Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer 3
Uploaded by
blessiejam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views2 pagesReviewer 3
Uploaded by
blessiejamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY LAB Synapses – where axon attach to a muscle
gland, organ or other neurons.
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Division of Nervous system Neuronal Pathways
o Converging pathways – two or more
1.Central Nervous System - brain and spinal neurons converge on the same
cord neurons.
2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves ( 12 o Diverging Pathways – Axon from one
cranial nerves, spinal nerves 31 spinal cord) neurons divides and synapse more than
on neuron.
Somatic Nervous Sytem ( Voluntary) – Neurotransmitter
impulses to skeletal muscles
Autonomic Nervou system ( Involuntary ) Spinal Cord (pls seeyour modules) – extends
– impulses to smooth muscle , cardiac from foramen magnum to 2nd lumbar vertebra
muscles. White matter divides into 3 columns
DORSAL, VENTRAL, LATERAL
Sympathetic Division Gray matter
Posterior Dorsal Horns – contains axons which
synapse with interneurons
Parasympathetic division Anterior (Ventral) Horns – contains somatic
(motor) neurons.
Enteric Nervous system – chemical changes in
gatrontestinal tract as well as stretching. SPINAL NERVE- Peripheral Nerve exiting from
spinal cord.
Cells of NVS 3 plexus - Cervicalplexus, Brachial plexus,
1. Neurons Lumbosacral Plexus
3 parts of Neurons
Cell body – has single nucleus Brain
Dendrites – receive information Branstem consist of
Axon – action potential AWAY from PONS
CNS MEDULLA OBLONGATA
Types of Neurons MIDBRAIN ( 2 INFERIOR CULLICULI – center
Multipolar Neuron - many for auditory nere pathways in CNS , 2 SUPERIOR
dendrites ,1 axon CULICULI – Visual reflexes and receive touch
Bipolar Neuron – 1 dendrite ,1 /auditory input.
axon
Psedo- unipolar – one single CEREBELLUM – Provide communication
process between cerebellum and other parts of CNS.
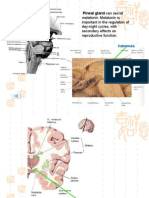
2. Glial cells – supportive cells of the CNS and DIENCEPHALON
PNS, cells do not conduct action. 3 Main Components
3. Astrocyte – major supporting cells in CNS o THALAMUS - Relay sensory
3. Ependymal cells – immune cells in CNS. information.
4. Oligodendrocytes – insulating material that o EPITHALAMUS – Penial gland
surrounds axon. influence onset on puberty.
5. Myelin Sheath – wrap around the axon o HYPOTHALAMUS – maintain
6. Nodes of Ranvier – Gaps in myelin sheath. homeostasis.
Third ventricles
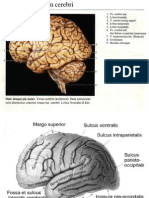
CEREBRUM – largest part. Fourth ventricles
4 LOBES Cerebral aqueduct
FRONTAL LOBE- voluntary motor Central canal
function, motivation , aggression,
mood and smell. CEREBROSPINAL FLUID – providing protective
PARIETLA LOBE – sensory cushion around CNS.
information such as touch, pain,
temperature and balance. CRANIAL NERVE
OCIPITAL LOBE – vision CN 1 – Smell
TEMPORAL LOBE – Hearing, CN 2 – Vision
smell ,memory. CN 3 – M- six extrinsic eye muscle and upper
eyelid
Motor Function CN – 4 ,6 Motor on one extrinsic eye muscle
Involuntary Movements – occurs with CN 3 – P- constrict pupils, thickens lens.
conscious though CN 5 – Sensory to face and teeth , motor to
Voluntary Movement – example walking and muscle of mastification.
typing. CN 7 – S – Motor to muscle muscles of facial
expression, P- salivary and tear glands
Upper motor neurons – cell bodies in cerebral CN 8 – Hearing and Balance
cortex CN 9 – S – Taste and touch to back of tongue .
Primary motor cortex located in posterior M- pharyngeal muscle , P- salivary glands
portion of frontal lobe. CN 10 – S- pharynx,larynx, and viscera , M-
Premotor area- frontal lobe motor function . palate ,pharyx and larynx , P- viscera of thorax
Prefrontal area – initiate movement occur in and abdomen.
anterior portion of frontal lobe. CN 11 – two neck and upper back muscle
CN 12 tongue muscle
BASAL NUCLEI - group of functionaly related
nuclei. DISEASE AND DSORDERS
2 nuclei
CORPUS STRIATUM – deep within IT IS – means inflammation
cerebrum
SUBSTANTIA NIGRA - darkly
pigmented cells in the midbrain
CEREBELLUM – involved in maintaining balance
and muscle tone and in coordinating fine motor
movement.
MENINGES – surround and protect the brain
and spinal cord.
