Professional Documents
Culture Documents
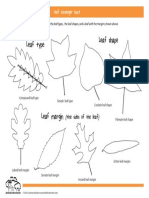
Leaf Base: Occur On The Same Side of The Stem
Uploaded by
Kamilatul Khoiroh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageThis document describes different types of leaf edges and tips. It identifies leaves whose edges meet and attach at the base, those whose edges meet on the opposite side of the stem, and those whose tips form a flat line. Examples of plant species are provided to illustrate each type of leaf edge or tip morphology, including castor, liman, olenader, pukul empat, hibiscus, and enceng leaves.
Original Description:
Original Title
11 Leaf Base
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes different types of leaf edges and tips. It identifies leaves whose edges meet and attach at the base, those whose edges meet on the opposite side of the stem, and those whose tips form a flat line. Examples of plant species are provided to illustrate each type of leaf edge or tip morphology, including castor, liman, olenader, pukul empat, hibiscus, and enceng leaves.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageLeaf Base: Occur On The Same Side of The Stem
Uploaded by
Kamilatul KhoirohThis document describes different types of leaf edges and tips. It identifies leaves whose edges meet and attach at the base, those whose edges meet on the opposite side of the stem, and those whose tips form a flat line. Examples of plant species are provided to illustrate each type of leaf edge or tip morphology, including castor, liman, olenader, pukul empat, hibiscus, and enceng leaves.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Right and left leaf edges never meet because they are Edges of leaves that meet and
Edges of leaves that meet and attach to one another
separated by the base of the mother's bone / leaf tips
LEAF BASE Leaf edges meet at the base to
Tapered occur on the same side of the stem
Spiky (acutus)
(acuminatus) and according to the location of the
leaves on the stem, the leaves wake
up shielding. Example: Castor leaf
(Ricinus communis Linn.).
Flat (truncatus)
The edges of the leaves meet at
the opposite side of the opposite
Tapered but the point of contact is stem or face to face with the
further back. Example: Liman leaves. Looks like the base of a
The edges of the mother's right and left footprint (Elephantopus scaber L.). leaf pierced by the tree
leaves form a sharp angle. Example: (perfoliatus). Example: Big Lotus
Olenader leaf (Nerium olender L.). Leaf tips form a flat line.
leaf
Example: Pukul Empat leaf
Rounded (Mirabilis Jalapa L.)
(rotundatus)
Blunt (obtusus)
Notched
(emarginatus)
The base of the leaf forms a kind Blunt Flat
Blunt (obtusus): In the leaves wake
ovate. Example: Nyamplung leaves of arc. Example: Hibiscus leaf
(Calophyllum inophyllum L.). (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.).
On the leaves of the heart's
wake, kidneys, arrows.
Example: Enceng leaves
Rounded Notched
Spiky Tapered SEPHYARANNY QURVINA SIWI (129)
SAFIRA NURISHITA SUGIARTO (133)
You might also like
- Identifying Trees of the East: An All-Season Guide to Eastern North AmericaFrom EverandIdentifying Trees of the East: An All-Season Guide to Eastern North AmericaNo ratings yet
- Modified Stem NMSSDocument6 pagesModified Stem NMSSPrazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- Leaf and Leaflet ShapesDocument10 pagesLeaf and Leaflet Shapesmansi bavliyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter BotanyDocument62 pagesChapter BotanyArockia RajaNo ratings yet
- ALEA - Exercise 13 Morphology of The LeafDocument6 pagesALEA - Exercise 13 Morphology of The LeafChristine AleaNo ratings yet
