Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uts Physical Self
Uploaded by
Shane Razal IIOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uts Physical Self
Uploaded by
Shane Razal IICopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Self
- Physical self is the concrete dimension, the tangible aspect of the person that can be directly
observed and examined.
- Sexual Intercourse
Male – Testes – Sperm Cell
Conception: Zygote – product of that unite.
Female – Ovary – Egg Cell
Importance of Conception:
1. Gender determination
2. No. of off springs
Twins:
o IDENTICAL (Monozygotic) 1 egg cell and same gender
o NON – IDENTICAL (Dizygotic) 2 egg cell and different gender
Stages of development:
1. Pre – natal (Conception of 9 months)
a. Germinal: Cell division
b. Embryonic: Facial features, Arms and Legs, Vital organs and not yet fully develop.
3 petals c. Fetal: Completion of the body parts.
2. Babyhood (2 week – 2 yrs.)
- Age of rapid growth and development
Physical changes
Psychomotor skills (Basic movements)
3. Puberty (10 – 13 yrs.)
- Primary sexual characteristics (testes and ovary)
wet dreams
menarche
- Secondary sexual characteristics
o Male – development of muscles, adams apple, pubic hair, voice and shoulder.
o Female – development of breast, pubic hair, voice and hips.
Stimulus (elicits) means reaction
Stimulus – reaction
Neural impulse – reaction
Transduction – process
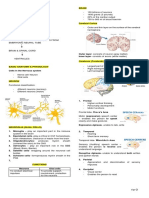
Neurons
- Basic unit
- Specialized brain cell with 2 extensions:
1. Receiving
2. Transmit
- Synaptic way (ring if neurons)
- Process of passing info. from 1 neuron to another neuron.
Three (3) kinds of neurons:
1. Sensory – senses “receivers”
Five (5) Senses:
1. Sight
2. Taste
3. Smell
4. Touch
5. Hearing
2. Motor – muscles “reactors”
3. Inter – connects to the sensory and motor neurons.
SENSE – ORGAN – STIMULUS
Sight – Eyes – Light
Taste – Tounge – Taste
Smell – Nose – Odor
Touch – Skin – Warm, Pressure, Cold, Pain
Hearing – Ears – Sound
Schizophrenia – Hallucination (reacting without a stimulus)
Multiple Self vs Unified Self
Three (3) domains of the self
1. Experiential Self Five (5) Senses acquires information from the environment.
- Theater of consiousness
- Tied closely to memory Value information
- Disappears when deep sleep.
2. Private Self
Nurture
- “narrator” or “interpreter”
- Verbally narrates what is happening Perception – interprets of info.
gathering by senses.
3. Public Self or Persona
- Public image (other people see about us)
- Interacts with other people
Real Self vs. Ideal Self
Real Self
- Who we actually are.
- It is how we think, feel, and act
- Observable to others
- Self-image
Ideal Self
- How we want to be
- Based on experience
- Learning
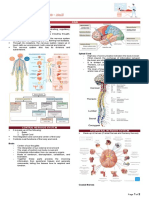
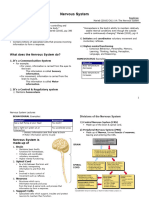
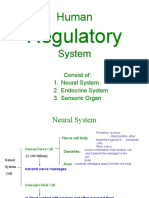
NERVOUS SYSTEM
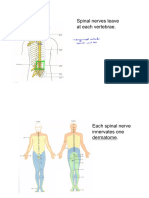
Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
- Nerves, glands &smooth muscles
Brain Spinal Cord - Somatic Nervous System
- 3 lbs. - Connects the Central N.S and Peripheral N.S - Sensor receiver
- Pinkish - Highway to the brain - Motor reactor
white - Autonomic Nervous System
Fore Brain - Sympathetic Nervous System
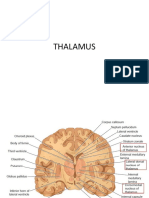
- Thalamus - Active during stressful situations
relay station of sensory experiences - Parasympathetic
- Hypothalamus - Active after stressful situations
Emotion
- Cerebrum
outer covering of the brain
Mid Brain
- reticular activating system level of arousal Four (4) Lobes Thinking:
and consciousness. 1. Frontal – higher mental function
Hind Brain 2. Parietal – thinking, touch
- Pons 3. Temporal – hearing (communication)
chemicals of sleep 4. Occipital – vision
- Cerebellum
balance & muscle coordination Two (2) Fissures:
- Medulla 1. Fissures of Rolando
2. Fissures of Sylvius
Vital reflexes
You might also like
- Intro To Psychology ReviewerDocument10 pagesIntro To Psychology ReviewermlpdmarasiganNo ratings yet
- Psychology 101 Flashcards - QuizletDocument32 pagesPsychology 101 Flashcards - QuizletDieter LudwigNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Reviewer: © Angelica GarciaDocument14 pagesPersonal Development Reviewer: © Angelica GarciaFat AjummaNo ratings yet
- Functions of the Nervous System in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesFunctions of the Nervous System in 40 CharactersXandra BasnilloNo ratings yet
- Biology Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesBiology Nervous SystemFatima PueblaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive PsychologyDocument5 pagesCognitive Psychologymain.22001454No ratings yet
- 2 Human Body Nervous System - PPT Grade12 Ch29 Lesson 2Document24 pages2 Human Body Nervous System - PPT Grade12 Ch29 Lesson 2kheloudmamdouhNo ratings yet
- The Brain: Key Terms-DefinitionsDocument12 pagesThe Brain: Key Terms-DefinitionsPem TNo ratings yet
- 2 Human Body Nervous SystemDocument24 pages2 Human Body Nervous SystemRain HuntsdaleNo ratings yet
- Psych 100 Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument3 pagesPsych 100 Physiological Basis of BehaviorEissel PaparonNo ratings yet
