss of chemical senses have
olfactory disorders,
Hemianopia (hem–e-ah-no¿pe-ah) is the loss of
the same side of the visual field of both eyes,
which results from damage to the visual cortex on Strabismus (strah-biz¿mus), which is commonly
one side only (as occurs in some strokes). called “crossed eyes,” results from unequal pulls by the
external eye muscles that prevent the baby from
Nearsightedness, or myopia (mi–o¿pe-ah; “short coordinating movement of the two eyes.
vision”), occurs when the parallel light rays from
distant objects fail to reach the retina and instead
are focused in front of it; see part (b) in the figure.
Another way to think of this is the focal point of a
Homeostatic Imbalance
myopic eye falls short of the retina. Therefore, Endocrine System
distant objects appear
DIABETES MILLITUS – a very common
disorder of the endocrine system. It is caused by a
Farsightedness, or hyperopia (hi–per-o¿pe-ah; deficiency in insulin production. Other individuals with
“far vision”), occurs when the parallel light rays diabetes have a decreased number of insulin receptors
from distant objects are focused behind the retina on target cells so that glucose is unable to move into
—at least in the resting eye, in which the lens is flat cells even with normal insulin amounts. This condition
and the ciliary muscle is relaxed; see part in the results in chronic elevations of glucose in the blood, a
figure. Hyperopia usually results from an eyeball condition known as hyperglycemia. There are 2 types
that is too short or from a “lazy” lens. of diabetes mellitus:
Type 1 diabetes – also known as juvenile- The disease is more common in women and appears to
onset diabetes because it usually develops be genetic in origin. It occurs between 30 and 60 years
between 11 and 13 years of age but before 30. of age. Other symptoms include weight loss, fatigue,
It is an autoimmune disease that destroys the palpitations of the heart, nervousness, and slight tremors
beta cells of the pancreas. Individuals with this in the hands. This disease is treated with drugs or
type of diabetes must take daily insulin radioactive iodine.
injections.
Type 2 diabetes – known as noninsulin- GOITERS – is an enlargement of the thyroid
dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and is gland that results when the diet is deficient in an iodine.
the most common form of the disease,
affecting about 90% of people with diabetes. It CRETINISM – a condition characterized by
usually develops after 40 years of age and physical deformity and learning disabilities that is
produces milder symptoms. caused by congenital thyroid deficiency. It results in
dwarfism in which the adult body proportions remain
DIABETES INSIPIDUS – is caused by either not childlike.
enough antidiuretic hormone (ADH) being produced by
the posterior pituitary gland or from ADH receptors that Hyposecretion of GH during childhood leads to
are not functioning properly. This is not to be confused pituitary dwarfism
with diabetes mellitus. Individuals with diabetes
insipidus excrete copious amounts of urine and thus Gigatism_ Hypersecretion of GH
become severely dehydrated.
Hyposecretion of FSH or LH leads to sterility, the
SEASONAL AFFECTIVE DISORDER – occurs lack of ability to successfully reproduce, in both
in individuals who are sensitive to an overproduction of males and females.
melatonin that occurs in climate zones that have cloudy
winter months with little bright sunshine. It produces a
type of depression. Since winter months also have short Homeostatic Imbalance
days, this also contributes to more melatonin being
secreted by the pineal gland (less light equals more
Blood
melatonin). Individuals with this condition can be
treated with daily doses of several hours of bright Anemia- A decrease in the oxygen-carrying ability
artificial light. of the blood, whatever the reason,
Anemia may be the result of (1) a lower-
ALDOSTERONISM – is caused by too much than-normal number of RBCs or (2) abnormal or
secretion of aldosterone, one of the mineralocorticoid deficient haemoglobin content in the RBCs
hormones from the adrenal cortex. Symptoms of this
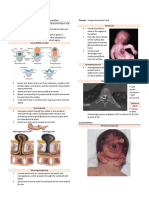
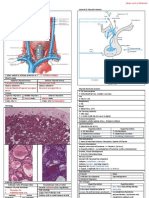
condition include high blood pressure. This results from A sickle cell anemia (SCA), the body does not
sodium and water retention by the kidneys, reduced form normal hemoglobin (as in the RBC shown in
levels of potassium in the blood, and an increase in part (a) of the figure). Instead, abnormal
blood pH. hemoglobin is formed that becomes spiky and
sharp (see part (b) of the figure) when either
CUSHING’S SYNDROME – caused by a long- oxygen is unloaded or the oxygen content in the
term excessive production of cortisol by the adrenal blood decreases below normal
cortex. Individuals with this condition have decreased
glucose tolerance levels. Symptoms of the condition polycythemia (pol′′e-si-the′me-ah)- An excessive
include excessive weight around the waist, and a round or abnormal increase in the number of erythrocytes.
