Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: Legend
Uploaded by
SOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: Legend
Uploaded by
SOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHECopyright:
Available Formats
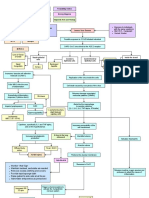
LEGEND:
Disease Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors
Disease Process Signs and Symptoms Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing Management Medical Management Diagnostic Tests and Findings
Exposure to individuals
Age: 44 Years Old with the same symptoms
Hypertension Corona Virus Disease BMI: 26.5 - Overweight
Diabetes Type 2 Current Smoker
Possible exposure to COVID infected individual
HCTZ Lisinopril
SARS-CoV-2 virus binds to the ACE 2 receptor
Metformin
Loss of Sense
of Smell Nasal epithelial Inside the alveoli
cells Gustatory Gastrointestinal
Epithelial cells Epithelial cells Nausea
Nasal Decreased
Congestion Coryza Appetite Diarrhea
Increases Vascular cell adhesion
molecule (VCAM-1)
Replication of the virus inside the cells
Pulls WBCs into the area
Cell death caused by exocytosis of the virus
of inflammation
Releases damage-associated
Exacerbates inflammatory molecular patterns (DAMPs)
Dizziness
response (Cytokine storm)
Alerts the the macrophage
Impairs lymphopoiesis SIRS to secrete cytokines
(IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-alpha, IFN-delta)
1+ peripheral pulses,
Hypercoagulability slight delayed
capillary refill
Leukopenia
WBC: 2.6 x 10^9/L
Cytokines, specifically IL-1 and TNF-alpha, Increases permeability of the
acts on the hypothalamus cell membranes
B-lines in the lung
Increased prostaglandin Interstitial edema
ultrasound
production Activates Neutrophils
Alveolar edema
Diffused body Fever: 39.2C
aches
Acetaminophen Thickens the alveolar membrane
Hyperthermia
Decrease in PaO2
Monitor Vital Sign
Maintain bedrest, ambulate as needed
Releases reactive oxygen species and
Remove excess clothing and covers
proteases to attack the cause of
Provide tepid sponge bath inflammation
Raise patient’s side rails at all times
Administer antipyretics as prescribed
Triggers chemoreceptors to
Increased RR activate the Sympathetic
22 cpm nervous system
Increased HR
Bronchospasm 140 bpm
Hypoxemia Impaired Gas Exchange Damages healthy alveolar cells
Salbutamol + Ipratropium
Assess respiratory status(rate, rhythm, depth, sounds)
Assess for cyanosis, changes in mentation, stress, and anxiety
Shortness of Breath Assist the patient in an upright (30 to 45 degrees) position as their
condition allows
Nasal Cannula Oxygen Provide small frequent meals and add supplements
@ 3LPM Provide rest periods between ADLs and pace activities.
Turn and reposition the patient at least every two hours
Encourage or assist with ambulation as indicated and tolerated
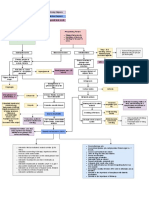
Releases cytokines
Activates the chemoreceptors
Sloughing of of dead cells to Decrease in Decrease in connected to the Vagus nerve
the center of the alveoli Type 2 Pneumocytes Type 1 Pneumocytes
Cough reflex
Decrease in gas
Accumulation of fluids, cell Decrease in the exchange
debris, and white blood cells production of surfactants
Dry cough or
productive cough
Hypoxemia
Crackles Consolidation Increase surface
Orthopnea
tension
X-ray and CT scan Light
headedness
Alveolar collapse
Shortness of Breath Chest Pain
Ineffective Airway Clearance
Impaired Gas Exchange
Assess respiratory status(rate, rhythm, depth, sounds)
Monitor ABG values, hemoglobin levels, skin color and mucus
membranes, and level of consciousness
Monitor sputum, noting amount, odor, consistency, and ease of
expectoration
Assist the patient to an optimal upright position
Encourage adequate fluid intake, if not contraindicatedEncourage the
client to cough and deep breathe; splinting while coughin
Turn and reposition the patient at least every two hours
Perform nasotracheal suctioning as necessary, especially if cough is
ineffective.
