Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHP 24
Uploaded by
Eeva The Diva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesOriginal Title
chp 24
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesCHP 24
Uploaded by
Eeva The DivaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
THE FACTORS AFFECTING PATTERNS OF TRADE BETWEEM COUNTRIES AND
CAUSES OF CHANGES IN THESE PATTERNS;
Impact of emerging economies – economies nowadays grow very fast or
slow. When GDP grows the country is likely to import more goods and
services than before. It also export more to pay for these imports. So
economic growth will affect the patterns of trade internationally.
Emerging economies tend to experience higher economic growth rates
than developed economies, which disrupt existing trade patterns a their
share of world exports and imports grows. Many emerging economy
have a cost advantage than developed. Overtime many developed
countires move to exporting secondary sector and high-tech sectors.
Patterns of trade changes between emerging economy and developed
because of the increase in global supply chain. The increase in FDI
between countries also have affected the pattern of trade. Emerging
economies have received FDI inflows from developed countries but
equally FDI flows occur between emerging economies. Many firms in
developed countries have shifted production overseas for the advantage
of lower costs. However the advanced technologies can help reduce the
costs despite the high wage labour. Emerging increasingly represent new
markets for developed economies. If economic growth rates of emerging
economies remain higher than those of a developed economies , this
will open up fast growing markets.
Changes in comparative advantage – this means that countries will
specialise in goods and services in which they have a comparative
advantage (Competitive advantage refers to factors that allow a
company to produce goods or services better or more cheaply than its
rivals. These factors allow the productive entity to generate more sales
or superior margins compared to its market rivals). The growth of
emerging economies means that many developed economies have
shifted their exports towards high valued goods and services. This makes
sense since advanced economies are likely to have a comparative
advantage in these. They can produce them at a lower opportunity cost
than emerging economies, because they have large supply of skilled
labour and technology.
Growth of trading blocs and bilateral trading agreements – bilateral
trade agreements , which are designed to increase trade between
parcipating countries at the expense of other countries. Hence the
change the pattern of trade in terms of geographical composition of
exports and imports.
Change in relative exchange rates – the exchange rate of one currency
for another affects the relative prices of goods between countries. So
changes in relative exchange rates affect patterns of trade unless they
very large. Its is long term changes which are sufficiently large that
impact trade.
Changes in protectionism between countries – restrictions on free trade
between countries affect trade flows between countries. Countries will
be able to export a higher volume of goods and services , overseas if
other countries reduce tarrifs and quotas. Some barriers may only some
goods and services overseas, which will affect the composition of
different type of goods and services which are traded. Joining a trading
bloc removes barriers.
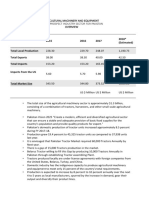
The volume of world trade
You might also like
- Smooth Sailing: A Quick Guide to Effective Cargo Import and Export: Logistics, #1From EverandSmooth Sailing: A Quick Guide to Effective Cargo Import and Export: Logistics, #1No ratings yet
- Trade Barriers, Dumping Anti DumpingDocument30 pagesTrade Barriers, Dumping Anti Dumpingqwertyuiop_6421100% (3)
