Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Binder 94
Uploaded by
Khaled AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Binder 94
Uploaded by
Khaled AliCopyright:
Available Formats
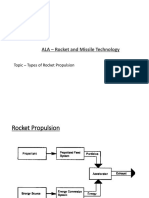
Types :
1. chemical
is defined as chemical propulsion fuel that does not need a separate oxidizer. here,
A fuel can operate alone. where the propellants made up of chemicals which also
release energy within catalyst in an exothermic chemical decomposition process .
2. Bipropellant
The majority of liquid-propellant rockets utilize bi-propellant systems. those with an
oxidizer tank separated from a fuel tank where they mix within combustion chamber.
The system of bipropellants has a minimum molecular weight and massive reaction
temperature outputs (for great exhaustion speed ), large density (for reducing the tank
weight).
3. Cryogenic
rocket motors require elevated mass flow rate of a oxidizers and fuel. Propellers can be
held as pressurized gas, but huge, bulky tanks would cause accomplishment of spaceflight
through orbit to be so difficult. Nevertheless, when the propellants get cooled enough, they
become more compact during the liquid process or under pressure.
Advantages
• Liquid-fueled rockets have higher specific impulse than solid rockets (highest
energy per unit of fuel mass)
• Raw materials, such as oxygen and hydrogen are in abundant supply and a
relatively easy to manufacture
• are capable of being throttled (to control them or in problems), shut down, restarted
Disadvantages
You might also like
- Hybrid RocketDocument6 pagesHybrid RocketAnonymous 0ZP9AmIENo ratings yet
- Materials For Liquid Propulsion SystemsDocument58 pagesMaterials For Liquid Propulsion SystemssazharpakNo ratings yet
- 2010 CH 87Document9 pages2010 CH 87Yasir AzeemNo ratings yet
- Innovative Assignment ON Cryogenics Rocket Engine: Submitted To: Prof. Anand BhattDocument23 pagesInnovative Assignment ON Cryogenics Rocket Engine: Submitted To: Prof. Anand BhattHarsh DholakiyaNo ratings yet
- Rocket Fuel: Propellant Used in RocketDocument4 pagesRocket Fuel: Propellant Used in RocketRajat PangiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Rocket PropulsionDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Rocket PropulsionShailaja UdtewarNo ratings yet
- ALA - Rocket and Missile Technology: Topic - Types of Rocket PropulsionDocument10 pagesALA - Rocket and Missile Technology: Topic - Types of Rocket PropulsionShivam PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Rocket PropellantDocument28 pagesRocket Propellantgautham kumarNo ratings yet
- Liquid Rocket: DisadvantagesDocument1 pageLiquid Rocket: DisadvantagesKhaled AliNo ratings yet
- Chemischemistry Project On Various Rocket Propellants and Their CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesChemischemistry Project On Various Rocket Propellants and Their Characteristicsswarnajit mondalNo ratings yet
- Rocket PropulsionDocument24 pagesRocket PropulsionPreetam BezbaruaNo ratings yet
- Submitted by Dhirendra Singh Roll No-1271940903 ME-3 YearDocument18 pagesSubmitted by Dhirendra Singh Roll No-1271940903 ME-3 YearAmal RajNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Rocket EngineDocument3 pagesCryogenic Rocket EngineAyan Kumar MajiNo ratings yet
- A475217323 22724 28 2018 Unit-6Document32 pagesA475217323 22724 28 2018 Unit-6bunnybond11No ratings yet
- All Cont. TruptiDocument14 pagesAll Cont. TruptiTruptimayee MishraNo ratings yet
- Rocket PropellantDocument19 pagesRocket PropellantsuryaNo ratings yet
- Sunder Deep Engineering College: Seminar PresentationDocument19 pagesSunder Deep Engineering College: Seminar PresentationKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Packed Bed ReactorDocument6 pagesPacked Bed ReactorCik Tiem Ngagiman80% (10)
- Cryogenic Rocket Engine SeminarDocument31 pagesCryogenic Rocket Engine SeminarMahaManthra100% (1)
- Lecture 4 Packed Bed ReactorDocument14 pagesLecture 4 Packed Bed ReactorRobinson ANo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Rocket Engine PropellentsDocument19 pagesCryogenic Rocket Engine PropellentsRavi KiranNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Lec30Document6 pagesUnit-5 Lec30HARSHEEN KOURNo ratings yet
- 05 Rocket Propulsion BasicsDocument5 pages05 Rocket Propulsion BasicsprasannabalajiNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On CRYOGENIC Rocket Engine: Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management, BBSRDocument26 pagesA Seminar On CRYOGENIC Rocket Engine: Gandhi Institute of Technology and Management, BBSRsuchismita swainNo ratings yet
