Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 2 KH5033MAA Thermofluid Mechanics Carnot
Tutorial 2 KH5033MAA Thermofluid Mechanics Carnot
Uploaded by
Mohamed Adel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesOriginal Title
Tutorial_2_KH5033MAA__Thermofluid_Mechanics_Carnot (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views11 pagesTutorial 2 KH5033MAA Thermofluid Mechanics Carnot
Tutorial 2 KH5033MAA Thermofluid Mechanics Carnot
Uploaded by
Mohamed AdelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Tutorial 2
Carnot Engines
KH5033MAA Thermo-Fluid Mechanics
School of Engineering and Computing
Second Low Applications
Carnot Principal
School of Engineering and Computing
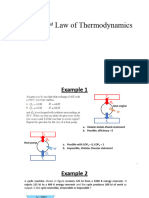
What’s a Carnot Engine ? When shall we use it ?
School of Engineering and Computing
QL T
6–9 The Carnot Heat Engine = L
QH TH
( 30 + 273) K
Figure 6–45
= = 0.328
𝑄𝐿 ( 652 + 273) K
𝜂th = 1 − Any heat engine The Carnot heat engine is the most efficient of all heat engines
𝑄𝐻 QL =
operating
500 kJ ( 0.328)
between the same high- and low-temperature
reservoirs.= 164 kJ
𝑇𝐿
𝜂th,rev = 1 − Carnot heat engine
𝑇𝐻
𝐶𝑎𝑛 𝑤𝑒 𝑔𝑒𝑡 100% 𝑒𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
𝑢𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑐𝑎𝑟𝑛𝑜𝑡 𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑒 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 ?
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
School of Engineering and Computing
6–7 The Carnot Principles 3 Figure 6–39
The Carnot principles.
1. The efficiency of an irreversible heat
engine is always less than the efficiency of
a reversible one operating between the
same two reservoirs.
2. The efficiencies of all reversible heat
engines operating between the same two
reservoirs are the same.
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
School of Engineering and Computing
Example 1
▪ An inventor claims to have developed a heat engine that receives 700 kJ of heat
from a source at 500 K and produces 300 kJ of net work while rejecting the waste
heat to a sink at 290 K. Is this a reasonable claim? Why?
School of Engineering and Computing
Solution 1
School of Engineering and Computing
Example 2 (Students)
▪ An air-conditioning system operating on the reversed Carnot cycle is required to
transfer heat from a house at a rate of 750 kJ/min to maintain its temperature at
24°C. If the outdoor air temperature is 35°C, determine the power required to
operate this air-conditioning system.
School of Engineering and Computing
Solution 2
School of Engineering and Computing
Example 3
▪ A heat pump is used to heat a house and maintain it at 24°C. On a
winter day when the outdoor air temperature is –5°C, the house is
estimated to lose heat at a rate of 80,000 kJ/h. Determine the
minimum power required to operate this heat pump.
School of Engineering and Computing
Solution 3
School of Engineering and Computing
You might also like
- E60 Hidden Navigation Menu InstructionsDocument5 pagesE60 Hidden Navigation Menu InstructionsNae Nicolae100% (2)
- Charcoal Briquet Ting Technology in The Province of Aurora, PhilippinesDocument18 pagesCharcoal Briquet Ting Technology in The Province of Aurora, PhilippinesEutiquio Rotaquio100% (8)
- Analytical Ability Answer Key: Word AssociationDocument3 pagesAnalytical Ability Answer Key: Word AssociationAni Pearl Panganiban100% (1)
- PWC Summary Guidance To BBMDocument3 pagesPWC Summary Guidance To BBMSantosh NathanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics For Engineers 1st Edition Kroos Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesThermodynamics For Engineers 1st Edition Kroos Solutions Manual 1JasonFergusonkgnew100% (23)
- Andrei Catalin Disca Roman Sites and DisDocument27 pagesAndrei Catalin Disca Roman Sites and DisBritta BurkhardtNo ratings yet
- Carnot Engine: by (Khlood Salim Al-Kafajy)Document11 pagesCarnot Engine: by (Khlood Salim Al-Kafajy)Ali Mohammed Alkafajy100% (1)
- Stec nc2 o PDFDocument153 pagesStec nc2 o PDFDanielson Santos100% (1)
- 6 Second LawDocument55 pages6 Second LawPoeil Sergio MoldezNo ratings yet
- Essential University Physics 3rd Edition Richard Wolfson Solutions Manual DownloadDocument28 pagesEssential University Physics 3rd Edition Richard Wolfson Solutions Manual DownloadJose Stepro100% (29)
- Physics I Thermodynamics: W JH J 4.186 J /calDocument12 pagesPhysics I Thermodynamics: W JH J 4.186 J /calmr shantosNo ratings yet
- M19 Wolf57139 03 Se C19Document27 pagesM19 Wolf57139 03 Se C19c.s.kalkmanNo ratings yet
- MR2207 Atd1 Q&aDocument33 pagesMR2207 Atd1 Q&ajeffreysingh jdNo ratings yet
