Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem
Uploaded by
Rashid Dayao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesClinical chemistry involves performing tests to determine increased or decreased levels of chemicals in the body compared to normal values. These tests provide evidence of what is causing a person's disease. To maintain quality results, tests are run with standards and controls. Common methods used in clinical chemistry analysis include spectrophotometry, nephelometry, turbidimetry, atomic absorption spectrophotometry, flame emission spectrophotometry, and electrophoresis. Each method works by measuring how substances absorb, scatter, or emit light to determine concentrations of analytes like metals, proteins, or electrolytes.
Original Description:
Original Title
chem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentClinical chemistry involves performing tests to determine increased or decreased levels of chemicals in the body compared to normal values. These tests provide evidence of what is causing a person's disease. To maintain quality results, tests are run with standards and controls. Common methods used in clinical chemistry analysis include spectrophotometry, nephelometry, turbidimetry, atomic absorption spectrophotometry, flame emission spectrophotometry, and electrophoresis. Each method works by measuring how substances absorb, scatter, or emit light to determine concentrations of analytes like metals, proteins, or electrolytes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesChem
Uploaded by
Rashid DayaoClinical chemistry involves performing tests to determine increased or decreased levels of chemicals in the body compared to normal values. These tests provide evidence of what is causing a person's disease. To maintain quality results, tests are run with standards and controls. Common methods used in clinical chemistry analysis include spectrophotometry, nephelometry, turbidimetry, atomic absorption spectrophotometry, flame emission spectrophotometry, and electrophoresis. Each method works by measuring how substances absorb, scatter, or emit light to determine concentrations of analytes like metals, proteins, or electrolytes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
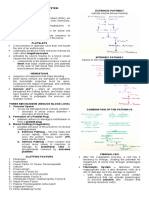
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY it means that the higher the
assays or tests are done to determine concentration of an analyte in a tube,
increased or decreased levels of chemicals in the higher its absorbance and the
the body (by comparing to normal values) lower is its transmittance
Biochemical in the body need Homeostasis
(balance) = Normal Values
Biochemicals – chemicals that make up living
things; that are found in life Cuvette
1. Carbohydrates
2. Proteins
3. Lipids
4. Nitric Acid
Performing Test with Quality
chemical levels in our body have been
minimum of five test tube
determined and these levels are called Normal
Values (NV) test tube 1 = blank
a. Hypo – if the chemical analyte determined to zero the machine
in the test goes below the normal values test tube 2 = normal control
b. Hyper – if the chemical analyte determined test tube 3 = abnormal control
in the test goes beyond the normal values tube 2 & 3 to check the acceptability of
these results provide vital evidences of what the test
is causing the disease of a person used predetermine concentrations
test tube 4 = standard
Examples: basis for the measurement of
Glucose level (normal value = 5.6 – 6.4 mmol/L) concentration of the test
Hyperglycemia – higher than the NV standard serve as a divisor
Hypoglycemia – lower than the NV concentration of standard serve as a
Sodium level multiplier
Hypernatremia test tube 5
Hyponatremia serum/plasma
Potassium level
Hyperkalemia 2. Nephelometry
Hypokalemia detection of light energy scattered or
reflected toward a detector that is not in the
To maintain quality results in Clinical Chemistry direct path of the transmitted light
procedures, tests are run simultaneously with
standards and controls. 3. Turbidimetry
a. Standards process of measuring the loss of intensity of
- basis for the concentration of the test transmitted light due to the scattering effect
- used as a constant variable to which the of particles suspended in it
tested analyte is computed and controls are measures the amount of light that is pass
used to determine accuracy of the test through (transmitted light), but it will