You might also like
- Conceptual Map - Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesConceptual Map - Diabetic KetoacidosisLovie Japhet LopezNo ratings yet
- DKA Draft 1 AM - Drawio 2Document1 pageDKA Draft 1 AM - Drawio 2Dud AccNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Emergencies: Sulaiman Usaid G. MBCHB V Facilatator: DR Jack TDocument44 pagesHypertensive Emergencies: Sulaiman Usaid G. MBCHB V Facilatator: DR Jack TUsaid SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants ParamedDocument20 pagesAnticoagulants ParamedManikanta GupthaNo ratings yet
- Acute Bronchiolitis EditedDocument19 pagesAcute Bronchiolitis EditedSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- A Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutFrom EverandA Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Medication Errors in AnaesthesiaDocument49 pagesMedication Errors in AnaesthesiaVithal Dhulkhed100% (1)
- CBT - Emergency Medicine EditedDocument14 pagesCBT - Emergency Medicine Editedchristy INo ratings yet
- Insulin, Oral Hypoglycaemic Agents, GlucagonDocument63 pagesInsulin, Oral Hypoglycaemic Agents, GlucagonBhavesh kunvarNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 TB MeningitisDocument50 pagesChapter6 TB MeningitisAldwin BagtasNo ratings yet
- DIC Case StudyDocument7 pagesDIC Case StudyRobertNo ratings yet
- UrosepsisDocument22 pagesUrosepsisWita Ferani KartikaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument37 pagesSystemic Lupus ErythematosusFirman Ichlasul AmalNo ratings yet
- Managing Nause and Vomiting-Crit-Care-Nurse-2003-Garrett-31-50 PDFDocument22 pagesManaging Nause and Vomiting-Crit-Care-Nurse-2003-Garrett-31-50 PDFpmuftiaNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetes Ketoacidosis in PregnancyDocument19 pagesManagement of Diabetes Ketoacidosis in PregnancySudhir PaulNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Pneumonia PharmacologyDocument70 pagesBacterial Pneumonia PharmacologyMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Initial Evaluation of Diabetes Mellitus in Adults - UpToDateDocument21 pagesClinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Initial Evaluation of Diabetes Mellitus in Adults - UpToDatePriscillaNo ratings yet
- Stevens Johnson DiseaseDocument5 pagesStevens Johnson DiseaseShammy RNNo ratings yet
- Rapid Response Team Whitepaper With Intro UPDATEDDocument24 pagesRapid Response Team Whitepaper With Intro UPDATEDHari Mas KuncoroNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- DKA Canadian ProtocolDocument2 pagesDKA Canadian Protocolplay_wright2084No ratings yet
- Bronchiolitis Clinical Practice GuidelineDocument21 pagesBronchiolitis Clinical Practice GuidelineJuwita PratiwiNo ratings yet
- UtiDocument38 pagesUtiAzra AzmunaNo ratings yet
- DKA Emergency Management GuideDocument18 pagesDKA Emergency Management GuideDr. Mamunul AbedinNo ratings yet
- Managing Angina: AHA Guidelines on Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument96 pagesManaging Angina: AHA Guidelines on Diagnosis and TreatmentJaymica Laggui DacquilNo ratings yet
- Nursing in The Emergency Department ED DDocument10 pagesNursing in The Emergency Department ED DMangayu TriNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument56 pagesUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenmedpedshospitalistNo ratings yet
- Fluid Resuscitation and Organ Perfusion EvaluationDocument66 pagesFluid Resuscitation and Organ Perfusion EvaluationDewiRatnasariNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Most Common Complication: Sabay SilaDocument6 pagesMost Common Complication: Sabay SilaSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- NCM103 12th Endoc IIDocument9 pagesNCM103 12th Endoc IIKamx MohammedNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis in Children - Diagnostic Imaging - UpToDateDocument28 pagesAcute Appendicitis in Children - Diagnostic Imaging - UpToDateHafiz Hari NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Overview With Report of A CaseDocument4 pagesIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Overview With Report of A CaseHernan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management System SoftwareDocument11 pagesHospital Management System SoftwareNikesh Solanki50% (2)