- International Trade and Economics DevelopmentDocument27 pagesInternational Trade and Economics DevelopmentMd Shahnawaz IslamNo ratings yet
- MGT 9Document12 pagesMGT 9Anjelika ViescaNo ratings yet
- Business Revision NotesDocument7 pagesBusiness Revision NotesRocio Rambla ArealNo ratings yet
- International Trade and GlobalizationDocument36 pagesInternational Trade and GlobalizationJING LINo ratings yet
- The Effect On Consumer Welfare of A TariffDocument7 pagesThe Effect On Consumer Welfare of A TariffAmna KashifNo ratings yet
- Trade and Integration: (WTO) World Trade OrganisationDocument3 pagesTrade and Integration: (WTO) World Trade Organisationmp11abiNo ratings yet
- Capital Goods Services International Borders Capitales Bienes Servicios Fronteras InternacionalesDocument3 pagesCapital Goods Services International Borders Capitales Bienes Servicios Fronteras InternacionalesKaren SNo ratings yet
- The Global Economy NotesDocument14 pagesThe Global Economy NotesAlvi100% (1)
- The Global EconomyDocument3 pagesThe Global Economym02k3No ratings yet
- Tariff and Non-Tariff BarriersDocument20 pagesTariff and Non-Tariff BarriersIsha Aggarwal100% (2)
- Chapter 4Document13 pagesChapter 4Ermias AtalayNo ratings yet
- Free Trade AgreementDocument2 pagesFree Trade AgreementGrave diggerNo ratings yet
- Key DefinitionsDocument15 pagesKey DefinitionsJoyceeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 International Trading EnvironmentDocument45 pagesMODULE 6 International Trading EnvironmentTrixieJoy TaglucopNo ratings yet
- Business Theme 4Document7 pagesBusiness Theme 4CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Chi IuvianamoNo ratings yet
- Macro Topic 5-1Document40 pagesMacro Topic 5-1samantha swalehNo ratings yet
- The Global Economy ModuleDocument3 pagesThe Global Economy ModuleYram GambzNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Free TradeDocument7 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Free Tradeolawuyi adedayoNo ratings yet
- International Trade Is Exchange of Capital, Goods, and Services Across International Borders orDocument14 pagesInternational Trade Is Exchange of Capital, Goods, and Services Across International Borders orMithun DeyNo ratings yet
- KTQT-2 (1)Document37 pagesKTQT-2 (1)thuyntp22No ratings yet
- Development Unit 3Document18 pagesDevelopment Unit 3VAIBHAV VERMANo ratings yet
- International TradeDocument27 pagesInternational TradePoorva KocharNo ratings yet
- Intenational TradeDocument30 pagesIntenational TradeDA YenNo ratings yet
- International TradeDocument12 pagesInternational TradeshivaniguptaNo ratings yet
- Exports Impact On EconomyDocument4 pagesExports Impact On EconomyjainchanchalNo ratings yet
- What Is Globalization?: and Some of The Investment Flows Among Advanced Economies, Mostly Focusing On The United StatesDocument5 pagesWhat Is Globalization?: and Some of The Investment Flows Among Advanced Economies, Mostly Focusing On The United StatesAnonymous xdh21yiapNo ratings yet
- IBT Assignment EditedDocument8 pagesIBT Assignment EditedLysss EpssssNo ratings yet
- International TradeDocument28 pagesInternational TradeVaishnavi KrushakthiNo ratings yet
- 1page (1)Document2 pages1page (1)vaidyajayesh006No ratings yet
- Free Trade: Start LookingDocument6 pagesFree Trade: Start LookingDarshika Singh - KumarNo ratings yet
- INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS GRAPHS AND TRADEDocument13 pagesINTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS GRAPHS AND TRADELeeKayHanNo ratings yet
- Team 3 ProjectDocument14 pagesTeam 3 ProjectGabriela LorenaNo ratings yet
- International Trade: Benefits, Challenges and RegulationsTITLEDocument2 pagesInternational Trade: Benefits, Challenges and RegulationsTITLEInformativeNo ratings yet
- Chap 2,5Document16 pagesChap 2,5Trâm PhạmNo ratings yet
- INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND ITS IMPLICATION FOR UGANDA ECONOMY AssignmentDocument14 pagesINTERNATIONAL TRADE AND ITS IMPLICATION FOR UGANDA ECONOMY Assignmentwandera samuel njoyaNo ratings yet