moonlike face caused by the accumulation of excessive Polycythemia may result from bone marrow cancer
adipose tissue on the trunk and face. The skin may (polycythemia vera).
become abnormally pigmented, causing reddish blotches
on the face of light-skinned individuals. Individuals Leukemia (lu-ke′me-ah), literally “white blood,”
with this syndrome are susceptible to having infections, the bone marrow becomes cancerous, and huge
which may become difficult to eradicate. numbers of WBCs are turned out rapidly
GRAVE’S DISEASE – is a symptom of Thrombus- A clot that develops and persists in an
hyperthyroidism. Symptoms include an abnormal unbroken blood vessel.
protrusion of the eyeballs and an enlarged thyroid gland.
Embolus- if a thrombus breaks away from the
vessel wall and floats freely in the bloodstream.
Thrombocytopenia results from an insufficient
number of circulating platelets. It can arise from
any condition that suppresses the bone marrow,
such as bone marrow cancer, radiation, or certain
drugs.
Hemophilia (he′′mo-fil′e-ah) applies to several
different hereditary bleeding disorders that result
from a lack of any of the factors needed for
clotting.
You might also like
- TetanusDocument4 pagesTetanusDiana Fadhilah SariNo ratings yet
- Iicp 1Document5 pagesIicp 1Melodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Lockjaw. Death Can Result From Spasms of The Respiratory Muscles and The DiaphragmDocument2 pagesLockjaw. Death Can Result From Spasms of The Respiratory Muscles and The Diaphragmenewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- 2015 Bookmatter FundamentalsOfNeurologicDiseasDocument18 pages2015 Bookmatter FundamentalsOfNeurologicDiseasSabrin BadarneNo ratings yet
- LO WEEK 4 NeurobehaviourDocument14 pagesLO WEEK 4 NeurobehaviourLydia Angel HartonoNo ratings yet
- Mrcs NeurosurgeryDocument28 pagesMrcs NeurosurgeryAdebisiNo ratings yet
- TBI QuizletDocument4 pagesTBI QuizletLoraine CometaNo ratings yet
- Pharyngeal ReflexDocument3 pagesPharyngeal ReflexAyra Nakrish AlvarezNo ratings yet
- (NCM116) Finals - CVDDocument10 pages(NCM116) Finals - CVDKrishelle Kate PannigNo ratings yet
- Bells PalsyDocument6 pagesBells PalsyPhub TsheringNo ratings yet
- Diseases Affecting The Human Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesDiseases Affecting The Human Nervous SystemErick AbuzoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System DysfunctionsDocument4 pagesNervous System Dysfunctionsvea domingoNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCentral Nervous SystemMiguel Ashi GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCM116 Finals CVDDocument11 pagesNCM116 Finals CVDRachelle DelantarNo ratings yet
- Bagaimana Struktur Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Pusat KesadaranDocument9 pagesBagaimana Struktur Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Pusat KesadaranAhmad AkbarNo ratings yet
- Pathologies of Central Nervous SystemDocument51 pagesPathologies of Central Nervous SystemSajjad AliNo ratings yet
- Hand Out2007Document36 pagesHand Out2007Roza IsmarniNo ratings yet
- Brain Abscess (MEDSURG)Document3 pagesBrain Abscess (MEDSURG)Yessamin Paith RoderosNo ratings yet
- KERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Document67 pagesKERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Tunjung TrihapsariNo ratings yet
- Concise Neurological DictionaryDocument36 pagesConcise Neurological DictionaryAleksios MiseyanidisNo ratings yet
- Causas Neurologicas de DisfagiaDocument5 pagesCausas Neurologicas de DisfagiaRocioBelénAlfaroUrrutiaNo ratings yet
- 2357 - KERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Document67 pages2357 - KERUSAKAN OTAK DAN NEUROPLASTISITAS Biopsikologi 2018Nurul HikmahNo ratings yet
- BELL's PALSY... FinalDocument67 pagesBELL's PALSY... FinalZainab Waqar100% (1)
- Neuro HXDocument7 pagesNeuro HXM NNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Disorders: Ernest E. WangDocument13 pagesCranial Nerve Disorders: Ernest E. Wangirsyad tsaniNo ratings yet
- Mention Abnormalities in The Central Nervous System: A.StrokeDocument3 pagesMention Abnormalities in The Central Nervous System: A.Strokeazizi yemahulNo ratings yet
- Jurnal SOL SerebriDocument5 pagesJurnal SOL SerebriKomang AyuNo ratings yet
- Guarin, Consuelito Danzelle G. PHARM 1-C 0994 Pathophysiology of Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesGuarin, Consuelito Danzelle G. PHARM 1-C 0994 Pathophysiology of Nervous SystemChelito GuarinNo ratings yet