b. Controls compute for the turbidity based on the
- Normal and Abnormal Controls to determine amount of light that is blocked
the acceptability of the test Light is passed through a filter creating a
- These provide a guide to determine whether light of known wavelength which is then
the test performed is reliable or not. passed through a cuvette containing a
solution
METHODS USED IN CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 4. Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry
ANALYSIS atomic absorption methods measure the
1. Spectrophotometry amount of energy absorbed by the sample
spectro = visible/seperated light; photo = can measure even smallest quantity/
light; metry = measurement concentration of analyte
make use of prisms or gratings to isolate a very sensitive method of elemental analysis
narrow range of visible (400 – 700 nm) and particularly trace metals, allowing the
invisible light determination of metals in a variety of
prism – separate different components samples at the picogram level
of white light Hollow Cathode Lamp – instrument uses a
each light has its own wavelength light source
wavelengths – measured in emits specific wavelengths of light that
nanometers (nm) are ideally only absorbable by the
analyte
Spectrophotometer 5. Flame Emission Spectrophotometry
equipment used in measuring concentration light source is flame; used in electrolytes
of analyte and substances that emit color when burn
uses the Beer-Lambert Law; states that the based on the characteristic emission of light
loss of light intensity when it propagates in a by atoms of many metallic elements when
medium is directly proportional to intensity given sufficient energy, such as that
and path length supplied by a hot flame
6. Electrophoresis
phoresis = movement
general term that describes the migration
and separation of charged particles (ions)
under the influence of an electric field
movement of substances depending on the
charges of particles called ions
the movement of substances is dependent
on the charges of analyte
You might also like
- Anachem Lec LQ 1Document8 pagesAnachem Lec LQ 1Macy MarianNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemDocument2 pagesClinical ChemRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- NefelometriaDocument25 pagesNefelometriaJuan Marcos Martinez ZevallosNo ratings yet
- INSTRUMENTATIONDocument43 pagesINSTRUMENTATIONLawrence Genelago GamboaNo ratings yet
- NepheloturbidimetryDocument4 pagesNepheloturbidimetrypranav.joshi2020No ratings yet
- Alanah Jane Garcia - Activity - ColorimetricDocument3 pagesAlanah Jane Garcia - Activity - ColorimetricAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- BMS481 - 4.0 (Part 2)Document37 pagesBMS481 - 4.0 (Part 2)syuhadahNo ratings yet
- NephelometryDocument22 pagesNephelometryBassem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Spectrophotometry - Part IIDocument4 pagesBasic Principles of Spectrophotometry - Part IISorinaLuciaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4B - Enviro Chem Anal2 - ModDocument14 pagesLec 4B - Enviro Chem Anal2 - ModBuTter ScoTch100% (1)
- Fluorometry NotesDocument5 pagesFluorometry NotesHayna RoseNo ratings yet
- Colorimetric MethodsDocument5 pagesColorimetric MethodsGraceNo ratings yet
- 3 Analytical Procedures and Instrumentation and InstrumentationDocument35 pages3 Analytical Procedures and Instrumentation and InstrumentationshiferagebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Analytic InstrumentsDocument10 pagesAnalytic InstrumentsClarence SantosNo ratings yet
- General Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Coagulation InstrumentsDocument24 pagesGeneral Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Coagulation InstrumentsArnab GhoshNo ratings yet
- Chem 102 Lle #1 CoverageDocument6 pagesChem 102 Lle #1 CoverageMaria JanelaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry: Precipitate - Turn The Soluble Substance Into An Insoluble SubstanceDocument7 pagesAnalytical Chemistry: Precipitate - Turn The Soluble Substance Into An Insoluble SubstanceSamantha Jesi Shania EstradaNo ratings yet
- Ei 6501 Analytical Instruments Unit-I Colorimetry and SpectrophotometryDocument24 pagesEi 6501 Analytical Instruments Unit-I Colorimetry and SpectrophotometryBarani DharanNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry - UAS 2020Document7 pagesAnalytical Chemistry - UAS 2020said agilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Instrumental AnalysisDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Instrumental AnalysisSanket SapateNo ratings yet