- (Finals) International Trade Practices and PoliciesDocument4 pages(Finals) International Trade Practices and PoliciesJUDE VINCENT MACALOSNo ratings yet
- Concept of GlobalizationDocument10 pagesConcept of GlobalizationRomario BartleyNo ratings yet
- International Trade GuideDocument47 pagesInternational Trade GuideShefey IbrahimNo ratings yet
- How Tariffs and Quotas Impact Global TradeDocument3 pagesHow Tariffs and Quotas Impact Global TradeMuhammad Ali GoheerNo ratings yet
- European Union Mercosur: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesEuropean Union Mercosur: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaTricia DazaNo ratings yet
- Nazeer Trade Barriers AsgnmntsDocument8 pagesNazeer Trade Barriers AsgnmntsNazeeruddin MohammedNo ratings yet
- Princess Eve's Guide to International Business TermsDocument5 pagesPrincess Eve's Guide to International Business TermsPrincess TorralbaNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument2 pagesGlobalizationЕкатерина РомашкевичNo ratings yet
- Ôn-tập-kinh-tế-quốc-tế-cuối-kỳ-6 (1)Document36 pagesÔn-tập-kinh-tế-quốc-tế-cuối-kỳ-6 (1)thuyntp22No ratings yet
- Question 1 - "The World Economy Is Globalizing at An Accelerating Pace". Discuss This Statement and List The Benefits of Globalization. Answer - 1Document7 pagesQuestion 1 - "The World Economy Is Globalizing at An Accelerating Pace". Discuss This Statement and List The Benefits of Globalization. Answer - 1Raghavendra SoniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 10 International Trade Theory and Development StrategyDocument2 pagesAssignment 10 International Trade Theory and Development StrategyAlyssa BerangberangNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: An Essay-Centric GuideDocument14 pagesMacro Economics: An Essay-Centric GuidezachNo ratings yet
- CBM 321_Assignment 6Document1 pageCBM 321_Assignment 6Julianne DasallaNo ratings yet
- Global Economy Topic Summary NotesDocument11 pagesGlobal Economy Topic Summary NotesjimNo ratings yet
- KTQT 3 37TDocument39 pagesKTQT 3 37TThùy Nguyễn NhưNo ratings yet
- Ge3 The Impact of Globalization On BWDocument4 pagesGe3 The Impact of Globalization On BWTrishia Tejada VistoNo ratings yet
- Meaning of International TradeDocument6 pagesMeaning of International TradeDaniel ConradNo ratings yet
- International TheaDocument4 pagesInternational TheaJhon Lloyd QuintanaNo ratings yet
- MarshallDocument9 pagesMarshallSam CatlinNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument2 pagesInternational BusinessFarhanAwaisiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 (CBM 321) - ReportDocument40 pagesWeek 2 (CBM 321) - ReportDianne PañoNo ratings yet
- Perfectly competitive market assumptionsDocument5 pagesPerfectly competitive market assumptionsEeva The DivaNo ratings yet
- CHP 27Document3 pagesCHP 27Eeva The DivaNo ratings yet
- The Factors That Influence The Suply of Labour To Particular OccupaitionDocument2 pagesThe Factors That Influence The Suply of Labour To Particular OccupaitionEeva The DivaNo ratings yet
- Government SpendingDocument2 pagesGovernment SpendingEeva The DivaNo ratings yet
- CHP 24Document2 pagesCHP 24Eeva The DivaNo ratings yet
- CHP 24Document2 pagesCHP 24Eeva The DivaNo ratings yet
- Accounting 9706 Notes Unit 2 RevisionDocument19 pagesAccounting 9706 Notes Unit 2 RevisionNehaNo ratings yet
- Accounting As Level NoteDocument38 pagesAccounting As Level NotedakshinNo ratings yet
- June WnshshshejejDocument32 pagesJune WnshshshejejXperiaNo ratings yet
- Accounting As Level NoteDocument38 pagesAccounting As Level NotedakshinNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Deutsche Bank and The Road To Basel IIIDocument14 pagesGroup 3 - Deutsche Bank and The Road To Basel IIIAmit Meshram0% (1)
- Canada ProiectDocument4 pagesCanada ProiectAndreea PetreNo ratings yet