- 15 Leaf AttachmentDocument1 page15 Leaf AttachmentKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Organoleptic Evaluation (Leaves)Document19 pagesOrganoleptic Evaluation (Leaves)Joanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- STD 5th Types of FlowersDocument7 pagesSTD 5th Types of FlowersSandeep CorreaNo ratings yet
- Leaves OkDocument2 pagesLeaves OkHarrivcha W.SNo ratings yet
- Plants VR Tropical 04 Canna ImperataDocument1 pagePlants VR Tropical 04 Canna ImperataOladimejiNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document6 pagesCH 5Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Leaf ClassificationDocument4 pagesLeaf ClassificationSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Research Paper About LeafDocument10 pagesResearch Paper About LeafGenevieve GanubNo ratings yet
- Types, Shapes and MarginsDocument10 pagesTypes, Shapes and MarginsAkhil KanukulaNo ratings yet
- Week 3and 4Document61 pagesWeek 3and 4HEMA 22No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Key Notes 2.0Document15 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Key Notes 2.0Aanchal Pandey100% (1)
- Leaves Are Parts of A Plant or Tree Attached To The Branches or StemsDocument1 pageLeaves Are Parts of A Plant or Tree Attached To The Branches or StemsKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Fire Ant: Earthworms (Lumbricus Terrestris)Document20 pagesFire Ant: Earthworms (Lumbricus Terrestris)MB LoterteNo ratings yet
- Brown and Beige Minimalist Vintage Scrapbook Self-Introduction PresentationDocument26 pagesBrown and Beige Minimalist Vintage Scrapbook Self-Introduction PresentationRhusella Adrianne de GraciaNo ratings yet
- AlismatalesDocument3 pagesAlismatalesSanchez MaroseNo ratings yet
- Leaf Type PrintableDocument1 pageLeaf Type PrintableNicolaus INNo ratings yet
- Folium (Leaf/ Daun)Document73 pagesFolium (Leaf/ Daun)Dian Ratna Sari AyeeNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument40 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantschdhrysudeepNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report TemplateDocument5 pagesLaboratory Report TemplateCedrick Bacuaja InutaoNo ratings yet
- What Exactly Is A Stem?Document47 pagesWhat Exactly Is A Stem?Labib HasnainNo ratings yet
- ALEA - Exercise 14 The Leaf Structure (Part 1)Document11 pagesALEA - Exercise 14 The Leaf Structure (Part 1)Christine AleaNo ratings yet
- Journal No. 3 "Specialized Leaves"Document10 pagesJournal No. 3 "Specialized Leaves"Ej AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- A Turfgrass Identification: Ligule AuricleDocument3 pagesA Turfgrass Identification: Ligule AuricleLuis de los SantosNo ratings yet
- LEAF FunctionDocument4 pagesLEAF Functionkaren segundoNo ratings yet
- EquisetumDocument6 pagesEquisetumJhon SmithNo ratings yet
- Lab Work 6Document3 pagesLab Work 6Bella LopezNo ratings yet
- Leaves 2021. Lec.1Document57 pagesLeaves 2021. Lec.1noreenmady2No ratings yet
- Types of LeavesDocument5 pagesTypes of LeavesravilullaNo ratings yet
- Leaf Activity BookDocument7 pagesLeaf Activity BookJoel TopfNo ratings yet
- How To Identify TreesDocument10 pagesHow To Identify TreesSarah LadeNo ratings yet
- The FruitDocument2 pagesThe Fruitriza HechanovaNo ratings yet
- Morfologi Batang Kel 3Document43 pagesMorfologi Batang Kel 3Gresia FalentinaNo ratings yet
- Project EditedDocument26 pagesProject Editedapi-174466857No ratings yet
- Activity 1Document6 pagesActivity 1Ronnie Jr DiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 35: Plant Structure, Growth & Development: 1. What Are The 3 Main Plant Organs? - Roots - Stems - LeavesDocument30 pagesChapter 35: Plant Structure, Growth & Development: 1. What Are The 3 Main Plant Organs? - Roots - Stems - LeavesgedeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- PRPM110L Module 6Document9 pagesPRPM110L Module 6CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Botany Language Basics For Identification of Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesBotany Language Basics For Identification of Flowering PlantsKiss ImreNo ratings yet