- Brain DisordersDocument21 pagesBrain DisordersKaren QuingNo ratings yet
- Cetebella Lesion TestDocument19 pagesCetebella Lesion TestMadhura Pushpa kumaraNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument4 pagesNeuro AnatomyMarianne Abnasan100% (1)
- Neuro Notes #3Document11 pagesNeuro Notes #3Monica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Nervous System GlossaryDocument4 pagesNervous System Glossarywilsonjaramillo51No ratings yet
- CCN Lecture Altered PerceptionDocument4 pagesCCN Lecture Altered PerceptionPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum: Usmle Target: Stanford School of Medicine NeurologyDocument8 pagesCerebellum: Usmle Target: Stanford School of Medicine NeurologyKarun BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Orbital Fractures:: Orbit Applied AspectsDocument4 pagesOrbital Fractures:: Orbit Applied AspectsTaimoor QadeerNo ratings yet
- SCI Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesSCI Cheat SheetJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemVinDiesel Balag-eyNo ratings yet
- Sefalgia Kronik Dan Hemiparese Sinistra E.C. Space Occupying LesionDocument5 pagesSefalgia Kronik Dan Hemiparese Sinistra E.C. Space Occupying LesionrivienaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesDisorders of The Nervous SystemAgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Neuro Test 2Document2 pagesNeuro Test 2Heather Wray-WilsonNo ratings yet
- Hi Per Bilirubin Emi ADocument25 pagesHi Per Bilirubin Emi ANovita Indah YantiNo ratings yet
- PATH - Cellular Injury of Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesPATH - Cellular Injury of Nervous SystemebizchatgptNo ratings yet
- Brain Damage and NeuroplasticityDocument40 pagesBrain Damage and NeuroplasticityChunelle Maria Victoria EspanolNo ratings yet
- Psy 03 Biopsychology-Ch. 10 ActivityDocument1 pagePsy 03 Biopsychology-Ch. 10 ActivityMitch Shyrelle BaclaoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Multiple SclerosisDocument4 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Multiple SclerosisTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- FACIAL NERVE ParalysisDocument35 pagesFACIAL NERVE ParalysisIgnasNo ratings yet
- Bilinguismo NeuroDocument6 pagesBilinguismo NeuroNatalia Garcia LoaizaNo ratings yet
- Ears Day 1Document3 pagesEars Day 1Rue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
- A-Z DiseasesDocument27 pagesA-Z Diseasesapi-463761938No ratings yet
- Birth Injuries, Head Injury and Injury To The Spinal Cord: Dr. Mehzabin AhmedDocument22 pagesBirth Injuries, Head Injury and Injury To The Spinal Cord: Dr. Mehzabin Ahmedbpt2No ratings yet
- Aracnoditis PDFDocument18 pagesAracnoditis PDFArockia Albert JerosonNo ratings yet
- Ailments of Nervous System 6-20-15Document19 pagesAilments of Nervous System 6-20-15JN MontessoriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Development of The Brain 2014 Clinical NeuroscienceDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Development of The Brain 2014 Clinical NeuroscienceMarta Casals CollNo ratings yet
- Diseases Affecting The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesDiseases Affecting The Nervous Systemrushy121No ratings yet
- Jan Marc S. Karganilla 10-Newton: Parkinson's Disease Cerebral Palsy AtaxiaDocument2 pagesJan Marc S. Karganilla 10-Newton: Parkinson's Disease Cerebral Palsy Ataxia박우진No ratings yet
- Coma, Defined As A Deep Sleeplike State From Which The Patient Cannot Be ArousedDocument41 pagesComa, Defined As A Deep Sleeplike State From Which The Patient Cannot Be Arousednathan asfahaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemFernanda AmigoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Spinal CordDocument10 pagesDisorders of The Spinal CordpazNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaFrom EverandThe Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaNo ratings yet
