Professional Documents
Culture Documents
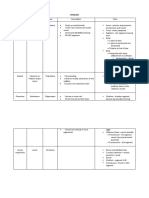
Types of Yolk: Structure Specific Origin Fate in Adult Body System Function
Uploaded by
Kobee BacolodOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Yolk: Structure Specific Origin Fate in Adult Body System Function
Uploaded by
Kobee BacolodCopyright:
Available Formats
Reviewer They contain moderate amount of yolk, 2.
Telolecithal Eggs:
e.g., eggs of lamprey, lung fish, frogs and
Mitosis and meiosis Yolk is concentrated in the vegetal half,
toads.
e.g. eggs of amphibians.
Types of Yolk
3. Macrolecithal (Megalecithal or
3. Meiolecithal Eggs:
Quantity Polylecithal) Eggs:
Yolk is very large which occupies nearly
1. Microlecithal Eggs: They contain large amount of yolk, e.g.,
the entire ooplasm, leaving free only a
eggs of insects, sharks, bony fishes,
They contain very small amount of yolk, small disc like area of cytoplasm for the
reptiles, birds and egg laying mammals.
e.g. eggs of Sea urchin, Herdmania, nucleus, e.g., eggs of reptiles, birds and
amphioxus. The eggs of man contain very egg laying mammals.
little amount of yolk, hence human egg is
Distribution of Yolk in Cytoplasm: 4. Centrolecithal Eggs:
alecithal (almost free of yolk).
1. Homolecithal Eggs: Yolk is localized at the centre, e.g. eggs of
2. Mesolecithal Eggs:
insects.
Yolk is uniformly distributed, e.g. eggs of
annelids, molluscs, echinoderms and
protochordates.
Structure Specific origin Fate in adult Body System Function
Ectoderm
Adhesive glands Pads
Auditory vesicles Auditory
Corneal epithelium Cornea
Dorsal fin
Epipharyngeal placode
Infundibulum -
Lens placodes Lens of eyes
Mesencephalon
Nasal placodes
Neural crest cells
Optic cups
Optic stalks
Pineal gland
Proctodeum
Prosencephalon
Rhombencephalon
Rudiment of the anterior
pituitary gland
Semilunar ganglia
Spinal cord Spinal Cord
Stomodeum
Ventral fin
Mesoderm
Conotruncus
Dorsal aortae
Dorsal mesocardium
First aotic arches
Notochord
Parietal pericardium
Pronephric kidneys Kidneys
Somites
Subnotochordal rod
Ventricle
Endoderm
Duodenum
Foregut
Hindgut
Liver rudiment Liver
Midgut
Pharynx -
Ectoderm and Endoderm
Cloacal membrane Cloaca
Oral membrane Mouth
You might also like
- Animal Kingdom-Subphylum Vertebrata-Class IXDocument2 pagesAnimal Kingdom-Subphylum Vertebrata-Class IXMonika Mehan100% (2)
- ADocument40 pagesAapi-3826751No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Subphylum Vertebrata Class IXDocument1 pageAnimal Kingdom Subphylum Vertebrata Class IXNandishwara ThonthanalNo ratings yet
- Group Endangered Species ZOO100LAB Exercise 3 Chordate Embryology Part 1Document7 pagesGroup Endangered Species ZOO100LAB Exercise 3 Chordate Embryology Part 1Kayl Dustin MalalisNo ratings yet
- 8539types of EggsDocument8 pages8539types of Eggsouafia liiamaniNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Notesss YehahahaDocument133 pagesIGCSE Biology Notesss YehahahaDIO yesNo ratings yet
- 4BMT CmparaDocument4 pages4BMT Cmparajay primaNo ratings yet
- Early DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEarly DevelopmentyelloweverglowNo ratings yet
- T. Parasitology Lec 4 CestodesDocument21 pagesT. Parasitology Lec 4 CestodesAbdalrhmanNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument7 pagesConnective TissueSaif AliNo ratings yet
- 06 GastrulationtxtDocument38 pages06 GastrulationtxtHafidzul HalimNo ratings yet
- AnimalsDocument9 pagesAnimalssolomon MekonninNo ratings yet
- Early DevelopmentDocument5 pagesEarly DevelopmentMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- Kel 8 Biology AvesDocument47 pagesKel 8 Biology AvesAbdu RohmanNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Whorl: Androecium: Distal End AntherDocument16 pagesMale Reproductive Whorl: Androecium: Distal End AntherAyush bhadaniNo ratings yet
- Biological Terminology (Bio Terms) :: Latin & Greek Word Parts (Prefixes, Root Words, and Suffixes)Document4 pagesBiological Terminology (Bio Terms) :: Latin & Greek Word Parts (Prefixes, Root Words, and Suffixes)Raodatul JannahNo ratings yet
- BIONOTES2016 ChenityDocument83 pagesBIONOTES2016 ChenityMeerab Shah100% (1)
- Female Anatomy 07Document41 pagesFemale Anatomy 07Rudolph Antony ThomasNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: OvariolesDocument11 pagesFemale Reproductive System: OvariolesCarlos Enrique Pijo PerezNo ratings yet
- 2 The Variety of Living OrganismsDocument10 pages2 The Variety of Living Organismsahasna.bandaraNo ratings yet
- Birds and Mammals Embryo DevelopmentDocument21 pagesBirds and Mammals Embryo Developmentyui kirigayayuukiNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Eggs With Example PDFDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Eggs With Example PDFAniruddh JhanwarNo ratings yet