- SEM II UNIT II Leaf Morphology DR - Prashant ShahareDocument37 pagesSEM II UNIT II Leaf Morphology DR - Prashant Shahareabhishekkumarsah5902No ratings yet
- AmiDocument12 pagesAmiAnonymous UoRu4sNo ratings yet
- Autumn FallDocument2 pagesAutumn FallАнастасия ФранцNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Leaves PDFDocument52 pagesLecture 10 - Leaves PDFChristine R. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Phyllotaxis by IisDocument20 pagesPhyllotaxis by IisAnonymous fbUJwFVPNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plantsaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Leaf Morph TemplateDocument8 pagesLeaf Morph TemplateJeriza AquinoNo ratings yet
- Morfologi Daun TunggalDocument32 pagesMorfologi Daun TunggalCahyatisyhrilNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Plant MorphologyDocument41 pagesLab Manual Plant MorphologySinggih PratomoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Leaf MorphologyDocument11 pagesCharacteristics of Leaf MorphologyJuwita PardedeNo ratings yet
- Tree Growth CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesTree Growth CharacteristicsMunganNo ratings yet
- TALLODocument2 pagesTALLOvictoria lopez quesquenNo ratings yet
- Table FinalDocument3 pagesTable Finallegendsac2000No ratings yet
- Leaf MorphologyDocument12 pagesLeaf MorphologyJeriza AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ex. 6 The LeafDocument14 pagesEx. 6 The LeafAlyssa Pauline PalacioNo ratings yet
- Morphology of AngiospermDocument7 pagesMorphology of AngiospermSagarNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Tumbuhan InggrisDocument10 pagesAnatomi Tumbuhan InggrisKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Tumbuhan InggrisDocument10 pagesAnatomi Tumbuhan InggrisKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Crinkled Leaf Surface: (Ipomea Batatas)Document1 pageCrinkled Leaf Surface: (Ipomea Batatas)Kamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Plant Morphology: Appendages Can Be Distinguish ToDocument1 pagePlant Morphology: Appendages Can Be Distinguish ToKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- 13 Leaf VenationDocument1 page13 Leaf VenationKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Palmate Leaves & DigitatopinnatusDocument1 pagePalmate Leaves & DigitatopinnatusKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Specialized Roots: Air Root or Hanging Root (Radix Aereus)Document1 pageSpecialized Roots: Air Root or Hanging Root (Radix Aereus)Kamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- 4 Stem and Branching TypesDocument2 pages4 Stem and Branching TypesKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- 6 PinnateDocument1 page6 PinnateKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Leaves Are Parts of A Plant or Tree Attached To The Branches or StemsDocument1 pageLeaves Are Parts of A Plant or Tree Attached To The Branches or StemsKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- Practical Work Reports Plant Morphology "The Development of Taproot System and Fibrous Root System"Document21 pagesPractical Work Reports Plant Morphology "The Development of Taproot System and Fibrous Root System"Kamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- 1 Root MorphologyDocument1 page1 Root MorphologyKamilatul KhoirohNo ratings yet
- The Practical Book of Outdoor Rose Growing For The Home GardenDocument462 pagesThe Practical Book of Outdoor Rose Growing For The Home GardenforsayiNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology Week 1 Lesson 2 Worksheet 2 and SolutionsDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Biology Week 1 Lesson 2 Worksheet 2 and SolutionsJamie LeNo ratings yet