DURA MATER
EPIDURAL SPACE
ARACHNOID MATER
SUBDURAL SPACE
PIA MATER
SUBARACHNOID SPACE
VETRICLES – fluid filled cavities
Lateral ventrcles
You might also like
- Francesca Filbey - The Neuroscience of Addiction-Cambridge University Press (2019) PDFDocument208 pagesFrancesca Filbey - The Neuroscience of Addiction-Cambridge University Press (2019) PDFBrujoucm100% (1)
- DebShapiroYourBodySpeaksY PDFDocument319 pagesDebShapiroYourBodySpeaksY PDFDương Bảo Thi Anh100% (10)
- How infant memories develop and last longer than expectedDocument4 pagesHow infant memories develop and last longer than expectedJuan MezaNo ratings yet
- Libet - Unconscious-Cerebral-Initiative-And-The-Role-Of-Conscious-Will-In-Voluntary-ActionDocument11 pagesLibet - Unconscious-Cerebral-Initiative-And-The-Role-Of-Conscious-Will-In-Voluntary-ActionAndreia CastroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesChapter 8: Nervous SystemAndrea BoocNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document8 pagesModule 1laaraybmehmood1503No ratings yet
- The Nervous System ExplainedDocument57 pagesThe Nervous System ExplainedGeelin Crizza AlbisNo ratings yet
- P2 W1 9 10 Autosaved .PptxDocument91 pagesP2 W1 9 10 Autosaved .Pptxkylacomanda04No ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument21 pagesNeurophysiologyKeya PatelNo ratings yet
- Neurology Week 1 Trans 01 31 23Document3 pagesNeurology Week 1 Trans 01 31 23anime listNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsZella ViaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer Anaphy LectureDocument15 pagesMidterm Reviewer Anaphy LectureCarlito FantilaganNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- 6j8s0 E0gbcDocument10 pages6j8s0 E0gbcBarbora BujdošováNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Transes 1Document6 pagesNervous System Transes 1Rhodie BatislaonNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1Document5 pagesNeuro 1Treng EstradaNo ratings yet
- 7-Nervous SystemDocument69 pages7-Nervous SystemCarl Vincent VingnoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec FDocument11 pagesAnaphy Lec FclarecielaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument85 pagesThe Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyJamie Bagundol100% (3)
- Module 12 Handouts Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesModule 12 Handouts Nervous Systemgianarido30No ratings yet
- Nervous System1Document76 pagesNervous System1ahmed jeylaaniNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY LAB W7 ReviewerDocument5 pagesANAPHY LAB W7 Reviewerangelmalang41No ratings yet
- Nervous System - All NotesDocument6 pagesNervous System - All NotesJNo ratings yet
- Neuro 0411-1323Document21 pagesNeuro 0411-1323Lea Jane ArmeñaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument69 pagesNervous SystemZekiah MagsayoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument45 pagesNervous SystemHarini kumaranNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Skull Cerebrospinal FluidDocument1 pageNervous System: Skull Cerebrospinal FluidVincent Franciz T. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Sensory Nervous System Motor Nervous System: Sometimes Aware, I.E. Menstrual CrampsDocument8 pagesSensory Nervous System Motor Nervous System: Sometimes Aware, I.E. Menstrual CrampsGaveen CoatesNo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument42 pagesNeurologybuzz Q100% (2)
- Neuro Week 1Document6 pagesNeuro Week 1Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- Human Regulatory SystemDocument37 pagesHuman Regulatory SystemRudolfNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ANAPHY NotesDocument10 pagesNervous System ANAPHY NotesAlloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Anatomy Neuro AssessmentDocument96 pagesNeuro Anatomy Neuro AssessmentJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Neuro Anatomy Neuro AssessmentDocument96 pagesNeuro Anatomy Neuro AssessmentJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7Document7 pagesExercise 7Gelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterm Week 2 Notes (Nervous System)Document20 pagesAnaphy Midterm Week 2 Notes (Nervous System)Zosia SageNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Ian Van V. Sumagaysay, RN, MAN St. Anthony's CollegeDocument182 pagesThe Nervous System: Ian Van V. Sumagaysay, RN, MAN St. Anthony's CollegeAlibasher MacalnasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous Systemmohd nazmieNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomy of Nervous SystemGrace CosmodNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous SystemYUAN FRANCIS SINGCULANNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument2 pagesScience ReviewerMarbel SsgNo ratings yet
- 3aDasar-Dasar Neuroanatomi (2016)Document157 pages3aDasar-Dasar Neuroanatomi (2016)Magfira Al HabsyiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous SystemJake SimNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument19 pagesNeuroanatomy: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversitySuardimanAchoNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Function: Anatomic and Physiologic ReviewDocument28 pagesNeurologic Function: Anatomic and Physiologic ReviewJeanette SampangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4.1Document9 pagesTutorial 4.1Rosa FinizioNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument58 pagesPeripheral Nervous Systemapi-26762768100% (4)