- Rash BookDocument12 pagesRash BookPhoebe UsmleNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The FutureDocument25 pagesSepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The Futuremontie13No ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice Case Study: Early Diagnosis and Treatment Prevents Brain DamageDocument6 pagesNeonatal Jaundice Case Study: Early Diagnosis and Treatment Prevents Brain DamagemuzamirNo ratings yet
- Wilms TumorDocument10 pagesWilms TumorRoscelie KhoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument7 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisetengNo ratings yet
- Dka GuidelineDocument16 pagesDka GuidelineGhada HusseinNo ratings yet
- Adolescents With Tuberculosis-A Review of 145 Cases, 2016Document5 pagesAdolescents With Tuberculosis-A Review of 145 Cases, 2016Yoseph Arif Putra100% (1)
- Integrative Literature AutosavedDocument21 pagesIntegrative Literature Autosavedapi-486981186No ratings yet
- Running Head: Integrative Literature Review 1Document22 pagesRunning Head: Integrative Literature Review 1api-456581702No ratings yet
- EM Practice 2018 InfluenzaDocument20 pagesEM Practice 2018 InfluenzaBarbara Yoon100% (1)
- Diabetic FootDocument104 pagesDiabetic FootadibeuutNo ratings yet
- Euglycemic DkaDocument15 pagesEuglycemic DkaVemuri SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Banana Leaf Dressing For Partial Thickness WoundsDocument6 pagesBanana Leaf Dressing For Partial Thickness Woundsapi-3801331100% (1)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Document39 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Nadya SabrinaNo ratings yet
- OS 215 02 Diabetes in AdultsDocument11 pagesOS 215 02 Diabetes in AdultsMigs Medina100% (1)
- Pediatrics: 2 Case ReportDocument50 pagesPediatrics: 2 Case ReportSam Raven AndresNo ratings yet
- Hypo Album inDocument11 pagesHypo Album inAndi Agung RiatmojoNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhyee S. Idjad Year&Sec: BSNIII-B: What Is in A Emergency Cart?Document3 pagesName: Muhyee S. Idjad Year&Sec: BSNIII-B: What Is in A Emergency Cart?Yeng Cries50% (2)
- DKA and HHSDocument16 pagesDKA and HHSGepengCungkringNo ratings yet
- Corona RadiataDocument89 pagesCorona RadiataPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument17 pagesNeonatal SepsisDhilla Feroh Kesuma TNo ratings yet
- Covid Pathogenesis TutorialDocument29 pagesCovid Pathogenesis TutorialfelixNo ratings yet
- CHF: Congestive Heart Failure Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and ManagementDocument6 pagesCHF: Congestive Heart Failure Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and ManagementSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Amputation and Appendectomy Nursing CareDocument2 pagesAmputation and Appendectomy Nursing CareSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendDocument3 pagesPredisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- DKA DrawioDocument2 pagesDKA DrawioSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendDocument3 pagesPredisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Cause PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Cause PathophysiologySOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Cause PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Cause PathophysiologySOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Cause PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Cause PathophysiologySOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- CHF: Congestive Heart Failure Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and ManagementDocument6 pagesCHF: Congestive Heart Failure Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and ManagementSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Medical Management: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesMedical Management: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- 3M NLP White PaperDocument12 pages3M NLP White PaperJayampathi SamarasingheNo ratings yet