- VP Director Strategic Marketing in New York City Resume Valerie ObenDocument2 pagesVP Director Strategic Marketing in New York City Resume Valerie ObenValerieObenNo ratings yet
- MDevs & MBF Day 1 Reading Exercise New (Answer)Document4 pagesMDevs & MBF Day 1 Reading Exercise New (Answer)Sai Aung MainnNo ratings yet
- DSP Inc 1099-11 Print - CFMDocument1 pageDSP Inc 1099-11 Print - CFMKenneth BarcottNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Philippine Financial SystemDocument20 pagesIntroduction to the Philippine Financial SystemSherwin Hila GammadNo ratings yet
- Performance of EXIM Bank's International Trade FinancingDocument17 pagesPerformance of EXIM Bank's International Trade FinancingSumaiya islamNo ratings yet
- Arslan Traders Imports Manufacturing Machinery for Various IndustriesDocument8 pagesArslan Traders Imports Manufacturing Machinery for Various Industriessattar abdulNo ratings yet
- Duck Special Release - JulytoSep2019 - Final - 0Document6 pagesDuck Special Release - JulytoSep2019 - Final - 0Adel MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice Details for Deepa PrasadDocument2 pagesTax Invoice Details for Deepa PrasadAmita BachhanNo ratings yet
- Coimbatore Capital Limited (In300175) : DP Division (NSDL)Document16 pagesCoimbatore Capital Limited (In300175) : DP Division (NSDL)Anonymous iwekCGNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World - Bretton WoodsDocument18 pagesContemporary World - Bretton WoodsFaith DomingoNo ratings yet
- Maritime Industry Advisory 2017-22 2017-22 - Availment of VAT ExemptionDocument3 pagesMaritime Industry Advisory 2017-22 2017-22 - Availment of VAT ExemptionPortCallsNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Overview of International BusinessDocument27 pages1.1 Overview of International BusinessCharles TuazonNo ratings yet
- History of Foreign Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesHistory of Foreign Exchange RatesDustin PlaasNo ratings yet
- Custom UnionDocument28 pagesCustom Unionkvisdoc100% (1)
- Tutorial 4 Exercises IFMDocument5 pagesTutorial 4 Exercises IFMNguyễn Gia Phương Anh100% (1)
- Sentix Indicator of Global Investor ConfidenceDocument1 pageSentix Indicator of Global Investor ConfidenceEduardo PetazzeNo ratings yet
- Overview of Tractor Assembling ProjectDocument1 pageOverview of Tractor Assembling ProjectAhmed Imtiaz RaoNo ratings yet
- 2 2 Total MSB Agents by State RemittanceDocument11 pages2 2 Total MSB Agents by State RemittancePrasanna RaoNo ratings yet
- RIYADH OPEN FOR BUSINESS AS GLOBAL HUBDocument25 pagesRIYADH OPEN FOR BUSINESS AS GLOBAL HUBPriy SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amazon BlazerDocument1 pageAmazon BlazerRomNo ratings yet
- PTI Two Years 2020 - Business Recorder SupplementDocument8 pagesPTI Two Years 2020 - Business Recorder SupplementBusiness Recorder100% (1)
- SWOT Analysis of YES BANK's Full Service Commercial BankingDocument4 pagesSWOT Analysis of YES BANK's Full Service Commercial BankingMadhuri SangareNo ratings yet
- Rich Countries Are Getting Richer While Poor Countries Are Getting PoorerDocument1 pageRich Countries Are Getting Richer While Poor Countries Are Getting PoorerErika PatrascaNo ratings yet
- Iso Tolerances For HolesDocument3 pagesIso Tolerances For HolesprasannaNo ratings yet
- Trade Related Investment Measures (TRIMS) : Current A Airs Quiz of Ve To Provide Social Media Details of Past 5 YearsDocument3 pagesTrade Related Investment Measures (TRIMS) : Current A Airs Quiz of Ve To Provide Social Media Details of Past 5 YearsGVFNo ratings yet
- Globalization & The Multinational Firm: Chapter 01 Eun ResnickDocument28 pagesGlobalization & The Multinational Firm: Chapter 01 Eun ResnickLuthfan FauzanNo ratings yet
- Dec'13Document1 pageDec'13ashish10mca9394100% (1)
- Davilla-Bond and The Latin American Sweater Market PDFDocument12 pagesDavilla-Bond and The Latin American Sweater Market PDFnamz bamzNo ratings yet