- 2 Human Body Nervous SystemDocument24 pages2 Human Body Nervous Systemanupama_rani_2No ratings yet
- The Nervous System (Notes)Document3 pagesThe Nervous System (Notes)Trisha LaidenNo ratings yet
- LP4 - Powers of The Mind - ABSORBDocument16 pagesLP4 - Powers of The Mind - ABSORBajNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Skull Cerebrospinal FluidDocument1 pageNervous System: Skull Cerebrospinal FluidVincent Franciz T. FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Nervous System Group 1Document45 pagesThe Human Body Nervous System Group 1Bai Nornica Abutazil UttoNo ratings yet
- 6j8s0 E0gbcDocument10 pages6j8s0 E0gbcBarbora BujdošováNo ratings yet
- Nervous System1Document76 pagesNervous System1ahmed jeylaaniNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Unit - 3Document26 pagesNervous System Unit - 3anupama_rani_2No ratings yet
- Nervous System Kel 4Document10 pagesNervous System Kel 4Talitha FatihahNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System Functions and StructuresDocument9 pagesNeurologic System Functions and StructuresBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- The Brain: Structure, Parts, and FunctionsDocument2 pagesThe Brain: Structure, Parts, and FunctionsJemimah Tostos GonzaloNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - 12. Integration of Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesModule 4 - 12. Integration of Nervous Systemjieannfaith.ausmolo-20No ratings yet
- Psychology I - Unit IIIDocument22 pagesPsychology I - Unit IIIMark DarketNo ratings yet
- 8B Coordination in Animals and Plants 8B Checkpoint: 8B.1 The Central Nervous SystemDocument8 pages8B Coordination in Animals and Plants 8B Checkpoint: 8B.1 The Central Nervous SystemsalmaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 3Document2 pagesReviewer 3blessiejamNo ratings yet
- Perdev The BrainDocument4 pagesPerdev The BrainJL BautistaNo ratings yet
- Science LT ReviewerDocument19 pagesScience LT ReviewerRayjohn Raphael OflariaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER Neurological SystemDocument5 pagesREVIEWER Neurological SystemKeren GaciasNo ratings yet
- Neuro Week 1Document6 pagesNeuro Week 1Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- 03 Nervous System BDocument41 pages03 Nervous System BBalew KassieNo ratings yet
- Control & Coordination: The Nervous SystemDocument45 pagesControl & Coordination: The Nervous SystemSanket JainNo ratings yet
- Sight Smell Taste: Unit 2 InteractionDocument3 pagesSight Smell Taste: Unit 2 InteractionmarcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesChapter 8: Nervous SystemAndrea BoocNo ratings yet
- Midterm #1 Neuro Anatomy and Physiology ReviewDocument15 pagesMidterm #1 Neuro Anatomy and Physiology ReviewMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Biology of MindCindy AvendanoNo ratings yet
- Neuro HandoutDocument13 pagesNeuro HandoutFatima Shaira PulahongNo ratings yet
- Pain (Pain and Surgery Notes)Document2 pagesPain (Pain and Surgery Notes)Adiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Anatomy and FunctionsDocument4 pagesNervous System Anatomy and FunctionsIrish Buaya Gementiza100% (1)
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Neuroanatomy &Document26 pagesCentral Nervous System (CNS) Neuroanatomy &Asaad JawedNo ratings yet
- Neurobiological Basis of PsychologyDocument62 pagesNeurobiological Basis of PsychologyJovelyn Morales JosolNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology: The Nervous System ExplainedDocument29 pagesHuman Physiology: The Nervous System Explainedzandrex delunaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Anatomy and Physiology226Document13 pagesPresentation of Anatomy and Physiology226owenspros5No ratings yet
- PY40 - BIO - GROUP3The Somatic Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesPY40 - BIO - GROUP3The Somatic Nervous SystemAdéọlá OnasanyaNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument46 pagesBrainSantosh DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Quarter 3 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Science Quarter 3 Reviewerselfie princessNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesNervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure and Function Explained in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesBrain Structure and Function Explained in 40 CharactersPem TNo ratings yet
- Interaction - The Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesInteraction - The Nervous SystemhelenafuertestoranNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Structure and Function of the Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesUnderstanding the Structure and Function of the Nervous SystemFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- General Psychology NotesDocument11 pagesGeneral Psychology NotesRei RinNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System - Lec 1Document6 pagesNeurologic System - Lec 1Farmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2Document23 pagesNervous System 2TinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Pre ReadingDocument9 pagesNervous System Pre Readingluseanepapani1No ratings yet