- UFD/MMC/SD Controller Flash Support Limitation and Interconnection NoteDocument5 pagesUFD/MMC/SD Controller Flash Support Limitation and Interconnection Noteمہرؤآنہ آبہرآهہيہمہNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Business Plan PreparationDocument26 pagesChapter Three: Business Plan PreparationwaqoleNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Notes: ©film Education 1Document20 pagesTeachers' Notes: ©film Education 1רז ברקוNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction in Maruti SuzukiDocument31 pagesCustomer Satisfaction in Maruti Suzukirajesh laddha100% (1)
- 6 Thinking Hats Detailed Model - UpdatedDocument32 pages6 Thinking Hats Detailed Model - Updatedgeetanshi mittalNo ratings yet
- Robert K Boscarato and Matthew Skaggs Corprate Credit Book Draft 1.Document70 pagesRobert K Boscarato and Matthew Skaggs Corprate Credit Book Draft 1.Robert BoscaratoNo ratings yet
- BITS ZG628T Dissertation (For Students of M. Tech. Software Systems)Document21 pagesBITS ZG628T Dissertation (For Students of M. Tech. Software Systems)Shiva Beduduri100% (1)
- Sax AltoDocument2 pagesSax AltoJohnny GervasioNo ratings yet
- Belotero Intense LidocaineDocument7 pagesBelotero Intense LidocaineAnnaNo ratings yet
- DEME Offshore Brochure_2022Document16 pagesDEME Offshore Brochure_2022amin32No ratings yet
- Understanding Arthrogyposis Multiplex Congenita and Muscular DystrophiesDocument38 pagesUnderstanding Arthrogyposis Multiplex Congenita and Muscular DystrophiessmrutiptNo ratings yet
- LFJ All OrdersDocument195 pagesLFJ All Orderskate jackNo ratings yet
- Student quiz answer sheetsDocument26 pagesStudent quiz answer sheetsSeverus S PotterNo ratings yet
- 178 - 7 - Fun For Flyers. Progress Tests - 2017, 4th - 91p.pdf Foods NatureDocument1 page178 - 7 - Fun For Flyers. Progress Tests - 2017, 4th - 91p.pdf Foods NatureYu KoNo ratings yet
- Staff Nurse HallticketDocument2 pagesStaff Nurse HallticketHiking DiaryNo ratings yet
- Smart Panels - Digitized Switchboards - Blokset Desing and Assembly GuideDocument94 pagesSmart Panels - Digitized Switchboards - Blokset Desing and Assembly Guidelorentz franklinNo ratings yet
- Probability Tree Diagrams Solutions Mathsupgrade Co UkDocument10 pagesProbability Tree Diagrams Solutions Mathsupgrade Co UknatsNo ratings yet
- Pavements ConstructedDocument16 pagesPavements ConstructedjoryNo ratings yet
- Lucknow Digital Members Directory 4 Jan22Document84 pagesLucknow Digital Members Directory 4 Jan22B2B InfomediaNo ratings yet
- Video Conferencing Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesVideo Conferencing Lesson PlanANN JILLIAN JOYCE MONDONEDO100% (1)
- READING U8Document4 pagesREADING U8Như TrầnNo ratings yet
- Piano: Grade 2: PiecesDocument4 pagesPiano: Grade 2: PiecesnolozeNo ratings yet
- Jun 2005 - AnsDocument13 pagesJun 2005 - AnsHubbak Khan100% (1)
- Improve Product Packaging at Annual Board MeetingDocument9 pagesImprove Product Packaging at Annual Board Meetingizzat89% (9)
- AmboooDocument39 pagesAmboooTesfaye DegefaNo ratings yet
- SKM 4 - COCU - CU2 - Child - Care - Centre - HealthDocument14 pagesSKM 4 - COCU - CU2 - Child - Care - Centre - HealthShireen TahirNo ratings yet
- WordPress Introduction: CMS BasicsDocument21 pagesWordPress Introduction: CMS BasicsNgô Ngọc Hải phươngNo ratings yet
- 01 - Narmada M PhilDocument200 pages01 - Narmada M PhilafaceanNo ratings yet
- Recipe of Medical AirDocument13 pagesRecipe of Medical AirMd. Rokib ChowdhuryNo ratings yet