Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Activity 2 GLOVA ND2
Laboratory Activity 2 GLOVA ND2
Uploaded by
andreyou99Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Activity 2 GLOVA ND2
Laboratory Activity 2 GLOVA ND2
Uploaded by
andreyou99Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: Andrea Colleen R.
Glova Date Due: September 24, 2021
Year and Section: BSN2 – ND Date Submitted: September 23, 2021
Professor’s Signature: Score:
1. Using a 1,500 caloric requirement, calculate and plan a high carbohydrate
diet allowing 70% to 80% of total caloric requirement for carbohydrates.
Prepare a sample menu for lunch.
Carbohydrates: 1500 kcal x .70 =1050/4kcal = 262.5 g = 263 g
Protein: 1500 kcal x .15= 225/4kcal = 56.25g = 55g
Fat: 1500 kcal x .15= 225/9 kcal= 25g
.: Diet Rx 1500kcal: C 263g P 55g F 25g in high carbohydrate diet.
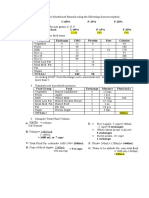
Table 2.1 Meal Plan for a High Carbohydrate Diet
Food No. of CHO PRO FAT ENERGY Meal Distributions
Exchanges Exchanges g g g kcal B L D Sn
I. Veg A 3 9 3 - 48 1 1 1 0
Veg B 1 3 1 - 16 0 0 1 0
II. Fruits 4 40 - - 160 1 1 1 1
III. Milk 1 12 8 10 170 0 0 1 0
IV. Rice 8 184 - - 736 3 2 3 0
V. Meat 5 - 40 5 205 1 3 1 0
VI. Sugar 3 15 - - 60 0 0 1 2
VII. Fat 2 - - 10 90 1 1 0 0
Total 263g 52g 25g 1485 kcal
Table 2.2 Sample Lunch Menu
Meals Household Measure
Tuna ¼ cup
Pasta 1 cup
Potato 2pcs
Garlic 1tsp
Onion 1tsp
Mushroom ¼ cup
Butter 1tbsp
Chicken breast 1 slice
Tomato Sauce ½ cup
Saging lakatan 1 pc
Table 2.3 Worksheet for Carbohydrate-related Diseases
Diseases Symptoms Causes Prevalence Dietary Changes
Obesity Over eating, High carbohydrate Overall, about 13% Establish daily
gaining weight foods promote of the world's adult meal and snack
satiety in the short population (11% of times, and eating
term. As fat is men and 15% of together as
stored more women) were frequently as
efficiently than obese in 2016. The possible. Make a
excess worldwide wide variety of
carbohydrate, use prevalence of healthful foods
of high obesity nearly available based on
carbohydrate foods tripled between the Food Guide
is likely to reduce 1975 and 2016 Pyramid for Young
the risk of obesity Children.
in the long term. Determine what
Much controversy food is offered and
surrounds the when, and let the
extent to which child decide
sugars and starch whether and how
promote obesity. much to eat.
Dental caries Tooth aches, Foods containing The overall Eat a variety of
cavities sugars or starch prevalence of foods from each of
may be easily dental caries in the five major food
broken down by a- primary and groups, including:
amylase and permanent teeth whole grains.
bacteria in the was almost 73% fruits.
mouth and can (n=711). Among vegetables.
produce acid which the 6-9-year-old, lean sources of
increases the risk the prevalence of protein such as lean
of caries. Starches caries was beef, skinless
with a high approximately 78% poultry and fish;
glycemic index (n=397) whereas, dry beans, peas and
produce more among the 10-12- other legumes.
pronounced year-old children, it low-fat and fat-free
changes in plaque was approximately dairy foods.
pH than low 68% (n=314).
glycemic index
starch, especially
when combined
with sugars
Easily thirsty and If you overdo the The global As for the general
Diabetes Miletus hungry, frequent carbs, your blood prevalence of population, people
urination sugar levels can get diabetes increased with diabetes are
too high. This from 211.2 million encouraged to
causes your body (196.0–228.5) in choose a variety of
to make more 1990 to 476.0 fiber-containing
insulin, which tells million (436.6– foods such as
your cells to save 522.8) in 2017, legumes, fiber-rich
the extra glucose as with a 129.7% cereals (≥5 g
fat. That can be increase fiber/serving),
unhealthy if you're fruits, vegetables,
already carrying a and whole grain
few extra pounds. products because
It can lead to they provide
diabetes and other vitamins, minerals,
related health and other
issues. substances
important for good
health.