- 2367-Article Text-18832-2-10-20210820Document8 pages2367-Article Text-18832-2-10-20210820desy meilinda putri firdauziNo ratings yet
- Tulbaghia ViolaceaDocument2 pagesTulbaghia ViolaceaRuby TubrezNo ratings yet
- Horticulture NCIIDocument12 pagesHorticulture NCIIShane Moran CanalesNo ratings yet
- (Advances in Biochemical Engineering Biotechnology) K.E.L. Eriksson-Biotechnology in The Pulp and Paper Industry-Springer Verlag (19Document335 pages(Advances in Biochemical Engineering Biotechnology) K.E.L. Eriksson-Biotechnology in The Pulp and Paper Industry-Springer Verlag (19Josepepe Bedolla BNo ratings yet
- Hort. 305 Turmeric Cultivation and Processing-6Document9 pagesHort. 305 Turmeric Cultivation and Processing-6meriiNo ratings yet
- Q&A Crop Protection LEADocument25 pagesQ&A Crop Protection LEAFernan Wood TravastaNo ratings yet
- All Grade 2 and Up Lesson Plans PPTSDocument65 pagesAll Grade 2 and Up Lesson Plans PPTSRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms Important in Food MicrobiologyDocument39 pagesMicroorganisms Important in Food MicrobiologyKumkum CRNo ratings yet
- My Fun Science Corner - Plant System How Do Plants Store Food Article 2Document2 pagesMy Fun Science Corner - Plant System How Do Plants Store Food Article 2api-243322195No ratings yet
- Seed Hybridization QuestionsDocument3 pagesSeed Hybridization QuestionsSolomon MbeweNo ratings yet
- Growth and Yield Response of String Beans On Various Soil MixtureDocument3 pagesGrowth and Yield Response of String Beans On Various Soil MixtureMAGDALINA COPITANo ratings yet
- Maize NotesDocument90 pagesMaize Notessamuel maina100% (1)
- Thesis PDFDocument165 pagesThesis PDFCarolina Del AguilaNo ratings yet
- Succulents - The Illustrated Dictionary (1997)Document233 pagesSucculents - The Illustrated Dictionary (1997)Vasile Anca100% (1)
- 5-Plant Physiology 2Document41 pages5-Plant Physiology 2Eka Puspa RiniNo ratings yet
- Flower Development and Anatomy of Agapanthus Praecox Ssp. Orientalis (Leighton) LeightonDocument9 pagesFlower Development and Anatomy of Agapanthus Praecox Ssp. Orientalis (Leighton) LeightonRicardo SouzaNo ratings yet
- DP1 BioHL - Topic 9 - Revision WorksheDocument32 pagesDP1 BioHL - Topic 9 - Revision WorkshelesedimamareganeNo ratings yet
- Saponification ChartDocument19 pagesSaponification Chartcharu latha100% (1)
- Ist-Aquatic and Wetland Plants of Northeastern North America, Volume I - A Revised and Enlarged Edition of Norman C. Fassett's A Manual of Aquatic Plants, Aquatic ADocument537 pagesIst-Aquatic and Wetland Plants of Northeastern North America, Volume I - A Revised and Enlarged Edition of Norman C. Fassett's A Manual of Aquatic Plants, Aquatic AM Ali AdamNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 HandoutDocument2 pagesGenbio2 HandoutDana HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Weed Identification BookDocument81 pagesWeed Identification BookEmily MertzNo ratings yet
- Benue SoilSample FarmerlistDocument3,210 pagesBenue SoilSample FarmerlistlivityhotNo ratings yet
- Ethno-Medicinal Plants Used by Tribes of Junona Village of Chandrapur District - M.SDocument7 pagesEthno-Medicinal Plants Used by Tribes of Junona Village of Chandrapur District - M.SESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Model PaperDocument38 pagesAgriculture Model Papervalmikisatish0% (1)
- Onion Seed PDFDocument31 pagesOnion Seed PDFBiserka Djuran ZigicNo ratings yet
- Alphabet of Flowers, Dean & Son's, Coloured Six-Penny BooksDocument16 pagesAlphabet of Flowers, Dean & Son's, Coloured Six-Penny BooksIngrid Vance Steighner100% (1)
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument28 pagesReproduction in PlantsMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Water Use Efficiency and Stomatal ConductanceDocument8 pagesWater Use Efficiency and Stomatal ConductanceIzabela AraujoNo ratings yet