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Document7 pagesChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ana and PhysioDocument2 pagesNeuro Ana and PhysioJacqueline de AsisNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System ExplainedDocument71 pagesThe Nervous System ExplainedShawn Henry CepedaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System - Module 4Document23 pagesThe Nervous System - Module 4CaityNo ratings yet
- P and C - OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument4 pagesP and C - OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEMRjayvie BadajosNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument39 pagesTrigeminal NerveRanjana RavindranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ANAPHY Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 8 ANAPHY Nervous Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- Intro To Psych PrelimDocument113 pagesIntro To Psych PrelimAlexandra San PedroNo ratings yet
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced Studies A.H. Banzon ST, Ibayo, Balanga CityDocument7 pagesAsia Pacific College of Advanced Studies A.H. Banzon ST, Ibayo, Balanga CityLore Anne Mhae SantosNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesNervous SystemSuvalari Mimi JonathanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy NS-BrainCranialNervesDocument13 pagesAnaphy NS-BrainCranialNervesYo1No ratings yet
- MS NeurologyDocument30 pagesMS NeurologyAu CassieNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ppt. Lec. 1Document49 pagesNeuro Ppt. Lec. 1Jay successNo ratings yet
- Neuro 2009Document181 pagesNeuro 2009mcie22dwestNo ratings yet
- FINALS 2 5-Nervoustissue-161014172642Document56 pagesFINALS 2 5-Nervoustissue-161014172642Maika Ysabelle RavaloNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesNervous SystemGwynth Mrgrtt GnzlsNo ratings yet
- How To Study Quickly and Effectively - 2. Breathing ExercisesDocument3 pagesHow To Study Quickly and Effectively - 2. Breathing ExercisesfuzzychanNo ratings yet
- The Triune BrainDocument2 pagesThe Triune BrainJames DriscollNo ratings yet
- NakakapanghinaDocument1 pageNakakapanghinaalexi thymiaNo ratings yet
- Dehaene, Stanislas - The Massive Impact of Literacy On The BrainDocument16 pagesDehaene, Stanislas - The Massive Impact of Literacy On The BrainIreneGálvezdeMontalbán100% (1)
- What Is MemoryDocument3 pagesWhat Is MemoryAkash KNo ratings yet
- Focus On Psychosis Gaebel Zielasek (2015)Document10 pagesFocus On Psychosis Gaebel Zielasek (2015)rap 2treyNo ratings yet
- Brain CancerDocument33 pagesBrain Cancermynoidanh19No ratings yet
- Brain Hemispheres, Lobes, and Cortical AreasDocument23 pagesBrain Hemispheres, Lobes, and Cortical AreasAnisa WahyuniartiNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Use DisorderDocument39 pagesAlcohol Use DisorderRibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Long-Term MemoryStructureDocument30 pagesLong-Term MemoryStructureALEXANDRA SAN PEDRONo ratings yet
- 13 DeLisa - 039 - sESPASTICIDAD-1343-1361Document19 pages13 DeLisa - 039 - sESPASTICIDAD-1343-1361Alexandra SotoNo ratings yet
- ZakriyaDocument2 pagesZakriyaapi-512107573No ratings yet
- Schemas: Cultural Differences in Social CognitionDocument2 pagesSchemas: Cultural Differences in Social Cognitionnguyễnthùy dươngNo ratings yet
- 4.sensorry ExaminationDocument27 pages4.sensorry Examinationtalha malikNo ratings yet
- Referat Gangguan Psikotik AkutDocument8 pagesReferat Gangguan Psikotik AkutanggunpuspaaNo ratings yet
- Types of Amnesia Explained in DetailDocument4 pagesTypes of Amnesia Explained in DetailHsnysbvNo ratings yet
- Horse Anatomy Pictures-Think Like A Horse-Rick Gore Horsemanship ®Document41 pagesHorse Anatomy Pictures-Think Like A Horse-Rick Gore Horsemanship ®Laura B.100% (2)
- MRI Findings in MalnutritionDocument9 pagesMRI Findings in MalnutritionAhmed AyazNo ratings yet
- Level of ConsciousnessDocument10 pagesLevel of ConsciousnessDinda Ramos100% (1)
- Nuero - Brain HerniationDocument87 pagesNuero - Brain Herniationapi-19916399No ratings yet
- The Importance of Sleep for Health and Learning /TITLEDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Sleep for Health and Learning /TITLEAJENG PENPADA AJENG0% (1)
- Renaissance Periodization - Evidenced Based Habit BuildingDocument170 pagesRenaissance Periodization - Evidenced Based Habit BuildingLeandro AisaNo ratings yet
- Dementia NCPDocument4 pagesDementia NCPkarl montano100% (3)
- Take Charge of Your EmotionsDocument28 pagesTake Charge of Your EmotionsBethany House PublishersNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum & DiencephalonDocument21 pagesCerebellum & Diencephalonprasun_vNo ratings yet
- FAMORCAN, MAVELLE A. - WEEK 6 PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - gRADE 11Document5 pagesFAMORCAN, MAVELLE A. - WEEK 6 PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - gRADE 11Mavelle FamorcanNo ratings yet