- Applications of Chemical AnalysisDocument18 pagesApplications of Chemical AnalysisJames Anthony ParasNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Basic and SpectrophotometerDocument11 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Basic and SpectrophotometerVirender BhattiNo ratings yet
- Different Techniques and AnalysisDocument4 pagesDifferent Techniques and AnalysisJamila SeifNo ratings yet
- M1 Spectrophotometric Qc2lab NewDocument49 pagesM1 Spectrophotometric Qc2lab NewKrisel AguilarNo ratings yet
- Biological Instrumentation Project Based Lab 2 Basic Spectrophotometer and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer DATE: 11/1/2021Document11 pagesBiological Instrumentation Project Based Lab 2 Basic Spectrophotometer and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer DATE: 11/1/2021wei linNo ratings yet
- 56 Vol. 3 Issue 12 December 2012 IJPSR RA 1960 Paper 56Document9 pages56 Vol. 3 Issue 12 December 2012 IJPSR RA 1960 Paper 56VAISHALI PATELNo ratings yet
- Uv-V ApplicationDocument42 pagesUv-V ApplicationTare ye TesfuNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument69 pagesProteinsRodger12No ratings yet
- A Project Report O1Document65 pagesA Project Report O1Pratik PacharneNo ratings yet
- Activity - ColorimetricDocument3 pagesActivity - ColorimetricbernantebellerryNo ratings yet
- AAC811S 2022 Chap 4Document122 pagesAAC811S 2022 Chap 4HUILE D’ORNo ratings yet
- MEDACDocument6 pagesMEDACMaye Zaidyle BorinagaNo ratings yet
- 06 - Immunoturbidimetria e NefelometriaDocument13 pages06 - Immunoturbidimetria e NefelometriaDoris MedinaNo ratings yet
- Effect of β-amylase on starchDocument13 pagesEffect of β-amylase on starchNUR SABRINA MOHD SHAHNo ratings yet
- Application of SpectrophotometerDocument16 pagesApplication of SpectrophotometerMuhammad RamzanNo ratings yet
- CCP 4.1 - PRELIMS (Updated)Document4 pagesCCP 4.1 - PRELIMS (Updated)baytadokiNo ratings yet
- Nephelometry and Turbidimetry: Cls 332 Lab 4Document13 pagesNephelometry and Turbidimetry: Cls 332 Lab 4xxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- BIO-CHEMISTRY PresentationDocument52 pagesBIO-CHEMISTRY Presentationmohammed alolfeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Environmental Instrumental AnalysisDocument68 pagesLecture 4 Environmental Instrumental AnalysisAbu WildanNo ratings yet
- DevicesDocument14 pagesDevicesBelal FatahNo ratings yet
- JNV Indira Devi Research Scholar Pharmaceutical Analysis Andhra UniversityDocument25 pagesJNV Indira Devi Research Scholar Pharmaceutical Analysis Andhra UniversityIndiraNo ratings yet
- Nephelometry and Turbidimetry: Cls 332 Lab 4Document13 pagesNephelometry and Turbidimetry: Cls 332 Lab 4Ita Maghfirah100% (1)
- Absorption Spectroscopy: Sanjay M. Nilapwar, Maria Nardelli, Hans V. Westerhoff, and Malkhey VermaDocument17 pagesAbsorption Spectroscopy: Sanjay M. Nilapwar, Maria Nardelli, Hans V. Westerhoff, and Malkhey VermaAbdo MohdyNo ratings yet
- Chemiluminescence and Bioluminescence MeasurementsDocument11 pagesChemiluminescence and Bioluminescence MeasurementsShelma Fitri AinulshidqiNo ratings yet
- Principles and MethodologyDocument33 pagesPrinciples and MethodologyPreetha PalaniswamyNo ratings yet
- III. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)Document20 pagesIII. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS)Chan PhengNo ratings yet
- AnaChem ReviewerDocument9 pagesAnaChem ReviewerIan Agustin CardanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Pharmaceutical Analysis - Defination and ScopeDocument45 pagesUnit 1 Pharmaceutical Analysis - Defination and ScopeAnis SayyedNo ratings yet
- Referensi SpektroDocument7 pagesReferensi SpektroSalman HakimNo ratings yet
- Detecting and Quantifying Biological Molecules Using SpectrophotometryDocument12 pagesDetecting and Quantifying Biological Molecules Using SpectrophotometryAGNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and AutomationDocument8 pagesInstrumentation and Automationkriss WongNo ratings yet
- Analytic Techniques and Instrumentation Lecture FormatDocument15 pagesAnalytic Techniques and Instrumentation Lecture FormatMandy A. DelfinNo ratings yet
- Chemical AnalysisDocument22 pagesChemical AnalysisAnjali KumbharNo ratings yet