1. What is the importance of the following to the body?
a. Insoluble Fibers
Insoluble fiber attracts water into your stool, making it softer and easier to
pass with less strain on your bowel. Insoluble fiber can help promote bowel
health and regularity. It also supports insulin sensitivity, and, like soluble
fiber, may help reduce your risk for diabetes.
b. Soluble Fibers
Soluble fiber attracts water and forms a gel-like substance with food as it's
digested. This in turn slows down digestion and helps you feel full faster,
which is important in weight management. It may also help lower your risk
of heart disease, regulate your blood sugar, and help reduce LDL
cholesterol.
2. What is ketosis?
Ketosis is a process that happens when your body doesn't have enough
carbohydrates to burn for energy. Instead, it burns fat and makes things called
ketones, which it can use for fuel. Ketosis is a word you'll probably see when
you're looking for information on diabetes or weight loss. Ketosis may be
beneficial for some people, but you should ask your doctor before switching to
a very low carb diet, in case it's not suitable for you. Ketosis is safe for most
people. However, some people may experience side effects, including bad
breath, headaches, and constipation.
3. What are the harmful effects of excessive fiber intake.
Too much fiber in the diet can cause bloating, gas, and constipation. A person
can relieve this discomfort by increasing their fluid intake, exercising, and
making dietary changes. These uncomfortable side effects of excessive fiber
can occur when someone eats more than 70 grams (g) of fiber a day.
4. How does the body make glucose from protein?
The liver supplies sugar or glucose by turning glycogen into glucose in a
process called glycogenolysis. When your body doesn't have enough
carbohydrate on hand, it will turn to protein and fat to make glucose. This
reaction happens in the liver instead of the digestive tract. Your body breaks
down the proteins, fats and enzymes it has to make glucose in a process
called "gluconeogenesis," or the making of new sugar. The down side to
gluconeogenesis is that your body will either tear down existing muscles to
make what it needs or it will use the proteins in your food, which will prevent
those proteins from helping you make new muscles and repair tissue damage.
You might also like
- Nutri Lab Activity 2 Macronutrients With DraftDocument6 pagesNutri Lab Activity 2 Macronutrients With DraftBeth78% (9)
- NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 8 Macronutrients - FatsDocument6 pagesNCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 8 Macronutrients - Fatsann campos67% (3)
- Week 10.IMCI Case Study - BenDocument6 pagesWeek 10.IMCI Case Study - BenGeorgia Shayne CubeloNo ratings yet
- Beginner's Guide To Healthy Keto™ - Intermittent Fasting PrintDocument28 pagesBeginner's Guide To Healthy Keto™ - Intermittent Fasting PrintRewat Sachdeva100% (1)
- Exercise - 6 - NCM-105A Group 1 2FDocument4 pagesExercise - 6 - NCM-105A Group 1 2FRALPH ELVIN MACANLALAYNo ratings yet
- Fat - and Water-Soluble Vitamins: NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy LaboratoryDocument4 pagesFat - and Water-Soluble Vitamins: NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy LaboratoryKryzza Leizell100% (1)
- Nutrition in The Life Cycle: NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy LaboratoryDocument3 pagesNutrition in The Life Cycle: NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy LaboratoryKryzza Leizell50% (2)
- NCM 105 - Lab Activity # 3 - Macronutrients: CarbohydrateDocument10 pagesNCM 105 - Lab Activity # 3 - Macronutrients: CarbohydrateclrssNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity #5 Soft and Mechanical DietDocument3 pagesLaboratory Activity #5 Soft and Mechanical DietBern NerquitNo ratings yet
- Henry D. Solatorio Jr. NCM 105: Promote Good Blood Sugar (Glucose) LevelsDocument2 pagesHenry D. Solatorio Jr. NCM 105: Promote Good Blood Sugar (Glucose) LevelsCristoper BodionganNo ratings yet
- Nepomuceno, Claudette May B. BSN 2Y0 - 1 Ncma215Laboratory Course Task 6 Week 3Document3 pagesNepomuceno, Claudette May B. BSN 2Y0 - 1 Ncma215Laboratory Course Task 6 Week 3CLAUDETTE MAY NEPOMUCENONo ratings yet