- Module 2: Biology and PsychologyDocument23 pagesModule 2: Biology and Psychologyshain aldovinoNo ratings yet
- Human Regulatory SystemDocument37 pagesHuman Regulatory SystemRudolfNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy Function Handout 2023Document3 pagesBrain Anatomy Function Handout 2023xtralargee.mbaNo ratings yet
- Itp ReviewerDocument24 pagesItp ReviewerNicole GarduqueNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document8 pagesModule 1laaraybmehmood1503No ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy and Function Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesBrain Anatomy and Function Cheat SheetminaNo ratings yet
- Neurology TractsDocument7 pagesNeurology TractsMuhammad HaneefNo ratings yet
- Brain & Organ FunctionsDocument5 pagesBrain & Organ FunctionsaysiiNo ratings yet
- 131central Nervous SystemDocument37 pages131central Nervous SystemXharisz DulinNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Nyeri 1Document10 pagesJurnal Nyeri 1Elly SufriadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Coordination and ControlDocument22 pagesChapter 12 Coordination and ControlXaundrae McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and 2 OverviewDocument28 pagesNeurofibromatosis Type 1 and 2 OverviewJino Onij BolandoNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Neuro Physiology and Anatomy Notes by DR of 2027-28Document91 pagesOsmosis Neuro Physiology and Anatomy Notes by DR of 2027-28tariq ullahNo ratings yet
- Psychology 5th Edition Ciccarelli Test BankDocument13 pagesPsychology 5th Edition Ciccarelli Test Bankkathetal.karn.gmasw100% (20)
- Organ Systems Working TogetherDocument6 pagesOrgan Systems Working TogetherGeoffrey Tolentino-Unida100% (1)
- Chiari CaseDocument27 pagesChiari CaseShaurya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Tutorilas On Ascending Tracts of The Spinal CordDocument7 pagesTutorilas On Ascending Tracts of The Spinal CordanojanNo ratings yet
- 3.bpt 1213 PDFDocument110 pages3.bpt 1213 PDFSafeer MNo ratings yet
- Basalganglia 160304172613 PDFDocument49 pagesBasalganglia 160304172613 PDFamna rashidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Coordination and ResponseDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Coordination and ResponseMastura Muhamad MuktarNo ratings yet
- ThalamusDocument30 pagesThalamusRho Vince Caño Malagueño100% (1)
- Brain Microelectrode Array Systems MITDocument114 pagesBrain Microelectrode Array Systems MITSri JunkNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus WPS OfficeDocument16 pagesHydrocephalus WPS OfficeOeyi Mutia SatifaNo ratings yet
- OV - Basic Anatomy and FunctionDocument25 pagesOV - Basic Anatomy and FunctionhpmonkeyzNo ratings yet
- Neurological Nursing Exam.Document3 pagesNeurological Nursing Exam.Jagveer ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument1 pageCentral Nervous Systemlez2No ratings yet
- Science g10 LM q3Document131 pagesScience g10 LM q3Seiza MwaNo ratings yet
- Experience Psychology 3rd Edition King Test BankDocument36 pagesExperience Psychology 3rd Edition King Test BankAlexandriaBarajasrnaxb100% (14)
- Ebook Ebook PDF Principles of Human Physiology 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Principles of Human Physiology 6th Edition PDFdonita.nichols650100% (34)
- Woreta Health Science and Business College Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument55 pagesWoreta Health Science and Business College Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- BASIC PHYSIOLOGY For ANESTHETISTSDocument468 pagesBASIC PHYSIOLOGY For ANESTHETISTSAris ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of Behavior AP Psych ChapterDocument18 pagesBiological Bases of Behavior AP Psych ChapterSulphia IqbalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument6 pagesNervous System WorksheetSteve MacarioNo ratings yet
- HSC 430 - Lesson Plan Underage DrinkingDocument11 pagesHSC 430 - Lesson Plan Underage Drinkingapi-487139726No ratings yet
- Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Overview of Neural SignalingDocument2 pagesMedical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Overview of Neural SignalingOmar AlemánNo ratings yet
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Daniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisFrom EverandDaniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (130)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- The Stress-Proof Brain: Master Your Emotional Response to Stress Using Mindfulness and NeuroplasticityFrom EverandThe Stress-Proof Brain: Master Your Emotional Response to Stress Using Mindfulness and NeuroplasticityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (109)
- Nonviolent Communication by Marshall B. Rosenberg - Book Summary: A Language of LifeFrom EverandNonviolent Communication by Marshall B. Rosenberg - Book Summary: A Language of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (50)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Hearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIFrom EverandHearts of Darkness: Serial Killers, The Behavioral Science Unit, and My Life as a Woman in the FBIRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)