- Solucionario - Termodinamica - Cengel - 7ed (1) - 519-528Document10 pagesSolucionario - Termodinamica - Cengel - 7ed (1) - 519-528Lizeth Maria lizarazoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Activity No. 1 3108Document1 pageModule 5 Activity No. 1 3108Sharmaine MauricioNo ratings yet
- HW07 Ch07 2nd Law CarnotDocument3 pagesHW07 Ch07 2nd Law Carnotabdoag1691998No ratings yet
- IV. Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument48 pagesIV. Second Law of ThermodynamicsBORASCA EZEKIELNo ratings yet
- IC Engine Lec 2 Fall 2018Document27 pagesIC Engine Lec 2 Fall 2018Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Che325 Tutorial KitDocument10 pagesChe325 Tutorial KitCharles BaileyNo ratings yet
- Atd Unit-Ii Second Law and Availability AnalysisDocument96 pagesAtd Unit-Ii Second Law and Availability AnalysisSurya KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Heat Engines: Richard Laugesen November 5, 2002Document9 pagesHeat Engines: Richard Laugesen November 5, 2002yus11No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: ENG 214 Chapter 5 - The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument38 pagesThermodynamics: ENG 214 Chapter 5 - The Second Law of ThermodynamicsGregory MacLeodNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document24 pagesWeek 3Mohamed nasserNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Airconditioning by S K Mondal T&Q .0001Document133 pagesRefrigeration and Airconditioning by S K Mondal T&Q .0001ANILNo ratings yet
- Topic: Reheat, Regenerative & Other Steam Power CycleDocument17 pagesTopic: Reheat, Regenerative & Other Steam Power CycleMurvin VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics IIDocument25 pagesThermodynamics IIpalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Analysis On Carnot AND Reversed Carnot Heat EngineDocument14 pagesThermodynamics Analysis On Carnot AND Reversed Carnot Heat Engine2K20B671 Shivam GargNo ratings yet
- Thermo 5th Chap06 P001Document17 pagesThermo 5th Chap06 P001Aslı ÖykünNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document15 pagesCH 06hirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- Topic: Reheat, Regenerative & Other Steam Power CycleDocument15 pagesTopic: Reheat, Regenerative & Other Steam Power CycleMurvin VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Gas Turbine Cycle Part 2Document11 pagesChapter 3 Gas Turbine Cycle Part 2Dhruwan ShahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2nd LawDocument15 pagesTutorial 2nd LawShivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Powerplant KitDocument30 pagesPowerplant Kitkim deygabiNo ratings yet
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument32 pagesSecond Law of ThermodynamicsParas kapoorNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Calculation NumbersDocument5 pagesRefrigeration Calculation Numbersodeke aronNo ratings yet
- Chen 1994Document7 pagesChen 1994aldoNo ratings yet
- BAB 5 - Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument34 pagesBAB 5 - Second Law of Thermodynamicsakun opsionalNo ratings yet
- Second Law Of: ThermodynamicsDocument35 pagesSecond Law Of: ThermodynamicsAnnisa AriestaNo ratings yet
- Carnot PrincipleDocument11 pagesCarnot Principleuwaqas.msee23seecsNo ratings yet
- 8carnot CycleDocument24 pages8carnot CycleMuhammad Randy AkbarNo ratings yet
- ME 354 Tutorial, Week#4 - Rankine CycleDocument7 pagesME 354 Tutorial, Week#4 - Rankine Cycleruppal42No ratings yet
- 11 - Ejemplo 9.2Document6 pages11 - Ejemplo 9.2CAMILA COBOS MOLANONo ratings yet
- Thermo EXAMPLE-CHAPTER 6 PDFDocument7 pagesThermo EXAMPLE-CHAPTER 6 PDFFattihiEkhmalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument31 pagesLecture 05 Second Law of ThermodynamicsdinurjNo ratings yet
- ETD - Unit 2 Day 4Document30 pagesETD - Unit 2 Day 4shobanaNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2023-02-19 في 2.51.13 ص PDFDocument35 pagesلقطة شاشة 2023-02-19 في 2.51.13 ص PDFkuno samaNo ratings yet
- Appendix C Design Calculations For Gas Power Generation Plant Design Alternative 2: Option ADocument44 pagesAppendix C Design Calculations For Gas Power Generation Plant Design Alternative 2: Option AAaronn RaphaaNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of Heat EnginesDocument38 pagesEfficiency of Heat EnginesGaming JcNo ratings yet
- Mere423 03Document3 pagesMere423 03Delia GantiaNo ratings yet
- II. Carnot Cycle: T Const T Const T TDocument6 pagesII. Carnot Cycle: T Const T Const T TDiana NurfitniNo ratings yet
- 31 Cogeneration PDFDocument70 pages31 Cogeneration PDFJunifero1No ratings yet
- 1.problem Sheet1Document1 page1.problem Sheet1Timothy SimirenNo ratings yet