- Nutrition (Diets Modified For Consistency)Document1 pageNutrition (Diets Modified For Consistency)Algen UbasaNo ratings yet
- 40g CHO 225cals 5g CHO 60calsDocument3 pages40g CHO 225cals 5g CHO 60calsBOBO GamingNo ratings yet
- Graziella Beatriz A. Cabuyadao BSN 2-B Nutrition and Diet Therapy Laboratory Activity No. 5 Nutrition Across LifespanDocument11 pagesGraziella Beatriz A. Cabuyadao BSN 2-B Nutrition and Diet Therapy Laboratory Activity No. 5 Nutrition Across LifespanBeverly CabuyadaoNo ratings yet
- Diets Modified in CompositionDocument10 pagesDiets Modified in CompositionDiane Angela67% (3)
- Longevity enDocument11 pagesLongevity enHaiNguyen100% (1)
- Activity # 7 (Part 1) - Santos, Aira Kristelle MDocument11 pagesActivity # 7 (Part 1) - Santos, Aira Kristelle MAi Mendoza100% (1)
- Procedure: Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesProcedure: Case Analysisandreyou99No ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Macronutrients - CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesExercise 1 Macronutrients - CarbohydratesBabs tvNo ratings yet
- Activity 10: Nutrition in The Life Cycle: Group 2Document7 pagesActivity 10: Nutrition in The Life Cycle: Group 2Ma. Lyn ArandiaNo ratings yet
- 2 DBW 7kg: Group 3-InfancyDocument2 pages2 DBW 7kg: Group 3-InfancyYzobel Phoebe ParoanNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - FILIPINO CULTURE, VALUES AND PRACTICES IN RELATION TO MATERNAL AND CHILD CAREDocument4 pagesModule 6 - FILIPINO CULTURE, VALUES AND PRACTICES IN RELATION TO MATERNAL AND CHILD CAREKatie Holmes0% (1)
- Fat-And Water-Soluble VitaminsDocument9 pagesFat-And Water-Soluble VitaminsJessa Mae OhaoNo ratings yet
- Table 4.2 and 4.3 q1Document4 pagesTable 4.2 and 4.3 q1JOVEMEA LIRAYNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients Lab ActivitiesDocument10 pagesMacronutrients Lab ActivitiesJeson Vien GuerraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Carbohydrate-Related Diseases1Document7 pagesWorksheet Carbohydrate-Related Diseases1Daniel Angelo Arango100% (1)
- BSN 2 4 GRP II Ndtlec WRDocument22 pagesBSN 2 4 GRP II Ndtlec WRChristine AnneNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 - Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Activity No. 4 Meal Planning For Macronutrient ObjectivesDocument3 pagesNCM 105 - Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Activity No. 4 Meal Planning For Macronutrient ObjectivesMary Charlotte PableoNo ratings yet
- Benbenen, Nichole Boguilis, Nikki Joi Carlos, Nathalia Salasibar, Trixie Ann Ubina, Sheila JoyDocument7 pagesBenbenen, Nichole Boguilis, Nikki Joi Carlos, Nathalia Salasibar, Trixie Ann Ubina, Sheila Joyann camposNo ratings yet
- Diet Modification and Diet TherapyDocument76 pagesDiet Modification and Diet TherapyFatima Ysabelle Marie RuizNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Feeding and Lactating WomenDocument2 pagesExercise On Feeding and Lactating WomenDenise Marienne MendezNo ratings yet
- NutridietDocument24 pagesNutridietDerick Nyl PascualNo ratings yet
- Bsn2c Dalipe de Los Reyes NDT Lab Activity Dietary ModificationsDocument2 pagesBsn2c Dalipe de Los Reyes NDT Lab Activity Dietary ModificationsXeyanNo ratings yet
- The Regular DietDocument16 pagesThe Regular Dietmarsan12100% (1)
- NCM 105 NutritionDocument28 pagesNCM 105 NutritionCyrill100% (2)
- Sammple Compute With Menu Plan OneDocument2 pagesSammple Compute With Menu Plan OnerhomaaanotesNo ratings yet
- Case Study Physiologic Changes in pregnancy-BALLON, KARLO C.Document3 pagesCase Study Physiologic Changes in pregnancy-BALLON, KARLO C.Melinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Nutrition & Diet Therapy (Laboratory) : Evaluation 4Document6 pagesNutrition & Diet Therapy (Laboratory) : Evaluation 4janina myka100% (1)
- FEL - Sample Computation and MenuDocument43 pagesFEL - Sample Computation and MenuKate Angelique RodriguezNo ratings yet
- NCM Lab Health & Illness and Diet Therapy DiscussDocument59 pagesNCM Lab Health & Illness and Diet Therapy DiscussPattNo ratings yet
- Meal PlanDocument3 pagesMeal PlanAJ Bay100% (1)