- SpectrophotometryDocument22 pagesSpectrophotometryaziskfNo ratings yet
- ColourimetricanalyisiDocument25 pagesColourimetricanalyisiSour GinNo ratings yet
- Analytical 1Document22 pagesAnalytical 1Viswapriya K.PNo ratings yet
- Analytical MethodsDocument9 pagesAnalytical Methodspiscestrading0324No ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument4 pagesAnalytical ChemistryAbdurrazaqNo ratings yet
- Analytical Instrumentation: A Guide to Laboratory, Portable and Miniaturized InstrumentsFrom EverandAnalytical Instrumentation: A Guide to Laboratory, Portable and Miniaturized InstrumentsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Human BodyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To The Human BodyRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - CirculatoryDocument5 pagesModule 5 - CirculatoryRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Module 10Document3 pagesModule 10Rashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Module 9 - Capillary PunctureDocument2 pagesModule 9 - Capillary PunctureRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- ANPATH1 ReviewerDocument17 pagesANPATH1 ReviewerRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Final: Gluconeogenesis - When The Liver and KidneysDocument43 pagesFinal: Gluconeogenesis - When The Liver and KidneysRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Universal Precautions For Healthcare Blood Borne PathogensDocument2 pagesUniversal Precautions For Healthcare Blood Borne PathogensRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Infectious ProcessDocument3 pagesModule 2 - Infectious ProcessRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Electrical SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System - Electrical SystemRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Outside Trauma (Tissue Trauma)Document2 pagesOutside Trauma (Tissue Trauma)Rashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Reproductive Overview: Peristaltic Movement of SpermDocument2 pagesMale Reproductive System Reproductive Overview: Peristaltic Movement of SpermRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Study of Blood and Blood Disorders Serum)Document2 pagesStudy of Blood and Blood Disorders Serum)Rashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Functions:: Four Functions of SpleenDocument5 pagesFunctions:: Four Functions of SpleenRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular / Circulatory System: Upper Chambers or Receiving ChambersDocument2 pagesCardiovascular / Circulatory System: Upper Chambers or Receiving ChambersRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Plyometric Exercises Plyometrics Fitt - Frequency Intensity Time and Type FittDocument3 pagesPlyometric Exercises Plyometrics Fitt - Frequency Intensity Time and Type FittRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Blood Collection Equipment, Additives, and Order of Draw Blood Collection Equipment and SuppliesDocument3 pagesBlood Collection Equipment, Additives, and Order of Draw Blood Collection Equipment and SuppliesRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory ScientistDocument2 pagesMedical Laboratory ScientistRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides Specifically Pair Up With Each Other: Father's Gene Mother's GeneDocument2 pagesNucleotides Specifically Pair Up With Each Other: Father's Gene Mother's GeneRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Key Biodiversity Areas in The Philippines: Priorities For ConservationDocument10 pagesKey Biodiversity Areas in The Philippines: Priorities For ConservationRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- 5 IntegumentaryDocument35 pages5 IntegumentaryRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- From The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughDocument3 pagesFrom The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- The Human - Brain - : Mallari, Jellie Anne A. Gomez, Alessandra LoisDocument54 pagesThe Human - Brain - : Mallari, Jellie Anne A. Gomez, Alessandra LoisRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Introduction To The Nervous System: - Organization - Cell TypesDocument71 pagesChapter 12 - Introduction To The Nervous System: - Organization - Cell TypesRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- 4) Faith and ReligionDocument2 pages4) Faith and ReligionRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Members: Bsmls - Lai: Activity #2 Filipino Cultural Value OrientationsDocument4 pagesMembers: Bsmls - Lai: Activity #2 Filipino Cultural Value OrientationsRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Group 5Document16 pagesRespiratory System: Group 5Rashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument27 pagesSpinal CordRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Accurate Wide-Range Design Equations For The Frequency-Dependent Characteristic of Parallel Coupled Microstrip LinesDocument8 pagesAccurate Wide-Range Design Equations For The Frequency-Dependent Characteristic of Parallel Coupled Microstrip LinesffukudaNo ratings yet
- Preprint Mass-Spring-Damper Modeling of The Human Body To Study Running and Hopping - An OverviewDocument35 pagesPreprint Mass-Spring-Damper Modeling of The Human Body To Study Running and Hopping - An Overviewmedardo77No ratings yet
- 5 Spheres and ConesDocument8 pages5 Spheres and Conesstemtutor kakwongNo ratings yet
- CTL RajasthanDocument7 pagesCTL RajasthanjaiqcNo ratings yet
- Mesl Problems Set 2Document5 pagesMesl Problems Set 2Crystian Kobee EmpeynadoNo ratings yet
- Phase-Changes OriginalDocument4 pagesPhase-Changes Originalapi-293306937No ratings yet
- D 6726 - 01 - Rdy3mjyDocument7 pagesD 6726 - 01 - Rdy3mjyRam Kailash YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - First Law of TMD - EngDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - First Law of TMD - EngPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- Aci318-08 Moment Shear Torsion DesignDocument7 pagesAci318-08 Moment Shear Torsion DesignMohammed HanafiNo ratings yet
- 6btaa5 9-G7Document10 pages6btaa5 9-G7Jakir HossainNo ratings yet
- BYK Gardner USA Cert and Scope File 07 25 2022 - 1658779904Document17 pagesBYK Gardner USA Cert and Scope File 07 25 2022 - 1658779904Raghunath DashNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument17 pagesDifferential Equationshyamala_guru1143No ratings yet
- Intera Standard Neuro: Changing How The World Looks at MRDocument46 pagesIntera Standard Neuro: Changing How The World Looks at MRJuan EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Envelope Detection Using MATLAB For Any Time Domain Signal (Thorugh Hilbert Transform)Document6 pagesEnvelope Detection Using MATLAB For Any Time Domain Signal (Thorugh Hilbert Transform)Saman fatimaNo ratings yet
- Lec4 PDFDocument91 pagesLec4 PDFArun ShalNo ratings yet
- Field Configurable Ceiling Strobes: Genesis SeriesDocument4 pagesField Configurable Ceiling Strobes: Genesis SeriesLwigy SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Govt-Job-Preparation-for-Assistant-Engineer-Civil-by-DESIGN-INTEGRITY (P)Document10 pagesGovt-Job-Preparation-for-Assistant-Engineer-Civil-by-DESIGN-INTEGRITY (P)S. M Ehasanul Haque MinhazNo ratings yet
- NX100 Epx2750Document69 pagesNX100 Epx2750Trí ChốtNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge/Bridge/Load Cell/Pressure Transducer To DC Transmitters, Field Rangeable APD 4059Document4 pagesStrain Gauge/Bridge/Load Cell/Pressure Transducer To DC Transmitters, Field Rangeable APD 4059luat1983No ratings yet
- Ch6 LateralEarthPressureDocument39 pagesCh6 LateralEarthPressure彭宇鑫No ratings yet
- Non-Closed Lie Subgroups of Lie GroupsDocument6 pagesNon-Closed Lie Subgroups of Lie Groupslaura lopezNo ratings yet
- Guided Review Exam 2Document7 pagesGuided Review Exam 2mattNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric Eocr I3bz User ManualDocument22 pagesSchneider Electric Eocr I3bz User Manualsaikat sarkarNo ratings yet
- EMC 22 Electric Motor CheckerDocument1 pageEMC 22 Electric Motor CheckerindustrialindiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 How Time and Interest Affect MoneyDocument22 pagesChapter 2 How Time and Interest Affect MoneyFlorDelaRamaNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 13: Exc K oDocument13 pagesPage 1 of 13: Exc K oSARAVANAN ANo ratings yet
- Coil CoatingsCoatings 8batDocument1 pageCoil CoatingsCoatings 8batDBICA TUDORNo ratings yet
- MMP-II, Course Outline Spring 2019Document3 pagesMMP-II, Course Outline Spring 2019Ehsan AdeebNo ratings yet
- Type Series Booklet: Submersible Borehole PumpDocument104 pagesType Series Booklet: Submersible Borehole PumpJoao PauloNo ratings yet
- Leaflet VertiDrive M3Document2 pagesLeaflet VertiDrive M3Kenan mira Mohammed NasherNo ratings yet