- Aissa Thermo1 Chapter 06 PDFDocument52 pagesAissa Thermo1 Chapter 06 PDFBang YosuaNo ratings yet
- CP213: Tutorial Notebook 4Document1 pageCP213: Tutorial Notebook 4Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hukum Kedua TermodinamikaDocument57 pagesHukum Kedua TermodinamikaElizabeth SihombingNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Calculation NumbersDocument14 pagesRefrigeration Calculation NumbersBit CoinNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Marine Engineering Thermodynamics (TDN620S)Document4 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Marine Engineering Thermodynamics (TDN620S)Wilbard IitulaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Chapter 5 ProblemsDocument6 pagesSolutions To Chapter 5 ProblemsAndre RoqueteNo ratings yet
- Rev Lect ThermodynamicDocument37 pagesRev Lect Thermodynamicapi-26797747No ratings yet
- Power Plants: CH 4 Gas Turbine Power Plants: Amer Al-AniDocument36 pagesPower Plants: CH 4 Gas Turbine Power Plants: Amer Al-AniEssop BedNo ratings yet
- Electronica y Electricidad Automotriz 4 Como Funcionan Los Sistemas de Encendido ElectronicoDocument11 pagesElectronica y Electricidad Automotriz 4 Como Funcionan Los Sistemas de Encendido ElectronicoJuan Francisco Garcia ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Topic+4+Note+2 2020 21Document10 pagesTopic+4+Note+2 2020 21李世聪No ratings yet
- Tut Sheet 2 SolutionDocument8 pagesTut Sheet 2 SolutionDevkriti SharmaNo ratings yet
- DMX9208 Lecture08 S2 V0 2021Document54 pagesDMX9208 Lecture08 S2 V0 2021Sampath WeeratungeNo ratings yet
- Vrettos Ec7 Workshop London 2013Document43 pagesVrettos Ec7 Workshop London 2013Hoang SuperGoatNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management in Urban India: Imperatives For ImprovementDocument44 pagesSolid Waste Management in Urban India: Imperatives For ImprovementJ NarenNo ratings yet
- Inpho GT Lom KMDocument11 pagesInpho GT Lom KMlash73752No ratings yet
- Concept Paper EAPPDocument15 pagesConcept Paper EAPPmerry annNo ratings yet
- CV 2022Document5 pagesCV 2022samsonNo ratings yet
- 546 Assign 2 Group Ganagagabo K K, Motlogelwa B, Mogapi IDocument6 pages546 Assign 2 Group Ganagagabo K K, Motlogelwa B, Mogapi IKgotla GanagagaboNo ratings yet
- Channel Migration and Incision On The Beatton Rlver: by Gerald C. Nanson and Edward J. HickinDocument11 pagesChannel Migration and Incision On The Beatton Rlver: by Gerald C. Nanson and Edward J. HickinSandesh PoudelNo ratings yet
- Lufft VENTUS-UMB Ultrasonic Wind SensorDocument3 pagesLufft VENTUS-UMB Ultrasonic Wind SensorMiqueiasNo ratings yet
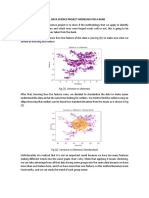
- Final Data Science Project-Modeling For A Bank: Fig (2) - Variance Vs SkewnessDocument3 pagesFinal Data Science Project-Modeling For A Bank: Fig (2) - Variance Vs SkewnessAlejo Guerra FernandezNo ratings yet
- Admission Notification 2024-2025Document12 pagesAdmission Notification 2024-2025jsbska88No ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 4 - Q1 - W6Document6 pagesDLL - Mapeh 4 - Q1 - W6Melanie Grace Ulgasan LuceroNo ratings yet
- Areas and Volumes of Solids - by TrockersDocument35 pagesAreas and Volumes of Solids - by TrockersRashidNo ratings yet
- EIM ErrorsDocument63 pagesEIM ErrorsSam KeplerNo ratings yet
- Development of The Planet EarthDocument14 pagesDevelopment of The Planet EarthHana CpnplnNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Science 6 No. 1Document2 pagesSummative Test Science 6 No. 1ChaMostierraNo ratings yet
- Bell Test ExperimentsDocument10 pagesBell Test ExperimentsDondieNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Choose The Right Answer: This Is For Questions 1 - 2 This Is MeDocument21 pagesInstruction: Choose The Right Answer: This Is For Questions 1 - 2 This Is MeImAs Chyntia Suki PraTamaNo ratings yet
- JVA Z14 User Manual 8v3xDocument80 pagesJVA Z14 User Manual 8v3xCarlos Roberto OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 27022875301Document2 pages27022875301mohammadznsalehNo ratings yet
- E12-Unit 8Document14 pagesE12-Unit 8Nguyễn Ái Vân Trường THPT Chuyên Lê Quý ĐônNo ratings yet
- E01: Vernier Caliper. Micrometer. MicroscopeDocument11 pagesE01: Vernier Caliper. Micrometer. MicroscopeTạ HạnhNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviourDocument11 pagesOrganizational BehaviourShefali PawarNo ratings yet
- Ticket 2 English Unit 10: Brain Drain: 1-VocabularyDocument2 pagesTicket 2 English Unit 10: Brain Drain: 1-VocabularykimoNo ratings yet
- 29-08-23 - Merged - PDF Version 1Document12 pages29-08-23 - Merged - PDF Version 1Arif laviNo ratings yet