- Macronutrients-Carbohydrates: NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy Laborator YDocument3 pagesMacronutrients-Carbohydrates: NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy Laborator YArriane Desepeda100% (1)
- Procreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableDocument11 pagesProcreative Health Is The Moral Obligation of Parents To Have The Healthiest Children Through All Natural and Artificial Means AvailableFrankie Macabada0% (2)
- Exercise No.2 Macronutrients-Carbohydrates ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExercise No.2 Macronutrients-Carbohydrates ObjectivesKenji Tolero0% (1)
- Health Teaching For PregnancyDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching For PregnancyAustin Escobar100% (1)
- Rice Is A Good Source of Calories, Carbs, Calcium, Iron, Thiamin, Pantothenic Acid, Folate, and Vitamin E, To Name A Few NutrientsDocument2 pagesRice Is A Good Source of Calories, Carbs, Calcium, Iron, Thiamin, Pantothenic Acid, Folate, and Vitamin E, To Name A Few Nutrientsmikhaela sencilNo ratings yet
- Journal Analysis-BALLON, Karlo CDocument4 pagesJournal Analysis-BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Perdido - ACTIVITY 3 NUTRI 1Document2 pagesPerdido - ACTIVITY 3 NUTRI 1Kariza PerdidoNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother, Child and Adolescent (Well Client) Related Learning ExperienceDocument7 pagesCare of The Mother, Child and Adolescent (Well Client) Related Learning ExperienceIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyMARWA MAMONGCALNo ratings yet
- Patient History-BALLON, KARLO C.Document5 pagesPatient History-BALLON, KARLO C.Melinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Vincent M. MaterialDocument5 pagesVincent M. MaterialVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Correlate Lifelong Learning To Studying Nutrition and Diet Therapy - HILARIODocument1 pageCorrelate Lifelong Learning To Studying Nutrition and Diet Therapy - HILARIOHilario Andrea100% (1)
- Sample Meal PlanningDocument6 pagesSample Meal PlanningSherrie Mae RoncalNo ratings yet
- School Age NCPDocument6 pagesSchool Age NCPNikki Coleen SantinNo ratings yet
- Diets Modified in ConsistencyDocument8 pagesDiets Modified in ConsistencyMartin Mitchelle Capistrano Monsod100% (1)
- Qualities and Responsibility of A Good Health Care ProviderDocument2 pagesQualities and Responsibility of A Good Health Care ProviderJan Dannielle Salazar60% (5)
- Worksheet For Vitamin-Related Diseases - ArangoDocument7 pagesWorksheet For Vitamin-Related Diseases - ArangoDaniel Angelo Arango100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Long TermDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Long TermSofia CartallaNo ratings yet
- Elderhood: Jerry Mae Chiong Joliza Lancara Dianne Kay Fernandez Rhea Joy GolenaDocument50 pagesElderhood: Jerry Mae Chiong Joliza Lancara Dianne Kay Fernandez Rhea Joy GolenaRj Santiago0% (1)
- Meal Planning For A College Student: Saint Louis University School of NursingDocument7 pagesMeal Planning For A College Student: Saint Louis University School of NursingMaranatha BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- TEST 1. Compare and Contrast The FFDocument3 pagesTEST 1. Compare and Contrast The FFChristian VillaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 ENTREPRENEURIAL MIND - EditedDocument7 pagesMODULE 4 ENTREPRENEURIAL MIND - Editedandreyou99No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Surgical GroupDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Surgical Groupandreyou99No ratings yet
- Analytic Geo 1 Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesAnalytic Geo 1 Practice Problemsandreyou99No ratings yet
- Integral Calculus 1 Rev 4Document32 pagesIntegral Calculus 1 Rev 4andreyou99No ratings yet
- MATHDocument30 pagesMATHandreyou99No ratings yet
- ALGEBRA 2 - Feb2022Document39 pagesALGEBRA 2 - Feb2022andreyou99No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No 2 - GLOVA-NDDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity No 2 - GLOVA-NDandreyou99No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No 1 (GlovaND)Document2 pagesLaboratory Activity No 1 (GlovaND)andreyou99No ratings yet