- Embryology-Lecture Notes-I Different Types of Eggs With ExamplesDocument8 pagesEmbryology-Lecture Notes-I Different Types of Eggs With ExamplesWilfordNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 02 Q4Document7 pagesGen Bio 02 Q4Charles EspiloyNo ratings yet
- Insect Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesInsect Reproductive SystemLiezl Bornales ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Plus 2 PracticalDocument16 pagesPlus 2 Practicaljayantaroy783360No ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy and Developmental of Vertebrates - DDocument124 pagesComparative Anatomy and Developmental of Vertebrates - DIzzy ChanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Class 12 NotesDocument45 pagesBIOLOGY Class 12 NotesssshuuushhhNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument30 pagesAnimal KingdomRupa MitraNo ratings yet
- Animal 3Document48 pagesAnimal 3Khairy IestNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantDocument21 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantagrimg80No ratings yet
- Animal 3Document48 pagesAnimal 3Khairy IestNo ratings yet
- Practical I Section Iii: Embryology (1) Egg of InsectDocument6 pagesPractical I Section Iii: Embryology (1) Egg of InsectAfridi ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Structure of GametesDocument4 pagesStructure of Gametesapi-481318101No ratings yet
- Chapter 24Document35 pagesChapter 24Konishko DeyNo ratings yet
- Larval Stages of Trematoda and CestodaDocument41 pagesLarval Stages of Trematoda and CestodaSneha ManjulNo ratings yet
- Animal EvolutionDocument2 pagesAnimal EvolutionAngel LynnNo ratings yet
- Cestodes: Diphyllobothrium Latum, Broad or FishDocument2 pagesCestodes: Diphyllobothrium Latum, Broad or FishFrance Louie JutizNo ratings yet
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDocument9 pagesBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickPunk Midget-FairyNo ratings yet
- Cestode SDocument15 pagesCestode Sali ayanNo ratings yet
- ENTOMOLOGY Chap 3 - 102148Document6 pagesENTOMOLOGY Chap 3 - 102148hainagrace0No ratings yet
- 2nd Week Online Class Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument62 pages2nd Week Online Class Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyHazel Anne Pelin PicañaNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument14 pagesClassificationCook TipsNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes (Flatworms, Tapeworms) : Diversity of Life - AnimalsDocument21 pagesPlatyhelminthes (Flatworms, Tapeworms) : Diversity of Life - AnimalskingNo ratings yet
- MolluscsDocument23 pagesMolluscsNimra NimraNo ratings yet
- Reproductive PhysiologyDocument13 pagesReproductive PhysiologyfacultyfisheriesNo ratings yet
- Jump To Navigationjump To Search: This Article Is About Biological Eggs. For Eggs As Food, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument5 pagesJump To Navigationjump To Search: This Article Is About Biological Eggs. For Eggs As Food, See - For Other Uses, SeeewbNo ratings yet
- AnimaliaDocument68 pagesAnimaliaNovelynLozano-EdrosoNo ratings yet
- Bio All Phylum SummaryDocument7 pagesBio All Phylum SummaryAbhishek yadavNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFDocument23 pagesPlatyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFAbdulla Hil KafiNo ratings yet
- Zoo301lex2 4 Intros Alviar2017Document2 pagesZoo301lex2 4 Intros Alviar2017Mary Rose SantiagoNo ratings yet
- TERMINOLOGIESDocument3 pagesTERMINOLOGIESYsabella PolanaNo ratings yet
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDocument6 pagesBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickMuhammad WildanulhaqNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Mind MapDocument4 pagesAnimal Kingdom Mind MapVedanti Naik100% (1)
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument6 pagesKingdom AnimaliaMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Zoo 116 LecturesDocument64 pagesZoo 116 LecturesIsrael OluwayomiNo ratings yet
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- De La Salle University Manila - OrdDocument2 pagesDe La Salle University Manila - OrdKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Bacolod Lab Activity 1Document8 pagesBacolod Lab Activity 1Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Gradual Resumption of In-Person Classes: Guidelines As of October 15, 2021Document8 pagesGradual Resumption of In-Person Classes: Guidelines As of October 15, 2021Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- 8 Terminologies 2020-1220Document2 pages8 Terminologies 2020-1220Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- 8 Terminologies 2020-1220Document2 pages8 Terminologies 2020-1220Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Notes CompanaDocument10 pagesNotes CompanaKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Species Tab.Document13 pagesSpecies Tab.Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- TaxonDocument7 pagesTaxonKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Unicellular Mostly Flagellated/ciliated Hetero/AutotrophsDocument9 pagesUnicellular Mostly Flagellated/ciliated Hetero/AutotrophsKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Fruit Name Fruit Type Diagnostic Characteristics (Based On The Provided Dichotomous Key)Document1 pageFruit Name Fruit Type Diagnostic Characteristics (Based On The Provided Dichotomous Key)Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Species Tab.Document13 pagesSpecies Tab.Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Species Tab.Document13 pagesSpecies Tab.Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- TaxonDocument7 pagesTaxonKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Saccoglossus Kowalevskyi (Dolichoglossus)Document4 pagesSaccoglossus Kowalevskyi (Dolichoglossus)Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Mds Po 14 FebDocument25 pagesMds Po 14 FebRuliana PatmasariNo ratings yet
- III. Procedure A. Preliminary Activities Teachers Activity A. Prayer Let Us Start Our Day With A Prayer Student ActivityDocument5 pagesIII. Procedure A. Preliminary Activities Teachers Activity A. Prayer Let Us Start Our Day With A Prayer Student ActivityKath PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4: Ans No 1.points To Be Considered While Purchasing FishDocument5 pagesWorksheet 4: Ans No 1.points To Be Considered While Purchasing FishDrHimanshu MalikNo ratings yet
- 2011 Carotenoids in Marine AnimalsDocument16 pages2011 Carotenoids in Marine AnimalsInesNo ratings yet
- IGFA International Angling RulesDocument14 pagesIGFA International Angling RulesDominicNo ratings yet
- Lexico 5 1Document201 pagesLexico 5 1Nguyên Hà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Robot Dolphins Upper IntermediateDocument4 pagesRobot Dolphins Upper IntermediateAngolTeadélutánAdrival0% (1)
- Cookery10 QRTR2 Week5 CoreloDocument9 pagesCookery10 QRTR2 Week5 CoreloArobia ANo ratings yet
- (Wings of Fire 10) Sutherland, Tui T. - Darkness of Dragons (2017, Scholastic Press) - Libgen - LiDocument356 pages(Wings of Fire 10) Sutherland, Tui T. - Darkness of Dragons (2017, Scholastic Press) - Libgen - LiUblingoNo ratings yet
- 07 The Swiss Family Robinson PDFDocument31 pages07 The Swiss Family Robinson PDFLeonardo Reyes Jiménez33% (3)
- Biology and Introduction: TILAPIA in The PhilippinesDocument55 pagesBiology and Introduction: TILAPIA in The PhilippinesKarl Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Assignment cc1 Specialpart2Document17 pagesAssignment cc1 Specialpart2DEVDEEP SIKDARNo ratings yet
- Rmse Storybook 1 g1 0076124584Document228 pagesRmse Storybook 1 g1 0076124584Thasmiya ThasmiyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Progress Test A: GrammarDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Progress Test A: GrammarIzabella Tar100% (3)
- Symbiosis Quiz PDFDocument2 pagesSymbiosis Quiz PDFJerson NidoNo ratings yet
- Tiger Monkey Elephant: Wild AnimalsDocument17 pagesTiger Monkey Elephant: Wild AnimalsAinhoaBjNo ratings yet
- Vargas Et Al. (2018)Document19 pagesVargas Et Al. (2018)Noor Asmiera HasNo ratings yet
- Short Story by Nurzaind PDFDocument9 pagesShort Story by Nurzaind PDFamy lalalaNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic Relationships Worksheet Review: Name - Core - DateDocument3 pagesSymbiotic Relationships Worksheet Review: Name - Core - DateVanessa RamírezNo ratings yet
- Classification & Characteristics of CrustaceaDocument21 pagesClassification & Characteristics of CrustaceaSalma Afreen HussainNo ratings yet
- Report Text 1 - Answer KeyDocument6 pagesReport Text 1 - Answer KeyIzmaya SumiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test, Form 2B: Name DateDocument2 pagesChapter Test, Form 2B: Name DateSamy ElmaseryNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.2 Vertebrates and InvertebratesDocument6 pagesUnit 3.2 Vertebrates and InvertebratesruszitasetapaNo ratings yet
- Identification Guide: Freshwater InvertebrateDocument2 pagesIdentification Guide: Freshwater InvertebrateLuc CardNo ratings yet
- Lessons Grade2 Figurative LanguageDocument32 pagesLessons Grade2 Figurative LanguageDian NurmalaNo ratings yet
- Science 6Document13 pagesScience 6Aris VillancioNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE YEAR 4 (19.05.2021) Vertebrates and Invertebrates: AnimalsDocument2 pagesSCIENCE YEAR 4 (19.05.2021) Vertebrates and Invertebrates: AnimalsAten KenangaNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument43 pagesFigures of SpeechCadeleen de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Fauna and Endangered Wildlife of PakistanDocument5 pagesFauna and Endangered Wildlife of Pakistanmc200200302 MUHAMMAD AWAISNo ratings yet
- THE RULES OF JUDGING RanchuDocument7 pagesTHE RULES OF JUDGING RanchuMarlofel ParaderoNo ratings yet