- EditedDocument13 pagesEditedenewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital Radiography and Pacs: Areej AloufiDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Digital Radiography and Pacs: Areej Aloufienewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: An Orientation: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument79 pagesThe Human Body: An Orientation: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical Collegeenewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document60 pagesChapter 8enewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- 2-Digital Imaging and Communications StandardsDocument6 pages2-Digital Imaging and Communications Standardsenewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential Electric PotentialDocument31 pagesElectric Potential Electric Potentialenewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- InfectionsDocument4 pagesInfectionsenewaw sabawNo ratings yet
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument2 pagesThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- Obstetric & Gynecology Nursing: Topic-Physiological Changes During LabourDocument54 pagesObstetric & Gynecology Nursing: Topic-Physiological Changes During LabourBhumi ChouhanNo ratings yet
- NG Teng Fong Discharge DocumentsDocument14 pagesNG Teng Fong Discharge DocumentsAnonymous yGwMIPJRawNo ratings yet
- Micro Electro Functional Ultrastructure - An Atlas of Tissue Biology and Pathology - M. Pavelka, J. Roth (Springer, 2005) WW PDFDocument341 pagesMicro Electro Functional Ultrastructure - An Atlas of Tissue Biology and Pathology - M. Pavelka, J. Roth (Springer, 2005) WW PDFOlteanu Dragos-NicolaeNo ratings yet
- MCQ Final 1981Document19 pagesMCQ Final 1981JohnSonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Lymphatic SystemDocument22 pagesChapter 3: Lymphatic Systemfatin harrisNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter ExamDocument6 pages2nd Quarter ExamLianne ChrisNo ratings yet
- DrawittoknowitDocument2 pagesDrawittoknowitByeongsu ParkNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Type A: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesHuman Reproduction: Type A: Multiple Choice Questionsriya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Tranaxemic AcidDocument6 pagesTranaxemic AcidCharan Teja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Threshold and RecruitmentDocument16 pagesThreshold and RecruitmentShamaine Anne SalvadorNo ratings yet
- BP201TPDocument1 pageBP201TPDarshanNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals Revision NotesDocument11 pagesTransport in Animals Revision Notesamr ahmedNo ratings yet
- Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria: Donath-Landstiener Screening TestDocument1 pageParoxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria: Donath-Landstiener Screening TestMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation. PDF My NoteDocument11 pagesUrine Formation. PDF My NoteSurya JoyNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Use of Classification-1Document20 pagesConcepts and Use of Classification-1joannavera2020No ratings yet
- B1 RevisionDocument17 pagesB1 RevisionPierre BrocasNo ratings yet
- Calixtro, Narrative HypertensionDocument2 pagesCalixtro, Narrative HypertensionKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic Management of Lumber PivdDocument21 pagesAnaesthetic Management of Lumber PivdSadasiv PandaNo ratings yet
- CYSTSDocument12 pagesCYSTSGowriNo ratings yet
- MCN Finals NotesDocument287 pagesMCN Finals NotesbabyboyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsRJNo ratings yet
- CH 7 The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCH 7 The Nervous Systemapi-267543553No ratings yet
- IGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 8 - Homeostasis and ExcretionDocument4 pagesIGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 8 - Homeostasis and ExcretionHisokagen0% (1)
- RhabdomyosarcomaDocument11 pagesRhabdomyosarcomaFrancia ToledanoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System - Lecture STEMDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory System - Lecture STEMMargeory Calatan100% (1)
- Blueprint For Questions Physiology Subject Matter Question # Recall Compre-Hension ApplicationDocument12 pagesBlueprint For Questions Physiology Subject Matter Question # Recall Compre-Hension ApplicationAde AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Script For PPT PresentationDocument4 pagesScript For PPT PresentationJanine Airah MorgadoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & DivisionDocument29 pagesCell Structure & DivisionDisaster Management Deptt Rampurhat-I BlockNo ratings yet
- Pharyngeal ArchesDocument35 pagesPharyngeal ArchesconstantinilieNo ratings yet