- Procedure: Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesProcedure: Case Analysisandreyou99No ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesLecture Notesandreyou99No ratings yet
- ME Laws Report 1Document41 pagesME Laws Report 1andreyou99No ratings yet
- Kirby Multiplication, DivisionDocument20 pagesKirby Multiplication, Divisionandreyou99No ratings yet
- Numerical Study of Refrigerant Flow in Capillary Tube Using Refrigerant (R134a)Document20 pagesNumerical Study of Refrigerant Flow in Capillary Tube Using Refrigerant (R134a)andreyou99No ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument1 pageNarrative Reportandreyou99No ratings yet
- Jonlo N. Aguilar Engr. Shahani L. Truza Bsme 5A M1 Safety Engineering For MeDocument3 pagesJonlo N. Aguilar Engr. Shahani L. Truza Bsme 5A M1 Safety Engineering For Meandreyou99No ratings yet
- OldDocument1 pageOldandreyou99No ratings yet
- 21 Days KetoDocument49 pages21 Days KetoIsmail Magh100% (4)
- Diet Cures More Than DoctorsDocument7 pagesDiet Cures More Than DoctorsRupali MohantyNo ratings yet
- Ben Bikman Extended Show NotesDocument6 pagesBen Bikman Extended Show NotesMonty GuildNo ratings yet
- Cetoacidosis Diabética y Estado Hiperosmolar.Document25 pagesCetoacidosis Diabética y Estado Hiperosmolar.Eduardo HernándezNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition-Related Diabetes Mellitus in Africa: PrevalenceDocument7 pagesMalnutrition-Related Diabetes Mellitus in Africa: PrevalenceAbdi KebedeNo ratings yet
- Benefits of KetosisDocument3 pagesBenefits of KetosisHumanyu KabeerNo ratings yet
- The Ketogenic Diet For Bodybuilders and Physique Athletes: Address Correspondence To Adam TzurDocument8 pagesThe Ketogenic Diet For Bodybuilders and Physique Athletes: Address Correspondence To Adam TzurBeni BolngNo ratings yet
- Stokerchapter25lipidmetabolism 160320032037Document29 pagesStokerchapter25lipidmetabolism 160320032037Dawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- Fastosis FAQ EDocument30 pagesFastosis FAQ ESeno TribrotoNo ratings yet
- Simple KetoDocument30 pagesSimple KetoMohamed Magdy100% (8)
- Homoeopathic MCQ Book For Upsc and MD 9788131932575Document26 pagesHomoeopathic MCQ Book For Upsc and MD 9788131932575NIYAS TTNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP HỌC KÌ 1-LỚP 12Document15 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP HỌC KÌ 1-LỚP 12Anh Duc VuNo ratings yet
- HypoglycemiaDocument34 pagesHypoglycemiaPrince Mendel100% (1)
- M.D - Oxidation of FAs & Ketone BodiesDocument48 pagesM.D - Oxidation of FAs & Ketone BodiesAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Hiperosmolar Non KetotikDocument24 pagesHiperosmolar Non KetotikMunawwar AweNo ratings yet
- Good Housekeeping - Easy KetoDocument98 pagesGood Housekeeping - Easy KetoStefan HNo ratings yet
- 105 Meal PlanDocument4 pages105 Meal PlanAisha MarieNo ratings yet
- Kisi Bing (Aat)Document22 pagesKisi Bing (Aat)Swesty ParamithaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Treatment GuidelinesDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) : Treatment GuidelinesArjun RaNo ratings yet
- Custom Keto EbookDocument7 pagesCustom Keto EbookSamNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI HSG 2021 2022 - 18Document8 pagesĐỀ THI HSG 2021 2022 - 18Anxiously SquidNo ratings yet
- What Is GKI, Glucose Ketone Index Calculate It KETO-MOJODocument1 pageWhat Is GKI, Glucose Ketone Index Calculate It KETO-MOJOsbtxbprm29No ratings yet
- 4 Metabolic Disorders Related To Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument18 pages4 Metabolic Disorders Related To Carbohydrate Metabolismsaxawan100% (3)
- Keto-Diet Starter GuideDocument8 pagesKeto-Diet Starter GuideEmmanuel Cabello67% (3)
- CB - Unit4 - Regulation of Lipid Metabolism and Ketone BodiesDocument27 pagesCB - Unit4 - Regulation of Lipid Metabolism and Ketone BodiesBoomi BoomiNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Ketone BodiesDocument22 pagesMetabolism of Ketone BodiesUbaid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Keto Built - Josh BryantDocument37 pagesKeto Built - Josh Bryantaaa100% (1)
- The Truth About Low-Carb DietsDocument6 pagesThe Truth About Low-Carb DietsMy SơnNo ratings yet