- Solid RocketDocument18 pagesSolid RocketVincent S Ryan100% (7)
- Propulsion SystemDocument17 pagesPropulsion SystemaquilesanchezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Astronautics: Sissejuhatus KosmonautikasseDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Astronautics: Sissejuhatus KosmonautikasserusumagNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Rocket PropulsionDocument38 pagesCryogenic Rocket PropulsionrachelNo ratings yet
- Cryogenics Unit 4Document15 pagesCryogenics Unit 4prasannaNo ratings yet
- Donaldson PaperDocument18 pagesDonaldson PaperShubham BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Design and Modal Analysis of Cryogenic Rocket Propellant TankDocument7 pagesDesign and Modal Analysis of Cryogenic Rocket Propellant TankWe learnNo ratings yet
- Cpi PPT Enrollment No 10 To 13Document32 pagesCpi PPT Enrollment No 10 To 13arshit5dobriyaNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesBatch Reactor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJoy Angeline Arcadio LactuanNo ratings yet
- Types of ReactorsDocument8 pagesTypes of ReactorsAli Ahmad94% (17)
- PBRDocument3 pagesPBRTio PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Cold Gas Rocket: DisadvantagesDocument1 pageCold Gas Rocket: DisadvantagesKhaled AliNo ratings yet
- Rocket Engine: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument34 pagesRocket Engine: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Electric Pump-Fed EngineDocument54 pagesElectric Pump-Fed Engineparthjoshi2023tybscNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactors ClassificationDocument18 pagesNuclear Reactors ClassificationAnonymous ROekWQNo ratings yet
- Unit V Rocket PropulsionDocument17 pagesUnit V Rocket PropulsionMuthuvel M0% (1)
- Cryo Rocket 2 MarkDocument9 pagesCryo Rocket 2 MarkrachelNo ratings yet
- Hybrid RocketsDocument13 pagesHybrid RocketsSASTIKA INo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed Reactor: Basic PrinciplesDocument4 pagesFluidized Bed Reactor: Basic PrinciplesMengist GezehagnNo ratings yet
- RSP - Module 2 - Lect2Document10 pagesRSP - Module 2 - Lect2BETTINANo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1. BackgroundDocument16 pagesChapter One 1.1. Backgroundchisom100% (1)
- Explain The Concept of Fuel Cells.: Advantages Over Conventional Energy SourcesDocument9 pagesExplain The Concept of Fuel Cells.: Advantages Over Conventional Energy SourcesAnusha AnandNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Aviation IndustryDocument17 pagesHydrogen Fuel Cells in Aviation IndustrySonu GopanNo ratings yet
- Rocket PropellantDocument16 pagesRocket PropellantSAI KIRANNo ratings yet
- Astronomy-Sphere of Influence, Mars Mission, OrbitDocument16 pagesAstronomy-Sphere of Influence, Mars Mission, Orbitcrackmains2014No ratings yet
- AE524 Rocket Engine PropulsionDocument26 pagesAE524 Rocket Engine PropulsionAerojet Rocketdyne RS-25No ratings yet
- Modeling of Hydrazine Decomposition For Monopropellant ThrustersDocument18 pagesModeling of Hydrazine Decomposition For Monopropellant ThrustersAlan Lanceloth100% (1)
- Ae6450 f04 Lecture1Document18 pagesAe6450 f04 Lecture1раджеш мунешварNo ratings yet
- Reusable Rocket DesignsDocument9 pagesReusable Rocket Designsruhamahchandekar25No ratings yet
- Spacecraft Propulsion Overview Oct22Document48 pagesSpacecraft Propulsion Overview Oct22grobboNo ratings yet
- Designingliquidrocketengine Injectorsforperformance, Stability, AndcostDocument13 pagesDesigningliquidrocketengine Injectorsforperformance, Stability, AndcostAditya PathakNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM Unit 5Document9 pagesBIOCHEM Unit 5Vignesh KNo ratings yet
- Reactor Sizing:) 9 Lecture (Document10 pagesReactor Sizing:) 9 Lecture (Eko PriyadiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Rocket PropulsionDocument17 pagesChemical Rocket PropulsionArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solid Rocket: OperationDocument1 pageSolid Rocket: OperationKhaled AliNo ratings yet
- Cold Gas Rocket: DisadvantagesDocument1 pageCold Gas Rocket: DisadvantagesKhaled AliNo ratings yet
- Liquid Rocket: DisadvantagesDocument1 pageLiquid Rocket: DisadvantagesKhaled AliNo ratings yet
- Binder 11Document1 pageBinder 11Khaled AliNo ratings yet